Angular에서 Navigate() 및 NavigateByUrl() 사용 방법의 차이점에 대한 간략한 설명
라우팅은 Angular 애플리케이션의 핵심입니다. 이 기사에서는 Angular Router를 이해하고 Navigate()와 NavigationByUrl() 사용법의 차이점을 자세히 소개합니다.

라우팅은 Angular 애플리케이션의 핵심으로, 요청된 경로와 관련된 구성 요소를 로드하고 특정 경로에 대한 관련 데이터를 가져옵니다. 이를 통해 우리는 다양한 경로를 제어하고, 다양한 데이터를 얻고, 다양한 페이지를 렌더링할 수 있습니다. [관련 튜토리얼 추천: "angular Tutorial"]
라우터 설치
먼저 Angular Router를 설치해야 합니다. 다음 작업 중 하나를 실행하여 이 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
yarn add @angular/router # OR npm i --save @angular/router
위 명령이 실행된 후 @angular/router 모듈이 node_modules 폴더에 자동으로 다운로드됩니다. . @angular/router 模块到 node_modules 文件夹中。
Base href
我们需要做的最后一件事,是将 <base> 标签添加到我们的 index.html 文件中。路由需要根据这个来确定应用程序的根目录。例如,当我们转到 http://example.com/page1 时,如果我们没有定义应用程序的基础路径,路由将无法知道我们的应用的托管地址是 http://example.com 还是 http://example.com/page1 。
这件事操作起来很简单,只需打开项目中的 index.html 文件,添加相应的 <base> 标签,具体如下:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<base href="/">
<title>Application</title>
</head>
<body>
<app-root></app-root>
</body>
</html>以上配置信息告诉 Angular 路由,应用程序的根目录是 / 。
Using the router
要使用路由,我们需要在 AppModule 模块中,导入 RouterModule。具体如下:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule
],
bootstrap: [
AppComponent
],
declarations: [
AppComponent
]
})
export class AppModule {}此时我们的路由还不能正常工作,因为我们还未配置应用程序路由的相关信息。RouterModule 对象为我们提供了两个静态的方法:forRoot() 和forChild() 来配置路由信息。
RouterModule.forRoot()
RouterModule.forRoot() 方法用于在主模块中定义主要的路由信息,通过调用该方法使得我们的主模块可以访问路由模块中定义的所有指令。接下来我们来看一下如何使用 forRoot() :
// ...
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [];
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(ROUTES)
],
// ...
})
export class AppModule {}我们通过使用 const 定义路由的配置信息,然后把它作为参数调用 RouterModule.forRoot() 方法,而不是直接使用 RouterModule.forRoot([...]) 这种方式,这样做的好处是方便我们在需要的时候导出 ROUTES 到其它模块中。
RouterModule.forChild()
RouterModule.forChild() 与 Router.forRoot() 方法类似,但它只能应用在特性模块中。
友情提示:根模块中使用 forRoot(),子模块中使用 forChild()
这个功能非常强大,因为我们不必在一个地方(我们的主模块)定义所有路由信息。反之,我们可以在特性模块中定义模块特有的路由信息,并在必要的时候将它们导入我们主模块。RouterModule.forChild() 的使用方法如下:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [];
@NgModule({
imports: [
CommonModule,
RouterModule.forChild(ROUTES)
],
// ...
})
export class ChildModule {}通过以上示例,我们知道在主模块和特性模块中,路由配置对象的类型是一样的,区别只是主模块和特性模块中需调用不同的方法,来配置模块路由。接下来我们来介绍一下如何配置 ROUTES 对象。
Configuring a route
我们定义的所有路由都是作为 ROUTES 数组中的对象。首先,为我们的主页定义一个路由:
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{ path: '', component: HomeComponent }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(ROUTES)
],
// ...
})
export class AppModule {}示例中我们通过 path 属性定义路由的匹配路径,而 component 属性用于定义路由匹配时需要加载的组件。
友情提示:我们使用 path: '' 来匹配空的路径,例如:https://yourdomain.com
Displaying routes
配置完路由信息后,下一步是使用一个名为 router-outlet 的指令告诉 Angular 在哪里加载组件。当 Angular 路由匹配到响应路径,并成功找到需要加载的组件时,它将动态创建对应的组件,并将其作为兄弟元素,插入到 router-outlet 元素中。
在我们 AppComponent 组件中,我们可以在任意位置插入 router-outlet
Base href
마지막으로 해야 할 일은 index.html 파일에 <base> 태그를 추가하는 것입니다. 라우터는 애플리케이션의 루트 디렉터리를 결정하기 위해 이 정보가 필요합니다. 예를 들어 http://example.com/page1로 이동할 때 앱의 기본 경로를 정의하지 않으면 라우터는 앱의 호스팅 주소가 < 코드>http: //example.com 또는 http://example.com/page1.
