JS EventEmitter를 사용하는 방법
이번에는 JS EventEmitter 사용법과 JS EventEmitter 사용 시 주의사항에 대해 알려드리겠습니다. 다음은 실제 사례입니다.
2달 전 Github의 eventemitter3 소스 코드와 Node.js 아래의 이벤트 모듈 이벤트를 복사했고, 마침내 JavaScript 이벤트를 알게 되었습니다.
저는 지난 주말에 소스 코드에 대한 이전 이해를 바탕으로 ES6를 사용하여 eventemitter8을 구현한 다음 npm에 게시했습니다. 제가 놀랐던 점은 readme 소개나 홍보 없이 이틀 전에만 출시되었다는 것입니다. . 실제로 다운로드 수는 45개입니다. 누가 다운로드했는지, 사용할 수 있는지 궁금합니다. 반은 복사하고 반은 원본 JavaScript 시간 처리 라이브러리인 now.js(npm 포털: now.js)에 많은 시간을 보냈습니다. 저의 활발한 프로모션으로 4개월 만에 다운로드 횟수는 177건에 불과했습니다. 마음대로 심은 꽃은 피지 않는다는 말이 사실이지만, 심지 않고 심은 버드나무는 그늘을 만든다!
eventemitter8 대부분은 제가 소스코드를 읽고 작성한 것입니다. Listeners, ListenerCount, EventNames 등 몇 가지 메소드가 지금은 무엇을 하는지 기억이 나지 않아서 다시 확인하겠습니다. 많은 테스트 사례에서 eventemitter3을 참조하고 있습니다. eventemitter3 개발자와 Node.js 이벤트 모듈 개발자에게 감사의 말씀을 전하고 싶습니다.
JavaScript 이벤트에 대한 나의 이해에 대해 이야기하겠습니다.
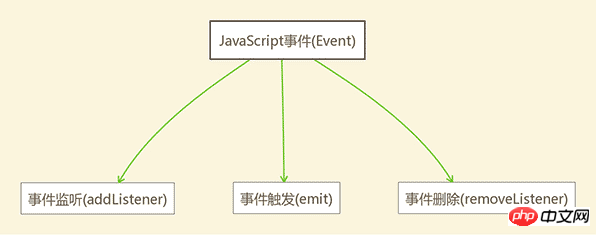
위 그림에서 볼 수 있듯이 JavaScript 이벤트의 핵심에는 이벤트 청취(addListener), 이벤트 트리거링(emit) 및 이벤트 삭제( 제거리스너) .
이벤트 청취(addListener)
우선 청취에는 모니터링 대상, 즉 대상을 구별하는 목적을 달성하기 위해서는 이름이 필수이며 이를 유형으로 정의합니다.
둘째, 모니터링 대상에는 여기에서 fn으로 정의된 JavaScript의 특정 메서드에 해당하는 일종의 작업이 있어야 합니다.
예를 들어, 유형이 add이고 메소드가 특정 변수 a의 값에 1을 더하는 fn = () => 이벤트를 모니터링할 수 있습니다. 변수 b에 2를 추가하는 메소드도 듣고 싶다면, 첫 번째 반응은 add2 유형과 fn1 = () => 메소드를 사용하여 이벤트를 생성하는 것일 수 있습니다. 당신은 이것이 너무 낭비라고 생각할 수도 있습니다. 하나의 이름을 듣고 두 개 이상의 메소드 이벤트를 실행하도록 할 수 있습니까? 물론 가능합니다.
그럼 어떻게 해야 할까요?
매우 간단합니다. 모니터링 방법을 배열에 넣고, 배열을 순회하고 순차적으로 실행하면 됩니다. 위의 예에서는 추가할 유형과 메소드를 [fn, fn1]로 변경합니다.
세분화하고 싶다면 무제한으로 실행할 수 있는 온(on)과 한 번만 실행할 수 있는 원스(이벤트는 실행 후 즉시 삭제됩니다)로 나눌 수도 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 나중에 확인하세요.
