이 기사에서는 java에 대한 관련 지식을 제공합니다. 우선 순위 대기열에 삽입된 요소는 크기가 비슷해야 합니다. 두 개의 학생 유형 요소를 삽입하는 등 크기를 비교할 수 없는 경우 ClassCastException이 보고됩니다. 다음은 Java에서 두 객체의 크기를 비교하는 세 가지 방법을 소개합니다. 이것이 모든 사람에게 도움이 되기를 바랍니다.

추천 학습: "java 비디오 튜토리얼"
이전 섹션에서는 우선순위 큐에 삽입된 요소의 크기가 비교 가능해야 합니다. 비교할 수 없습니다. 크기, 학생 유형의 두 요소가 삽입되면 ClassCastException이 보고됩니다.
예:
class Student{
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三",25);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",31);
PriorityQueue<Student> p = new PriorityQueue<>();
p.offer(s1);
p.offer(s2);
}
}결과:
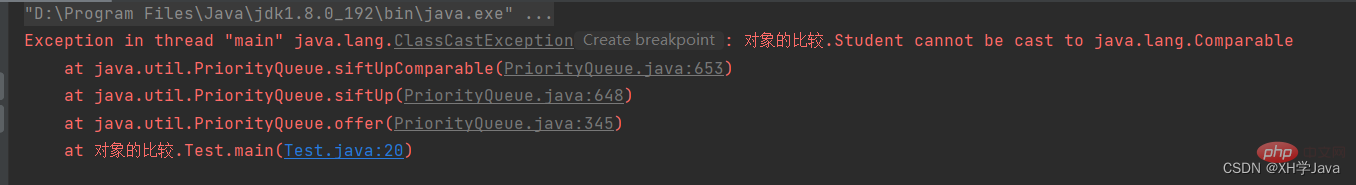
원인: 우선순위 큐의 하위 계층이 힙 데이터 구조를 사용하기 때문입니다. , 힙에 요소를 삽입하려면 비교 요소가 필요하며 학생은 직접 비교할 수 없으므로 예외가 발생합니다.
Java에서는 기본 유형의 요소가 직접 비교
public class TestCompare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(a>b);
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(a<b);
char c1 = 'a';
char c2 = 'b';
System.out.println(c1==c2);
System.out.println(c1>c2);
System.out.println(c1<c2);
boolean b1 = true;
boolean b2 = false;
System.out.println(b1==b2);
System.out.println(b1!=b2);
}
}class Student{
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三",25);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",31);
Student s3 = s1;
System.out.println(s1==s2); //false
System.out.println(s1==s3); //true
//System.out.println(s1<s2); 编译报错
//System.out.println(s1>s3); 编译报错
}
}위 결과로 볼 때 >, <를 사용하여 사용자 정의 유형을 비교할 수 없는 이유는 무엇입니까?
==사용자 정의 유형을 비교할 때 비교되는 것은 개체의 주소가 동일한지 여부입니다
하지만 개체의 내용을 비교해야 하는 경우가 많습니다. 예를 들어 개체를 우선순위 큐에 삽입할 때 힙이 발생합니다. 그러면 개체의 내용에 따라 조정해야 합니다. 그러면 어떻게 비교합니까?