이 작업은 매우 간단합니다. 프로젝트에서 index.html 파일을 열고 다음과 같이 해당 <base> 태그를 추가하면 됩니다. 위의 구성 정보는 Angular 라우팅에 애플리케이션의 루트 디렉터리가 /임을 알려줍니다. 라우터 사용
🎜🎜라우팅을 사용하려면 AppModule 모듈에서 RouterModule을 가져와야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 다음과 같습니다. 🎜import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<div class="app">
<h3 id="Our-nbsp-app">Our app</h3>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent {}forRoot() 및 forChild()라는 두 가지 정적 메서드를 제공합니다. 🎜🎜RouterModule.forRoot()🎜
🎜RouterModule.forRoot() 이 메소드는 메인 모듈에서 주요 라우팅 정보를 정의하는 데 사용됩니다. module 라우팅 모듈에 정의된 모든 지시문에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 다음으로 forRoot() 사용법을 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
import { ProfileComponent } from './profile/profile.component';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{ path: '', component: HomeComponent },
{ path: '/profile/:username', component: ProfileComponent }
];RouterModule.forRoot()의 매개변수로 호출합니다. <code>RouterModule.forRoot([...])를 직접 사용하는 대신 메서드를 사용하면 ROUTES를 다른 항목으로 내보내는 것이 편리하다는 장점이 있습니다. 필요할 때 모듈. 🎜🎜RouterModule.forChild()🎜
🎜RouterModule.forChild()는 Router.forRoot() 메서드와 유사하지만 기능 모듈에 적용됩니다. 알림: 루트 모듈에서는
forRoot()를 사용하고 하위 모듈에서는 forChild()를 사용하세요. 모든 라우팅 정보가 정의되어 있는 곳(메인 모듈)에서 사용할 필요는 없습니다. 대신 기능 모듈에서 모듈별 라우팅 정보를 정의하고 필요할 때 기본 모듈로 가져올 수 있습니다.
RouterModule.forChild()의 사용법은 다음과 같습니다. 🎜import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'profile-page',
template: `
<div class="profile">
<h3 id="nbsp-username-nbsp">{{ username }}</h3>
</div>
`
})
export class SettingsComponent implements OnInit {
username: string;
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.route.params.subscribe((params) => this.username = params.username);
}
}ROUTES 객체를 구성하는 방법을 소개하겠습니다. 🎜🎜🎜경로 구성🎜🎜🎜우리가 정의하는 모든 경로는 ROUTES 배열의 객체입니다. 먼저 홈페이지에 대한 경로를 정의합니다. 🎜import { SettingsComponent } from './settings/settings.component';
import { ProfileSettingsComponent } from './settings/profile/profile.component';
import { PasswordSettingsComponent } from './settings/password/password.component';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{
path: 'settings',
component: SettingsComponent,
children: [
{ path: 'profile', component: ProfileSettingsComponent },
{ path: 'password', component: PasswordSettingsComponent }
]
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(ROUTES)
],
})
export class AppModule {}경로: ''를 사용하여 빈 경로를 일치시킵니다. 예: https://yourdomain.com🎜🎜🎜경로 표시 중🎜🎜🎜구성 완료 라우팅 정보를 사용하여 다음 단계는 router-outlet이라는 지시문을 사용하여 구성 요소를 로드할 위치를 Angular에 알려주는 것입니다. Angular 라우팅이 응답 경로와 일치하고 로드해야 하는 구성 요소를 성공적으로 찾으면 해당 구성 요소를 동적으로 생성하고 router-outlet 요소에 형제 요소로 삽입합니다. 🎜🎜AppComponent 구성 요소에서 router-outlet 지시문을 어디에나 삽입할 수 있습니다. 🎜import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'settings-page',
template: `
<div class="settings">
<settings-header></settings-header>
<settings-sidebar></settings-sidebar>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
`
})
export class SettingsComponent {}如果路由始终是静态的,那没有多大的用处。例如 path: '' 是加载我们 HomeComponent 组件的静态路由。我们将介绍动态路由,基于动态路由我们可以根据不同的路由参数,渲染不同的页面。
例如,如果我们想要在个人资料页面根据不同的用户名显示不同的用户信息,我们可以使用以下方式定义路由:
import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
import { ProfileComponent } from './profile/profile.component';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{ path: '', component: HomeComponent },
{ path: '/profile/:username', component: ProfileComponent }
];这里的关键点是 : ,它告诉 Angular 路由,:username 是路由参数,而不是 URL 中实际的部分。
友情提示:如果没有使用 : ,它将作为静态路由,仅匹配 /profile/username 路径
