js에서 사용자 정의 객체 구문 분석
이 글은 주로 js의 커스텀 객체 분석을 소개합니다. 이제는 모든 사람과 공유합니다. 도움이 필요한 친구들이 참고할 수 있습니다
1. 리터럴로 객체 만들기
var person = {
name: "sun",
age: 18,
work: function () {
console.log(this.name + "is working...");
},
address: {
home: "大屯里xxx路xxx小区xx单元xxx室",
phone: "123456789",
}
};
person.work();
console.log(person.address.home);2 .데이터 설명 및 액세스 설명 설정
var person = {
age: 18,
address: {
home: "大屯里xxx路xxx小区xx单元xxx室",
phone: "123456789",
}
};
Object.defineProperties(person, {
name: {
value: "sun", // 该属性的值,可被读取
writable: true, // 表示能否修改属性的值,默认值为true
configurable: true, // 表示能否delete该属性并重新定义,直接在对象上定义的属性默认值为true
enumerable: true // 表示能否通过for-in枚举,直接在对象上定义的属性默认值为true
},
work: {
value: function(){
console.log(this.name + "is working...");
},
// 通过Object.defineProperty和Object.defineProperties定义属性,
// 如果没有声明writable、configurable、enumerable,它们的默认值都是false
}
});
person.work();
console.log(person.address.home);3. get 및 set
var circle = {
value: 10,
get girth(){
return 2 * 3.14 * this.R
},
get area(){
return 3.4 * this.R * this.R
},
};
Object.defineProperty(circle, "R", {
get : function () {
return this.value;
},
set : function (val) {
console.log("半径被修改了!");
this.value = val;
}
});
circle.R = 100;
console.log("girth: " + circle.girth + "area: " + circle.area);4. 데이터 설명 및 액세스 설명 확인
var circle = {
R: 10,
// __proto__: null,
get area(){
return 3.4 * this.R * this.R
},
};
Object.defineProperty(circle, "site", {
value: [0, 2.2, 4.1],
// enumerable: true, // 是否可配置(读取),不设置为true时,Object.keys(circle))和Object.values(circle))将获取不到该键值对
});
console.log("R" in circle); // 检查属性
console.log(circle.hasOwnProperty("R")); // 检查自有的属性
console.log(circle.propertyIsEnumerable("R")); // 检查属性是否是可枚举的
// Object对象的方法
console.log(Object.keys(circle));
console.log(Object.values(circle));
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(circle)); // 检查对象自身所有属性
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(circle, "R")); // 得到circle对象关于R属性的描述2. 프로토타입
1. 프로토타입 해석
- 每一次创建函数,解析器都会向函数中添加一个属性:prototype - 如果函数作为普通函数调用prototype,没有任何作用 - 当该函数以构造函数的形式调用时,它会有一个隐含的属性__proto__指向其原型对象 - 每个实例有各自的__proto__指向原型对象的prototype, 也就是原型对象中的属性和方法被调用函数"共享" - 当类的原型对象prototype指向的内存地址发生改变时,已创建实例的__proto__ !== prototype,也就是不会被覆盖。而新创建的实例仍然是__proto__ === prototyp
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// Person.prototype.gender = "male";
// Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
// return this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old."
// };
Person.prototype = {
gender: "male",
sayHello: function () {
return this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old."
