Node.js를 사용하여 간단한 HTTP 서버를 만드는 방법에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다.
NodeJS를 사용하여 HTTP 서버를 만드는 방법은 무엇입니까? 다음 글에서는 Node를 사용하여 간단한 HTTP 서버를 만드는 방법을 소개하겠습니다. 도움이 되길 바랍니다.

1. Node.js를 사용하여 JavaScript 스크립트를 직접 실행
node.jsnode.js基于Chrome的v8引擎运行js代码,因此我们可以摆脱浏览器环境,直接在控制台中运行js代码,比如下面这个hello world代码
console.log('hello world');控制台中直接使用node即可运行

2. 创建一个简单的HTTP服务器
node.js的内置模块http提供了基本的http服务的能力,基于CommonJS规范,我们可以使用require导入http模块进行使用http模块中有一个createServer函数能够让我们创建一个httpChromev8 엔진 기반 /code> js 코드를 실행하면 브라우저 환경을 제거하고 다음 hello world와 같이 콘솔에서 직접 js 코드를 실행할 수 있습니다. code> code request和response
-
request包括所有客户端请求的信息,比如url、请求头header、请求方式和请求体等 -
response主要用于返回信息给客户端,封装了一些操作响应体相关的操作,比如response.writeHead方法就可以让我们自定义返回体的头部信息和状态码
当我们将响应体处理好了之后,调用response.end()
const { createServer } = require('http');
const HOST = 'localhost';
const PORT = '8080';
const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
// the first param is status code it returns
// and the second param is response header info
resp.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
console.log('server is working...');
// call end method to tell server that the request has been fulfilled
resp.end('hello nodejs http server');
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log('Something wrong: ', error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});createServer函数只是帮我们创建了一个Server对象,并没有让其开启监听,我们还需要调用server对象的listen方法才可以进行监听,真正作为一个服务器开始运行-
listen方法的第一个参数是监听的端口号,第二个参数则是绑定的主机ip,第三个参数是一个回调函数,会被http模块异步调用,当遇到错误的时候,就能够在这个回调函数的第一个参数中获取到抛出的异常 ,我们可以选择对异常进行处理,让我们的服务器更加健壮
下面是使用http模块创建一个简单服务器的例子
npm i -g nodemon
可以直接尝试用node运行它,创造一个属于你的服务器!服务器运行后,浏览器访问http://localhost:8080即可访问到这个服务器

也可以使用nodemon运行它,这样当我们的代码发生变化的时候就不需要手动终止程序再重新运行了
nodemon http-server.js
建议全局安装它,这样就可以直接使用,不需要通过npx nodemon 콘솔에서 직접 node를 사용하여 실행node命令改成nodemon命令即可
{ "compilerOptions": {
"checkJs": true
},
"exclude": ["node_modules", "**/node_modules/*"]
}
3. 加上类型提示
前面我们在使用createServer以及resp对象的时候,看不到任何的语法提示,必须随时跟着nodets的.d.ts文件帮助我们提供语法提示功能,注意,我们不是使用ts进行开发,只是使用它的语法提示功能而已
- 初始化项目 --
npm init -y - 安装
@types/node--pnpm i @types/node -D - 在项目目录下创建
jsconfig.json文件,将node_modules排除在外,没必要对其进行检查
const { createServer } = require("http");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;
const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
console.log("server is working...");
// write some lorem sentences
resp.write("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit.\n");
resp.write("Omnis eligendi aperiam delectus?\n");
resp.write("Aut, quam quo!\n");
resp.end();
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});不知道你是否有发现上面的代码其实是有一处错误的呢?checkJs
 2. 간단한 HTTP 서버 만들기
2. 간단한 HTTP 서버 만들기
listennode.js 내장- http 모듈에서는 기본 http 서비스 기능을 제공합니다. CommonJS 사양을 기반으로 require를 사용하여 가져올 수 있습니다. http 모듈 http 모듈에는 http 서버를 생성할 수 있는 createServer 함수가 있습니다.
