Vue의 라이프사이클 및 소스코드 구현(코드)
이 기사에서 제공하는 내용은 Vue의 라이프사이클과 소스 코드 구현(코드)에 대한 내용입니다. 도움이 필요한 친구들이 참고할 수 있기를 바랍니다.
학습을 통해 우리는 다음을 포함하여 Vue의 모든 기본 구문을 배웠습니다.
1, {{Mustache}} 구문
2. v-if, v-else, v-else-if, v-show
3. v-for
4. V-바인드
5. V-모델
6. v-on
이 문법을 이미 염두에 두셨다면 계속해서 읽어보시기 바랍니다. 이 문법에 능숙하지 않다면 이전 내용을 검토하시기 바랍니다.
이 장에서는 Vue의 수명주기를 알아봅니다. 먼저 Vue의 수명주기에 대한 정의를 살펴보겠습니다.
각 Vue 인스턴스는 생성될 때 일련의 초기화 프로세스를 거쳐야 합니다. 예를 들어 데이터 모니터링 설정, 템플릿 컴파일, 인스턴스를 DOM에 마운트, 데이터 변경 시 DOM 업데이트 등이 필요합니다. 동시에 라이프 사이클 후크라는 일부 기능도 이 프로세스 중에 실행되어 사용자가 다양한 단계에서 자신의 코드를 추가할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다.
Vue 공식 홈페이지에서 제공하는 설명 정보입니다. Vue가 인스턴스를 생성하고 최종적으로 완전히 소멸시키는 과정에서 Vue의 현재 상태에 맞춰 일련의 메서드가 실행됩니다. . 이러한 메서드를 It: 수명 주기 후크라고 합니다. 아래의 라이프 사이클 다이어그램을 살펴보겠습니다.
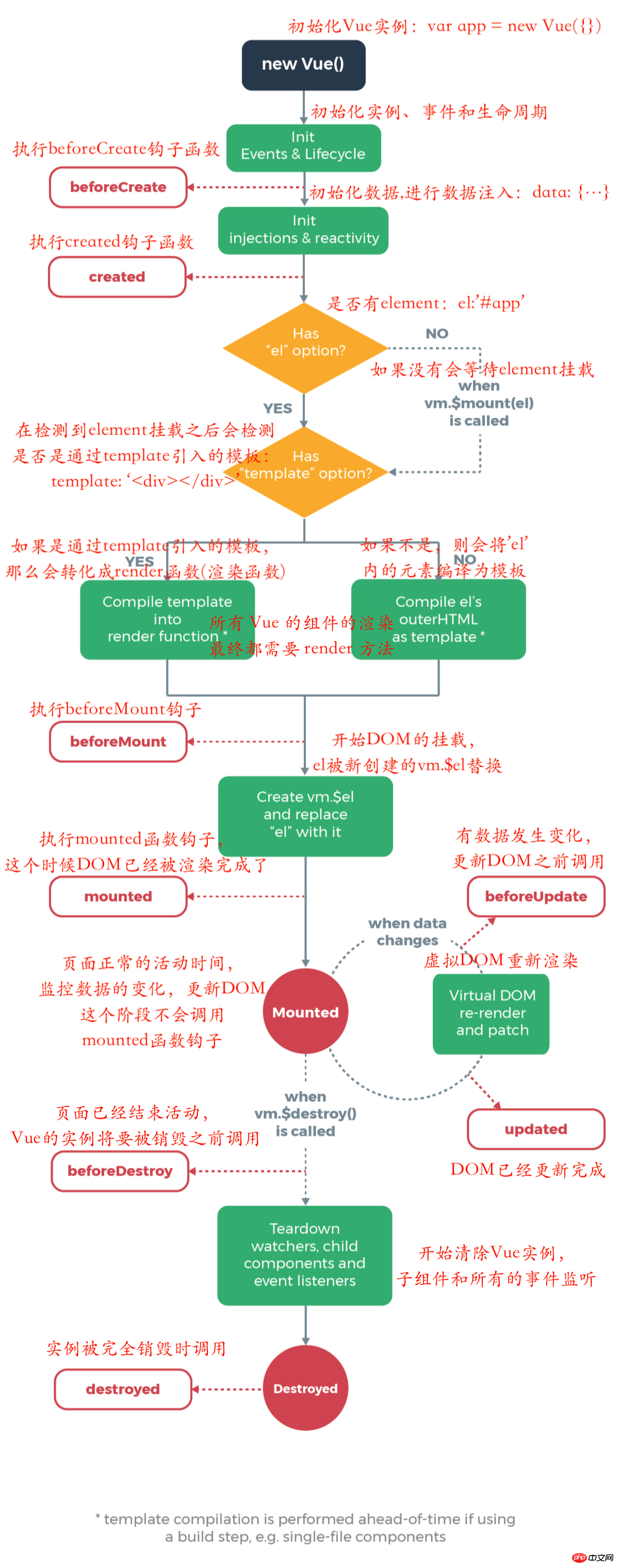
8개의 라이프 사이클 후크 함수가 표시되어 있습니다. 이 8개의 함수는 Vue의 전체 실행 주기를 나타냅니다. 현재 Vue 버전은 -2.5.16입니다. Vue에는 총 11개의 선언 주기 후크가 있습니다. 지금의 8개 외에도 컴포넌트에 대한 3개의 수명 주기 후크도 있습니다. 후크 기능 설명을 모두 살펴보겠습니다. 위의 다이어그램과 함께 Vue의 실행 주기를 더 잘 이해할 수 있습니다.
