PHP7의 문자열 처리 로직 최적화에 대해!
추천 튜토리얼: "PHP7"
1. 코드를 통해 PHP 5와 PHP 7의 문자열 처리 차이점 비교
먼저 다음 샘플 코드를 살펴보세요.
$a = 'foo'; $b = 'bar'; $c = "I like $a and $b";
PHP 5.6에서 코드 실행 그리고 get opcode 출력은 다음과 같습니다. 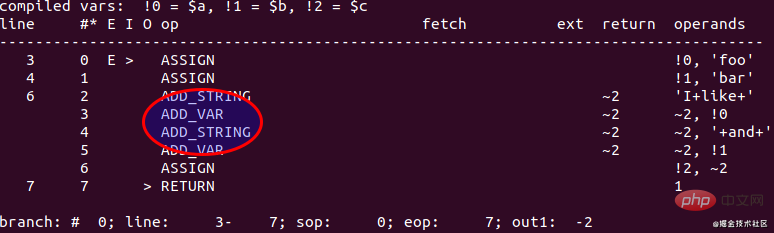
구체적인 실행 프로세스:
- 먼저 I like에 대한 메모리를 적용합니다.
- 그런 다음 I like foo에 대한 메모리를 적용한 다음 새로 적용된 메모리에 I like와 foo를 복사합니다. space 및 return
- 계속해서 I like foo에 대한 메모리 신청을 한 다음 I like foo 및 and를 새로 적용된 메모리 공간에 복사하고 return
- 마지막으로 I like foo 및 bar에 대한 메모리 신청을 한 다음 I like foo를 복사합니다. 그리고 새로 적용된 메모리에 바를 추가하여 반환
- 문자열 처리 중에 요청한 메모리 공간을 해제합니다
PHP 7에서 코드를 실행하면 결과 opcode 출력은 다음과 같습니다. 
PHP 7의 문자열 처리 과정 먼저 스택을 스택으로 만든 다음 연결할 문자열 조각을 스택 공간에 저장합니다. 마지막으로 메모리 공간을 한 번만 할당한 다음 스택에서 할당된 메모리 공간으로 결과를 이동하면 됩니다. . PHP 5와 비교하여 PHP 7은 처리 중에 메모리를 반복적으로 적용하는 프로세스를 피합니다. 문자열 처리에서 PHP 7의 성능 향상은 데이터 구조 로프를 사용함으로써 이점을 얻습니다.
2. Rope 데이터 구조 소개
⒈ Rope 소개
Rope는 이진 트리로 각 리프 노드는 문자열의 하위 문자열을 저장하고 각 리프가 아닌 노드는 왼쪽에 있는 각 하위 문자열을 저장합니다. 각 리프 노드에 저장된 하위 문자열에 포함된 총 문자 수(인덱스를 기반으로 지정된 문자 검색을 용이하게 함) 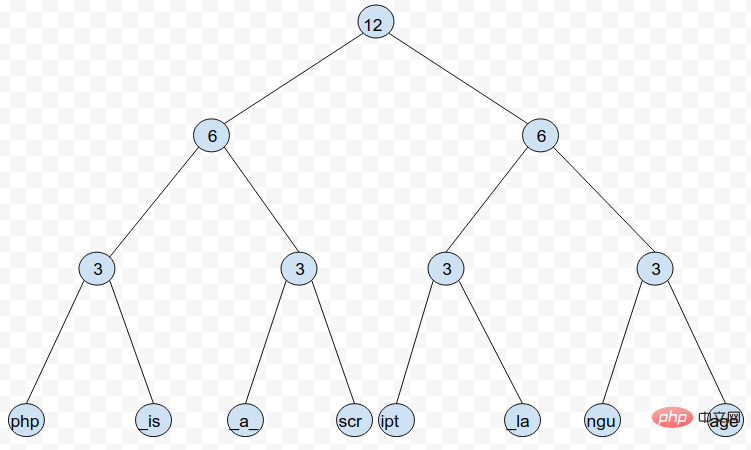
⒉ 로프의 장점과 단점
장점:
- Rope는 문자열 삽입, 삭제 및 기타 작업을 더 빠르게 만듭니다. 기존 문자 배열 방법에 비해 Rope의 시간 복잡도는 , 문자의 시간 복잡도 배열은 문자열을 문자 배열로 연산할 때는 먼저 배열을 복사해야 하는데, 이 작업에는 추가 메모리 공간이 필요합니다
- 또한 작업의 시간 복잡도를 최소화하기 위해 Rope를 AVL 트리로 구성하여 각 작업이 완료된 후 자체 균형을 이룰 수 있습니다. 그러나 이는 일부 실행 취소 작업의 복잡성을 증가시킬 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 높이가 다른 두 개의 로프를 연결하여 형성된 새로운 로프는 노드 회전을 통해 자체 균형을 달성한 후 원래 두 트리의 구조를 파괴할 수 있습니다. 이러한 방식으로 이전 연결 작업을 취소하면 매우 복잡해집니다.
