
일상 업무에서는 Node.js를 사용하는 것이 상대적으로 피상적입니다. 아직 어려서 좀 더 고급 내용을 배워 보겠습니다.
Nicholas Zhang San은 "질문을 가지고 공부하는 것이 더 좋은 방법"이라고 말했습니다. 한번 시도해 보세요.
클러스터를 처음 사용했을 때 다음 코드와 같이 여러 하위 프로세스가 충돌 없이 동일한 포트를 수신할 수 있는 방법에 대해 항상 궁금했습니다.
const cluster = require('cluster')
const net = require('net')
const cpus = require('os').cpus()
if (cluster.isPrimary) {
for (let i = 0; i < cpus.length; i++) {
cluster.fork()
}
} else {
net
.createServer(function (socket) {
socket.on('data', function (data) {
socket.write(`Reply from ${process.pid}: ` + data.toString())
})
socket.on('end', function () {
console.log('Close')
})
socket.write('Hello!\n')
})
.listen(9999)
}이 코드는 상위 프로세스 fork를 통해 내보내집니다. 여러 하위 프로세스가 생성되고 이러한 하위 프로세스는 모두 포트 9999를 수신하고 정상적으로 서비스를 제공할 수 있습니다. 그것을 연구해보자. [권장 관련 튜토리얼: nodejs 동영상 튜토리얼, 프로그래밍 교육]fork 出了多个子进程,且这些子进程都监听了 9999 这个端口并能正常提供服务,这是如何做到的呢?我们来研究一下。【相关教程推荐:nodejs视频教程、编程教学】
学习 Node.js 官方提供库最好的方式当然是调试一下,所以,我们先来准备一下环境。注:本文的操作系统为 macOS Big Sur 11.6.6,其他系统请自行准备相应环境。
编译 Node.js
下载 Node.js 源码
git clone https://github.com/nodejs/node.git
然后在下面这两个地方加入断点,方便后面调试用:
// lib/internal/cluster/primary.js
function queryServer(worker, message) {
debugger;
// Stop processing if worker already disconnecting
if (worker.exitedAfterDisconnect) return;
...
}// lib/internal/cluster/child.js
send(message, (reply, handle) => {
debugger
if (typeof obj._setServerData === 'function') obj._setServerData(reply.data)
if (handle) {
// Shared listen socket
shared(reply, {handle, indexesKey, index}, cb)
} else {
// Round-robin.
rr(reply, {indexesKey, index}, cb)
}
})进入目录,执行
./configure --debug make -j4
之后会生成 out/Debug/node
准备 IDE 环境
使用 vscode 调试,配置好 launch.json 就可以了(其他 IDE 类似,请自行解决):
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Debug C++",
"type": "cppdbg",
"program": "/Users/youxingzhi/ayou/node/out/Debug/node",
"request": "launch",
"args": ["/Users/youxingzhi/ayou/node/index.js"],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "lldb"
},
{
"name": "Debug Node",
"type": "node",
"runtimeExecutable": "/Users/youxingzhi/ayou/node/out/Debug/node",
"request": "launch",
"args": ["--expose-internals", "--nolazy"],
"skipFiles": [],
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/index.js"
}
]
}其中第一个是用于调式 C++ 代码(需要安装 C/C++ 插件),第二个用于调式 JS 代码。接下来就可以开始调试了,我们暂时用调式 JS 代码的那个配置就好了。
准备好调试代码(为了调试而已,这里启动一个子进程就够了):
debugger
const cluster = require('cluster')
const net = require('net')
if (cluster.isPrimary) {
debugger
cluster.fork()
} else {
const server = net.createServer(function (socket) {
socket.on('data', function (data) {
socket.write(`Reply from ${process.pid}: ` + data.toString())
})
socket.on('end', function () {
console.log('Close')
})
socket.write('Hello!\n')
})
debugger
server.listen(9999)
}很明显,我们的程序可以分父进程和子进程这两部分来进行分析。
首先进入的是父进程:
执行 require('cluster') 时,会进入 lib/cluster.js 这个文件:
const childOrPrimary = 'NODE_UNIQUE_ID' in process.env ? 'child' : 'primary'
module.exports = require(`internal/cluster/${childOrPrimary}`)会根据当前 process.env 上是否有 NODE_UNIQUE_ID 来引入不同的模块,此时是没有的,所以会引入 internal/cluster/primary.js 这个模块:
...
const cluster = new EventEmitter();
...
module.exports = cluster
const handles = new SafeMap()
cluster.isWorker = false
cluster.isMaster = true // Deprecated alias. Must be same as isPrimary.
cluster.isPrimary = true
cluster.Worker = Worker
cluster.workers = {}
cluster.settings = {}
cluster.SCHED_NONE = SCHED_NONE // Leave it to the operating system.
cluster.SCHED_RR = SCHED_RR // Primary distributes connections.