이벤트 트리거(발산)
이벤트 모니터링만으로는 충분하지 않으며 전체 프로세스를 완료하려면 이벤트 트리거가 있어야 합니다. 방출은 특정 유형의 청취에 해당하는 단일 이벤트 또는 일련의 이벤트를 트리거하는 것입니다. 이전 예에서 단일 이벤트는 fn을 실행하는 것이며 일련의 이벤트는 fn 및 fn1을 탐색하고 실행하는 것입니다.
이벤트 삭제(removeListener)
엄밀히 말하면 이벤트 모니터링과 이벤트 트리거링이 전체 프로세스를 완료할 수 있습니다. 이벤트 삭제는 선택사항입니다. 하지만 여전히 이벤트를 삭제해야 하는 경우가 많습니다. 예를 들어 앞서 언급한 Once 이벤트는 한 번만 실행되도록 허용되며, 삭제 방법이 제공되지 않으면 언제 다시 실행할지 보장하기 어렵습니다. 일반적으로 이벤트가 더 이상 필요하지 않으면 삭제해야 합니다.
이제 핵심 부분이 끝났으니 eventemitter8의 소스 코드를 간략하게 분석해 보겠습니다.
소스 코드 분석
모든 소스 코드:
const toString = Object.prototype.toString;
const isType = obj => toString.call(obj).slice(8, -1).toLowerCase();
const isArray = obj => Array.isArray(obj) || isType(obj) === 'array';
const isNullOrUndefined = obj => obj === null || obj === undefined;
const _addListener = function(type, fn, context, once) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('fn must be a function');
}
fn.context = context;
fn.once = !!once;
const event = this._events[type];
// only one, let `this._events[type]` to be a function
if (isNullOrUndefined(event)) {
this._events[type] = fn;
} else if (typeof event === 'function') {
// already has one function, `this._events[type]` must be a function before
this._events[type] = [event, fn];
} else if (isArray(event)) {
// already has more than one function, just push
this._events[type].push(fn);
}
return this;
};
class EventEmitter {
constructor() {
if (this._events === undefined) {
this._events = Object.create(null);
}
}
addListener(type, fn, context) {
return _addListener.call(this, type, fn, context);
}
on(type, fn, context) {
return this.addListener(type, fn, context);
}
once(type, fn, context) {
return _addListener.call(this, type, fn, context, true);
}
emit(type, ...rest) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(type)) {
throw new Error('emit must receive at lease one argument');
}
const events = this._events[type];
if (isNullOrUndefined(events)) return false;
if (typeof events === 'function') {
events.call(events.context || null, rest);
if (events.once) {
this.removeListener(type, events);
}
} else if (isArray(events)) {
events.map(e => {
e.call(e.context || null, rest);
if (e.once) {
this.removeListener(type, e);
}
});
}
return true;
}
removeListener(type, fn) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return this;
// if type is undefined or null, nothing to do, just return this
if (isNullOrUndefined(type)) return this;
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new Error('fn must be a function');
}
const events = this._events[type];
if (typeof events === 'function') {
events === fn && delete this._events[type];
} else {
const findIndex = events.findIndex(e => e === fn);
if (findIndex === -1) return this;
// match the first one, shift faster than splice
if (findIndex === 0) {
events.shift();
} else {
events.splice(findIndex, 1);
}
// just left one listener, change Array to Function
if (events.length === 1) {
this._events[type] = events[0];
}
}
return this;
}
removeAllListeners(type) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return this;
// if not provide type, remove all
if (isNullOrUndefined(type)) this._events = Object.create(null);
const events = this._events[type];
if (!isNullOrUndefined(events)) {
// check if `type` is the last one
if (Object.keys(this._events).length === 1) {
this._events = Object.create(null);
} else {
delete this._events[type];
}
}
return this;
}
listeners(type) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return [];
const events = this._events[type];
// use `map` because we need to return a new array
return isNullOrUndefined(events) ? [] : (typeof events === 'function' ? [events] : events.map(o => o));
}
listenerCount(type) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return 0;
const events = this._events[type];
return isNullOrUndefined(events) ? 0 : (typeof events === 'function' ? 1 : events.length);
}
eventNames() {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return [];
return Object.keys(this._events);
}
}
export default EventEmitter;코드는 매우 작습니다. 단 151줄입니다. 간단한 버전이고 ES6를 사용하기 때문에 Node.js 이벤트와 eventemitter3가 더 적습니다. 그리고 이보다 더 복잡한 것도 꽤 있으니 관심이 있으시면 스스로 더 많은 연구를 해보시면 됩니다.