콜백 함수를 매개변수로 받습니다. 이 콜백 함수는 요청 및 응답
-
요청이라는 두 개의 매개변수를 받습니다.url, 요청 헤더header, 요청 방법 및 요청 본문 등 클라이언트가 요청한 정보 -
응답주로 클라이언트에 정보를 반환하고 응답 본문과 관련된 일부 작업을 캡슐화하는 데 사용됩니다. 예를 들어response.writeHead메서드를 사용하면 반환 본문의 헤더 정보와 상태 코드를 사용자 정의할 수 있습니다. 🎜응답 본문을 처리한 후 - 메서드의 첫 번째 매개변수는 수신 포트 번호이고 두 번째 매개변수는 바인딩된 호스트
ip입니다. 세 개의 매개변수는http모듈에 의해 비동기적으로 호출되는 콜백 함수입니다. 오류가 발생하면 이 콜백 함수의 첫 번째 매개변수에서 예외를 처리하도록 선택할 수 있습니다. 서버를 더욱 강력하게 만들기 위한 예외
response.end() 메서드를 호출하여 클라이언트에 응답 본문을 보냅니다.
createServer 함수를 사용하면 Server 개체가 생성되지만 모니터링할 수는 없습니다. 또한 server의 🎜 메서드를 호출해야 합니다. code> 객체를 모니터링하고 실제로 서버로 실행할 수 있습니다🎜http 모듈을 사용하여 간단한 서버를 만드는 예입니다🎜const { createServer } = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
// change the MIME type from text/plain to text/html
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/html" });
// read the html file content
fs.readFile("index.html", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.error(
"an error occurred while reading the html file content: ",
err
); throw err;
}
console.log("operation success!");
resp.write(data);
resp.end();
});
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});node를 직접 사용해 볼 수 있습니다 실행하고 나만의 서버를 만들어보세요! 서버가 실행된 후 브라우저는 http://localhost:8080🎜이 서버에 액세스할 수 있습니다🎜🎜 🎜🎜
🎜🎜nodemon을 사용하여 실행할 수도 있습니다. 변경사항 그러면 프로그램을 수동으로 종료하고 다시 실행할 필요가 없습니다🎜const { createServer } = require("http");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;
const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
// change the MIME type to application/json
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
// create a json data by using an object
const jsonDataObj = {
code: 0,
message: "success",
data: {
name: "plasticine",
age: 20,
hobby: "coding",
},
};
resp.write(JSON.stringify(jsonDataObj));
resp.end();
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});npx nodemon을 사용하지 않고 바로 사용할 수 있도록 전역으로 설치하는 것을 권장합니다.
사용하기도 매우 간단합니다. node 명령을 nodemon 명령🎜pnpm i pdfkit
 🎜
🎜🎜🎜3. 유형 힌트 추가🎜🎜🎜
를 사용하고 있었습니다. 이전에Server 및 resp 객체를 생성할 때 구문 프롬프트를 볼 수 없습니다. 사용하는 동안 언제든지 node의 공식 문서를 따라야 합니다. 조금 불편합니다.
하지만 문제가 되지 않습니다. ts의 .d.ts 파일을 사용하여 구문 프롬프트를 제공할 수 있습니다. ts를 개발용으로 사용하세요.🎜<ol>
<li>프로젝트 초기화-- <code>npm init -y
@types/node 설치 - - pnpm i @types/node -D
jsconfig.json 파일을 생성하고 를 제외합니다. node_modules 외부에서는 확인할 필요가 없습니다/**
* @description 创建 pdf 文件
*/const createPdf = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (!fs.existsSync("example.pdf")) {
// create a PDFDocument object
const doc = new PDFDocument();
// create write stream by piping the pdf content.
doc.pipe(fs.createWriteStream("example.pdf"));
// add some contents to pdf document
doc.fontSize(16).text("Hello PDF", 100, 100);
// complete the operation of generating PDF file.
doc.end();
}
resolve("success");
});
};checkJs는 유형 오류를 확인하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 필요에 따라 활성화 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다.