...
cluster.schedulingPolicy = schedulingPolicy
cluster.setupPrimary = function (options) {
...
}
// Deprecated alias must be same as setupPrimary
cluster.setupMaster = cluster.setupPrimary
function setupSettingsNT(settings) {
...
}
function createWorkerProcess(id, env) {
...
}
function removeWorker(worker) {
...
}
function removeHandlesForWorker(worker) {
...
}
cluster.fork = function (env) {
...
}该模块主要是在 cluster 对象上挂载了一些属性和方法,并导出,这些后面回过头再看,我们继续往下调试。往下调试会进入 if (cluster.isPrimary) 分支,代码很简单,仅仅是 fork 出了一个新的子进程而已:
// lib/internal/cluster/primary.js
cluster.fork = function (env) {
cluster.setupPrimary()
const id = ++ids
const workerProcess = createWorkerProcess(id, env)
const worker = new Worker({
id: id,
process: workerProcess,
})
...
worker.process.on('internalMessage', internal(worker, onmessage))
process.nextTick(emitForkNT, worker)
cluster.workers[worker.id] = worker
return worker
}cluster.setupPrimary():比较简单,初始化一些参数啥的。
createWorkerProcess(id, env):
// lib/internal/cluster/primary.js
function createWorkerProcess(id, env) {
const workerEnv = {...process.env, ...env, NODE_UNIQUE_ID: `${id}`}
const execArgv = [...cluster.settings.execArgv]
...
return fork(cluster.settings.exec, cluster.settings.args, {
cwd: cluster.settings.cwd,
env: workerEnv,
serialization: cluster.settings.serialization,
silent: cluster.settings.silent,
windowsHide: cluster.settings.windowsHide,
execArgv: execArgv,
stdio: cluster.settings.stdio,
gid: cluster.settings.gid,
uid: cluster.settings.uid,
})
}可以看到,该方法主要是通过 fork 启动了一个子进程来执行我们的 index.js,且启动子进程的时候设置了环境变量 NODE_UNIQUE_ID,这样 index.js 中 require('cluster') 的时候,引入的就是 internal/cluster/child.js 模块了。
worker.process.on('internalMessage', internal(worker, onmessage)):监听子进程传递过来的消息并处理。
接下来就进入了子进程的逻辑:
前面说了,此时引入的是 internal/cluster/child.js 模块,我们先跳过,继续往下,执行 server.listen(9999) 时实际上是调用了 Server 上的方法:
// lib/net.js
Server.prototype.listen = function (...args) {
...
listenInCluster(
this,
null,
options.port | 0,
4,
backlog,
undefined,
options.exclusive
);
}可以看到,最终是调用了 listenInCluster:
// lib/net.js
function listenInCluster(
server,
address,
port,
addressType,
backlog,
fd,
exclusive,
flags,
options
) {
exclusive = !!exclusive
if (cluster === undefined) cluster = require('cluster')
if (cluster.isPrimary || exclusive) {
// Will create a new handle
// _listen2 sets up the listened handle, it is still named like this
// to avoid breaking code that wraps this method
server._listen2(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags)
return
}
const serverQuery = {
address: address,
port: port,
addressType: addressType,
fd: fd,
flags,
backlog,
...options,
}
// Get the primary's server handle, and listen on it
cluster._getServer(server, serverQuery, listenOnPrimaryHandle)
function listenOnPrimaryHandle(err, handle) {
err = checkBindError(err, port, handle)
if (err) {
const ex = exceptionWithHostPort(err, 'bind', address, port)
return server.emit('error', ex)
}
// Reuse primary's server handle
server._handle = handle
// _listen2 sets up the listened handle, it is still named like this
// to avoid breaking code that wraps this method
server._listen2(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags)
}
}由于是在子进程中执行,所以最后会调用 cluster._getServer(server, serverQuery, listenOnPrimaryHandle):
// lib/internal/cluster/child.js
// 这里的 cb 就是上面的 listenOnPrimaryHandle
cluster._getServer = function (obj, options, cb) {
...
send(message, (reply, handle) => {
debugger
if (typeof obj._setServerData === 'function') obj._setServerData(reply.data)
if (handle) {
// Shared listen socket
shared(reply, {handle, indexesKey, index}, cb)
} else {
// Round-robin.
rr(reply, {indexesKey, index}, cb)
}
})
...