}
};
var p1 = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p1.sayHello();
console.log(Person.prototype);
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person);2. 프로토타입 및 __proto__
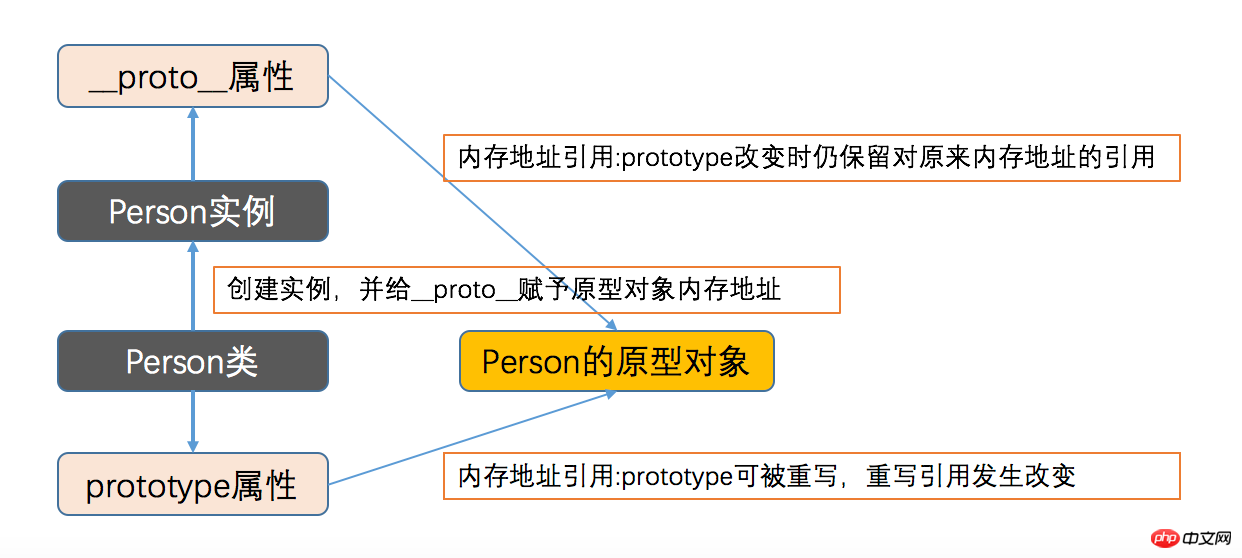
function Person() {}
var obj1 = { gender: "male"}; // 创建两个内存地址
var obj2 = { age: 200 };
Person.prototype = obj1;
var p1 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype);
console.log(p1.__proto__.gender);
console.log(Person.prototype);
Person.prototype = obj2;
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p2.__proto__.age);
console.log(Person.prototype);
console.log(p1.__proto__.age); // undefined
console.log(p2.__proto__.gender); // undefined
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // false,表示当prototype指向的内存地址改变时,已经创建的实例对象的__proto__仍指向原来的内存地址
console.log(p2.__proto__ === Person.prototype);function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {name: "xxx", age: 100,};
var p1 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__.name);
Person.prototype = { price: 998,};
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p2.__proto__.price);
console.log(p1.__proto__.price); // undefined
console.log(p2.__proto__.name); // undefiend
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // false, 原型对象的内存地址引用已发生改变
console.log(p1.__proto__.age); // __proto__指向的内存地址被保留
console.log(p2.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // truefunction Person() {}
Person.prototype = { price: 60 };
var p1 = new Person();
Person.prototype = { price: 998};
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // 依然是false
console.log(p2.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // true3. 프로토타입의 공유성
// prototype非常类似python中的静态属性和静态方法。每个实例都可以访问同一块内存空间。
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {price: 60};
var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__.price);
console.log(p2.__proto__.price);
console.log(Person.prototype.price);로그인 후 복사 4. 프로토타입의 상속
// prototype非常类似python中的静态属性和静态方法。每个实例都可以访问同一块内存空间。
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {price: 60};
var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__.price);
console.log(p2.__proto__.price);
console.log(Person.prototype.price);// 当访问实例对象的一个属性或方法时,它会先在对象自身中查找,如果有则直接使用;如果没有则在原型对象中继续查找,如果有则直接使用
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {price: 60};
var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.price);
console.log(p2.price);
console.log(Person.prototype.price);로그인 후 복사 3. 클래스
// 当访问实例对象的一个属性或方法时,它会先在对象自身中查找,如果有则直接使用;如果没有则在原型对象中继续查找,如果有则直接使用
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {price: 60};
var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.price);
console.log(p2.price);
console.log(Person.prototype.price);1. 클래스의 캡슐화
// 字面量方法(工厂方法) -- 直接在var obj = {}内部写代码,缺点是只实例化一次
// 构造函数方法 -- 只用构造函数声明this,缺点是可扩展性差,数据重复
// 原型方法 -- 只用prototype声明共有的属性和方法,缺点是实例的数据相同,不满足多态1. 혼합 생성자/프로토타입 방식
// 最广泛的使用方法
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// prototype写在外面是为了保证其动态增加公共属性和方法
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + " years old."); // 把共有的属性和方法封装到prototype中
};
var p = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p.sayHello();// 我把它写给Person的属性,让父类也能够访问
function Person(name, age) {
Person.group = Person.prototype.group = "西天取经组";
Person.toString = Person.prototype.toString = function (){
console.log("Person: " + Person.group)
};
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old.")