1. beforeCreate: 인스턴스가 초기화된 후 데이터 관찰자 및 이벤트/감시자 이벤트 구성 전에 호출됩니다.
2. 생성됨: 인스턴스가 생성된 직후 호출됩니다. 이 단계에서 인스턴스는 데이터 관찰자, 속성 및 메서드에 대한 작업, 감시/이벤트 이벤트 콜백 구성을 완료했습니다. 그러나 마운팅 단계가 아직 시작되지 않았으며 $el 속성이 현재 표시되지 않습니다.
3. beforeMount: 마운팅 시작 전 호출: 관련 렌더 함수가 처음 호출됩니다. $el 属性目前不可见。
3、beforeMount:在挂载开始之前被调用:相关的 render 函数首次被调用。
4、mounted:el 被新创建的 vm.$el 替换,并挂载到实例上去之后调用该钩子。如果 root 实例挂载了一个文档内元素,当 mounted 被调用时 vm.$el 也在文档内(PS:注意 mounted 不会承诺所有的子组件也都一起被挂载。如果你希望等到整个视图都渲染完毕,可以用 vm.$nextTick 替换掉 mounted:)。vm.$nextTick
4. 마운트됨: el이 새로 생성된 vm.$el로 대체되고, 인스턴스에 마운트된 후 후크가 호출됩니다. 루트 인스턴스가 문서 내 요소를 마운트하는 경우 vm.$el은 마운트가 호출될 때 문서에도 포함됩니다. (PS: Mounted는 모든 하위 구성 요소도 마운트된다는 것을 약속하지 않습니다. 전체 뷰가 렌더링될 때까지 기다리려면 Mounted를 vm.$nextTick으로 바꿀 수 있습니다 :). vm.$nextTick에 대해서는 다음 장에서 자세히 설명하겠습니다. 여기서는 누구나 이 내용을 알아야 합니다.
5. beforeUpdate: 가상 DOM이 패치되기 전에 발생하는 데이터가 업데이트될 때 호출됩니다. 추가된 이벤트 리스너를 수동으로 제거하는 등 업데이트하기 전에 기존 DOM에 액세스하는 데 적합합니다.
6. 업데이트됨: 이 후크는 데이터 변경으로 인해 가상 DOM이 다시 렌더링되고 패치된 후에 호출됩니다. 이 후크가 호출되면 컴포넌트 DOM이 업데이트되었으므로 이제 DOM에 의존하는 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다. 그러나 대부분의 경우 이 기간 동안 상태 변경을 피해야 합니다. 상태 변경에 응답하려면 일반적으로 계산된 속성이나 감시자를 대신 사용하는 것이 가장 좋습니다(PS: 계산된 속성과 감시자는 이후 장에서 소개됩니다).
7. 활성화됨: 연결 유지 구성 요소가 활성화될 때 호출됩니다. (PS: 구성 요소와 관련하여 구성 요소를 설명할 때 연결 유지가 소개됩니다.)
8. 비활성화됨: 연결 유지 구성 요소가 비활성화될 때 호출됩니다. (PS: 구성 요소와 관련하여 구성 요소를 설명할 때 연결 유지에 대해 소개합니다.)
