MySQL은 어떻게 인덱싱을 보다 효율적으로 만들 수 있습니까?
이제 데이터베이스 시리즈가 업데이트되었으니 모든 개념이 대략적으로 이해되셨을 것 같습니다. 이번 주 댓글을 읽다가 매우 흥미로운 네티즌의 질문을 발견했습니다. 인덱스를 디자인하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 인덱스를 어떻게 디자인하나요? 보다 효율적으로 디자인하는 방법은 무엇입니까?

머리말
우리는 인덱스가 연결된 목록을 기반으로 한 트리형 트리 구조로, 현재 거의 모든 RDBMS 데이터베이스에 MySQL의 B+Tree와 같은 인덱스 기능이 구현되어 있다는 것을 알고 있습니다. 인덱스, MongoDB의 BTree 인덱스 등
비즈니스 개발 과정에서 인덱스 설계가 효율적인지 여부는 인터페이스에 해당하는 SQL의 실행 효율성을 결정합니다. 효율적인 인덱스는 인터페이스의 응답 시간을 줄이고 비용도 절감할 수 있는 것입니다. : 인덱스 디자인 -> 인터페이스 응답시간 단축 -> 서버 구성 단축 -> 비용 절감, 이는 결국 비용으로 반영됩니다. 사장님께서 비용을 가장 걱정하시기 때문입니다.
오늘은 MySQL의 인덱스와 인덱스 설계 방법에 대해 이야기하겠습니다. 인덱스를 사용해야만 하위 인터페이스의 RT를 개선하고 사용자 건강을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
Index in MySQL
MySQL의 InnoDB 엔진은 B+Tree 구조를 사용하여 인덱스를 저장하므로 데이터 쿼리 중 디스크 IO 횟수를 최소화할 수 있습니다. 동시에 트리 높이가 성능에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다. 일반적으로 트리의 높이는 3~4개의 레이어로 유지됩니다.
B+Tree는 루트, 브랜치, 리프의 세 부분으로 구성됩니다. 루트와 브랜치는 데이터를 저장하지 않고 포인터 주소만 저장합니다. 동시에 리프 노드는 이중 링크로 연결됩니다. list.구조는 다음과 같습니다.
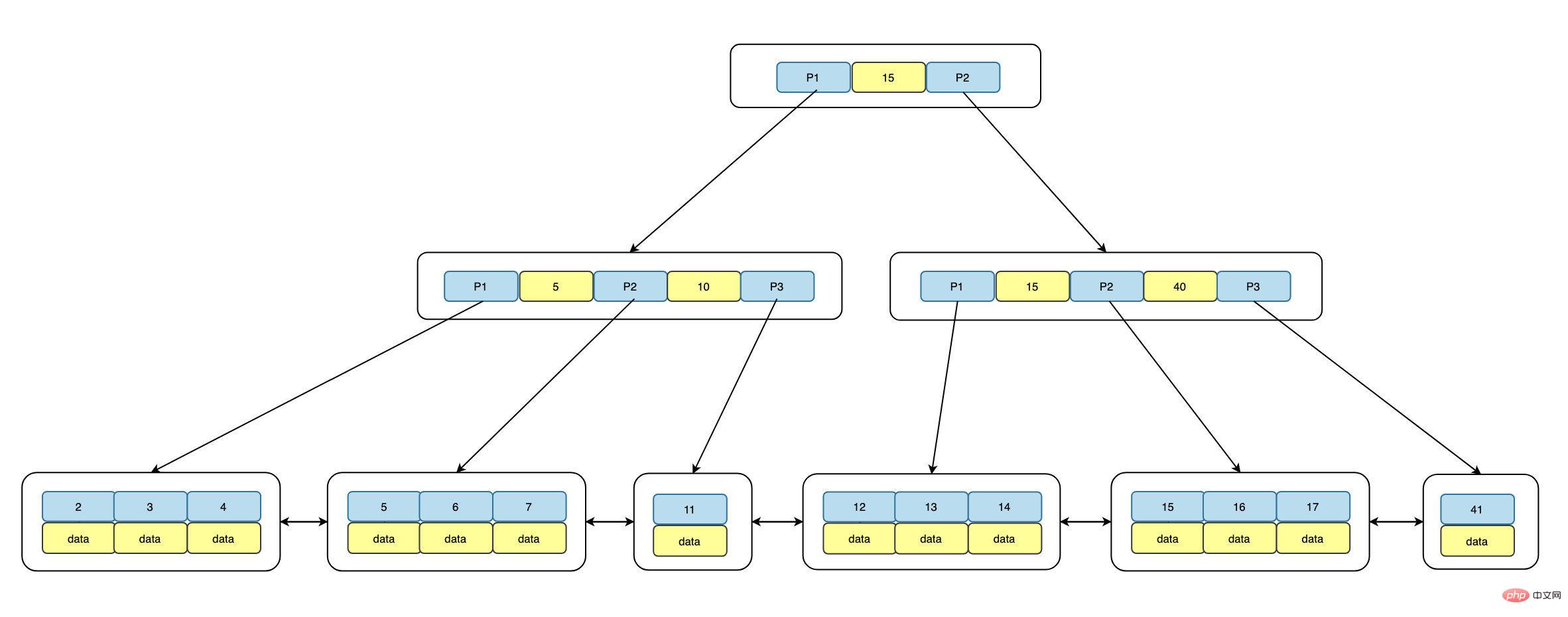
위에서 볼 수 있듯이 각 리프 노드는 선행 포인터 p_prev, 데이터 데이터 및 후속 포인터 p_next의 세 부분으로 구성됩니다. B+트리의 오른쪽에 있는 키 값은 항상 왼쪽에 있는 키 값보다 큽니다. 동시에 루트에서 각 리프까지의 거리는 동일합니다. , 모든 리프 노드에 액세스하는 데 필요한 IO는 동일합니다. 즉, 인덱스 트리 높이 + 1 IO가 작동합니다.
MySQL의 인덱스는 디스크 공간을 차지하는 작은 테이블로 생각하면 됩니다. 인덱스를 생성하는 과정은 실제로 정렬된 데이터의 양이 많은 경우 인덱스 열에 따라 정렬하는 과정입니다. sort_buffer_size의 용량이 충분하지 않으면 임시 파일을 통한 정렬이 필요하며 가장 중요하게는 인덱스를 통해 정렬 작업(고유, 그룹화, 정렬 기준)을 피할 수 있습니다.
Clustered Index