const toString = Object.prototype.toString; const isType = obj => toString.call(obj).slice(8, -1).toLowerCase(); const isArray = obj => Array.isArray(obj) || isType(obj) === 'array'; const isNullOrUndefined = obj => obj === null || obj === undefined;
이 4줄은 유형과 null인지 정의되지 않은지 여부를 결정하는 일부 도구 기능입니다.
constructor() {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) {
this._events = Object.create(null);
}
}创建了一个 EventEmitter 类,然后在构造函数里初始化一个类的 _events 属性,这个属性不需要要继承任何东西,所以用了 Object.create(null)。当然这里 isNullOrUndefined(this._events) 还去判断了一下 this._events 是否为 undefined 或者 null,如果是才需要创建。但这不是必要的,因为实例化一个 EventEmitter 都会调用构造函数,皆为初始状态,this._events 应该是不可能已经定义了的,可去掉。
addListener(type, fn, context) {
return _addListener.call(this, type, fn, context);
}
on(type, fn, context) {
return this.addListener(type, fn, context);
}
once(type, fn, context) {
return _addListener.call(this, type, fn, context, true);
}接下来是三个方法 addListener、on、once ,其中 on 是 addListener 的别名,可执行多次。once 只能执行一次。
三个方法都用到了 _addListener 方法:
const _addListener = function(type, fn, context, once) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('fn must be a function');
}
fn.context = context;
fn.once = !!once;
const event = this._events[type];
// only one, let `this._events[type]` to be a function
if (isNullOrUndefined(event)) {
this._events[type] = fn;
} else if (typeof event === 'function') {
// already has one function, `this._events[type]` must be a function before
this._events[type] = [event, fn];
} else if (isArray(event)) {
// already has more than one function, just push
this._events[type].push(fn);
}
return this;
};方法有四个参数,type 是监听事件的名称,fn 是监听事件对应的方法,context 俗称爸爸,改变 this 指向的,也就是执行的主体。once 是一个布尔型,用来标志是否只执行一次。
首先判断 fn 的类型,如果不是方法,抛出一个类型错误。fn.context = context;fn.once = !!once 把执行主体和是否执行一次作为方法的属性。const event = this._events[type] 把该对应 type 的所有已经监听的方法存到变量 event。
// only one, let `this._events[type]` to be a function
if (isNullOrUndefined(event)) {
this._events[type] = fn;
} else if (typeof event === 'function') {
// already has one function, `this._events[type]` must be a function before
this._events[type] = [event, fn];
} else if (isArray(event)) {
// already has more than one function, just push
this._events[type].push(fn);
}
return this;如果 type 本身没有正在监听任何方法,this._events[type] = fn 直接把监听的方法 fn 赋给 type 属性 ;如果正在监听一个方法,则把要添加的 fn 和之前的方法变成一个含有2个元素的数组 [event, fn],然后再赋给 type 属性,如果正在监听超过2个方法,直接 push 即可。最后返回 this ,也就是 EventEmitter 实例本身。
简单来讲不管是监听多少方法,都放到数组里是没必要像上面细分。但性能较差,只有一个方法时 key: fn 的效率比 key: [fn] 要高。
再回头看看三个方法:
addListener(type, fn, context) {
return _addListener.call(this, type, fn, context);
}
on(type, fn, context) {
return this.addListener(type, fn, context);
}
once(type, fn, context) {
return _addListener.call(this, type, fn, context, true);
}addListener 需要用 call 来改变 this 指向,指到了类的实例。once 则多传了一个标志位 true 来标志它只需要执行一次。这里你会看到我在 addListener 并没有传 false 作为标志位,主要是因为我懒,但并不会影响到程序的逻辑。因为前面的 fn.once = !!once 已经能很好的处理不传值的情况。没传值 !!once 为 false。