9. beforeDestroy: 인스턴스가 소멸되기 전에 호출됩니다. 이 단계에서는 인스턴스를 여전히 완전히 사용할 수 있습니다.
10. 파괴됨: Vue 인스턴스가 파괴된 후에 호출됩니다. 호출되면 Vue 인스턴스가 가리키는 모든 것이 바인딩 해제되고 모든 이벤트 리스너가 제거되며 모든 하위 인스턴스가 삭제됩니다.
11. errorCaptured(2.5.0+의 새로운 기능): 하위 구성 요소의 오류가 캡처될 때 호출됩니다. 이 후크는 오류 개체, 오류가 발생한 구성 요소 인스턴스, 오류 소스에 대한 정보가 포함된 문자열 등 세 가지 매개 변수를 받습니다. 이 후크는 오류가 더 위쪽으로 전파되는 것을 방지하기 위해 false를 반환할 수 있습니다.
Vue(2.5.16)의 모든 라이프사이클 후크는 모두가 쉽게 이해할 수 있도록 creation에서 destroy까지의 프로세스가 Vue의 코드에서 어떻게 구현되는지 살펴보겠습니다. 여기를 클릭하면 Vue의 최신 코드를 다운로드할 수 있습니다.
Vue 소스코드의 기본 구조를 간략하게 살펴보겠습니다. Vue源代码的基础结构。
. ├── BACKERS.md ├── LICENSE ├── README.md├── benchmarks ├── dist ├── examples ├── flow ├── node_modules ├── package.json├── packages ├── scripts ├── src ├── test ├── types └── yarn.lock
这是下载下来代码之后的一级目录,dist文件夹下为Vue编译之后的代码,我们平时引入的Vue.js文件都在这里,Vue使用了flow作为JavaScript静态类型检查工具,相关的代码都在flow文件夹下面,scripts文件夹下面是代码构建的相关配置,Vue主要使用Rollup进行的代码构建,src文件夹下面就是所有Vue的源代码。我们这里不对其他的内容进行过多的描述,还是专注于我们的主题,Vue的声明周期代码是如何实现,我们看一下src文件夹。
. ├── compiler :Vue编译相关 ├── core :Vue的核心代码 ├── platforms :web/weex平台支持,入口文件 ├── server :服务端 ├── sfc :解析.vue文件 └── shared :公共代码
这是我们src文件夹下的目录结构,而我们Vue生成的地方就在/src/core/instance/index.js中。
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
} this._init(options)
}我们可以看到:Vue是一个方法,是一个使用Function来实现的构造函数,所以我们只能通过 new 的方式来去创建Vue的实例。然后通过Vue实例的_init方法来进行Vue的初始化。_init是Vue通过prototype来实现的一个原型属性。我们来看一下他的_init方法实现。
在/src/core/instance/init.js文件夹下,Vue实现了_init方法
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) { ...
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created') ...
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}我主要看与它生命周期有关的代码,我们可以看到,Vue先调用了initLifecycle(vm)、initEvents(vm)、initRender(vm)这三个方法,用于初始化生命周期、事件、渲染函数,这些过程发生在Vue初始化的过程(_init方法)中,并在调用beforeCreate钩子之前。
然后Vue通过callHook (vm: Component, hook: string)方法来去调用钩子函数(hook),它接收vm(Vue实例对象),hook(钩子函数名称)来去执行生命周期函数。在Vue中几乎所有的钩子(errorCaptured除外)函数执行都是通过callHook (vm: Component, hook: string)来调用的。我们来看一下callHook的代码,在/src/core/instance/lifecycle.js下:
export function callHook (vm: Component, hook: string) {
// #7573 disable dep collection when invoking lifecycle hooks
pushTarget() const handlers = vm.$options[hook]
if (handlers) {
for (let i = 0, j = handlers.length; i < j; i++) {
try {
handlers[i].call(vm)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `${hook} hook`)
}
}
} if (vm._hasHookEvent) {
vm.$emit('hook:' + hook)
}
popTarget()
}它的逻辑也非常简单,根据传入的hook从实例中拿到对应的回调函数数组(在/packages/vue-template-compiler/browser.js下的LIFECYCLE_HOOKS),然后便利执行。
然后在初始化生命周期、事件、渲染函数之后调用了beforeCreate钩子,在这个时候:我们还没有办法获取到data、props等数据。
在调用了beforeCreate钩子之后,Vue调用了initInjections(vm)、initState(vm)、initProvide(vm)这三个方法用于初始化data、props、watcher等等,在这些初始化执行完成之后,调用了created钩子函数,在这个时候:我们已经可以获取到data、props等数据了,但是Vue并没有开始渲染DOM,所以我们还不能够访问DOM(PS:我们可以通过vm.$nextTick来访问,在后面的章节我们会详细讲解)。
在调用了created钩子之后,Vue开始进行DOM的挂载,执行vm.$mount(vm.$options.el),在Vue中DOM的挂载就是通过Vue.prototype.$mount这个原型方法来去实现的。Vue.prototype.$mount原型方法的声明是在/src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js,我们看一下这个代码的实现:
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`
) return this
} const options = this.$options
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
if (template) {
if (typeof template === 'string') {
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
template = idToTemplate(template)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) {
warn(
`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`, this