MySQL의 테이블은 IOT(Index Organization Table, Index Organization Table)이며, 데이터는 기본 키 ID(논리적으로 연속, 물리적으로 불연속) 순서로 저장되며, 기본 키 ID는 클러스터형입니다. index(클러스터형 인덱스)는 데이터의 전체 행을 저장합니다. 명시적인 기본 키가 지정되지 않은 경우 MySQL은 모든 열을 결합하여 row_id를 기본 키로 구성합니다. 예를 들어 users(id, user_id, user_name, 전화, 기본 키(id)), ID는 다음과 같습니다. 클러스터형 인덱스는 데이터 ID, user_id, user_name, 전화의 전체 행을 저장합니다.
보조 인덱스
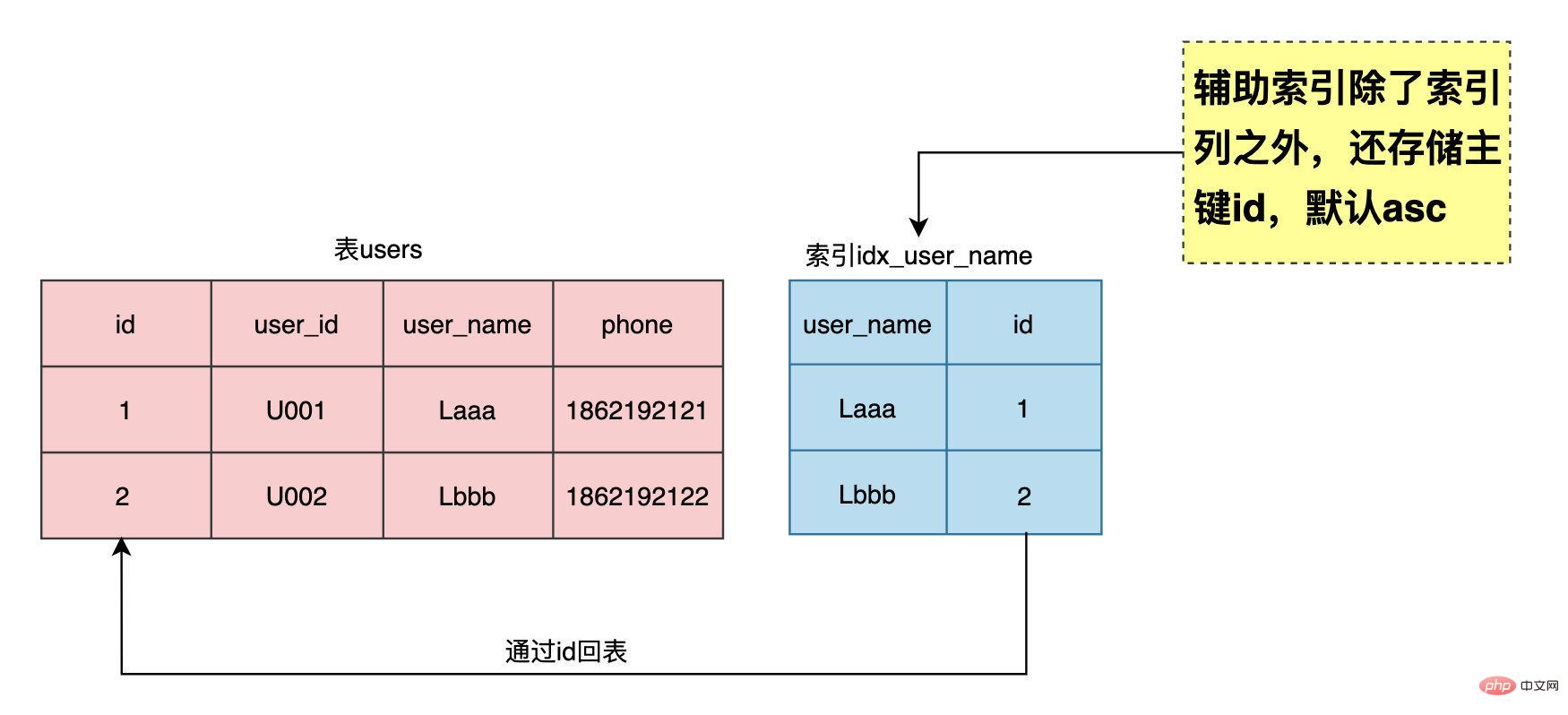
보조 인덱스는 인덱스 열을 저장하는 것 외에도 user_name의 인덱스 idx_user_name(user_name)에 대한 기본 키 ID도 저장합니다. idx_user_name(user_name, id)을 사용하면 MySQL은 자동으로 보조 인덱스 끝에 기본 키 ID를 추가합니다. Oracle 데이터베이스에 익숙한 사람이라면 인덱스가 인덱스 열 외에도 row_id도 저장한다는 사실을 알고 있을 것입니다. 데이터는 객체 번호 + 데이터 파일 번호 + 데이터 블록 번호 + 데이터 행 번호의 네 부분으로 구성됩니다. 보조 인덱스를 생성할 때 기본 키 ID를 표시할 수도 있습니다.
-- 创建user_name列上的索引 mysql> create index idx_user_name on users(user_name); -- 显示添加主键id创建索引 mysql> create index idx_user_name_id on users(user_name,id); -- 对比两个索引的统计数据 mysql> select a.space as tbl_spaceid, a.table_id, a.name as table_name, row_format, space_type, b.index_id , b.name as index_name, n_fields, page_no, b.type as index_type from information_schema.INNODB_TABLES a left join information_schema.INNODB_INDEXES b on a.table_id =b.table_id where a.name = 'test/users'; +-------------+----------+------------+------------+------------+----------+------------------+----------+------ | tbl_spaceid | table_id | table_name | row_format | space_type | index_id | index_name | n_fields | page_no | index_type | +-------------+----------+------------+------------+------------+----------+------------------+----------+------ | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 1254 | PRIMARY | 9 | 4 | 3 | | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 4003 | idx_user_name | 2 | 5 | 0 | | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 4004 | idx_user_name_id | 2 | 45 | 0 | mysql> select index_name, last_update, stat_name, stat_value, stat_description from mysql.innodb_index_stats where index_name in ('idx_user_name','idx_user_name_id'); +------------------+---------------------+--------------+------------+-----------------------------------+ | index_name | last_update | stat_name | stat_value | stat_description | +------------------+---------------------+--------------+------------+-----------------------------------+ | idx_user_name | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | n_leaf_pages | 1358 | Number of leaf pages in the index | | idx_user_name | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | size | 1572 | Number of pages in the index | | idx_user_name_id | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | n_leaf_pages | 1358 | Number of leaf pages in the index | | idx_user_name_id | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | size | 1572 | Number of pages in the index |
두 인덱스의 결과를 비교합니다. n_fields는 인덱스의 열 수를 나타내고, n_leaf_pages는 인덱스의 리프 페이지 수를 나타내며, size는 인덱스의 총 페이지 수를 나타냅니다. 보조 인덱스가 기본 키 ID를 포함한다는 것은 두 인덱스가 완전히 일관성이 있음을 보여줍니다.