}该函数最终会向父进程发送 queryServer 的消息,父进程处理完后会调用回调函数,回调函数中会调用 cb 即 listenOnPrimaryHandle。看来,listen 的逻辑是在父进程中进行的了。
接下来进入父进程:
父进程收到 queryServer 的消息后,最终会调用 queryServer 这个方法:
// lib/internal/cluster/primary.js
function queryServer(worker, message) {
// Stop processing if worker already disconnecting
if (worker.exitedAfterDisconnect) return
const key =
`${message.address}:${message.port}:${message.addressType}:` +
`${message.fd}:${message.index}`
let handle = handles.get(key)
if (handle === undefined) {
let address = message.address
// Find shortest path for unix sockets because of the ~100 byte limit
if (
message.port < 0 &&
typeof address === 'string' &&
process.platform !== 'win32'
) {
address = path.relative(process.cwd(), address)
if (message.address.length < address.length) address = message.address
}
// UDP is exempt from round-robin connection balancing for what should
// be obvious reasons: it's connectionless. There is nothing to send to
// the workers except raw datagrams and that's pointless.
if (
schedulingPolicy !== SCHED_RR ||
message.addressType === 'udp4' ||
message.addressType === 'udp6'
) {
handle = new SharedHandle(key, address, message)
} else {
handle = new RoundRobinHandle(key, address, message)
}
handles.set(key, handle)
}
...
}可以看到,这里主要是对 handle 的处理,这里的 handle 指的是调度策略,分为 SharedHandle 和 RoundRobinHandle
// lib/internal/cluster/shared_handle.js
function SharedHandle(key, address, {port, addressType, fd, flags}) {
this.key = key
this.workers = new SafeMap()
this.handle = null
this.errno = 0
let rval
if (addressType === 'udp4' || addressType === 'udp6')
rval = dgram._createSocketHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags)
else rval = net._createServerHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags)
if (typeof rval === 'number') this.errno = rval
else this.handle = rval
}// lib/net.js
function createServerHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags) {
...
} else {
handle = new TCP(TCPConstants.SERVER);
isTCP = true;
}
if (address || port || isTCP) {
...
err = handle.bind6(address, port, flags);
} else {
err = handle.bind(address, port);
}
}
...
return handle;
}// lib/internal/cluster/primary.js
function queryServer(worker, message) {
...
if (!handle.data) handle.data = message.data
// Set custom server data
handle.add(worker, (errno, reply, handle) => {
const {data} = handles.get(key)
if (errno) handles.delete(key) // Gives other workers a chance to retry.
send(
worker,
{
errno,
key,
ack: message.seq,
data,
...reply,
},
handle // TCP 对象
)
})
...
}// lib/internal/cluster/child.js
// `obj` is a net#Server or a dgram#Socket object.
cluster._getServer = function (obj, options, cb) {
...
send(message, (reply, handle) => {
if (typeof obj._setServerData === 'function') obj._setServerData(reply.data)
if (handle) {
// Shared listen socket
shared(reply, {handle, indexesKey, index}, cb)
} else {
// Round-robin.
rr(reply, {indexesKey, index}, cb) // cb 是 listenOnPrimaryHandle
}
})
...
}out/Debug/node🎜🎜🎜🎜vscode를 사용하여 launch.json을 디버깅하고 구성합니다(다른 IDE도 유사하므로 직접 해결하세요): 🎜// lib/net.js
function listenOnPrimaryHandle(err, handle) {
err = checkBindError(err, port, handle)
if (err) {
const ex = exceptionWithHostPort(err, 'bind', address, port)
return server.emit('error', ex)
}
// Reuse primary's server handle 这里的 server 是 index.js 中 net.createServer 返回的那个对象
server._handle = handle
// _listen2 sets up the listened handle, it is still named like this
// to avoid breaking code that wraps this method
server._listen2(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags)
}// lib/net.js
function setupListenHandle(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags) {
debug('setupListenHandle', address, port, addressType, backlog, fd)
// If there is not yet a handle, we need to create one and bind.