)
}
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML
} else { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn('invalid template option:' + template, this)
} return this
}
} else if (el) {
template = getOuterHTML(el)
} if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile')
}
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile end')
measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end')
}
}
} return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
/**
* Get outerHTML of elements, taking care
* of SVG elements in IE as well.
*/function getOuterHTML (el: Element): string {
if (el.outerHTML) {
return el.outerHTML
} else {
const container = document.createElement('p')
container.appendChild(el.cloneNode(true))
return container.innerHTML
}
}这一部分代码的主要作用:就是进行template模板的解析。从上面的代码中可以看出,el不允许被挂载到body和html这样的根标签上面。然后判断是否有render函数 -> if (!options.render) {...},然后判断有没有template,template可以是string类型的id、DOM节点。没有的话则解析el作为template。由上面的代码可以看出我们无论是使用单文件组件(.Vue)或是通过el、template属性,它最终都会通过render函数的形式来进行整个模板的解析。
由我们的图示可以看出模板解析完成之后,会调用beforeMount钩子,那么这个beforeMount钩子是在哪里被调用的呢?我们接着往下看。$mount原型方法有一个可复用的设计,在/src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js
// public mount method
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}dist 폴더는 Vue용으로 컴파일된 코드입니다. 우리가 일반적으로 소개하는 Vue.js 파일은 모두 여기에 있습니다, Vue는 flow는 JavaScript 정적 유형 검사 도구입니다. <code>scripts 폴더 아래에는 Vue가 코드 구성을 위해 주로 Rollup을 사용합니다. code>src 폴더 아래에는 Vue의 모든 소스 코드가 있습니다. 여기서는 다른 내용을 너무 많이 설명하지 않지만 Vue의 수명 주기 코드가 구현되는 방법이라는 주제에 중점을 두고 src 폴더를 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if ((vm.$options.template && vm.$options.template.charAt(0) !== '#') ||
vm.$options.el || el) {
warn(
'You are using the runtime-only build of Vue where the template ' +
'compiler is not available. Either pre-compile the templates into ' +
'render functions, or use the compiler-included build.',
vm
)
} else {
warn(
'Failed to mount component: template or render function not defined.',
vm
)
}
}
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
const name = vm._name
const id = vm._uid
const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}`
const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}`
mark(startTag)
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor
// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child
// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, null, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}src 폴더 아래의 디렉토리 구조이며 Vue가 생성되는 위치는 /src/core/instance/index.js<입니다. /코드>. 🎜<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, &#39;beforeUpdate&#39;)
} const prevEl = vm.$el
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const prevActiveInstance = activeInstance
activeInstance = vm
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) {
// initial render
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(
vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false
/* removeOnly */,
vm.$options._parentElm,
vm.$options._refElm
)
// no need for the ref nodes after initial patch
// this prevents keeping a detached DOM tree in memory (#5851)
vm.$options._parentElm = vm.$options._refElm = null
} else {
// updates
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
activeInstance = prevActiveInstance
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
} if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent&#39;s updated hook.