现在我们已经建立一个动态路由,此时最重要的事情就是如何获取路由参数。要访问当前路由的相关信息,我们需要先从 @angular/router 模块中导入 ActivatedRoute ,然后在组件类的构造函数中注入该对象,最后通过订阅该对象的 params 属性,来获取路由参数,具体示例如下:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'profile-page',
template: `
<div class="profile">
<h3 id="nbsp-username-nbsp">{{ username }}</h3>
</div>
`
})
export class SettingsComponent implements OnInit {
username: string;
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.route.params.subscribe((params) => this.username = params.username);
}
}介绍完动态路由,我们来探讨一下如何创建 child routes。
Child routes
实际上每个路由都支持子路由,假设在我们 /settings 设置页面下有 /settings/profile 和 /settings/password 两个页面,分别表示个人资料页和修改密码页。
我们可能希望我们的 /settings 页面拥有自己的组件,然后在设置页面组件中显示 /settings/profile 和 /settings/password 页面。我们可以这样做:
import { SettingsComponent } from './settings/settings.component';
import { ProfileSettingsComponent } from './settings/profile/profile.component';
import { PasswordSettingsComponent } from './settings/password/password.component';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{
path: 'settings',
component: SettingsComponent,
children: [
{ path: 'profile', component: ProfileSettingsComponent },
{ path: 'password', component: PasswordSettingsComponent }
]
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(ROUTES)
],
})
export class AppModule {}在这里,我们在 setttings 路由中定义了两个子路由,它们将继承父路由的路径,因此修改密码页面的路由匹配地址是 /settings/password ,依此类推。
接下来,我们需要做的最后一件事是在我们的 SettingsComponent 组件中添加 router-outlet 指令,因为我们要在设置页面中呈现子路由。如果我们没有在 SettingsComponent 组件中添加 router-outlet 指令,尽管 /settings/password 匹配修改密码页面的路由地址,但修改密码页面将无法正常显示。具体代码如下:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'settings-page',
template: `
<div class="settings">
<settings-header></settings-header>
<settings-sidebar></settings-sidebar>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
`
})
export class SettingsComponent {}Component-less routes
另一个很有用的路由功能是 component-less 路由。使用 component-less 路由允许我们将路由组合在一起,并让它们共享路由配置信息和 outlet。
例如,我们可以定义 setttings 路由而不需要使用 SettingsComponent 组件:
import { ProfileSettingsComponent } from './settings/profile/profile.component';
import { PasswordSettingsComponent } from './settings/password/password.component';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{
path: 'settings',
children: [
{ path: 'profile', component: ProfileSettingsComponent },
{ path: 'password', component: PasswordSettingsComponent }
]
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(ROUTES)
],
})
export class AppModule {}此时, /settings/profile 和 /settings/password 路由定义的内容,将显示在 AppComponent 组件的 router-outlet 元素中。
loadChildren
我们也可以告诉路由从另一个模块中获取子路由。这将我们谈论的两个想法联系在一起 - 我们可以指定另一个模块中定义的子路由,以及通过将这些子路由设置到特定的路径下,来充分利用 component-less 路由的功能。
让我们创建一个 SettingsModule 模块,用来保存所有 setttings 相关的路由信息:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: SettingsComponent,
children: [
{ path: 'profile', component: ProfileSettingsComponent },
{ path: 'password', component: PasswordSettingsComponent }
]
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
CommonModule,
RouterModule.forChild(ROUTES)
],
})
export class SettingsModule {}需要注意的是,在 SettingsModule 模块中我们使用 forChild() 方法,因为 SettingsModule 不是我们应用的主模块。
另一个主要的区别是我们将 SettingsModule 模块的主路径设置为空路径 (’’)。因为如果我们路径设置为 /settings ,它将匹配 /settings/settings ,很明显这不是我们想要的结果。通过指定一个空的路径,它就会匹配 /settings 路径,这就是我们想要的结果。
那么 /settings 路由信息,需要在哪里配置?答案是在 AppModule 中。这时我们就需要用到 loadChildren 属性,具体如下:
export const ROUTES: Routes = [
{
path: 'settings',
loadChildren: () => import('./settings/settings.module').then(it => it.SettingsModule)
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(ROUTES)
],
// ...
