Redis 해시를 구현하는 방법

0. 서문
redis는 KV형 인메모리 데이터베이스입니다. 데이터베이스 저장소의 핵심은 Hash 테이블을 사용하여 저장된 db를 선택하는 것입니다. 다음은 redis의 해시 데이터 구조와 구현을 분석합니다.
1.hash 데이터 구조
/*Hash表一个节点包含Key,Value数据对 */
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; /* 指向下一个节点, 链接表的方式解决Hash冲突 */
} dictEntry;
/* 存储不同数据类型对应不同操作的回调函数 */
typedef struct dictType {
unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table; /* dictEntry*数组,Hash表 */
unsigned long size; /* Hash表总大小 */
unsigned long sizemask; /* 计算在table中索引的掩码, 值是size-1 */
unsigned long used; /* Hash表已使用的大小 */
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2]; /* 两个hash表,rehash时使用*/
long rehashidx; /* rehash的索引, -1表示没有进行rehash */
int iterators; /* */
} dict;2.hash 데이터 구조 다이어그램
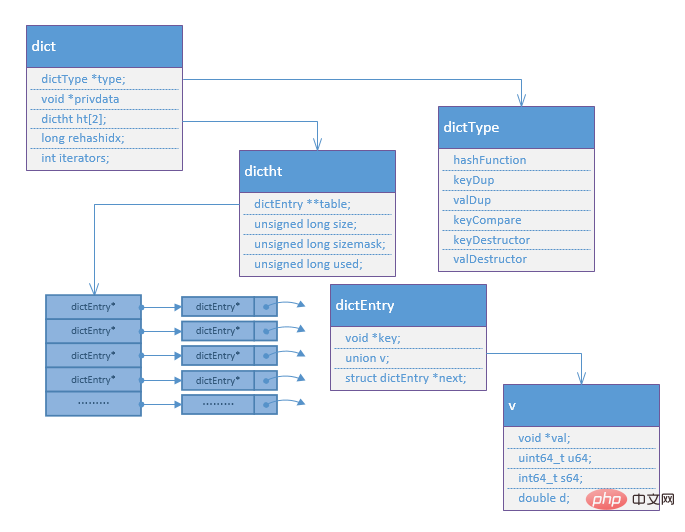
3. 프로그레시브 해시 설명
ht[2]에는 두 개의 해시가 있습니다. dict 테이블에서 처음으로 데이터를 저장할 때 ht[0]은 최소 4개의 해시 테이블을 생성합니다. ht[0]에서 사용된 크기와 크기가 동일하면 ht[에 크기가 생성됩니다. 1] dict *2 크기 해시 테이블에서 이때 ht[0]의 데이터는 ht[0]에 직접 복사되지 않지만 후속 작업(find, set)에서 점진적인 재해시가 수행됩니다. , get 등) 천천히 복사하면 새로 추가된 요소가 앞으로 ht[0]에 추가됩니다. 따라서 ht[1]이 가득 차면 ht[0]에 있는 모든 데이터가 확실해집니다. ]는 ht[1]에 복사됩니다.
4. 해시 테이블 생성
해시 테이블 생성 과정은 매우 간단합니다. dictCreate 함수를 호출하고, 메모리를 할당하고, 중간 변수를 초기화하면 됩니다.
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type, void *privDataPtr)
{
/*分配内存*/
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));
/*初始化操作*/
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}5. 요소 추가
해시 테이블에 요소를 추가하려면 먼저 공간이 충분한지 확인한 다음 키에 해당하는 해시 값을 계산한 다음 추가해야 할 키와 값을 테이블에 넣습니다.
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
/*添加入hash表中, 返回新添加元素的实体结构体*/
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key);
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
/*元素val值放入元素实体结构中*/
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
/*
*添加元素实体函数
*/
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key)
{
int index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
/*根据key值计算新元素在hash表中的索引, 返回-1则表示元素已存在, 直接返回NULL*/
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1)
return NULL;
/*如果在进行rehash过程,则新元素添加到ht[1]中, 否则添加到ht[0]中 */
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
/*设置元素key*/
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
/*
*计算索引的函数
*/
static int _dictKeyIndex(dict *d, const void *key)
{
unsigned int h, idx, table;
dictEntry *he;
/* 判断hash表是否空间足够, 不足则需要扩展 */
if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR)
return -1;
/* 计算key对应的hash值 */
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
/*计算索引*/
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
/*遍历冲突列表, 判断需要查找的key是否已经在冲突列表中*/
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return -1;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return idx;
}
/*
*判断hash表是否需要扩展空间
*/
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
/*redis的rehash采用的渐进式hash, rehash时分配了原来两倍的内存空间, 在rehash阶段空间必定够用*/
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
/* hash表是空的需要初始化空间, 默认是4*/
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
/* 已使用空间满足不了设置的条件*/
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
/*扩展空间, 使用空间的两倍*/
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
/*
*扩展空间或者初始化hash表空间
*/
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size)
{
dictht n;
/* 对需要分配大小圆整为2的倍数 */
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
/* 如果空间足够则表明调用错误 */
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
/*hash表为空初始化hash表*/
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
/*新分配的空间放入ht[1], 后面一步一步进行rehash*/
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}6. 요소 찾기
요소를 찾는 과정은 먼저 해시 값을 계산한 다음 ht[0]과 ht 사이의 값을 계산합니다. [1]의 인덱스 위치에서 검색합니다.