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div>🎜우리는 다음을 볼 수 있습니다:<strong>Vue는 함수를 사용하여 구현된 생성자 메서드이므로 new를 통해서만 Vue 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있습니다. </strong>그런 다음 <code>Vue 인스턴스의 _init 메서드를 통해 Vue를 초기화합니다. _init는 prototype을 통해 Vue에서 구현한 prototype 속성입니다. 그의 _init 메소드 구현을 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜🎜/src/core/instance/init.js 폴더에는 Vue가 _init 메소드를 구현하고 있습니다🎜/**
* Flush both queues and run the watchers.
*/function flushSchedulerQueue () { ...
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue) ...}function callUpdatedHooks (queue) {
let i = queue.length while (i--) {
const watcher = queue[i]
const vm = watcher.vm
if (vm._watcher === watcher && vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'updated')
}
}
}Vue가 먼저 initLifecycle(vm), initEvents(vm) 및 initRender(vm)의 세 가지 메소드를 호출하여 라이프사이클, 이벤트 및 렌더링 함수 코드를 초기화하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. > 이러한 프로세스는 Vue 초기화 프로세스(_init 메서드)에서 beforeCreate 후크를 호출하기 전에 발생합니다. 🎜🎜그런 다음 Vue는 vm(Vue 인스턴스 객체)을 수신하는 <code>callHook(vm: Component, Hook: string) 메서드를 통해 hook 함수(hook)를 호출합니다. , 라이프사이클 함수를 실행하기 위한 후크(후크 함수 이름)입니다. Vue에서 거의 모든 후크(errorCaptured 제외) 함수 실행은 callHook(vm: Component, Hook: string)을 통해 호출됩니다. /src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 아래의 callHook 코드를 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜 Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {
const vm: Component = this
if (vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
return
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy')
vm._isBeingDestroyed = true
// remove self from parent
const parent = vm.$parent
if (parent && !parent._isBeingDestroyed && !vm.$options.abstract) {
remove(parent.$children, vm)
}
// teardown watchers
if (vm._watcher) {
vm._watcher.teardown()
}
let i = vm._watchers.length
while (i--) {
vm._watchers[i].teardown()
}
// remove reference from data ob
// frozen object may not have observer.
if (vm._data.__ob__) {
vm._data.__ob__.vmCount--
}
// call the last hook...
vm._isDestroyed = true
// invoke destroy hooks on current rendered tree
vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null)
// fire destroyed hook
callHook(vm, 'destroyed')
// turn off all instance listeners.
vm.$off()
// remove __vue__ reference
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = null
}
// release circular reference (#6759)
if (vm.$vnode) {
vm.$vnode.parent = null
}
}/packages/vue-template-compiler/browser.js 아래의 LIFECYCLE_HOOKS)에서 해당 콜백 함수 배열을 가져온 다음 실행. 🎜🎜그런 다음 라이프 사이클, 이벤트, 렌더링 함수를 초기화한 후 beforeCreate 후크가 호출되었습니다. 이때: 데이터를 얻을 수 있는 방법이 없습니다. 소품및 기타 데이터. 🎜🎜beforeCreate 후크를 호출한 후 Vue는 initInjections(vm), initState(vm) 및 initProvide(vm)의 세 가지 메서드를 호출하여 데이터, 소품을 초기화합니다. , watcher 등, 이러한 초기화가 완료된 후 생성된 후크 함수가 호출됩니다. 이때: 이미 데이터, 소품</code을 얻을 수 있습니다. >데이터를 기다리는 중이지만 Vue가 <code>DOM 렌더링을 시작하지 않았기 때문에 아직 DOM에 액세스할 수 없습니다. (PS: vm.$nextTick을 통해 액세스할 수 있습니다. 이에 대해서는 다음 장에서 자세히 설명하겠습니다.) 🎜🎜 생성된 후크를 호출한 후 Vue는 DOM 마운트를 시작하고 vm.$mount(vm.$options.el )<을 실행합니다. /code>, Vue의 DOM 마운팅은 프로토타입 메소드 <code>Vue.prototype.$mount를 통해 구현됩니다. Vue.prototype.$mount 프로토타입 메소드의 선언은 /src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js에 있습니다. :🎜export function activateChildComponent (vm: Component, direct?: boolean) {
if (direct) {
vm._directInactive = false
if (isInInactiveTree(vm)) {
return
}
} else if (vm._directInactive) {
return
} if (vm._inactive || vm._inactive === null) {
vm._inactive = false
for (let i = 0; i < vm.$children.length; i++) {