})
export class AppModule {}需要注意的是,我们没有将 SettingsModule 导入到我们的 AppModule 中,而是通过 loadChildren 属性,告诉 Angular 路由依据 loadChildren 属性配置的路径去加载 SettingsModule 模块。这就是模块懒加载功能的具体应用,当用户访问 /settings/** 路径的时候,才会加载对应的 SettingsModule 模块,这减少了应用启动时加载资源的大小。
另外我们传递一个字符串作为 loadChildren 的属性值,该字符串由三部分组成:
需要导入模块的相对路径 # 分隔符 导出模块类的名称
了解完路由的一些高级选项和功能,接下来我们来介绍路由指令。
Router Directives
除了 router-outlet 指令,路由模块中还提供了一些其它指令。让我们来看看它们如何与我们之前介绍的内容结合使用。
routerLink
为了让我们链接到已设置的路由,我们需要使用 routerLink 指令,具体示例如下:
<nav> <a routerLink="/">Home</a> <a routerLink="/settings/password">Change password</a> <a routerLink="/settings/profile">Profile Settings</a> </nav>
当我们点击以上的任意链接时,页面不会被重新加载。反之,我们的路径将在 URL 地址栏中显示,随后进行后续视图更新,以匹配 routerLink 中设置的值。
友情提示:我们也可以将 routerLink 的属性值,改成数组形式,以便我们传递特定的路由信息
如果我们想要链接到动态的路由地址,且该地址有一个 username 的路由变量,则我们可以按照以下方式配置 routerLink 对应的属性值:
<a [routerLink]="['/profile', username]">
Go to {{ username }}'s profile.
</a>routerLinkActive
在实际开发中,我们需要让用户知道哪个路由处于激活状态,通常情况下我们通过向激活的链接添加一个 class 来实现该功能。为了解决上述问题,Angular 路由模块为我们提供了 routerLinkActive 指令,该指令的使用示例如下:
<nav> <a routerLink="/settings" routerLinkActive="active">Home</a> <a routerLink="/settings/password" routerLinkActive="active">Change password</a> <a routerLink="/settings/profile" routerLinkActive="active">Profile Settings</a> </nav>
通过使用 routerLinkActive 指令,当 a 元素对应的路由处于激活状态时,active 类将会自动添加到 a 元素上。
最后,我们来简单介绍一下 Router API。
Router API
我们可以通过路由还提供的 API 实现与 routerLink 相同的功能。要使用 Router API,我们需要在组件类中注入 Router 对象,具体如下:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<div class="app">
<h3 id="Our-nbsp-app">Our app</h3>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent {
constructor(private router: Router) {}
}组件类中注入的 router 对象中有一个 navigate() 方法,该方法支持的参数类型与 routerLink 指令一样,当调用该方法后,页面将会自动跳转到对应的路由地址。具体使用示例如下:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<div class="app">
<h3 id="Our-nbsp-app">Our app</h3>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private router: Router) {}
ngOnInit() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.router.navigate(['/settings']);
}, 5000);
}
}若以上代码成功运行,用户界面将在 5 秒后被重定向到 /settings 页面。这个方法非常有用,例如当检测到用户尚未登录时,自动重定向到登录页面。
另一个使用示例是演示页面跳转时如何传递数据,具体如下:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<div class="app">
<h3 id="Users">Users</h3>
<div *ngFor="let user of users">
<user-component
[user]="user"
(select)="handleSelect($event)">
</user-component>
</div>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
users: Username[] = [
{ name: 'toddmotto', id: 0 },