接下来讲 emit
emit(type, ...rest) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(type)) {
throw new Error('emit must receive at lease one argument');
}
const events = this._events[type];
if (isNullOrUndefined(events)) return false;
if (typeof events === 'function') {
events.call(events.context || null, rest);
if (events.once) {
this.removeListener(type, events);
}
} else if (isArray(events)) {
events.map(e => {
e.call(e.context || null, rest);
if (e.once) {
this.removeListener(type, e);
}
});
}
return true;
}事件触发需要指定具体的 type 否则直接抛出错误。这个很容易理解,你都没有指定名称,我怎么知道该去执行谁的事件。if (isNullOrUndefined(events)) return false,如果 type 对应的方法是 undefined 或者 null ,直接返回 false 。因为压根没有对应 type 的方法可以执行。而 emit 需要知道是否被成功触发。
接着判断 evnts 是不是一个方法,如果是, events.call(events.context || null, rest) 执行该方法,如果指定了执行主体,用 call 改变 this 的指向指向 events.context 主体,否则指向 null ,全局环境。对于浏览器环境来说就是 window。差点忘了 rest ,rest 是方法执行时的其他参数变量,可以不传,也可以为一个或多个。执行结束后判断 events.once ,如果为 true ,就用 removeListener 移除该监听事件。
如果 evnts 是数组,逻辑一样,只是需要遍历数组去执行所有的监听方法。
成功执行结束后返回 true 。
removeListener(type, fn) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return this;
// if type is undefined or null, nothing to do, just return this
if (isNullOrUndefined(type)) return this;
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new Error('fn must be a function');
}
const events = this._events[type];
if (typeof events === 'function') {
events === fn && delete this._events[type];
} else {
const findIndex = events.findIndex(e => e === fn);
if (findIndex === -1) return this;
// match the first one, shift faster than splice
if (findIndex === 0) {
events.shift();
} else {
events.splice(findIndex, 1);
}
// just left one listener, change Array to Function
if (events.length === 1) {
this._events[type] = events[0];
}
}
return this;
}removeListener 接收一个事件名称 type 和一个将要被移除的方法 fn 。if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return this 这里表示如果 EventEmitter 实例本身的 _events 为 null 或者 undefined 的话,没有任何事件监听,直接返回 this 。
if (isNullOrUndefined(type)) return this 如果没有提供事件名称,也直接返回 this 。
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new Error('fn must be a function');
}fn 如果不是一个方法,直接抛出错误,很好理解。
接着判断 type 对应的 events 是不是一个方法,是,并且 events === fn 说明 type 对应的方法有且仅有一个,等于我们指定要删除的方法。这个时候 delete this._events[type] 直接删除掉 this._events 对象里 type 即可。
所有的 type 对应的方法都被移除后。想一想 this._events[type] = undefined 和 delete this._events[type] 会有什么不同?
差异是很大的,this._events[type] = undefined 仅仅是将 this._events 对象里的 type 属性赋值为 undefined ,type 这一属性依然占用内存空间,但其实已经没什么用了。如果这样的 type 一多,有可能造成内存泄漏。delete this._events[type] 则直接删除,不占内存空间。前者也是 Node.js 事件模块和 eventemitter3 早期实现的做法。
如果 events 是数组,这里我没有用 isArray 进行判断,而是直接用一个 else ,原因是 this._events[type] 的输入限制在 on 或者 once 中,而它们已经限制了 this._events[type] 只能是方法组成的数组或者是一个方法,最多加上不小心或者人为赋成 undefined 或 null 的情况,但这个情况我们也在前面判断过了。