보시다시피 체크를 켜면 바로 매개변수 유형 불일치 문제가 발생합니다🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜이때 🎜 메소드 위에 마우스를 올리면 해당 메소드의 서명을 볼 수 있습니다🎜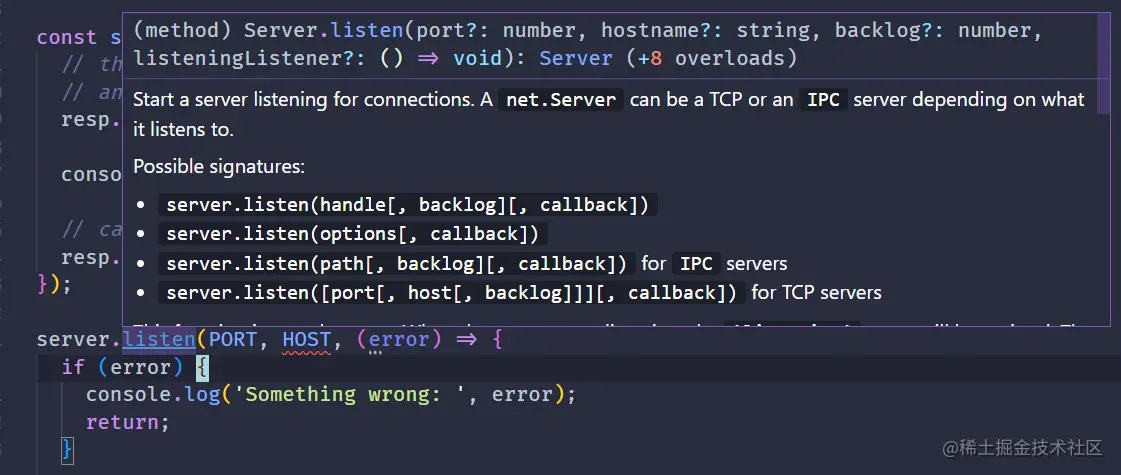
可以看到,原来port参数需要是number类型,但是我们定义的时候是string类型,所以没匹配上,将其修改为number的8080即可
而且可以直接查看到相关api的文档,不需要打开node官方的文档找半天去查看了
4. 返回多个字符串的响应体
前面我们的简单http server中只返回了一句话,那么是否能够返回多句话呢?
这就要用到resp对象的write方法了,end只能够返回一次内容,而是用write方法,我们可以多次写入内容到响应体中,最后只用调用一次end,并且不传递任何参数,只让他完成发送响应体的功能
const { createServer } = require("http");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;
const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
console.log("server is working...");
// write some lorem sentences
resp.write("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit.\n");
resp.write("Omnis eligendi aperiam delectus?\n");
resp.write("Aut, quam quo!\n");
resp.end();
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});这次我们写入了三句话,现在的效果就变成这样啦

5. 返回html
我们不仅可以返回字符串给浏览器,还可以直接读取html文件的内容并将其作为结果返回给浏览器
这就需要用到另一个Node.js的内置模块 -- fs,该模块提供了文件操作的功能
使用fs.readFile可以异步进行读取文件的操作,但是它不会返回promise对象,因此我们需要传入回调去处理读取到文件后的操作
还可以使用fs.readFileSync进行同步阻塞读取文件,这里我们选择异步读取
const { createServer } = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
// change the MIME type from text/plain to text/html
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/html" });
// read the html file content
fs.readFile("index.html", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.error(
"an error occurred while reading the html file content: ",
err
); throw err;
}
console.log("operation success!");
resp.write(data);
resp.end();
});
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});现在的结果就像下面这样:

成功将html返回注意:这里需要将响应头的**Content-Type**改为**text/html**,告知浏览器我们返回的是**html**文件的内容,如果仍然以**text/plain**返回的话,浏览器不会对返回的内容进行解析,即便它是符合**html**语法的也不会解析,就像下面这样:
6. 返回JSON
当我们需要编写一个后端服务器,只负责返回接口数据的时候,就需要返回json格式的内容了,相信聪明的你也知道该怎么处理了:
- 将
MIME类型设置为application/json -
resp.write的时候传入的是json字符串,可以使用JSON.stringify处理对象后返回
const { createServer } = require("http");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;
const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
// change the MIME type to application/json
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
// create a json data by using an object
const jsonDataObj = {
code: 0,
message: "success",
data: {
name: "plasticine",
age: 20,
hobby: "coding",
},
};
resp.write(JSON.stringify(jsonDataObj));
resp.end();
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});结果如下:
7. 返回pdf文件
和之前返回html文件的思路类似,都是一个设置响应头MIME类型,读取文件,返回文件内容的过程
但是这次我们搞点不一样的
我们的思路是在服务器运行的时候生成一个pdf文件,并将它返回
还需要将MIME的类型改为application/pdf生成pdf文件需要用到一个库 -- pdfkit
pnpm i pdfkit
首先我们编写一个创建pdf文件的函数,因为创建pdf文件还需要进行一些写入操作,不确定什么时候会完成,但是我们的请求必须等到pdf文件创建完成后才能得到响应
所以我们需要将它变成异步进行的,返回一个promise
/**
* @description 创建 pdf 文件
*/const createPdf = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (!fs.existsSync("example.pdf")) {
// create a PDFDocument object
const doc = new PDFDocument();
// create write stream by piping the pdf content.