{ name: 'travisbarker', id: 1 },
{ name: 'tomdelonge', id: 2 }
];
constructor(private router: Router) {}
handleSelect(event) {
this.router.navigate(['/profile', event.name]);
}
}Angular 路由的功能非常强大,既可以使用指令方式也可以使用命令式 API,希望本文可以帮助你尽快入门,若要进一步了解路由详细信息,请访问 - Angular Router 官文文档。
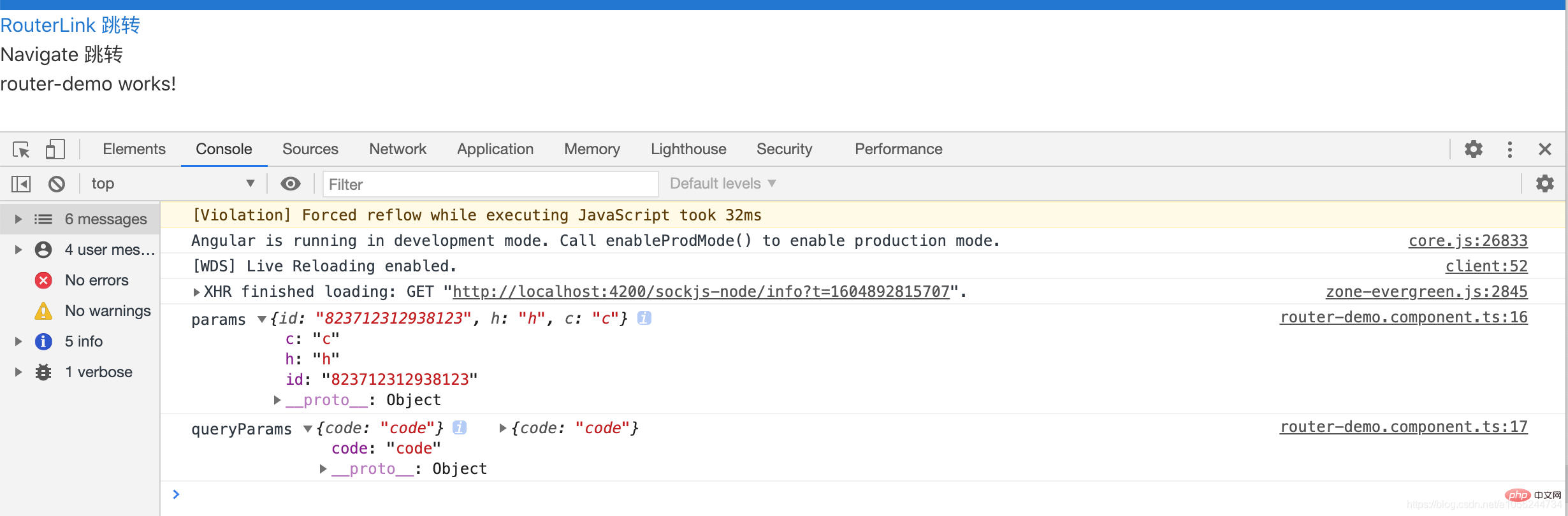
路由传参示例/router/823712312938123;h=h;c=c?code=code
- HTML:
<a [routerLink]="['/router', '823712312938123', {h:'h',c:'c'}]"
[queryParams]="{code:'code'}">RouterLink 跳转</a>
<a (click)="goToDetail()">Navigate 跳转</a>- TS:
this.router.navigate([`router/823712312938123`, {h: 'h', c: 'c'}],
{queryParams: {code: 'code'}})在component中取数据
router-demo.component.ts
import {Component, OnInit} from '@angular/core'
import {ActivatedRoute} from '@angular/router'
@Component({
selector: 'app-router-demo',
templateUrl: './router-demo.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./router-demo.component.less']
})
export class RouterDemoComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private activatedRoute: ActivatedRoute) {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
const {params, queryParams} = this.activatedRoute.snapshot
console.log('params', params)
console.log('queryParams', queryParams, queryParams)
}
}
Angular Router API 提供了 navigate() 和 navigateByUrl() 两个方法来实现页面导航。两者区别如下:
- 使用
router.navigateByUrl()方法与直接改变地址栏上的 URL 地址一样,我们使用了一个新的 URL 地址。 - 然而
router.navigate()方法基于一系列输入参数,产生一个新的 URL 地址。
为了更好理解两者区别,有例子,假设当前的 URL 地址是:
/inbox/11/message/22(popup:compose)
当调用 router.navigateByUrl('/inbox/33/message/44') 方法后,当前的 URL 地址将变成/inbox/33/message/44 。
但若是调用 router.navigate('/inbox/33/message/44') 方法,当前的 URL 地址将变成 /inbox/33/message/44(popup:compose)。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
위 내용은 Angular에서 Navigate() 및 NavigateByUrl() 사용 방법의 차이점에 대한 간략한 설명의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7328
7328
 9
9
 1626
1626
 14
14
 1350
1350
 46
46
 1262
1262
 25
25
 1209
1209
 29
29
 Ubuntu 24.04에 Angular를 설치하는 방법
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Ubuntu 24.04에 Angular를 설치하는 방법
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Angular.js는 동적 애플리케이션을 만들기 위해 자유롭게 액세스할 수 있는 JavaScript 플랫폼입니다. HTML 구문을 템플릿 언어로 확장하여 애플리케이션의 다양한 측면을 빠르고 명확하게 표현할 수 있습니다. Angular.js는 코드를 작성, 업데이트 및 테스트하는 데 도움이 되는 다양한 도구를 제공합니다. 또한 라우팅 및 양식 관리와 같은 많은 기능을 제공합니다. 이 가이드에서는 Ubuntu24에 Angular를 설치하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다. 먼저 Node.js를 설치해야 합니다. Node.js는 서버 측에서 JavaScript 코드를 실행할 수 있게 해주는 ChromeV8 엔진 기반의 JavaScript 실행 환경입니다. Ub에 있으려면