activateChildComponent(vm.$children[i])
}
callHook(vm, 'activated')
}
}
export function deactivateChildComponent (vm: Component, direct?: boolean) {
if (direct) {
vm._directInactive = true
if (isInInactiveTree(vm)) { return
}
} if (!vm._inactive) {
vm._inactive = true
for (let i = 0; i < vm.$children.length; i++) {
deactivateChildComponent(vm.$children[i])
}
callHook(vm, 'deactivated')
}
}템플릿 템플릿을 구문 분석하는 것입니다. 위 코드에서 볼 수 있듯이 el은 body 및 html와 같은 루트 태그에 마운트될 수 없습니다. 그런 다음 렌더링 함수-> if (!options.render) {...}가 있는지 확인하고 템플릿이 있는지 확인합니다. 템플릿은 문자열 유형 ID, DOM 노드일 수 있습니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 el을 템플릿으로 구문 분석하세요. 위 코드에서 단일 파일 구성 요소(.Vue)를 사용하든 el, 템플릿 속성을 사용하든 결국 를 통과한다는 것을 알 수 있습니다. render 함수를 사용하여 전체 템플릿을 구문 분석합니다. 🎜🎜다이어그램에서 템플릿 구문 분석이 완료된 후 beforeMount 후크가 호출되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 그러면 이 beforeMount 후크는 어디에서 호출됩니까? 아래를 살펴보자. $mount 프로토타입 메소드는 재사용 가능한 디자인을 가지고 있습니다. /src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js에는 이러한 코드 조각이 있습니다🎜// public mount method
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}这是一个公共的挂载方法,目的是为了被runtime only版本的Vue直接使用,它调用了mountComponent方法。我们看一下mountComponent方法的实现,实现在/src/core/instance/lifecycle.js下。
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if ((vm.$options.template && vm.$options.template.charAt(0) !== '#') ||
vm.$options.el || el) {
warn(
'You are using the runtime-only build of Vue where the template ' +
'compiler is not available. Either pre-compile the templates into ' +
'render functions, or use the compiler-included build.',
vm
)
} else {
warn(
'Failed to mount component: template or render function not defined.',
vm
)
}
}
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
const name = vm._name
const id = vm._uid
const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}`
const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}`
mark(startTag)
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor
// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child
// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, null, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}由上面的代码可以看出在执行vm._render()之前,调用了callHook(vm, 'beforeMount'),这个时候相关的 render 函数首次被调用,调用完成之后,执行了callHook(vm, 'mounted')方法,标记着el 被新创建的 vm.$el 替换,并被挂载到实例上。
然后就进入了我们页面正常交互的时间,也就是beforeUpdate和updated这两个回调钩子的执行时机。这两个钩子函数是在数据更新的时候进行回调的函数,Vue在/src/core/instance/lifecycle.js文件下有一个_update的原型声明:
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
} const prevEl = vm.$el
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const prevActiveInstance = activeInstance
activeInstance = vm
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) {
// initial render
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(
vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false
/* removeOnly */,
vm.$options._parentElm,
vm.$options._refElm
)
// no need for the ref nodes after initial patch
// this prevents keeping a detached DOM tree in memory (#5851)
vm.$options._parentElm = vm.$options._refElm = null
} else {
// updates
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
activeInstance = prevActiveInstance
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
} if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}我们可以看到在如果_isMounted为ture的话(DOM已经被挂载)则会调用callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')方法,然后会对虚拟DOM进行重新渲染。然后在/src/core/observer/scheduler.js下的flushSchedulerQueue()函数中渲染DOM,在渲染完成调用callHook(vm, 'updated'),代码如下:。
/**
* Flush both queues and run the watchers.
*/function flushSchedulerQueue () { ...