| Index_name | n_fields | n_leaf_pages | size |
|---|---|---|---|
| idx_user_name | 2 | 1358 | 15 2 |
| idx_user_name_id | 2 | 1358 | 1572 |
索引回表
上面证明了辅助索引包含主键id,如果通过辅助索引列去过滤数据有可能需要回表,举个例子:业务需要通过用户名user_name去查询用户表users的信息,业务接口对应的SQL:
select user_id, user_name, phone from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
我们知道,对于索引idx_user_name而言,其实就是一个小表idx_user_name(user_name, id),如果只查询索引中的列,只需要扫描索引就能获取到所需数据,是不需要回表的,如下SQL语句:
SQL 1: select id, user_name from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
SQL 2: select id from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
mysql> explain select id, name from users where name = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_user_name | idx_user_name | 82 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | mysql> explain select id from users where name = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_user_name | idx_user_name | 82 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
SQL 1和SQL 2的执行计划中的Extra=Using index 表示使用覆盖索引扫描,不需要回表,再来看上面的业务SQL:
select user_id, user_name, phone from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
可以看到select后面的user_id,phone列不在索引idx_user_name中,就需要通过主键id进行回表查找,MySQL内部分如下两个阶段处理:
Section 1: select **id** from users where user_name = 'Laaa' //id = 100101
Section 2: select user_id, user_name, phone from users where id = 100101;
将Section 2的操作称为回表,即通过辅助索引中的主键id去原表中查找数据。
索引高度
MySQL的索引时B+tree结构,即使表里有上亿条数据,索引的高度都不会很高,通常维持在3-4层左右,我来计算下索引idx_name的高度,从上面知道索引信息:index_id = 4003, page_no = 5,它的偏移量offset就是page_no x innodo_page_size + 64 = 81984,通过hexdump进行查看
$hexdump -s 81984 -n 10 /usr/local/var/mysql/test/users.ibd 0014040 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 0f a3 001404a
其中索引的PAGE_LEVEL为00,即idx_user_name索引高度为1,0f a3 代表索引编号,转换为十进制是4003,正是index_id。
数据扫描方式
全表扫描
从左到右依次扫描整个B+Tree获取数据,扫描整个表数据,IO开销大,速度慢,锁等严重,影响MySQL的并发。
对于OLAP的业务场景,需要扫描返回大量数据,这时候全表扫描的顺序IO效率更高。
索引扫描
通常来讲索引比表小,扫描的数据量小,消耗的IO少,执行速度块,几乎没有锁等,能够提高MySQL的并发。
对于OLTP系统,希望所有的SQL都能命中合适的索引总是美好的。
主要区别就是扫描数据量大小以及IO的操作,全表扫描是顺序IO,索引扫描是随机IO,MySQL对此做了优化,增加了change buffer特性来提高IO性能。
索引优化案例
分页查询优化
业务要根据时间范围查询交易记录,接口原始的SQL如下:
select * from trade_info where status = 0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59' order by id desc limit 102120, 20;
表trade_info上有索引idx_status_create_time(status,create_time),通过上面分析知道,等价于索引**(status,create_time,id)**,对于典型的分页limit m, n来说,越往后翻页越慢,也就是m越大会越慢,因为要定位m位置需要扫描的数据越来越多,导致IO开销比较大,这里可以利用辅助索引的覆盖扫描来进行优化,先获取id,这一步就是索引覆盖扫描,不需要回表,然后通过id跟原表trade_info进行关联,改写后的SQL如下:
select * from trade_info a , (select id from trade_info where status = 0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59' order by id desc limit 102120, 20) as b //这一步走的是索引覆盖扫描,不需要回表 where a.id = b.id;
很多同学只知道这样写效率高,但是未必知道为什么要这样改写,理解索引特性对编写高质量的SQL尤为重要。
分而治之总是不错的
营销系统有一批过期的优惠卷要失效,核心SQL如下:
-- 需要更新的数据量500w update coupons set status = 1 where status =0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59';
在Oracle里更新500w数据是很快,因为可以利用多个cpu core去执行,但是MySQL就需要注意了,一个SQL只能使用一个cpu core去处理,如果SQL很复杂或执行很慢,就会阻塞后面的SQL请求,造成活动连接数暴增,MySQL CPU 100%,相应的接口Timeout,同时对于主从复制架构,而且做了业务读写分离,更新500w数据需要5分钟,Master上执行了5分钟,binlog传到了slave也需要执行5分钟,那就是Slave延迟5分钟,在这期间会造成业务脏数据,比如重复下单等。
优化思路:先获取where条件中的最小id和最大id,然后分批次去更新,每个批次1000条,这样既能快速完成更新,又能保证主从复制不会出现延迟。
优化如下:
- 先获取要更新的数据范围内的最小id和最大id(表没有物理delete,所以id是连续的)
mysql> explain select min(id) min_id, max(id) max_id from coupons where status =0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+--- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+--- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time | idx_status_create_time | 6 | NULL | 180300 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
Extra=Using where; Using index使用了索引idx_status_create_time,同时需要的数据都在索引中能找到,所以不需要回表查询数据。
- 以每次1000条commit一次进行循环update,主要代码如下:
current_id = min_id; for current_id < max_id do update coupons set status = 1 where id >=current_id and id <= current_id + 1000; //通过主键id更新1000条很快 commit; current_id += 1000; done
这两个案例告诉我们,要充分利用辅助索引包含主键id的特性,先通过索引获取主键id走覆盖索引扫描,不需要回表,然后再通过id去关联操作是高效的,同时根据MySQL的特性使用分而治之的思想既能高效完成操作,又能避免主从复制延迟产生的业务数据混乱。
MySQL索引设计
熟悉了索引的特性之后,就可以在业务开发过程中设计高质量的索引,降低接口的响应时间。
前缀索引
对于使用REDUNDANT或者COMPACT格式的InnoDB表,索引键前缀长度限制为767字节。如果TEXT或VARCHAR列的列前缀索引超过191个字符,则可能会达到此限制,假定为utf8mb4字符集,每个字符最多4个字节。
可以通过设置参数innodb_large_prefix来开启或禁用索引前缀长度的限制,即是设置为OFF,索引虽然可以创建成功,也会有一个警告,主要是因为index size会很大,效率大量的IO的操作,即使MySQL优化器命中了该索引,效率也不会很高。
-- 设置innodb_large_prefix=OFF禁用索引前缀限制,虽然可以创建成功,但是有警告。 mysql> create index idx_nickname on users(nickname); // `nickname` varchar(255) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 1 mysql> show warnings; +---------+------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Level | Code | Message | +---------+------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Warning | 1071 | Specified key was too long; max key length is 767 bytes |
业务发展初期,为了快速实现功能,对一些数据表字段的长度定义都比较宽松,比如用户表users的昵称nickname定义为varchar(128),而且有业务接口需要通过nickname查询,系统运行了一段时间之后,查询users表最大的nickname长度为30,这个时候就可以创建前缀索引来减小索引的长度提升性能。
-- `nickname` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL定义的执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where nickname = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+-------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+-------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_nickname | idx_nickname | 515 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
key_len=515,由于表和列都是utf8mb4字符集,每个字符占4个字节,变长数据类型+2Bytes,允许NULL额外+1Bytes,即128 x 4 + 2 + 1 = 515Bytes。创建前缀索引,前缀长度也可以不是当前表的数据列最大值,应该是区分度最高的那部分长度,一般能达到90%以上即可,例如email字段存储都是类似这样的值xxxx@yyy.com,前缀索引的最大长度可以是xxxx这部分的最大长度即可。