// In the case of a server sent via IPC, we don't need to do this.
if (this._handle) {
debug('setupListenHandle: have a handle already')
} else {
...
}
this[async_id_symbol] = getNewAsyncId(this._handle)
this._handle.onconnection = onconnection
this._handle[owner_symbol] = this
// Use a backlog of 512 entries. We pass 511 to the listen() call because
// the kernel does: backlogsize = roundup_pow_of_two(backlogsize + 1);
// which will thus give us a backlog of 512 entries.
const err = this._handle.listen(backlog || 511)
if (err) {
const ex = uvExceptionWithHostPort(err, 'listen', address, port)
this._handle.close()
this._handle = null
defaultTriggerAsyncIdScope(
this[async_id_symbol],
process.nextTick,
emitErrorNT,
this,
ex
)
return
}
}require('cluster')를 실행하면 lib/cluster.js 파일이 입력 :🎜function queryServer(worker, message) {
debugger;
// Stop processing if worker already disconnecting
if (worker.exitedAfterDisconnect) return;
const key =
`${message.address}:${message.port}:${message.addressType}:` +
`${message.fd}:${message.index}`;
let handle = handles.get(key);
...
}process.env에 NODE_UNIQUE_ID가 있는지 여부에 따라 다른 모듈을 도입합니다. 따라서 internal/cluster / 소개됩니다. 계속해서 디버깅하겠습니다. 디버깅할 때 <code>if (cluster.isPrimary) 분기를 입력합니다. 코드는 매우 간단합니다. 단지 fork로 새 하위 프로세스가 생성됩니다: 🎜// lib/internal/cluster/round_robin_handle.js
function RoundRobinHandle(
key,
address,
{port, fd, flags, backlog, readableAll, writableAll}
) {
...
this.server = net.createServer(assert.fail)
...
else if (port >= 0) {
this.server.listen({
port,
host: address,
// Currently, net module only supports `ipv6Only` option in `flags`.
ipv6Only: Boolean(flags & constants.UV_TCP_IPV6ONLY),
backlog,
})
}
...
this.server.once('listening', () => {
this.handle = this.server._handle
this.handle.onconnection = (err, handle) => {
this.distribute(err, handle)
}
this.server._handle = null
this.server = null
})
} Cluster .setupPrimary(): 일부 매개변수 초기화 등 비교적 간단합니다. 🎜🎜createWorkerProcess(id, env): 🎜// lib/net.js
function setupListenHandle(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags) {
debug('setupListenHandle', address, port, addressType, backlog, fd)
// If there is not yet a handle, we need to create one and bind.
// In the case of a server sent via IPC, we don't need to do this.
if (this._handle) {
debug('setupListenHandle: have a handle already')
} else {
debug('setupListenHandle: create a handle')
let rval = null
// Try to bind to the unspecified IPv6 address, see if IPv6 is available
if (!address && typeof fd !== 'number') {
rval = createServerHandle(DEFAULT_IPV6_ADDR, port, 6, fd, flags)
if (typeof rval === 'number') {
rval = null
address = DEFAULT_IPV4_ADDR
addressType = 4
} else {
address = DEFAULT_IPV6_ADDR
addressType = 6
}
}
if (rval === null)
rval = createServerHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags)
if (typeof rval === 'number') {
const error = uvExceptionWithHostPort(rval, 'listen', address, port)
process.nextTick(emitErrorNT, this, error)
return
}
this._handle = rval
}
this[async_id_symbol] = getNewAsyncId(this._handle)
this._handle.onconnection = onconnection
this._handle[owner_symbol] = this
...