 각도 학습 상태 관리자 NgRx에 대한 자세한 설명
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
각도 학습 상태 관리자 NgRx에 대한 자세한 설명
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
이 글은 Angular의 상태 관리자 NgRx에 대한 심층적인 이해를 제공하고 NgRx 사용 방법을 소개하는 글이 될 것입니다.
 React Router 사용자 가이드: 프런트엔드 라우팅 제어 구현 방법
Sep 29, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
React Router 사용자 가이드: 프런트엔드 라우팅 제어 구현 방법
Sep 29, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
ReactRouter 사용자 가이드: 프런트엔드 라우팅 제어 구현 방법 단일 페이지 애플리케이션의 인기로 인해 프런트엔드 라우팅은 무시할 수 없는 중요한 부분이 되었습니다. React 생태계에서 가장 널리 사용되는 라우팅 라이브러리인 ReactRouter는 풍부한 기능과 사용하기 쉬운 API를 제공하여 프런트 엔드 라우팅 구현을 매우 간단하고 유연하게 만듭니다. 이 기사에서는 ReactRouter를 사용하는 방법을 소개하고 몇 가지 구체적인 코드 예제를 제공합니다. ReactRouter를 먼저 설치하려면 다음이 필요합니다.
 각도에서 monaco-editor를 사용하는 방법에 대한 간략한 분석
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
각도에서 monaco-editor를 사용하는 방법에 대한 간략한 분석
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
각도에서 모나코 편집기를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 다음 글은 최근 비즈니스에서 사용되는 Monaco-Editor의 활용 사례를 기록한 글입니다.
 Angular의 서버 측 렌더링(SSR)을 탐색하는 기사
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
Angular의 서버 측 렌더링(SSR)을 탐색하는 기사
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
앵귤러 유니버셜(Angular Universal)을 아시나요? 웹사이트가 더 나은 SEO 지원을 제공하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다!
 프로젝트가 너무 크면 어떻게 해야 하나요? Angular 프로젝트를 합리적으로 분할하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jul 26, 2022 pm 07:18 PM
프로젝트가 너무 크면 어떻게 해야 하나요? Angular 프로젝트를 합리적으로 분할하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jul 26, 2022 pm 07:18 PM
Angular 프로젝트가 너무 큽니다. 합리적으로 분할하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 다음 글에서는 Angular 프로젝트를 합리적으로 분할하는 방법을 소개하겠습니다. 도움이 되셨으면 좋겠습니다!
 각도-날짜/시간 선택기 형식을 사용자 정의하는 방법에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다.
Sep 08, 2022 pm 08:29 PM
각도-날짜/시간 선택기 형식을 사용자 정의하는 방법에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다.
Sep 08, 2022 pm 08:29 PM
각도-날짜/시간 선택기 형식을 사용자 정의하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 다음 기사에서는 형식을 사용자 정의하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다. 모든 사람에게 도움이 되기를 바랍니다.
 Angular + NG-ZORRO로 백엔드 시스템을 빠르게 개발
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
Angular + NG-ZORRO로 백엔드 시스템을 빠르게 개발
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
이 기사는 Angular의 실제 경험을 공유하고 ng-zorro와 결합된 angualr을 사용하여 백엔드 시스템을 빠르게 개발하는 방법을 배우게 될 것입니다. 모든 사람에게 도움이 되기를 바랍니다.