-- 创建前缀索引,前缀长度为30 mysql> create index idx_nickname_part on users(nickname(30)); -- 查看执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where nickname = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+--------------------------------+-------------------+---------+- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+--------------------------------+-------------------+---------+- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_nickname_part,idx_nickname | idx_nickname_part | 123 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
可以看到优化器选择了前缀索引,索引长度为123,即30 x 4 + 2 + 1 = 123 Bytes,大小不到原来的四分之。
前缀索引虽然可以减小索引的大小,但是不能消除排序。
mysql> explain select gender,count(*) from users where nickname like 'User100%' group by nickname limit 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+--------------------------------+--------------+---------+----- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+--------------------------------+--------------+---------+----- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_nickname_part,idx_nickname | idx_nickname | 515 | NULL | 899 | 100.00 | Using index condition | --可以看到Extra= Using index condition表示使用了索引,但是需要回表查询数据,没有发生排序操作。 mysql> explain select gender,count(*) from users where nickname like 'User100%' group by nickname limit 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------ | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_nickname_part | idx_nickname_part | 123 | NULL | 899 | 100.00 | Using where; Using temporary | --可以看到Extra= Using where; Using temporaryn表示在使用了索引的情况下,需要回表去查询所需的数据,同时发生了排序操作。
复合索引
在单列索引不能很好的过滤数据的时候,可以结合where条件中其他字段来创建复合索引,更好的去过滤数据,减少IO的扫描次数,举个例子:业务需要按照时间段来查询交易记录,有如下的SQL:
select * from trade_info where status = 1 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59';
开发同学根据以往复合索引的设计的经验:唯一值多选择性好的列作为复合索引的前导列,所以创建复合索idx_create_time_status是高效的,因为create_time是一秒一个值,唯一值很多,选择性很好,而status只有离散的6个值,所以认为这样创建是没问题的,但是这个经验只适合于等值条件过滤,不适合有范围条件过滤的情况,例如idx_user_id_status(user_id,status)这个是没问题的,但是对于包含有create_time范围的复合索引来说,就不适应了,我们来看下这两种不同索引顺序的差异,即idx_status_create_time和idx_create_time_status。
-- 分别创建两种不同的复合索引 mysql> create index idx_status_create_time on trade_info(status, create_time); mysql> create index idx_create_time_status on trade_info(create_time,status); -- 查看SQL的执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where status = 1 and create_time >='2021-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2021-10-07 23:59:59'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-----------------------------------------------+--------------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-----------------------------------------------+--------------- | 1 | SIMPLE | trade_info | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time,idx_create_time_status | idx_status_create_time | 6 | NULL | 98518 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