}fork를 통해 하위 프로세스를 시작하여 index js</를 실행하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. code>, 환경 변수 <code>NODE_UNIQUE_ID는 하위 프로세스를 시작할 때 설정되므로 index.js의 require('cluster')가 , internal/cluster/child.js 모듈이 도입되었습니다. 🎜🎜worker.process.on('internalMessage', Internal(worker, onmessage)): 하위 프로세스가 전달한 메시지를 듣고 처리합니다. 🎜🎜그런 다음 하위 프로세스의 논리를 입력합니다.🎜🎜앞서 언급했듯이 internal/cluster/child.js 모듈이 이때 도입되었으니 건너뛰겠습니다. 먼저 계속해서 server.listen(9999)를 실행하면 Server의 메서드가 실제로 호출됩니다. 🎜// lib/internal/cluster/child.js
// `obj` is a net#Server or a dgram#Socket object.
cluster._getServer = function (obj, options, cb) {
...
send(message, (reply, handle) => {
if (typeof obj._setServerData === 'function') obj._setServerData(reply.data)
if (handle) {
// Shared listen socket
shared(reply, {handle, indexesKey, index}, cb)
} else {
// Round-robin.
rr(reply, {indexesKey, index}, cb) // cb 是 listenOnPrimaryHandle
}
})
...
}를 볼 수 있습니다. listeningInCluster: 🎜function rr(message, {indexesKey, index}, cb) {
...
// Faux handle. Mimics a TCPWrap with just enough fidelity to get away
// with it. Fools net.Server into thinking that it's backed by a real
// handle. Use a noop function for ref() and unref() because the control
// channel is going to keep the worker alive anyway.
const handle = {close, listen, ref: noop, unref: noop}
if (message.sockname) {
handle.getsockname = getsockname // TCP handles only.
}
assert(handles.has(key) === false)
handles.set(key, handle)
debugger
cb(0, handle)
}cluster._getServer(server, serverQuery, listeningOnPrimaryHandle)를 호출합니다. 🎜// lib/internal/cluster/round_robin_handle.js
this.server.once('listening', () => {
this.handle = this.server._handle
this.handle.onconnection = (err, handle) => {
this.distribute(err, handle)
}
this.server._handle = null
this.server = null
})queryServer 메시지를 전송하면 상위 프로세스는 처리 후 콜백 함수를 호출합니다. 콜백 함수는 cb, 즉 listenOnPrimaryHandle<을 호출합니다. /코드>. <code>listen 로직은 상위 프로세스에서 수행되는 것 같습니다. 🎜🎜다음으로 상위 프로세스를 입력하세요.🎜🎜상위 프로세스가 queryServer에서 메시지를 받은 후 결국 queryServer 메서드를 호출합니다. 🎜 // lib/internal/cluster/round_robin_handle.js
RoundRobinHandle.prototype.handoff = function (worker) {
...
const message = { act: 'newconn', key: this.key };
// 这里的 handle 是 clientHandle
sendHelper(worker.process, message, handle, (reply) => {
if (reply.accepted) handle.close();
else this.distribute(0, handle); // Worker is shutting down. Send to another.
this.handoff(worker);
});
};handle 처리에 관한 것입니다. 여기서 handle은 SharedHandle</code로 구분되는 스케줄링 전략을 나타냅니다. > 및 <code>RoundRobinHandle 는 각각 선점 및 폴링의 두 가지 전략에 해당합니다(기사 끝 부분의 보충 섹션에 두 전략 간의 비교 예가 있음). 🎜Node.js 中默认是 RoundRobinHandle 策略,可通过环境变量 NODE_CLUSTER_SCHED_POLICY 来修改,取值可以为 none(SharedHandle) 或 rr(RoundRobinHandle)。
<span style="font-size: 18px;">SharedHandle</span>
首先,我们来看一下 SharedHandle,由于我们这里是 TCP 协议,所以最后会通过 net._createServerHandle 创建一个 TCP 对象挂载在 handle 属性上(注意这里又有一个 handle,别搞混了):
// lib/internal/cluster/shared_handle.js
function SharedHandle(key, address, {port, addressType, fd, flags}) {
this.key = key
this.workers = new SafeMap()
this.handle = null
this.errno = 0
let rval
if (addressType === 'udp4' || addressType === 'udp6')
rval = dgram._createSocketHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags)
else rval = net._createServerHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags)
if (typeof rval === 'number') this.errno = rval
else this.handle = rval
}在 createServerHandle 中除了创建 TCP 对象外,还绑定了端口和地址:
// lib/net.js
function createServerHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags) {
...