doc.pipe(fs.createWriteStream("example.pdf"));
// add some contents to pdf document
doc.fontSize(16).text("Hello PDF", 100, 100);
// complete the operation of generating PDF file.
doc.end();
}
resolve("success");
});
};这里使用到了管道操作,将PDFDocument对象的内容通过管道传到新创建的写入流中,当完成操作后我们就通过resovle告知外界已经创建好pdf文件了
然后在服务端代码中调用
const server = createServer(async (req, resp) => {
// change the MIME type to application/pdf
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/pdf" });
// create pdf file
await createPdf();
// read created pdf file
fs.readFile("example.pdf", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.error(
"an error occurred while reading the pdf file content: ",
err
);
throw err;
}
console.log("operation success!");
resp.end(data);
});
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});现在浏览器就可以读取到创建的pdf文件了
8. 返回音频文件
思路依然是一样的,读取一个音频文件,然后通过管道将它送到resp对象中再返回即可
const { createServer } = require("http");
const { stat, createReadStream } = require("fs");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;
const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
// change the MIME type to audio/mpe
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "audio/mp3" });
const mp3FileName = "audio.mp3";
stat(mp3FileName, (err, stats) => {
if (stats.isFile()) {
const rs = createReadStream(mp3FileName);
// pipe the read stream to resp
rs.pipe(resp);
} else {
resp.end("mp3 file not exists");
}
});
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});效果如下
打开后就是一个播放音频的界面,这是chrome提供的对音频文件的展示,并且打开控制台会发现有返回音频文件
注意:将音频文件流通过管道传到**resp**后,不需要调用**resp.end()**方法,因为这会关闭整个响应,导致音频文件无法获取
9. 返回视频文件
视频文件和音频文件的处理是一样的,只是MIME的类型要改成video/mp4,其他都一样
const { createServer } = require("http");
const { stat, createReadStream } = require("fs");
const HOST = "localhost";
const PORT = 8080;
const server = createServer((req, resp) => {
// change the MIME type to audio/mpe
resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "audio/mp4" });
const mp4FileName = "video.mp4";
stat(mp4FileName, (err, stats) => {
if (stats.isFile()) {
const rs = createReadStream(mp4FileName);
// pipe the read stream to resp
rs.pipe(resp);
} else {
resp.end("mp4 file not exists");
}
});
});
server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => {
if (error) {
console.log("Something wrong: ", error);
return;
}
console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);
});总结
我们学会了:
- 如何使用
Node创建一个http服务器 - 给
js加上类型提示 - 如何返回字符串响应体
- 如何返回
html - 如何返回
JSON - 如何生成并返回
pdf文件 - 如何返回音频文件
- 如何返回视频文件
虽然内容简单,但还是希望你能跟着动手敲一敲,不要以为简单就看看就算了,看了不代表会了,真正动手实现过后才会找到自己的问题
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
위 내용은 Node.js를 사용하여 간단한 HTTP 서버를 만드는 방법에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다.의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7540
7540
 15
15
 1381
1381
 52
52
 83
83
 11
11
 55
55
 19
19
 21
21
 86
86
 nodejs는 백엔드 프레임워크인가요?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
nodejs는 백엔드 프레임워크인가요?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js는 고성능, 확장성, 크로스 플랫폼 지원, 풍부한 생태계, 개발 용이성 등의 기능을 제공하므로 백엔드 프레임워크로 사용할 수 있습니다.
 nodejs를 mysql 데이터베이스에 연결하는 방법
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
nodejs를 mysql 데이터베이스에 연결하는 방법
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결하려면 다음 단계를 따라야 합니다. mysql2 드라이버를 설치합니다. mysql2.createConnection()을 사용하여 호스트 주소, 포트, 사용자 이름, 비밀번호 및 데이터베이스 이름이 포함된 연결 개체를 만듭니다. 쿼리를 수행하려면 Connection.query()를 사용하세요. 마지막으로 Connection.end()를 사용하여 연결을 종료합니다.