- ⓵ concat
- concat 작업은 상대적으로 간단합니다. 두 개의 로프 트리를 새로운 로프 트리로 결합하기만 하면 됩니다.
- ⓶ Split
로프 트리를 분할할 때 두 가지 상황에 직면하게 됩니다. 분할 위치는 정확히 노드의 끝 또는 분할 위치가 리프 노드의 중간에 있습니다. 두 번째 경우의 경우 해당 리프 노드를 분할하여 첫 번째 경우로 변환할 수 있습니다. 첫 번째 경우는 노드의 위치에 따라 두 가지 상황으로 나눌 수 있습니다.
- a. 노드가 가장 왼쪽 또는 가장 오른쪽에 있는 지점
- b. 로프트리 안에 위치해 있어요
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.parent = None
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
self.weight = 0
def __repr__(self):
return str(self.__dict__)
def __str__(self):
return str(self.__dict__)
class Rope:
# 每个叶子节点最多存储 5 个字符,包括空字符在内
LEAF_DATA_LEN = 5
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def create_rope(self, parent, data, left_index, right_index):
"""
创建 rope 数据结构
:param parent: 父节点(根节点的父节点为空)
:param data: 用于创建 rope 数据结构的原始数据,这里只接受 list 和 str 两种类型
:param left_index: 起始位置索引
:param right_index: 结束位置索引
:return: Node
"""
if isinstance(data, str):
data = list(data)
elif not isinstance(data, list):
return
if right_index - left_index > self.LEAF_DATA_LEN:
node = Node("")
node.parent = parent
middle_index = (left_index + right_index) // 2
node.weight = middle_index - left_index
node.left = self.create_rope(node, data, left_index, middle_index)
node.right = self.create_rope(node, data, middle_index, right_index)
else:
node = Node(data[left_index: right_index])
node.parent = parent
node.weight = right_index - left_index
if node.parent is None:
self.root = node
return node
@staticmethod
def calc_weight(node):
"""
计算节点 weight 值
:param node:
:return:
"""
if node is None:
return 0
init_weight = node.weight
while node.right is not None:
node = node.right
init_weight += node.weight
return init_weight
def concat_rope(self, data1, data2):
"""
字符串连接
:param data1:
:param data2:
:return:
"""
r1 = Rope()
r1.create_rope(None, data1, 0, len(data1))
r2 = Rope()
r2.create_rope(None, data2, 0, len(data2))
node = Node("")
node.left = r1.root
node.right = r2.root
r1.root.parent = node
r2.root.parent = node
node.weight = self.calc_weight(r1)
self.root = node
def split_rope(self, data, index):
"""
字符串拆分
:param data: 要拆分的字符串
:param index: 拆分的位置(字符串索引从 0 开始计算)
:return: Rope
"""
if index < 0 or index > len(data) - 1:
return
node = self.create_rope(None, data, 0, len(data))
original_index = index
if index == self.root.weight - 1:
# 在根节点拆分
rope_left = node.left
rope_left.parent = None
rope_right = node.right
rope_right.parent = None
return rope_left, rope_right
elif index < self.root.weight - 1:
while index < node.weight - 1 and node.data == "":
node = node.left
else:
while index > node.weight - 1 and node.data == "":
index -= node.weight
node = node.right
if node.data != "":
# index 落在了最左侧和最右侧的两个叶子节点
if original_index < self.root.weight - 1:
# index 落在了最左侧的叶子节点
rope_left = self.create_rope(None, node.data[0:index + 1], 0, index + 1)
rope_right = self.root
# 更新 rope_right 的 weight
node.data = node.data[index + 1:]
while node is not None:
node.weight -= (index + 1)
node = node.parent
else:
# index 落在了最右侧的叶子节点
rope_left = self.root
rope_right = self.create_rope(None, node.data[index + 1:], 0, len(node.data[index + 1:]))
node.data = node.data[0:index + 1]