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue) ...}function callUpdatedHooks (queue) {
let i = queue.length while (i--) {
const watcher = queue[i]
const vm = watcher.vm
if (vm._watcher === watcher && vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'updated')
}
}
}当Vue实例需要进行销毁的时候回调beforeDestroy 、destroyed这两个函数钩子,它们的实现是在/src/core/instance/lifecycle.js下的Vue.prototype.$destroy中:
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {
const vm: Component = this
if (vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
return
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy')
vm._isBeingDestroyed = true
// remove self from parent
const parent = vm.$parent
if (parent && !parent._isBeingDestroyed && !vm.$options.abstract) {
remove(parent.$children, vm)
}
// teardown watchers
if (vm._watcher) {
vm._watcher.teardown()
}
let i = vm._watchers.length
while (i--) {
vm._watchers[i].teardown()
}
// remove reference from data ob
// frozen object may not have observer.
if (vm._data.__ob__) {
vm._data.__ob__.vmCount--
}
// call the last hook...
vm._isDestroyed = true
// invoke destroy hooks on current rendered tree
vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null)
// fire destroyed hook
callHook(vm, 'destroyed')
// turn off all instance listeners.
vm.$off()
// remove __vue__ reference
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = null
}
// release circular reference (#6759)
if (vm.$vnode) {
vm.$vnode.parent = null
}
}在$destroy这个原型函数中,执行了Vue的销毁操作,我们可以看到在执行销毁操作之前调用了callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy'),然后执行了一系列的销毁操作,包括删除掉所有的自身(self)、_watcher、数据引用等等,删除完成之后调用callHook(vm, 'destroyed')。
截止到这里,整个Vue生命周期图示中的所有生命周期钩子都已经被执行完成了。那么剩下的activated、deactivated、errorCaptured这三个钩子函数是在何时被执行的呢?我们知道这三个函数都是针对于组件(component)的钩子函数。其中activated、deactivated这两个钩子函数分别是在keep-alive 组件激活和停用之后回调的,它们不牵扯到整个Vue的生命周期之中,activated、deactivated这两个钩子函数的实现代码都在/src/core/instance/lifecycle.js下:
export function activateChildComponent (vm: Component, direct?: boolean) {
if (direct) {
vm._directInactive = false
if (isInInactiveTree(vm)) {
return
}
} else if (vm._directInactive) {
return
} if (vm._inactive || vm._inactive === null) {
vm._inactive = false
for (let i = 0; i < vm.$children.length; i++) {
activateChildComponent(vm.$children[i])
}
callHook(vm, 'activated')
}
}
export function deactivateChildComponent (vm: Component, direct?: boolean) {
if (direct) {
vm._directInactive = true
if (isInInactiveTree(vm)) { return
}
} if (!vm._inactive) {
vm._inactive = true
for (let i = 0; i < vm.$children.length; i++) {
deactivateChildComponent(vm.$children[i])
}
callHook(vm, 'deactivated')
}
}而对于errorCaptured来说,它是在2.5.0之后新增的一个钩子函数,它的代码在/src/core/util/error.js中:
export function handleError (err: Error, vm: any, info: string) {
if (vm) { let cur = vm while ((cur = cur.$parent)) {
const hooks = cur.$options.errorCaptured
if (hooks) {
for (let i = 0; i < hooks.length; i++) {
try {
const capture = hooks[i].call(cur, err, vm, info) === false
if (capture) return
} catch (e) {
globalHandleError(e, cur, 'errorCaptured hook')
}
}
}
}
}
globalHandleError(err, vm, info)
}function globalHandleError (err, vm, info) {
if (config.errorHandler) {
try {
return config.errorHandler.call(null, err, vm, info)
} catch (e) {
logError(e, null, 'config.errorHandler')
}
}
logError(err, vm, info)
}function logError (err, vm, info) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(`Error in ${info}: "${err.toString()}"`, vm)
} /* istanbul ignore else */
if ((inBrowser || inWeex) && typeof console !== 'undefined') {
console.error(err)
} else {
throw err
}
}他是唯一一个没有通过callHook方法来执行的钩子函数,而是直接通过遍历cur(vm).$options.errorCaptured,来执行config.errorHandler.call(null, err, vm, info)的钩子函数。整个逻辑的结构与callHook使非常类似的。
截止到目前Vue中所有的生命周期钩子我们都已经介绍完成了,其中涉及到了一些源码的基础,是因为我觉得配合源码来一起看的话,会对整个Vue的运行过程有个更好的理解。大家一定要下载下来Vue的源代码,对照着我们的讲解来走一遍这个流程。
相关推荐:
위 내용은 Vue의 라이프사이클 및 소스코드 구현(코드)의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7518
7518
 15
15
 1378
1378
 52
52
 81
81
 11
11
 53
53
 19
19
 21
21
 68
68
 Vue 용 버튼에 기능을 추가하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
Vue 용 버튼에 기능을 추가하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
HTML 템플릿의 버튼을 메소드에 바인딩하여 VUE 버튼에 함수를 추가 할 수 있습니다. 메소드를 정의하고 VUE 인스턴스에서 기능 로직을 작성하십시오.