因为 isArray 这个工具方法其实运行效率是不高的,为了追求一些效率,在不影响运行逻辑情况下可以不用 isArray 。而且 typeof events === 'function' 用 typeof 判断方法也比 isArray 的效率要高,这也是为什么不先判断是否是数组的原因。用 typeof 去判断一个方法也比 Object.prototype.toSting.call(events) === '[object Function] 效率要高。但数组不能用 typeof 进行判断,因为返回的是 object, 这众所周知。虽然如此,在我面试过的很多人中,仍然有很多人不知道。。。
const findIndex = events.findIndex(e => e === fn) 此处用 ES6 的数组方法 findIndex 直接去查找 fn 在 events 中的索引。如果 findIndex === -1 说明我们没有找到要删除的 fn ,直接返回 this 就好。如果 findIndex === 0 ,是数组第一个元素,shift 剔除,否则用 splice 剔除。因为 shift 比 splice 效率高。
findIndex 的效率其实没有 for 循环去查找的高,所以 eventemitter8 的效率在我没有做 benchmark 之前我就知道肯定会比 eventemitter3 效率要低不少。不那么追求执行效率时当然是用最懒的方式来写最爽。所谓的懒即正义。。。
最后还得判断移除 fn 后 events 剩余的数量,如果只有一个,基于之前要做的优化,this._events[type] = events[0] 把含有一个元素的数组变成一个方法,降维打击一下。。。
最后的最后 return this 返回自身,链式调用还能用得上。
removeAllListeners(type) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return this;
// if not provide type, remove all
if (isNullOrUndefined(type)) this._events = Object.create(null);
const events = this._events[type];
if (!isNullOrUndefined(events)) {
// check if type is the last one
if (Object.keys(this._events).length === 1) {
this._events = Object.create(null);
} else {
delete this._events[type];
}
}
return this;
};removeAllListeners 指的是要删除一个 type 对应的所有方法。参数 type 是可选的,如果未指定 type ,默认把所有的监听事件删除,直接 this._events = Object.create(null) 操作即可,跟初始化 EventEmitter 类一样。
如果 events 既不是 null 且不是 undefined 说明有可删除的 type ,先用 Object.keys(this._events).length === 1 判断是不是最后一个 type 了,如果是,直接初始化 this._events = Object.create(null),否则 delete this._events[type] 直接删除 type 属性,一步到位。
最后返回 this 。
到目前为止,所有的核心功能已经讲完。
listeners(type) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return [];
const events = this._events[type];
// use `map` because we need to return a new array
return isNullOrUndefined(events) ? [] : (typeof events === 'function' ? [events] : events.map(o => o));
}
listenerCount(type) {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return 0;
const events = this._events[type];
return isNullOrUndefined(events) ? 0 : (typeof events === 'function' ? 1 : events.length);
}
eventNames() {
if (isNullOrUndefined(this._events)) return [];
return Object.keys(this._events);
}listeners 返回的是 type 对应的所有方法。结果都是一个数组,如果没有,返回空数组;如果只有一个,把它的方法放到一个数组中返回;如果本来就是一个数组,map 返回。之所以用 map 返回而不是直接 return this._events[type] 是因为 map 返回一个新的数组,是深度复制,修改数组中的值不会影响到原数组。this._events[type] 则返回原数组的一个引用,是浅度复制,稍不小心改变值会影响到原数组。造成这个差异的底层原因是数组是一个引用类型,浅度复制只是指针拷贝。这可以单独写一篇文章,不展开了。
listenerCount 返回的是 type 对应的方法的个数,代码一眼就明白,不多说。
eventNames 这个返回的是所有 type 组成的数组,没有返回空数组,否则用 Object.keys(this._events) 直接返回。
最后的最后,export default EventEmitter 把 EventEmitter 导出。
结语
我是先看了两个库才知道怎么写的,其实最好的学习方法是知道 EventEmitter 是干什么用的以后自己动手写,写完以后再和那些库进行对比,找出差距,修正再修正。
但也不是说先看再写没有收获,至少比只看不写和看都没看的有收获不是。。。
水平有限,代码错漏或者文章讲不清楚之处在所难免,欢迎大家批评指正。
이 기사의 사례를 읽으신 후 방법을 마스터하셨다고 생각합니다. 더 흥미로운 정보를 보려면 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 다른 관련 기사를 주목하세요!