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
unsigned int h, idx, table;
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return NULL;
/*如果正在进行rehash, 执行一次rehash*/
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
/*由于可能正在rehash, 因此要从ht[0]和ht[1]中分别进行查找, 找不到返回NULL*/
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
/*遍历冲突列表查找元素*/
while(he) {
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}7. elements
요소를 삭제하려면 먼저 해당 요소를 검색한 후 해시 테이블에서 요소를 제거하세요. dictDelete를 호출하여 요소를 삭제하면 해당 요소가 차지한 공간도 동시에 삭제됩니다
int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0);
}
static int dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree)
{
unsigned int h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return DICT_ERR;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
/*查找元素到元素,进行删除操作, 并释放占用的内存*/
while(he) {
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
/* Unlink the element from the list */
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
if (!nofree) {
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
}
zfree(he);
d->ht[table].used--;
return DICT_OK;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return DICT_ERR; /* not found */
}hash 명령
hash 명령 작업은 비교적 간단합니다. 해시를 생성할 때 이는 dict가 아닌 ziplist 구조를 나타내는 기본 저장 구조를 나타냅니다. redis의 Ziplist 데이터 구조를 참조할 수 있습니다. , hash_max_ziplist_entries 및 hash_max_ziplist_value 값을 임계값으로, hash_max_ziplist_entries는 ziplist의 요소 수가 이 값을 초과하면 dict 구조로 변환해야 함을 의미합니다. hash_max_ziplist_value는 ziplist의 데이터 길이가 이 값보다 크다는 것을 의미합니다. , dict 구조로 변환해야 합니다.
더 많은 Redis 관련 기술 기사를 보려면 Redis Tutorial 칼럼을 방문하여 알아보세요!
위 내용은 Redis 해시를 구현하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7936
7936
 15
15
 1652
1652
 14
14
 1412
1412
 52
52
 1303
1303
 25
25
 1250
1250
 29
29
 Redis 클러스터 모드를 구축하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis 클러스터 모드를 구축하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis Cluster Mode는 Sharding을 통해 Redis 인스턴스를 여러 서버에 배포하여 확장 성 및 가용성을 향상시킵니다. 시공 단계는 다음과 같습니다. 포트가 다른 홀수 redis 인스턴스를 만듭니다. 3 개의 센티넬 인스턴스를 만들고, Redis 인스턴스 및 장애 조치를 모니터링합니다. Sentinel 구성 파일 구성, Redis 인스턴스 정보 및 장애 조치 설정 모니터링 추가; Redis 인스턴스 구성 파일 구성, 클러스터 모드 활성화 및 클러스터 정보 파일 경로를 지정합니다. 각 redis 인스턴스의 정보를 포함하는 Nodes.conf 파일을 작성합니다. 클러스터를 시작하고 Create 명령을 실행하여 클러스터를 작성하고 복제본 수를 지정하십시오. 클러스터에 로그인하여 클러스터 정보 명령을 실행하여 클러스터 상태를 확인하십시오. 만들다
 Redis 데이터를 지우는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Redis 데이터를 지우는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Redis 데이터를 지우는 방법 : Flushall 명령을 사용하여 모든 키 값을 지우십시오. FlushDB 명령을 사용하여 현재 선택한 데이터베이스의 키 값을 지우십시오. 선택을 사용하여 데이터베이스를 전환 한 다음 FlushDB를 사용하여 여러 데이터베이스를 지우십시오. del 명령을 사용하여 특정 키를 삭제하십시오. Redis-Cli 도구를 사용하여 데이터를 지우십시오.