从执行计划可以看到,两种不同顺序的复合索引都存在的情况,MySQL优化器选择的是idx_status_create_time索引,那为什么不选择idx_create_time_status,我们通过optimizer_trace来跟踪优化器的选择。
-- 开启optimizer_trace跟踪 mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; -- 执行SQL语句 mysql> select * from trade_info where status = 1 and create_time >='2021-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2021-10-07 23:59:59'; -- 查看跟踪结果 mysql>SELECT trace FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE\G;
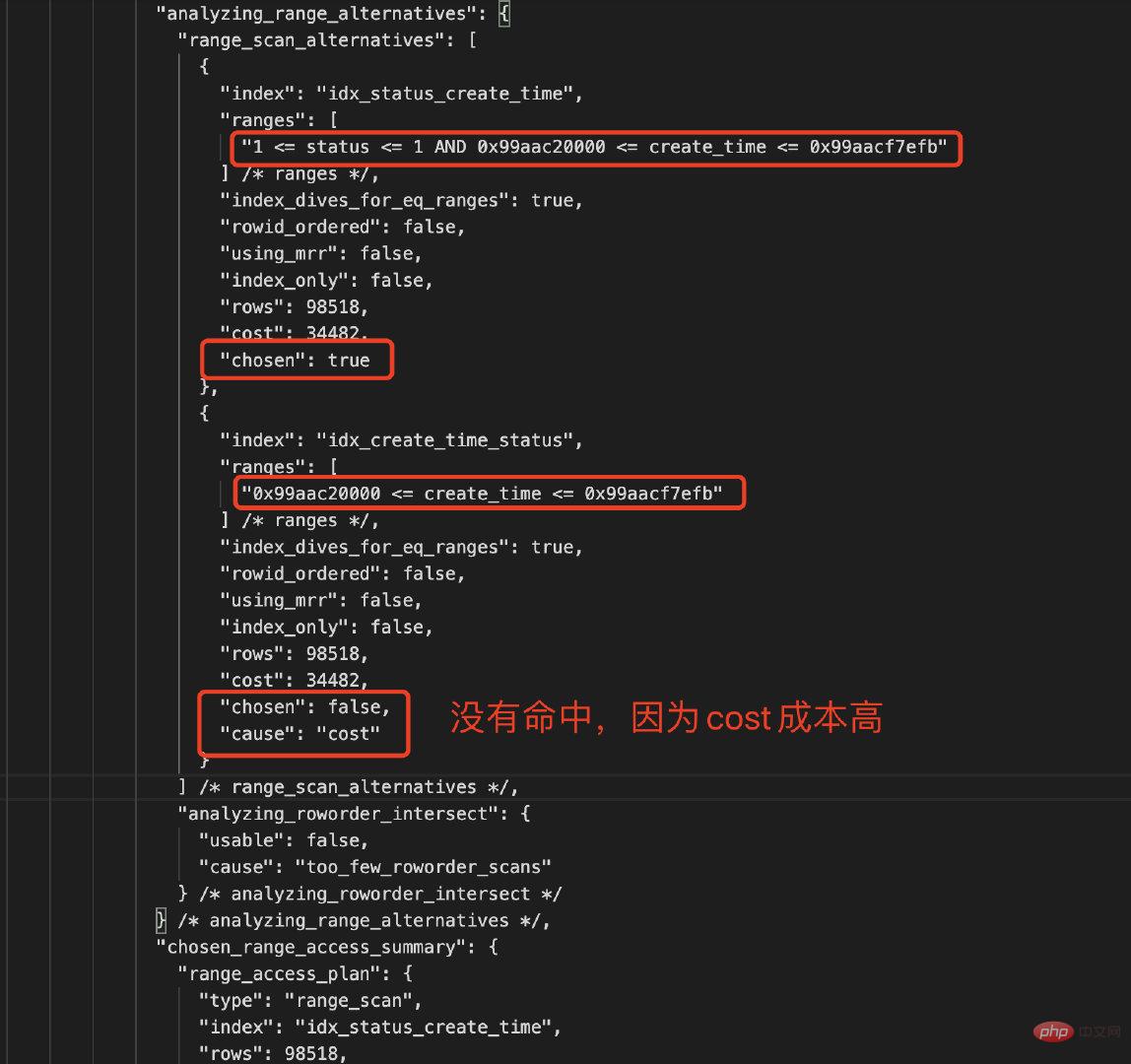
对比下两个索引的统计数据,如下所示:
| 复合索引 | Type | Rows | 参与过滤索引列 | Chosen | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| idx_status_create_time | Index Range Scan | 98518 | status AND create_time | True | Cost低 |
| idx_create_time_status | Index Range Scan | 98518 | create_time | False | Cost高 |
MySQL优化器是基于Cost的,COST主要包括IO_COST和CPU_COST,MySQL的CBO(Cost-Based Optimizer基于成本的优化器)总是选择Cost最小的作为最终的执行计划去执行,从上面的分析,CBO选择的是复合索引idx_status_create_time,因为该索引中的status和create_time都能参与了数据过滤,成本较低;而idx_create_time_status只有create_time参数数据过滤,status被忽略了,其实CBO将其简化为单列索引idx_create_time,选择性没有复合索引idx_status_create_time好。
复合索引设计原则
将范围查询的列放在复合索引的最后面,例如idx_status_create_time。
列过滤的频繁越高,选择性越好,应该作为复合索引的前导列,适用于等值查找,例如idx_user_id_status。
这两个原则不是矛盾的,而是相辅相成的。
跳跃索引
一般情况下,如果表users有复合索引idx_status_create_time,我们都知道,单独用create_time去查询,MySQL优化器是不走索引,所以还需要再创建一个单列索引idx_create_time。用过Oracle的同学都知道,是可以走索引跳跃扫描(Index Skip Scan),在MySQL 8.0也实现Oracle类似的索引跳跃扫描,在优化器选项也可以看到skip_scan=on。
| optimizer_switch |use_invisible_indexes=off,skip_scan=on,hash_join=on |
适合复合索引前导列唯一值少,后导列唯一值多的情况,如果前导列唯一值变多了,则MySQL CBO不会选择索引跳跃扫描,取决于索引列的数据分表情况。
mysql> explain select id, user_id,status, phone from users where create_time >='2021-01-02 23:01:00' and create_time <= '2021-01-03 23:01:00'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+---- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+---- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time | idx_status_create_time | NULL | NULL | 15636 | 11.11 | Using where; Using index for skip scan|
也可以通过optimizer_switch='skip_scan=off’来关闭索引跳跃扫描特性。
总结
本位为大家介绍了MySQL中的索引,包括聚集索引和辅助索引,辅助索引包含了主键id用于回表操作,同时利用覆盖索引扫描可以更好的优化SQL。
同时也介绍了如何更好做MySQL索引设计,包括前缀索引,复合索引的顺序问题以及MySQL 8.0推出的索引跳跃扫描,我们都知道,索引可以加快数据的检索,减少IO开销,会占用磁盘空间,是一种用空间换时间的优化手段,同时更新操作会导致索引频繁的合并分裂,影响索引性能,在实际的业务开发中,如何根据业务场景去设计合适的索引是非常重要的,今天就聊这么多,希望对大家有所帮助。
相关推荐:《mysql教程》
위 내용은 MySQL은 어떻게 인덱싱을 보다 효율적으로 만들 수 있습니까?의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7369
7369
 15
15
 1628
1628
 14
14
 1354
1354
 52
52
 1266
1266
 25
25
 1214
1214
 29
29
 PHP의 빅데이터 구조 처리 능력
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
PHP의 빅데이터 구조 처리 능력
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
빅 데이터 구조 처리 기술: 청킹(Chunking): 데이터 세트를 분할하고 청크로 처리하여 메모리 소비를 줄입니다. 생성기: 전체 데이터 세트를 로드하지 않고 데이터 항목을 하나씩 생성하므로 무제한 데이터 세트에 적합합니다. 스트리밍: 파일을 읽거나 결과를 한 줄씩 쿼리하므로 대용량 파일이나 원격 데이터에 적합합니다. 외부 저장소: 매우 큰 데이터 세트의 경우 데이터를 데이터베이스 또는 NoSQL에 저장합니다.