추천 자료:
Angular4를 사용하여 여러 구성 요소 간에 데이터를 통신하는 방법
Vue 단일 페이지 애플리케이션을 사용할 때 별도의 스타일 파일을 참조하는 방법
위 내용은 JS EventEmitter를 사용하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7554
7554
 15
15
 1382
1382
 52
52
 83
83
 11
11
 59
59
 19
19
 28
28
 96
96
 마그넷 링크 사용 방법
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
마그넷 링크 사용 방법
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
마그넷 링크는 리소스를 다운로드하기 위한 링크 방식으로, 기존 다운로드 방식보다 더 편리하고 효율적입니다. 마그넷 링크를 사용하면 중간 서버에 의존하지 않고 P2P 방식으로 리소스를 다운로드할 수 있습니다. 이번 글에서는 마그넷 링크의 사용법과 주의할 점을 소개하겠습니다. 1. 마그넷 링크란 무엇인가요? 마그넷 링크는 P2P(Peer-to-Peer) 프로토콜을 기반으로 한 다운로드 방식입니다. 마그넷 링크를 통해 사용자는 리소스 게시자에 직접 연결하여 리소스 공유 및 다운로드를 완료할 수 있습니다. 전통적인 다운로드 방법과 비교하여 자기
 mdf 및 mds 파일을 사용하는 방법
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
mdf 및 mds 파일을 사용하는 방법
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
mdf 파일, mds 파일 사용법 컴퓨터 기술의 지속적인 발전으로 우리는 다양한 방법으로 데이터를 저장하고 공유할 수 있게 되었습니다. 디지털 미디어 분야에서는 특별한 파일 형식을 자주 접하게 됩니다. 이 기사에서는 일반적인 파일 형식인 mdf 및 mds 파일에 대해 설명하고 사용 방법을 소개합니다. 먼저 mdf 파일과 mds 파일의 의미를 이해해야 합니다. mdf는 CD/DVD 이미지 파일의 확장자이고, mds 파일은 mdf 파일의 메타데이터 파일입니다.
 크리스탈디스크마크란 어떤 소프트웨어인가요? -크리스탈디스크마크는 어떻게 사용하나요?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
크리스탈디스크마크란 어떤 소프트웨어인가요? -크리스탈디스크마크는 어떻게 사용하나요?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark는 순차 및 무작위 읽기/쓰기 속도를 빠르게 측정하는 하드 드라이브용 소형 HDD 벤치마크 도구입니다. 다음으로 편집자님에게 CrystalDiskMark 소개와 crystaldiskmark 사용법을 소개하겠습니다~ 1. CrystalDiskMark 소개 CrystalDiskMark는 기계식 하드 드라이브와 솔리드 스테이트 드라이브(SSD)의 읽기 및 쓰기 속도와 성능을 평가하는 데 널리 사용되는 디스크 성능 테스트 도구입니다. ). 무작위 I/O 성능. 무료 Windows 응용 프로그램이며 사용자 친화적인 인터페이스와 다양한 테스트 모드를 제공하여 하드 드라이브 성능의 다양한 측면을 평가하고 하드웨어 검토에 널리 사용됩니다.
 foobar2000을 어떻게 다운로드하나요? - foobar2000 사용법
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000을 어떻게 다운로드하나요? - foobar2000 사용법
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000은 언제든지 음악 리소스를 들을 수 있는 소프트웨어입니다. 모든 종류의 음악을 무손실 음질로 제공합니다. 음악 플레이어의 향상된 버전을 사용하면 더욱 포괄적이고 편안한 음악 경험을 얻을 수 있습니다. 컴퓨터에서 고급 오디오를 재생합니다. 이 장치는 보다 편리하고 효율적인 음악 재생 경험을 제공합니다. 인터페이스 디자인은 단순하고 명확하며 사용하기 쉽습니다. 또한 다양한 스킨과 테마를 지원하고, 자신의 선호도에 따라 설정을 개인화하며, 다양한 오디오 형식의 재생을 지원하는 전용 음악 플레이어를 생성합니다. 또한 볼륨을 조정하는 오디오 게인 기능도 지원합니다. 과도한 볼륨으로 인한 청력 손상을 방지하려면 자신의 청력 상태에 따라 조정하십시오. 다음엔 내가 도와줄게
 NetEase 메일박스 마스터를 사용하는 방법
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase 메일박스 마스터를 사용하는 방법
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox는 중국 네티즌들이 널리 사용하는 이메일 주소로, 안정적이고 효율적인 서비스로 항상 사용자들의 신뢰를 얻어 왔습니다. NetEase Mailbox Master는 휴대폰 사용자를 위해 특별히 제작된 이메일 소프트웨어로 이메일 보내기 및 받기 프로세스를 크게 단순화하고 이메일 처리를 더욱 편리하게 만듭니다. 따라서 NetEase Mailbox Master를 사용하는 방법과 그 기능이 무엇인지 아래에서 이 사이트의 편집자가 자세한 소개를 제공하여 도움을 드릴 것입니다! 먼저, 모바일 앱스토어에서 NetEase Mailbox Master 앱을 검색하여 다운로드하실 수 있습니다. App Store 또는 Baidu Mobile Assistant에서 "NetEase Mailbox Master"를 검색한 후 안내에 따라 설치하세요. 다운로드 및 설치가 완료되면 NetEase 이메일 계정을 열고 로그인합니다. 로그인 인터페이스는 아래와 같습니다.