 Redis 대기열을 읽는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
Redis 대기열을 읽는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
Redis의 대기열을 읽으려면 대기열 이름을 얻고 LPOP 명령을 사용하여 요소를 읽고 빈 큐를 처리해야합니다. 특정 단계는 다음과 같습니다. 대기열 이름 가져 오기 : "큐 :"와 같은 "대기열 : my-queue"의 접두사로 이름을 지정하십시오. LPOP 명령을 사용하십시오. 빈 대기열 처리 : 대기열이 비어 있으면 LPOP이 NIL을 반환하고 요소를 읽기 전에 대기열이 존재하는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
 Centos redis에서 lua 스크립트 실행 시간을 구성하는 방법
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
Centos redis에서 lua 스크립트 실행 시간을 구성하는 방법
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
CentOS 시스템에서는 Redis 구성 파일을 수정하거나 Redis 명령을 사용하여 악의적 인 스크립트가 너무 많은 리소스를 소비하지 못하게하여 LUA 스크립트의 실행 시간을 제한 할 수 있습니다. 방법 1 : Redis 구성 파일을 수정하고 Redis 구성 파일을 찾으십시오. Redis 구성 파일은 일반적으로 /etc/redis/redis.conf에 있습니다. 구성 파일 편집 : 텍스트 편집기 (예 : VI 또는 Nano)를 사용하여 구성 파일을 엽니 다. Sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf LUA 스크립트 실행 시간 제한을 설정 : 구성 파일에서 다음 줄을 추가 또는 수정하여 LUA 스크립트의 최대 실행 시간을 설정하십시오 (Unit : Milliseconds).
 Redis 만료 정책을 설정하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Redis 만료 정책을 설정하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
REDIS 데이터 만료 전략에는 두 가지 유형이 있습니다. 정기 삭제 : 만료 된 기간 캡-프리브-컨트 컨트 및 만료 된 시간 캡-프레임 딜레이 매개 변수를 통해 설정할 수있는 만료 된 키를 삭제하기위한주기 스캔. LAZY DELETION : 키를 읽거나 쓰는 경우에만 삭제가 만료 된 키를 확인하십시오. 그것들은 게으른 불쾌한 말입니다. 게으른 유발, 게으른 게으른 expire, Lazyfree Lazy-user-del 매개 변수를 통해 설정할 수 있습니다.
 Redis 명령 줄을 사용하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Redis 명령 줄을 사용하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Redis Command Line 도구 (Redis-Cli)를 사용하여 다음 단계를 통해 Redis를 관리하고 작동하십시오. 서버에 연결하고 주소와 포트를 지정하십시오. 명령 이름과 매개 변수를 사용하여 서버에 명령을 보냅니다. 도움말 명령을 사용하여 특정 명령에 대한 도움말 정보를 봅니다. 종금 명령을 사용하여 명령 줄 도구를 종료하십시오.
 Redis 카운터를 구현하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis 카운터를 구현하는 방법
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis Counter는 Redis Key-Value Pair 스토리지를 사용하여 다음 단계를 포함하여 계산 작업을 구현하는 메커니즘입니다. 카운터 키 생성, 카운트 증가, 카운트 감소, 카운트 재설정 및 카운트 얻기. Redis 카운터의 장점에는 빠른 속도, 높은 동시성, 내구성 및 단순성 및 사용 편의성이 포함됩니다. 사용자 액세스 계산, 실시간 메트릭 추적, 게임 점수 및 순위 및 주문 처리 계산과 같은 시나리오에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
 Debian Readdir의 성능을 최적화하는 방법
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
Debian Readdir의 성능을 최적화하는 방법
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
Debian Systems에서 ReadDir 시스템 호출은 디렉토리 내용을 읽는 데 사용됩니다. 성능이 좋지 않은 경우 다음과 같은 최적화 전략을 시도해보십시오. 디렉토리 파일 수를 단순화하십시오. 대규모 디렉토리를 가능한 한 여러 소규모 디렉토리로 나누어 읽기마다 처리 된 항목 수를 줄입니다. 디렉토리 컨텐츠 캐싱 활성화 : 캐시 메커니즘을 구축하고 정기적으로 캐시를 업데이트하거나 디렉토리 컨텐츠가 변경 될 때 캐시를 업데이트하며 readDir로 자주 호출을 줄입니다. 메모리 캐시 (예 : Memcached 또는 Redis) 또는 로컬 캐시 (예 : 파일 또는 데이터베이스)를 고려할 수 있습니다. 효율적인 데이터 구조 채택 : 디렉토리 트래버스를 직접 구현하는 경우 디렉토리 정보를 저장하고 액세스하기 위해보다 효율적인 데이터 구조 (예 : 선형 검색 대신 해시 테이블)를 선택하십시오.




