이 기사에서는 js의 일반적인 상속 방법에 대한 예를 제공합니다. (예시 포함) 참고할만한 가치가 있으니 도움이 필요한 친구들이 참고하시면 좋을 것 같습니다.
객체 지향 프로그래밍에서 매우 중요한 측면은 객체 상속입니다. B 객체를 상속함으로써 A 객체는 B 객체의 모든 속성과 메소드를 직접 소유할 수 있습니다 . 이는 코드 재사용에 매우 유용합니다.
대부분의 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어는 "클래스"를 통해 객체 상속을 구현합니다. 전통적으로 JavaScript 언어 상속은 클래스(ES6에서 클래스 구문 도입)를 통해 구현되지 않고 "프로토타입 개체"를 통해 구현됩니다. 그렇다면 JS의 일반적인 상속 방법은 무엇입니까?
이 기사의 소스 코드를 원하시면 6가지 공통 상속 방법
방법 1. 프로토타입 체인 상속#🎜 🎜#
이 메서드의 핵심은 다음과 같습니다.하위 유형의 프로토타입은 상위 유형의 인스턴스 개체입니다.
//父类型
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.play = [1, 2, 3]
this.setName = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () { }
//子类型
function Student(price) {
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = new Person() // 子类型的原型为父类型的一个实例对象
var s1 = new Student(15000)
var s2 = new Student(14000)
console.log(s1,s2)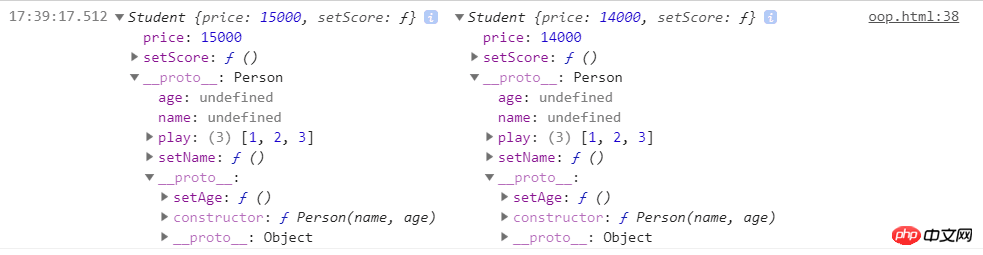 그러나 이 방법의 핵심은 하위 클래스의 프로토타입이 상위 클래스의 인스턴스를 가리키도록 하는 것입니다. , 그래서
그러나 이 방법의 핵심은 하위 클래스의 프로토타입이 상위 클래스의 인스턴스를 가리키도록 하는 것입니다. , 그래서
하위 클래스의 인스턴스는 __proto__를 통해 Person의 인스턴스인 Student.prototype에 접근할 수 있으므로 부모 클래스의 private 메소드에 접근한 후 부모 클래스의 프로토타입을 가리킬 수 있습니다. __proto__를 통해 상위 클래스 프로토타입에서 메서드를 가져옵니다. 따라서 상위 클래스의 프라이빗 및 퍼블릭 메서드와 속성은 하위 클래스의 퍼블릭 속성으로 처리됩니다. 메서드는 자체 공용 속성 및 메서드로 사용됩니다. . 값에 대해 작동하고 참조 데이터 유형에 대해 작동할 때 상위 클래스에 개인 속성이 있는 경우 하위 클래스에서 상속될 때 참조 유형의 속성이 공용 속성으로 사용됩니다. 1이 이 속성을 작동하면 하위 클래스 2에 영향을 미칩니다.
s1.play.push(4) console.log(s1.play, s2.play) console.log(s1.__proto__ === s2.__proto__)//true console.log(s1.__proto__.__proto__ === s2.__proto__.__proto__)//true
The play attribute in s1 동시에 s2의 play 속성도 변경됩니다.  또 주목해야 할 점은 하위 클래스에 새 메서드를 추가하거나 상위 클래스의 메서드를 재정의해야 할 때 프로토타입을 대체하는 문 뒤에 놓는 것을 잊지 마세요# 🎜 🎜#
또 주목해야 할 점은 하위 클래스에 새 메서드를 추가하거나 상위 클래스의 메서드를 재정의해야 할 때 프로토타입을 대체하는 문 뒤에 놓는 것을 잊지 마세요# 🎜 🎜#
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(price) {
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
// Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }//在这里写子类的原型方法和属性是无效的,
//因为会改变原型的指向,所以应该放到重新指定之后
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student(15000)
console.log(s1)Features:
부모 클래스에는 새로운 프로토타입 메서드/프로토타입 속성이 있으며, 하위 클래스에는 새로운 프로토타입 메소드/프로토타입 속성이 있습니다.
:# 🎜🎜#
모든 속성은 프로토타입 객체는 모든 인스턴스에서 공유됩니다
하위 클래스 인스턴스를 생성할 때 매개변수를 상위 클래스 생성자에 전달할 수 없습니다
속성과 메소드를 추가하려면
다음에 실행해야 하며 생성자에 배치할 수 없습니다이 메서드의 핵심은 다음과 같습니다. Student.prototype = new Person()하위 유형 생성자에서 범용 호출()을 사용하여 상위 유형 생성자를 호출합니다
<script>
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setName = function () {}
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age) // 相当于: this.Person(name, age)
/*this.name = name
this.age = age*/
this.price = price
}
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)</script># 🎜🎜#이 메서드는 부모 클래스의 프로토타입에도 메서드와 속성이 있는 경우 하위 클래스가 이러한 메서드와 속성을 가져올 수 없습니다.