 PHP에서 MySQL 백업 및 복원을 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
PHP에서 MySQL 백업 및 복원을 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
PHP에서 MySQL 데이터베이스를 백업하고 복원하는 작업은 다음 단계에 따라 수행할 수 있습니다. 데이터베이스 백업: mysqldump 명령을 사용하여 데이터베이스를 SQL 파일로 덤프합니다. 데이터베이스 복원: mysql 명령을 사용하여 SQL 파일에서 데이터베이스를 복원합니다.
 PHP에서 MySQL 쿼리 성능을 최적화하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
PHP에서 MySQL 쿼리 성능을 최적화하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
선형 복잡성에서 로그 복잡성까지 조회 시간을 줄이는 인덱스를 구축하여 MySQL 쿼리 성능을 최적화할 수 있습니다. SQL 삽입을 방지하고 쿼리 성능을 향상하려면 PREPAREDStatements를 사용하세요. 쿼리 결과를 제한하고 서버에서 처리되는 데이터의 양을 줄입니다. 적절한 조인 유형 사용, 인덱스 생성, 하위 쿼리 사용 고려 등 조인 쿼리를 최적화합니다. 쿼리를 분석하여 병목 현상을 식별하고, 캐싱을 사용하여 데이터베이스 로드를 줄이고, 오버헤드를 최소화합니다.
 PHP를 사용하여 MySQL 테이블에 데이터를 삽입하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
PHP를 사용하여 MySQL 테이블에 데이터를 삽입하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
MySQL 테이블에 데이터를 삽입하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 데이터베이스에 연결: mysqli를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 대한 연결을 설정합니다. SQL 쿼리 준비: 삽입할 열과 값을 지정하는 INSERT 문을 작성합니다. 쿼리 실행: query() 메서드를 사용하여 삽입 쿼리를 실행하면 확인 메시지가 출력됩니다.
 PHP를 사용하여 MySQL 테이블을 만드는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
PHP를 사용하여 MySQL 테이블을 만드는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
PHP를 사용하여 MySQL 테이블을 생성하려면 다음 단계가 필요합니다. 데이터베이스에 연결합니다. 데이터베이스가 없으면 작성하십시오. 데이터베이스를 선택합니다. 테이블을 생성합니다. 쿼리를 실행합니다. 연결을 닫습니다.
 PHP에서 MySQL 저장 프로시저를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
PHP에서 MySQL 저장 프로시저를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
PHP에서 MySQL 저장 프로시저를 사용하려면: PDO 또는 MySQLi 확장을 사용하여 MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결합니다. 저장 프로시저를 호출하는 문을 준비합니다. 저장 프로시저를 실행합니다. 결과 집합을 처리합니다(저장 프로시저가 결과를 반환하는 경우). 데이터베이스 연결을 닫습니다.
 MySQL 8.4에서 mysql_native_password가 로드되지 않음 오류를 수정하는 방법
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
MySQL 8.4에서 mysql_native_password가 로드되지 않음 오류를 수정하는 방법
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
MySQL 8.4(2024년 최신 LTS 릴리스)에 도입된 주요 변경 사항 중 하나는 "MySQL 기본 비밀번호" 플러그인이 더 이상 기본적으로 활성화되지 않는다는 것입니다. 또한 MySQL 9.0에서는 이 플러그인을 완전히 제거합니다. 이 변경 사항은 PHP 및 기타 앱에 영향을 미칩니다.
 오라클 데이터베이스와 mysql의 차이점
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
오라클 데이터베이스와 mysql의 차이점
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
Oracle 데이터베이스와 MySQL은 모두 관계형 모델을 기반으로 하는 데이터베이스이지만 호환성, 확장성, 데이터 유형 및 보안 측면에서 Oracle이 우수하고, MySQL은 속도와 유연성에 중점을 두고 중소 규모 데이터 세트에 더 적합합니다. ① Oracle은 광범위한 데이터 유형을 제공하고, ② 고급 보안 기능을 제공하고, ③ 엔터프라이즈급 애플리케이션에 적합하고, ① MySQL은 NoSQL 데이터 유형을 지원하고, ② 보안 조치가 적고, ③ 중소 규모 애플리케이션에 적합합니다.