};
}
var person = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
console.log(person.constructor); // 检查构造器函数
console.log(person instanceof Person); // 检查是否为其原型类
person.sayHello();
Person.toString();2. 동적 프로토타입 메소드
// 也是常用的方法
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
if (typeof Person._initialized === "undefined"){
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + " years old.");
};
Person._initialized = true;
}
}
var p = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p.sayHello();3. 혼합 팩토리 메소드
// 混合工厂方法 -- 存在与工厂方法类似的问题,不建议使用
function Person(name, age) {
var obj = {};
obj.name = name;
obj.age = age;
obj.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + " years old.");
};
return obj
}
var p = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p.sayHello();4. 클래스 구조 재논의
function Person(name, age) {
// 静态属性
Person.group = "西天取经四人组,暗合金木水火土";
// 静态方法
Person.introduce = function () {
console.log("贫僧自东土大唐而来")
};
// 实例属性
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
// 实例方法,应该写在prototype中
this.say = function () {
console.log("hello, i'm " + this.name);
};
Person.prototype.introduce = Person.introduce; // 此时Person类和其实例都可以使用introduce方法
// 父类使用实例方法
Person.example = Person.prototype.example = function (self) {
self = self || this;
console.log(self.name + " " + self.age);
}
}
// 在python中,实例可以访问父类的属性和方法,父类也可以使用实例方法
// 在java和js中,实例不能调用父类的静态属性和静态方法,父类不能使用实例方法
// 如果想让实例和父类共享一个属性或者方法,就只能放到方法区并创建引用
var sun = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
Person.introduce(); // 父类调用静态方法
sun.say();
sun.introduce(); // 实例调用静态方法
Person.example(sun); // 父类调用实例方法
sun.example(); // 子类调用实例方法
// 可见,prototype是父类和实例的沟通桥梁2. 사용자 정의 클래스
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old.")
};
}
function New(Person) {
return function () {
var obj = {"__proto__": Person.prototype}; // 必须写在这里
Person.apply(obj, arguments); // arguments同this一样,是默认自带的关键字,用于存储传入的参数
return obj
}
}
var temp = New(Person);
var p1 = temp("孙悟空", 2000);
var p2 = temp("猪八戒", 1);
p1.sayHello();
p2.sayHello();3. 클래스 상속
1. 상속 복사 리터럴 객체(인스턴스)
var person = {
name: "Li",
age: 16,
address: {
home: "none",
city: "none",
},
say: function(){
console.log("hello, guy.")
}
};
var child = {gender:"female",};
function extendDeeply (p, c){
var c = c || {};
for (var prop in p) {
if (typeof p[prop] === "object") {
c[prop] = (p[prop].constructor === Array) ? [] : {};
extendDeeply(p[prop], c[prop]);
} else {
c[prop] = p[prop];
}
}
}
extendDeeply(person, child);
console.log(child);
child.say();2. 구현 객체 상속 호출 및 적용
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = {
home: "none",
city: "none",
}
}
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log("hello, guy.")