console.log(s1.setAge())//Uncaught TypeError: s1.setAge is not a function
기능 :
 프로토타입 체인에서 상위 클래스 참조 속성을 공유하는 하위 클래스 인스턴스 문제 해결 상속 질문
프로토타입 체인에서 상위 클래스 참조 속성을 공유하는 하위 클래스 인스턴스 문제 해결 상속 질문
하위 클래스 인스턴스를 생성할 때 매개변수를 상위 클래스에 전달할 수 있습니다
:
# 🎜🎜#함수 재사용은 불가능합니다. 각 하위 클래스에는 성능에 영향을 미치는 상위 클래스 인스턴스 함수의 복사본이 있습니다
#🎜🎜 # function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setAge = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this,name,age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = new Person()
Student.prototype.constructor = Student//组合继承也是需要修复构造函数指向的
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
var s2 = new Student('Jack', 22, 14000)
console.log(s1)
console.log(s1.constructor) //Student
console.log(p1.constructor) //Person
这种方式融合原型链继承和构造函数的优点,是 JavaScript 中最常用的继承模式。不过也存在缺点就是无论在什么情况下,都会调用两次构造函数:一次是在创建子类型原型的时候,另一次是在子类型构造函数的内部,子类型最终会包含父类型对象的全部实例属性,但我们不得不在调用子类构造函数时重写这些属性。
优点:
可以继承实例属性/方法,也可以继承原型属性/方法
不存在引用属性共享问题
可传参
函数可复用
缺点:
调用了两次父类构造函数,生成了两份实例
方式四: 组合继承优化1
这种方式通过父类原型和子类原型指向同一对象,子类可以继承到父类的公有方法当做自己的公有方法,而且不会初始化两次实例方法/属性,避免的组合继承的缺点。
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age,
this.setAge = function () { }
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () { }
}
Student.prototype = Person.prototype
Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { }
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
console.log(s1)
但这种方式没办法辨别是对象是子类还是父类实例化
console.log(s1 instanceof Student, s1 instanceof Person)//true true console.log(s1.constructor)//Person
优点:
不会初始化两次实例方法/属性,避免的组合继承的缺点
缺点:
没办法辨别是实例是子类还是父类创造的,子类和父类的构造函数指向是同一个。
方式五: 组合继承优化2
借助原型可以基于已有的对象来创建对象,var B = Object.create(A)以A对象为原型,生成了B对象。B继承了A的所有属性和方法。
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name,
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
console.log("111")
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.price = price
this.setScore = function () {}
}
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype)//核心代码
Student.prototype.constructor = Student//核心代码
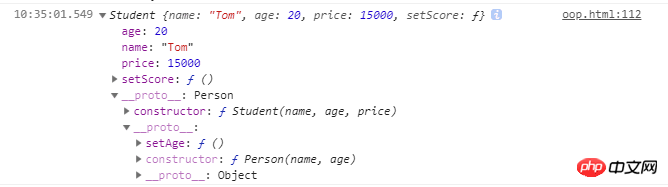
var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000)
console.log(s1 instanceof Student, s1 instanceof Person) // true true
console.log(s1.constructor) //Student
console.log(s1)同样的,Student继承了所有的Person原型对象的属性和方法。目前来说,最完美的继承方法!
方式六:ES6中class 的继承
ES6中引入了class关键字,class可以通过extends关键字实现继承,还可以通过static关键字定义类的静态方法,这比 ES5 的通过修改原型链实现继承,要清晰和方便很多。
ES5 的继承,实质是先创造子类的实例对象this,然后再将父类的方法添加到this上面(Parent.apply(this))。ES6 的继承机制完全不同,实质是先将父类实例对象的属性和方法,加到this上面(所以必须先调用super方法),然后再用子类的构造函数修改this。
需要注意的是,class关键字只是原型的语法糖,JavaScript继承仍然是基于原型实现的。
class Person {
//调用类的构造方法
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
//定义一般的方法
showName() {
console.log("调用父类的方法")
console.log(this.name, this.age);
}
}
let p1 = new Person('kobe', 39)
console.log(p1)
//定义一个子类
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, salary) {
super(name, age)//通过super调用父类的构造方法
this.salary = salary
}
showName() {//在子类自身定义方法
console.log("调用子类的方法")
console.log(this.name, this.age, this.salary);
}
}
let s1 = new Student('wade', 38, 1000000000)
console.log(s1)
s1.showName()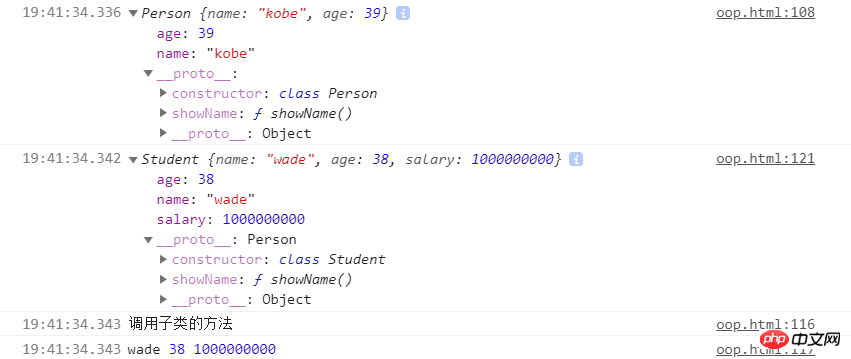
优点:
语法简单易懂,操作更方便
缺点:
并不是所有的浏览器都支持class关键字
위 내용은 js의 일반적인 상속 방법은 무엇입니까? (예제 포함)의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!