 Baidu Netdisk 앱 사용 방법
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Baidu Netdisk 앱 사용 방법
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
오늘날 클라우드 스토리지는 우리의 일상 생활과 업무에 없어서는 안 될 부분이 되었습니다. 중국 최고의 클라우드 스토리지 서비스 중 하나인 Baidu Netdisk는 강력한 스토리지 기능, 효율적인 전송 속도 및 편리한 운영 경험으로 많은 사용자의 호감을 얻었습니다. 중요한 파일을 백업하고, 정보를 공유하고, 온라인으로 비디오를 시청하고, 음악을 듣고 싶은 경우 Baidu Cloud Disk는 귀하의 요구를 충족할 수 있습니다. 그러나 많은 사용자가 Baidu Netdisk 앱의 구체적인 사용 방법을 이해하지 못할 수 있으므로 이 튜토리얼에서는 Baidu Netdisk 앱 사용 방법을 자세히 소개합니다. Baidu 클라우드 네트워크 디스크 사용 방법: 1. 설치 먼저 Baidu Cloud 소프트웨어를 다운로드하고 설치할 때 사용자 정의 설치 옵션을 선택하십시오.
 BTCC 튜토리얼: BTCC 교환에서 MetaMask 지갑을 바인딩하고 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC 튜토리얼: BTCC 교환에서 MetaMask 지갑을 바인딩하고 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask(중국어로 Little Fox Wallet이라고도 함)는 무료이며 호평을 받는 암호화 지갑 소프트웨어입니다. 현재 BTCC는 MetaMask 지갑에 대한 바인딩을 지원합니다. 바인딩 후 MetaMask 지갑을 사용하여 빠르게 로그인하고 가치를 저장하고 코인을 구매할 수 있으며 첫 바인딩에는 20 USDT 평가판 보너스도 받을 수 있습니다. BTCCMetaMask 지갑 튜토리얼에서는 MetaMask 등록 및 사용 방법, BTCC에서 Little Fox 지갑을 바인딩하고 사용하는 방법을 자세히 소개합니다. MetaMask 지갑이란 무엇입니까? 3천만 명 이상의 사용자를 보유한 MetaMask Little Fox Wallet은 오늘날 가장 인기 있는 암호화폐 지갑 중 하나입니다. 무료로 사용할 수 있으며 확장으로 네트워크에 설치할 수 있습니다.
 pip 미러 소스에 대한 간단한 가이드: 사용 방법을 쉽게 익힐 수 있습니다.
Jan 16, 2024 am 10:18 AM
pip 미러 소스에 대한 간단한 가이드: 사용 방법을 쉽게 익힐 수 있습니다.
Jan 16, 2024 am 10:18 AM
쉽게 시작하기: pip 미러 소스 사용 방법 전 세계적으로 Python이 인기를 끌면서 pip는 Python 패키지 관리를 위한 표준 도구가 되었습니다. 그러나 pip를 사용하여 패키지를 설치할 때 많은 개발자가 직면하는 일반적인 문제는 속도 저하입니다. 이는 기본적으로 pip가 Python 공식 소스나 기타 외부 소스에서 패키지를 다운로드하는데, 이러한 소스가 해외 서버에 있을 수 있어 다운로드 속도가 느려질 수 있기 때문입니다. 다운로드 속도를 향상시키기 위해 pip 미러 소스를 사용할 수 있습니다. pip 미러 소스란 무엇입니까? 쉽게 말하면 그냥