} else {
handle = new TCP(TCPConstants.SERVER);
isTCP = true;
}
if (address || port || isTCP) {
...
err = handle.bind6(address, port, flags);
} else {
err = handle.bind(address, port);
}
}
...
return handle;
}然后,queryServer 中继续执行,会调用 add 方法,最终会将 handle 也就是 TCP 对象传递给子进程:
// lib/internal/cluster/primary.js
function queryServer(worker, message) {
...
if (!handle.data) handle.data = message.data
// Set custom server data
handle.add(worker, (errno, reply, handle) => {
const {data} = handles.get(key)
if (errno) handles.delete(key) // Gives other workers a chance to retry.
send(
worker,
{
errno,
key,
ack: message.seq,
data,
...reply,
},
handle // TCP 对象
)
})
...
}之后进入子进程:
子进程收到父进程对于 queryServer 的回复后,会调用 shared:
// lib/internal/cluster/child.js
// `obj` is a net#Server or a dgram#Socket object.
cluster._getServer = function (obj, options, cb) {
...
send(message, (reply, handle) => {
if (typeof obj._setServerData === 'function') obj._setServerData(reply.data)
if (handle) {
// Shared listen socket
shared(reply, {handle, indexesKey, index}, cb)
} else {
// Round-robin.
rr(reply, {indexesKey, index}, cb) // cb 是 listenOnPrimaryHandle
}
})
...
}shared 中最后会调用 cb 也就是 listenOnPrimaryHandle:
// lib/net.js
function listenOnPrimaryHandle(err, handle) {
err = checkBindError(err, port, handle)
if (err) {
const ex = exceptionWithHostPort(err, 'bind', address, port)
return server.emit('error', ex)
}
// Reuse primary's server handle 这里的 server 是 index.js 中 net.createServer 返回的那个对象
server._handle = handle
// _listen2 sets up the listened handle, it is still named like this
// to avoid breaking code that wraps this method
server._listen2(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags)
}这里会把 handle 赋值给 server._handle,这里的 server 是 index.js 中 net.createServer 返回的那个对象,并调用 server._listen2,也就是 setupListenHandle:
// lib/net.js
function setupListenHandle(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags) {
debug('setupListenHandle', address, port, addressType, backlog, fd)
// If there is not yet a handle, we need to create one and bind.
// In the case of a server sent via IPC, we don't need to do this.
if (this._handle) {
debug('setupListenHandle: have a handle already')
} else {
...
}
this[async_id_symbol] = getNewAsyncId(this._handle)
this._handle.onconnection = onconnection
this._handle[owner_symbol] = this
// Use a backlog of 512 entries. We pass 511 to the listen() call because
// the kernel does: backlogsize = roundup_pow_of_two(backlogsize + 1);
// which will thus give us a backlog of 512 entries.
const err = this._handle.listen(backlog || 511)
if (err) {
const ex = uvExceptionWithHostPort(err, 'listen', address, port)
this._handle.close()
this._handle = null
defaultTriggerAsyncIdScope(
this[async_id_symbol],
process.nextTick,
emitErrorNT,
this,
ex
)
return
}
}首先会执行 this._handle.onconnection = onconnection,由于客户端请求过来时会调用 this._handle(也就是 TCP 对象)上的 onconnection 方法,也就是会执行lib/net.js 中的 onconnection 方法建立连接,之后就可以通信了。为了控制篇幅,该方法就不继续往下了。
然后调用 listen 监听,注意这里参数 backlog 跟之前不同,不是表示端口,而是表示在拒绝连接之前,操作系统可以挂起的最大连接数量,也就是连接请求的排队数量。我们平时遇到的 listen EADDRINUSE: address already in use 错误就是因为这行代码返回了非 0 的错误。
如果还有其他子进程,也会同样走一遍上述的步骤,不同之处是在主进程中 queryServer 时,由于已经有 handle 了,不需要再重新创建了:
function queryServer(worker, message) {
debugger;
// Stop processing if worker already disconnecting
if (worker.exitedAfterDisconnect) return;
const key =
`${message.address}:${message.port}:${message.addressType}:` +
`${message.fd}:${message.index}`;
let handle = handles.get(key);
...