};
// 它继承的只是实例对象this,无法继承父类原型prototyp
function Child(name, age) {
Person.call(this, name, age);
this.gender = "female";
}
var child = new Child("Li", 16);
console.log(child);
// child.say(); 报错: child.say is not a function.对象继承的缺点:只继承了实例对象的可访问的属性和方法,没有继承原型
3. 프로토타입 체인 상속
// 原型链继承
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.name = "Person";
Person.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child(name, age) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
Child.prototype = Person.prototype;
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
var child = new Child("Li", 16);
console.log(child.name + " " + child.age);
child.toString();
// 其缺点是之继承了原型,没有继承实例4. 구현 클래스 상속 생성
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = {
home: "none",
city: "none",
}
}
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log("hello, guy.")
};
function Child(P, name, age) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = new P(name, age);
var c = new F();
return c;
}
Child.prototype.constructor = Child; // 无法修正
var child = new Child(Person, "Li", 16);
console.log(child);
console.log(child.name);
child.say();
console.log(child.constructor); // 结果为[Function: Person],构造器指向无法修正
console.log(child instanceof Child); // false
console.log(child instanceof Person); // true5. Object.create가 클래스 상속 구현 - 권장 방식
// Object.create继承,实现原理和上面的create类似
// 1.创建父类
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.sayPerson = function () {
console.log("hello, Person.")
};
// 2.创建子类
function Child(gender) {this.gender = gender;}
// 3.create继承
// Object.create的第二个参数是属性描述
Child.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype, {
name: {
value: "Li",
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
age: {
value: 16,
writable:true,
configurable:true,
enumerable:true,
},