객체 클래스는 내용이 같은지 비교하는 equals() 메소드를 제공하는 클래스입니다. in Object 기본적으로 이 메소드는 ==를 사용하여 비교, 즉 두 객체의 주소를 비교하므로 사용자 정의 유형을 비교하려면 기본 클래스의 equals() 메소드를 재정의할 수 있습니다
예제 : 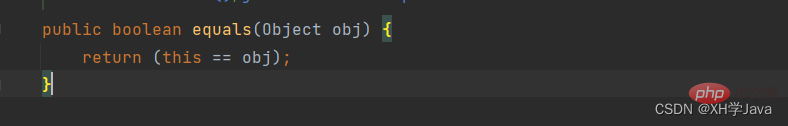
class Student{
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
if(obj==null || !(obj instanceof Student)){
return false;
}
Student s = (Student) obj;
return this.age==s.age && this.name.equals(s.name);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三",25);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",31);
Student s3 = new Student("李四",31);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s2.equals(s3));
}
}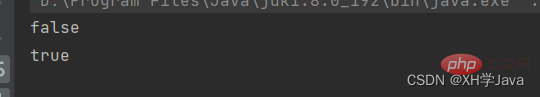
두 객체의 주소가 동일하면 true를 반환합니다.객체가 통과되면 in이 null이면 false를 반환
2. 참조 유형을 기준으로 비교합니다. 크기를 기준으로 비교하려면 클래스를 정의할 때 Comparable 인터페이스를 구현한 다음 클래스에서 CompareTo 메서드를 재정의하세요
예: 비교 두 사람의 크기는 일반적으로 나이에 따라 비교됩니다class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
if(o == null){
return 1;
}
return this.age-o.age;
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("小王",22);
Person p2 = new Person("小张",21);
Person p3 = new Person("小方",22);
System.out.println(p1.compareTo(p2)); //>0表示大于
System.out.println(p2.compareTo(p3)); //<0表示小于
System.out.println(p1.compareTo(p3)); //==0表示相等
}
}import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
if(o == null){
return -1;
}
return this.age-o.age;
}
}
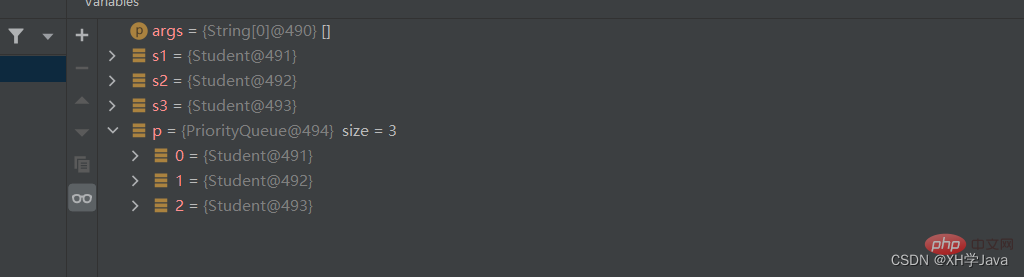
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三",25);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",31);
Student s3 = new Student("李四",35);
PriorityQueue<Student> p = new PriorityQueue<>();
p.offer(s1);
p.offer(s2);
p.offer(s3);
}
}3. 비교기 인터페이스 기반 비교
비교기에 따른 구체적인 비교 단계는 다음과 같습니다.
 비교기 클래스 생성 및 비교기 인터페이스 구현
비교기 클래스 생성 및 비교기 인터페이스 구현
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Student {
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
class StudentComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if(o1 == o2){
return 0;
}
if(o1 == null){
return -1;
}
if(o2 == null){
return 1;
}
return o1.age-o2.age;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三",25);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",31);
Student s3 = new Student("李四",35);
PriorityQueue<Student> p = new PriorityQueue<>(new StudentComparator());
p.offer(s1);
p.offer(s2);
p.offer(s3);
}
}Comparator는 java.util 패키지의 일반 함수입니다. 인터페이스 클래스 유형, 해당 패키지
4. 세 가지 비교 방법 비교
재정의된 방법
| 은 두 개체의 내용이 같은지 여부만 비교할 수 있으며 크기를 비교할 수 없습니다. | |
|---|---|
| 클래스는 클래스에 매우 방해가 되고 원래 클래스의 구조를 파괴하는 인터페이스를 구현해야 합니다. | |
| 는 비교기 클래스를 구현해야 합니다. 수업에 방해가 됨 덜 방해가 되며 원래 수업을 파괴하지 않습니다 |
위 내용은 Java에서 두 객체의 크기를 비교하는 세 가지 방법 요약 및 공유의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!