elif index == node.weight - 1:
# index 正好落在了节点的末尾
if original_index < self.root.weight:
# index 落在了最左侧分支中的非叶子节点的末尾
weight_sub = node.weight
rope_left = node.left
rope_left.parent = None
node.left = None
rope_right = self.root
# 更新节点 weight
while node is not None:
node.weight -= weight_sub
node = node.parent
else:
# index 落在了最右侧分支中的非叶子节点的末尾
rope_left = self.root
rope_right = node.right
rope_right.parent = None
node.right = None
else:
stack = []
if original_index < self.root.weight:
# index 落在了左子树中的节点
index -= node.weight
rope_left = node
rope_right = self.root
node.parent.left = None
node.parent = None
node = node.right
else:
# index 落在了右子树中的节点
rope_left = self.root
stack.append(node.right)
rope_right = None
node.right = None
node = node.left
while node.data == "" and index >= 0:
if index < node.weight - 1:
stack.append(node.right)
node.right = None
node = node.left
elif index > node.weight - 1:
node = node.right
index -= node.weight
else:
stack.append(node.right)
node.right = None
break
if node.data != "":
# 需要拆分叶子节点
new_node = Node(node.data[index + 1:])
new_node.weight = node.weight - index - 1
stack.append(new_node)
node.data = node.data[0:index + 1]
# 更新节点的 weight 信息
while node is not None:
if node.data != "":
node.weight = len(node.data)
else:
node.weight = self.calc_weight(node.left)
node = node.parent
# 组装 rope_right并更新节点的 weight 值
left_node = None
while len(stack) > 0:
root_node = Node("")
if left_node is None:
left_node = stack.pop()
root_node = left_node
else:
root_node.left = left_node
left_node.parent = root_node
right_node = stack.pop()
root_node.right = right_node
right_node.parent = root_node
root_node.weight = self.calc_weight(root_node.left)
left_node = root_node
if rope_right is None:
# index > self.root.weight - 1
rope_right = root_node
else:
# index < self.root.weight - 1
tmp = rope_right
while tmp.left is not None:
tmp = tmp.left
tmp.left = root_node
root_node.parent = tmp
while tmp.parent is not None:
tmp.weight = self.calc_weight(tmp.left)
tmp = tmp.parent
rope_right = tmp
rope_right.weight = self.calc_weight(rope_right.left)
return rope_left, rope_right
rope = Rope()
data = "php is a script language"
index = 18
left, right = rope.split_rope(data, index)
print(left)
print(right)三、 PHP 5 和 PHP 7 底层字符串处理逻辑比较
⒈ PHP 5 中字符串处理逻辑以及存在的问题
⓵ 处理逻辑
- PHP 5 中的字符串并没有固定的数据结构,而是采用 C 中以 NULL 结尾的字符数组的方式来处理
- 为了支持二进制字符串(字符串中包含 NULL 字符),还需要额外记录字符串的长度
⓶ 存在的问题
a. 字符串的长度
PHP 5 中 zval 中定义的字符串的长度为 int(有符号整型) 类型,这就导致即使是在 64 为机器上字符串的长度也不能超过 (LP64 数据模型中,int 永远只有 32 位)。
b. 格式不统一
// zval 中对字符串的定义,长度为 int 类型
typedef union _zvalue_value {
long lval;
double dval;
struct {
char *val; /* C string buffer, NULL terminated */
int len; /* String length : num of ASCII chars */
} str; /* string structure */
HashTable *ht;
zend_object_value obj;
zend_ast *ast;
} zvalue_value;
// 类实例结构体中对字符串的定义,此时字符串的长度为 zend_uint 类型,相较于 int 类型,字符串长度提升了一倍
struct _zend_class_entry {
char type;
const char *name; /* C string buffer, NULL terminated */
zend_uint name_length; /* String length : num of ASCII chars */
struct _zend_class_entry *parent;
int refcount;
zend_uint ce_flags;
/*……*/
}
// hashtable 的 key 中对字符串的定义,长度为 uint 类型