}); // 重写子类prototype
Child.prototype.constructor = Child; // constructor 修正
// 4.在create之后写子类的prototype
Child.prototype.sayChild = function () {
console.log("hello, Child.")
};
var child = new Child("female");
console.log(child);
console.log(child.name + " " + child.age);
child.sayChild();
child.sayPerson();5. 조합 상속 - 권장 way
function Person(name, age) {
this.name =name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log(this.name + " " + this.age);
};
function Child(name, age, gender) {
Person.call(this, name, age);
this.gender = gender;
}
Child.prototype = new Person(); // new时不传参数,是为了只继承原型,即Child.prototype = Person.prototype
// Child.prototype = Person.prototype; // 两者等价
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
var child = new Child("Li", 16, "female");
console.log(child);
child.toString();
console.log(child instanceof Child); // true
console.log(child instanceof Person); // true6. 상속 요약
js继承需要继承两部分内容: - 一部分是父类构造函数中的this定义属性和方法,相当于继承初始化的数据 - 另一部分是父类的prototype,相当于继承实例方法- 要实现this的继承,可以用call(apply);要实现prtotype的继承,可以用原型链 - 要实现两者的继承,可以用this+prototype的组合方式,Object.create本质上也是这种思路
7. 상속에서 프로토타입, 생성자 및 __proto__의 관계
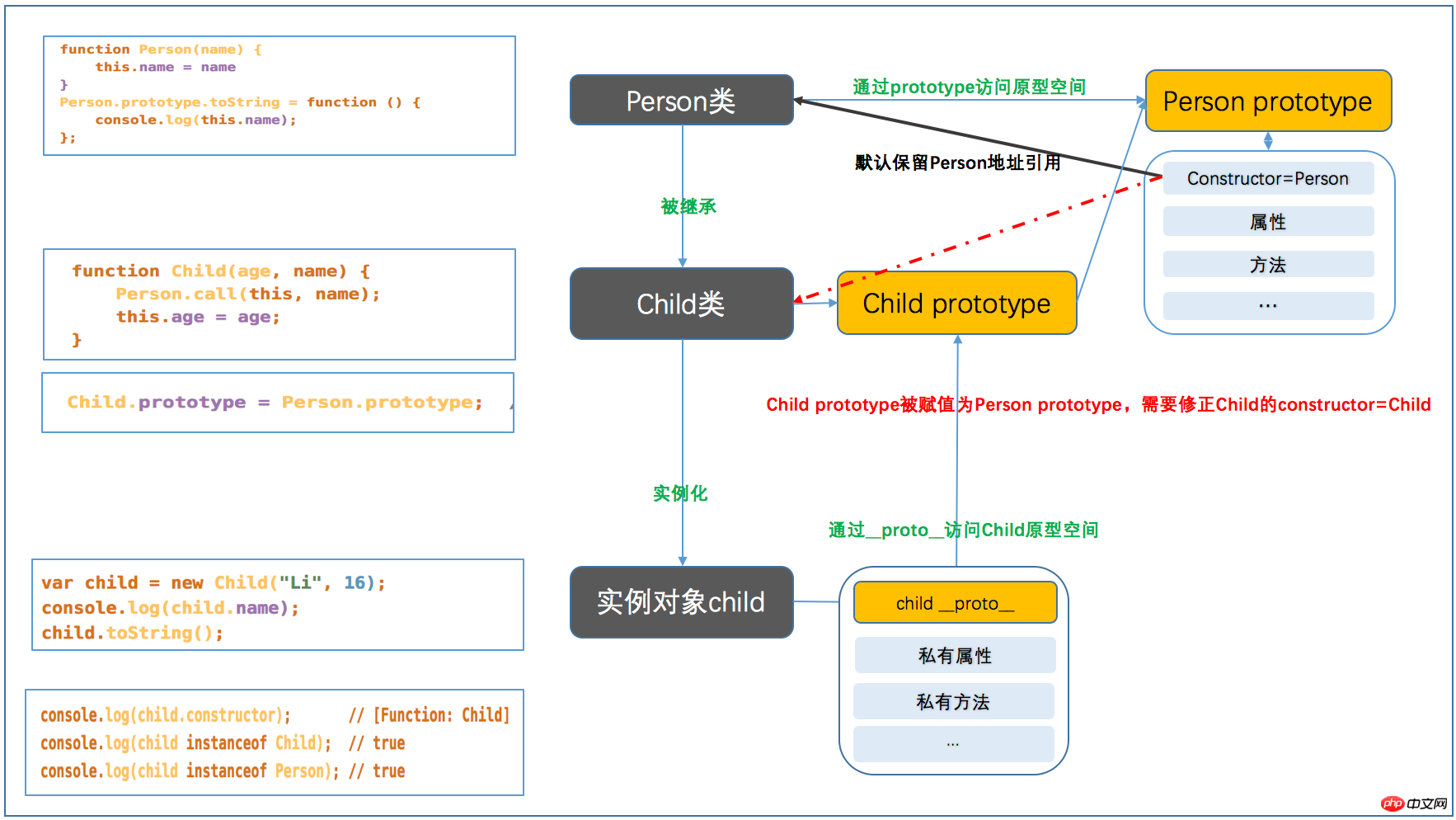 위 내용은 이 글의 전체 내용입니다. 여러분에게 도움이 되길 바랍니다. 도움이 됩니다. 더 많은 관련 내용을 보려면 PHP 중국어 웹사이트를 주목하세요!
위 내용은 이 글의 전체 내용입니다. 여러분에게 도움이 되길 바랍니다. 도움이 됩니다. 더 많은 관련 내용을 보려면 PHP 중국어 웹사이트를 주목하세요!
관련 권장 사항:
js의 이벤트 모델 분석js 변수 값을 php
위 내용은 js에서 사용자 정의 객체 구문 분석의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7518
7518
 15
15
 1378
1378
 52
52
 80
80
 11
11
 53
53
 19
19
 21
21
 67
67
 내 자신의 JavaScript 라이브러리를 어떻게 작성하고 게시합니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
내 자신의 JavaScript 라이브러리를 어떻게 작성하고 게시합니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
기사는 JavaScript 라이브러리 작성, 게시 및 유지 관리, 계획, 개발, 테스트, 문서 및 홍보 전략에 중점을 둡니다.