 Vue에서 부트 스트랩을 사용하는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Vue에서 부트 스트랩을 사용하는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
vue.js에서 bootstrap 사용은 5 단계로 나뉩니다 : Bootstrap 설치. main.js.의 부트 스트랩 가져 오기 부트 스트랩 구성 요소를 템플릿에서 직접 사용하십시오. 선택 사항 : 사용자 정의 스타일. 선택 사항 : 플러그인을 사용하십시오.
 vue.js로 JS 파일을 참조하는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
vue.js로 JS 파일을 참조하는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
vue.js에서 JS 파일을 참조하는 세 가지 방법이 있습니다. & lt; script & gt; 꼬리표;; mounted () 라이프 사이클 후크를 사용한 동적 가져 오기; Vuex State Management Library를 통해 수입.
 Vue에서 시계를 사용하는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
Vue에서 시계를 사용하는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
vue.js의 시계 옵션을 사용하면 개발자가 특정 데이터의 변경 사항을들을 수 있습니다. 데이터가 변경되면 콜백 기능을 트리거하여 업데이트보기 또는 기타 작업을 수행합니다. 구성 옵션에는 즉시 콜백을 실행할지 여부와 DEEP를 지정하는 즉시 포함되며, 이는 객체 또는 어레이에 대한 변경 사항을 재귀 적으로 듣는 지 여부를 지정합니다.
 Vue가 이전 페이지로 돌아 오는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue가 이전 페이지로 돌아 오는 방법
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
vue.js는 이전 페이지로 돌아갈 수있는 네 가지 방법이 있습니다. $ router.go (-1) $ router.back () 사용 & lt; router-link to = & quot;/quot; Component Window.history.back () 및 메소드 선택은 장면에 따라 다릅니다.
 Vue는 천막/텍스트 스크롤 효과를 인식합니다
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Vue는 천막/텍스트 스크롤 효과를 인식합니다
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
CSS 애니메이션 또는 타사 라이브러리를 사용하여 VUE에서 Marquee/Text Scrolling Effects를 구현하십시오. 이 기사는 CSS 애니메이션 사용 방법을 소개합니다. & lt; div & gt; CSS 애니메이션을 정의하고 오버플로를 설정하십시오 : 숨겨진, 너비 및 애니메이션. 키 프레임을 정의하고 변환을 설정하십시오 : Translatex () 애니메이션의 시작과 끝에서. 지속 시간, 스크롤 속도 및 방향과 같은 애니메이션 속성을 조정하십시오.
 함수 인터셉트 vue를 사용하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:51 AM
함수 인터셉트 vue를 사용하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:51 AM
VUE의 기능 차단은 지정된 기간 내에 기능이 호출되는 횟수를 제한하고 성능 문제를 방지하는 데 사용되는 기술입니다. 구현 방법은 다음과 같습니다. lodash 라이브러리 가져 오기 : 'lodash'에서 import {debounce}; Debounce 기능을 사용하여 인터셉트 기능을 만듭니다. const debouncedfunction = debounce (() = & gt; { / logical /}, 500); 인터셉트 함수를 호출하면 제어 기능이 최대 500 밀리 초 안에 한 번 호출됩니다.
 Vue 다중 페이지 개발은 무엇을 의미합니까?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue 다중 페이지 개발은 무엇을 의미합니까?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
VUE 멀티 페이지 개발은 vue.js 프레임 워크를 사용하여 응용 프로그램을 구축하는 방법입니다. 여기서 응용 프로그램은 별도의 페이지로 나뉩니다. 코드 유지 보수 : 응용 프로그램을 여러 페이지로 분할하면 코드를보다 쉽게 관리하고 유지 관리 할 수 있습니다. 모듈 식 : 각 페이지는 쉬운 재사용 및 교체를 위해 별도의 모듈로 사용할 수 있습니다. 간단한 라우팅 : 페이지 간의 탐색은 간단한 라우팅 구성을 통해 관리 할 수 있습니다. SEO 최적화 : 각 페이지에는 자체 URL이있어 SEO가 도움이됩니다.