 nodejs 설치 디렉토리에 있는 npm과 npm.cmd 파일의 차이점은 무엇입니까?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
nodejs 설치 디렉토리에 있는 npm과 npm.cmd 파일의 차이점은 무엇입니까?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
Node.js 설치 디렉터리에는 npm과 npm.cmd라는 두 가지 npm 관련 파일이 있습니다. 차이점은 다음과 같습니다. 확장자가 다릅니다. npm은 실행 파일이고 npm.cmd는 명령 창 바로 가기입니다. Windows 사용자: npm.cmd는 명령 프롬프트에서 사용할 수 있으며, npm은 명령줄에서만 실행할 수 있습니다. 호환성: npm.cmd는 Windows 시스템에만 해당되며 npm은 크로스 플랫폼에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 사용 권장사항: Windows 사용자는 npm.cmd를 사용하고, 기타 운영 체제는 npm을 사용합니다.
 nodejs의 전역 변수는 무엇입니까
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
nodejs의 전역 변수는 무엇입니까
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
Node.js에는 다음과 같은 전역 변수가 존재합니다. 전역 개체: 전역 핵심 모듈: 프로세스, 콘솔, 필수 런타임 환경 변수: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column 상수: undefine, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 nodejs와 java 사이에 큰 차이가 있나요?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
nodejs와 java 사이에 큰 차이가 있나요?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Node.js와 Java의 주요 차이점은 디자인과 기능입니다. 이벤트 중심 대 스레드 중심: Node.js는 이벤트 중심이고 Java는 스레드 중심입니다. 단일 스레드 대 다중 스레드: Node.js는 단일 스레드 이벤트 루프를 사용하고 Java는 다중 스레드 아키텍처를 사용합니다. 런타임 환경: Node.js는 V8 JavaScript 엔진에서 실행되는 반면 Java는 JVM에서 실행됩니다. 구문: Node.js는 JavaScript 구문을 사용하고 Java는 Java 구문을 사용합니다. 목적: Node.js는 I/O 집약적인 작업에 적합한 반면, Java는 대규모 엔터프라이즈 애플리케이션에 적합합니다.
 PI 노드 교육 : PI 노드 란 무엇입니까? Pi 노드를 설치하고 설정하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
PI 노드 교육 : PI 노드 란 무엇입니까? Pi 노드를 설치하고 설정하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pinetwork 노드에 대한 자세한 설명 및 설치 안내서이 기사에서는 Pinetwork Ecosystem을 자세히 소개합니다. Pi 노드, Pinetwork 생태계의 주요 역할을 수행하고 설치 및 구성을위한 전체 단계를 제공합니다. Pinetwork 블록 체인 테스트 네트워크가 출시 된 후, PI 노드는 다가오는 주요 네트워크 릴리스를 준비하여 테스트에 적극적으로 참여하는 많은 개척자들의 중요한 부분이되었습니다. 아직 Pinetwork를 모른다면 Picoin이 무엇인지 참조하십시오. 리스팅 가격은 얼마입니까? PI 사용, 광업 및 보안 분석. Pinetwork 란 무엇입니까? Pinetwork 프로젝트는 2019 년에 시작되었으며 독점적 인 Cryptocurrency Pi Coin을 소유하고 있습니다. 이 프로젝트는 모든 사람이 참여할 수있는 사람을 만드는 것을 목표로합니다.
 nodejs는 백엔드 개발 언어인가요?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
nodejs는 백엔드 개발 언어인가요?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
예, Node.js는 백엔드 개발 언어입니다. 서버 측 비즈니스 로직 처리, 데이터베이스 연결 관리, API 제공 등 백엔드 개발에 사용됩니다.
 nodejs 프로젝트를 서버에 배포하는 방법
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
nodejs 프로젝트를 서버에 배포하는 방법
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Node.js 프로젝트의 서버 배포 단계: 배포 환경 준비: 서버 액세스 권한 획득, Node.js 설치, Git 저장소 설정. 애플리케이션 빌드: npm run build를 사용하여 배포 가능한 코드와 종속성을 생성합니다. Git 또는 파일 전송 프로토콜을 통해 서버에 코드를 업로드합니다. 종속성 설치: SSH를 서버에 연결하고 npm install을 사용하여 애플리케이션 종속성을 설치합니다. 애플리케이션 시작: node index.js와 같은 명령을 사용하여 애플리케이션을 시작하거나 pm2와 같은 프로세스 관리자를 사용합니다. 역방향 프록시 구성(선택 사항): Nginx 또는 Apache와 같은 역방향 프록시를 사용하여 트래픽을 애플리케이션으로 라우팅합니다.