 브라우저에서 성능을 위해 JavaScript 코드를 최적화하려면 어떻게해야합니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
브라우저에서 성능을 위해 JavaScript 코드를 최적화하려면 어떻게해야합니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
이 기사는 브라우저에서 JavaScript 성능을 최적화하기위한 전략에 대해 설명하고 실행 시간을 줄이고 페이지로드 속도에 미치는 영향을 최소화하는 데 중점을 둡니다.
 프론트 엔드 열 용지 영수증에 대한 차량 코드 인쇄를 만나면 어떻게해야합니까?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
프론트 엔드 열 용지 영수증에 대한 차량 코드 인쇄를 만나면 어떻게해야합니까?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
프론트 엔드 개발시 프론트 엔드 열지대 티켓 인쇄를위한 자주 묻는 질문과 솔루션, 티켓 인쇄는 일반적인 요구 사항입니다. 그러나 많은 개발자들이 구현하고 있습니다 ...
 브라우저 개발자 도구를 사용하여 JavaScript 코드를 효과적으로 디버그하려면 어떻게해야합니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
브라우저 개발자 도구를 사용하여 JavaScript 코드를 효과적으로 디버그하려면 어떻게해야합니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
이 기사는 브라우저 개발자 도구를 사용하여 효과적인 JavaScript 디버깅, 중단 점 설정, 콘솔 사용 및 성능 분석에 중점을 둡니다.
 누가 더 많은 파이썬이나 자바 스크립트를 지불합니까?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
누가 더 많은 파이썬이나 자바 스크립트를 지불합니까?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
기술 및 산업 요구에 따라 Python 및 JavaScript 개발자에 대한 절대 급여는 없습니다. 1. 파이썬은 데이터 과학 및 기계 학습에서 더 많은 비용을 지불 할 수 있습니다. 2. JavaScript는 프론트 엔드 및 풀 스택 개발에 큰 수요가 있으며 급여도 상당합니다. 3. 영향 요인에는 경험, 지리적 위치, 회사 규모 및 특정 기술이 포함됩니다.
 소스 맵을 사용하여 조정 된 JavaScript 코드를 디버그하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:17 PM
소스 맵을 사용하여 조정 된 JavaScript 코드를 디버그하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:17 PM
이 기사는 소스 맵을 사용하여 원래 코드에 다시 매핑하여 미니어링 된 JavaScript를 디버그하는 방법을 설명합니다. 소스 맵 활성화, 브레이크 포인트 설정 및 Chrome Devtools 및 Webpack과 같은 도구 사용에 대해 설명합니다.
 Console.log 출력 결과의 차이 : 두 통화가 다른 이유는 무엇입니까?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
Console.log 출력 결과의 차이 : 두 통화가 다른 이유는 무엇입니까?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
Console.log 출력의 차이의 근본 원인에 대한 심층적 인 논의. 이 기사에서는 Console.log 함수의 출력 결과의 차이점을 코드에서 분석하고 그에 따른 이유를 설명합니다. � ...
 초보자를위한 타이프 스크립트, 2 부 : 기본 데이터 유형
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:10 AM
초보자를위한 타이프 스크립트, 2 부 : 기본 데이터 유형
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:10 AM
엔트리 레벨 타입 스크립트 자습서를 마스터 한 후에는 TypeScript를 지원하고 JavaScript로 컴파일하는 IDE에서 자신의 코드를 작성할 수 있어야합니다. 이 튜토리얼은 TypeScript의 다양한 데이터 유형으로 뛰어납니다. JavaScript에는 NULL, UNDEFINED, BOOLEAN, 번호, 문자열, 기호 (ES6에 의해 소개 됨) 및 객체의 7 가지 데이터 유형이 있습니다. TypeScript는이 기반으로 더 많은 유형을 정의 하며이 튜토리얼은이 모든 튜토리얼을 자세히 다룹니다. 널 데이터 유형 JavaScript와 마찬가지로 Null in TypeScript