typedef struct _zend_hash_key {
const char *arKey; /* C string buffer, NULL terminated */
uint nKeyLength; /* String length : num of ASCII chars */
ulong h;
} zend_hash_key;PHP 5 中很多地方都支持二进制字符串,由于字符串没有一个固定的结构体,这就导致很多地方都有对字符串的定义。同时,由于各处对字符串长度的定义不同,导致各处支持的字符串长度也不同。
c. 内存消耗大
在较老版本的 PHP 中,由于没有引入 interned string,同一个字符串如果在多处被使用,为了互不影响,就需要复制多份出来,这就造成了对内存空间大量消耗。
static PHP_FUNCTION(session_id)
{
char *name = NULL;
int name_len, argc = ZEND_NUM_ARGS();
if (zend_parse_parameters(argc TSRMLS_CC, "|s", &name, &name_len) == FAILURE) {
return;
}
/* …… */
if (name) {
if (PS(id)) {
efree(PS(id));
}
PS(id) = estrndup(name, name_len);
}
}以 PHP 函数 session_id 为例,该函数最终将 name 完全复制一份然后存入 PS(id)。这样,后续代码对 name 进行的任何操作都不会影响 PS(id) 中存储的值。
⓷ interned string
从 PHP 5.4 起,为了解决上述字符串复制导致内存消耗大的问题,PHP 引入了 interned string 。另外,由于 interned string 需要共享内存空间,所以在线程安全的 PHP 版本中并不被支持。
所谓 interned string,即一个字符串在一个进程中只存储一次。当一个 php-fpm 进程启动时,会申请一块 size 为 1MB 的 buffer,持久化的字符串(字符串常量、函数名、变量名、类名、方法名……)会被存储到该缓冲并添加到一个 hashtable 中。由于 PHP 处理的 request 之间是相互独立的,所以一个 request 处理完成后,其间在内存中产生的数据都会被销毁。为了在处理 request 的过程中也能使用 interned string,在 request 到来时 PHP 会记录当前 interned string buffer 的 top 位置,在该 request 请求的处理完成后,top 位置之后消耗的空间又会被恢复。

- interned string 的初始化,只会发生在 PHP 启动以及 PHP 脚本的编译阶段
- interned string 是只读的,既不能修改,也不能销毁
- 由于 interned string buffer 只有 1MB 的空间,当 1MB 的空间存满后,后续的字符串处理还会回到引入 interned string 之前的状态
interned string 的优势
- 一个字符串只会存储一次,节省了内存空间
- interned string 的 hash 只会计算一次,然后被多次使用
- interned string 的比较最终转换成了指针地址的比较
由于需要操作 hashtable,interned string 的初始化和创建会比较复杂,也正因为如此,并不是所有的字符串都适合存入 interned string。
⒉ PHP 7 中对字符串处理进行的优化
struct _zend_string {
zend_refcounted_h gc;
zend_ulong h; /* hash value */
size_t len;
char val[1];
};
typedef struct _zend_refcounted_h {
uint32_t refcount; /* reference counter 32-bit */
union {
uint32_t type_info;
} u;
} zend_refcounted_h;PHP 7 中字符串有了固定的结构 zend_string
PHP 7 中字符串的长度类型为 size_t,字符串的长度不再局限于 PHP 5 中的 ,尤其在 64 位的机器上,字符串的长度取决于平台支持的最大长度。
PHP 7 中字符串内容的存储不再像之前使用 char * ,而是使用了 struct hack ,使得字符串内容和 zend_string 一起存储在一块连续的内存空间。同时,zend_string 还内嵌了字符串的 hash 值,这样,对于一个指定的字符串只需要进行一次 hash 计算。
PHP 7 中字符串引入了引用计数,这样,只要字符串还在被使用,就不用担心会被销毁。
static PHP_FUNCTION(session_id)
{
zend_string *name = NULL;
int argc = ZEND_NUM_ARGS();
/* …… */
if (name) {
if (PS(id)) {
zend_string_release(PS(id));
}
PS(id) = zend_string_copy(name);
}
}
static zend_always_inline zend_string *zend_string_copy(zend_string *s)
{
if (!ZSTR_IS_INTERNED(s)) {
GC_REFCOUNT(s)++;
}
return s;
}
static zend_always_inline void zend_string_release(zend_string *s)
{
if (!ZSTR_IS_INTERNED(s)) {
if (--GC_REFCOUNT(s) == 0) {
pefree(s, GC_FLAGS(s) & IS_STR_PERSISTENT);
}
}
}仍以函数 session_id 为例,设置 session_id 时不再需要将 name 完全复制,而只是将 name 的引用计数加 1。在删除字符串时也是同样,将字符串的引用计数减 1,只有引用计数为 0 时才会真正销毁字符串。
PHP 7 中的 interned string 不再需要单独申请 interned string buffer 来存储,而是在 zend_string 的 gc 中将 type_info 标记为 IS_STR_INTERNED。这样,在销毁字符串时,zend_string_release 会检查字符串是否为 interned string,如果是则不会进行任何操作。
위 내용은 PHP7의 문자열 처리 로직 최적화에 대해!의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7470
7470
 15
15
 1377
1377
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 48
48
 19
19
 19
19
 29
29