}以上内容整理成流程图如下:
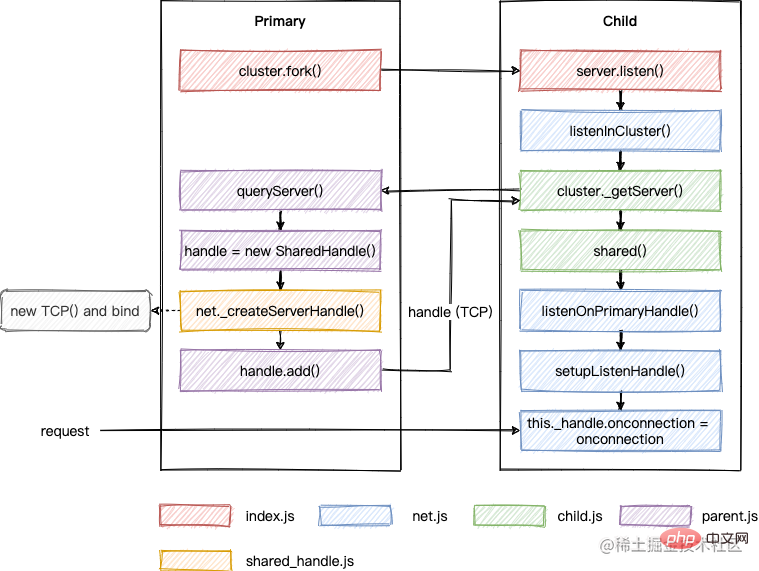
所谓的 SharedHandle,其实是在多个子进程中共享 TCP 对象的句柄,当客户端请求过来时,多个进程会去竞争该请求的处理权,会导致任务分配不均的问题,这也是为什么需要 RoundRobinHandle 的原因。接下来继续看看这种调度方式。
RoundRobinHandle
// lib/internal/cluster/round_robin_handle.js
function RoundRobinHandle(
key,
address,
{port, fd, flags, backlog, readableAll, writableAll}
) {
...
this.server = net.createServer(assert.fail)
...
else if (port >= 0) {
this.server.listen({
port,
host: address,
// Currently, net module only supports `ipv6Only` option in `flags`.
ipv6Only: Boolean(flags & constants.UV_TCP_IPV6ONLY),
backlog,
})
}
...
this.server.once('listening', () => {
this.handle = this.server._handle
this.handle.onconnection = (err, handle) => {
this.distribute(err, handle)
}
this.server._handle = null
this.server = null
})
}如上所示,RoundRobinHandle 会调用 net.createServer() 创建一个 server,然后调用 listen 方法,最终会来到 setupListenHandle:
// lib/net.js
function setupListenHandle(address, port, addressType, backlog, fd, flags) {
debug('setupListenHandle', address, port, addressType, backlog, fd)
// If there is not yet a handle, we need to create one and bind.
// In the case of a server sent via IPC, we don't need to do this.
if (this._handle) {
debug('setupListenHandle: have a handle already')
} else {
debug('setupListenHandle: create a handle')
let rval = null
// Try to bind to the unspecified IPv6 address, see if IPv6 is available
if (!address && typeof fd !== 'number') {
rval = createServerHandle(DEFAULT_IPV6_ADDR, port, 6, fd, flags)
if (typeof rval === 'number') {
rval = null
address = DEFAULT_IPV4_ADDR
addressType = 4
} else {
address = DEFAULT_IPV6_ADDR
addressType = 6
}
}
if (rval === null)
rval = createServerHandle(address, port, addressType, fd, flags)
if (typeof rval === 'number') {
const error = uvExceptionWithHostPort(rval, 'listen', address, port)
process.nextTick(emitErrorNT, this, error)
return
}
this._handle = rval
}
this[async_id_symbol] = getNewAsyncId(this._handle)
this._handle.onconnection = onconnection
this._handle[owner_symbol] = this
...
}且由于此时 this._handle 为空,会调用 createServerHandle() 生成一个 TCP 对象作为 _handle。之后就跟 SharedHandle 一样了,最后也会回到子进程:
// lib/internal/cluster/child.js
// `obj` is a net#Server or a dgram#Socket object.
cluster._getServer = function (obj, options, cb) {
...
send(message, (reply, handle) => {
if (typeof obj._setServerData === 'function') obj._setServerData(reply.data)
if (handle) {
// Shared listen socket
shared(reply, {handle, indexesKey, index}, cb)
} else {
// Round-robin.
rr(reply, {indexesKey, index}, cb) // cb 是 listenOnPrimaryHandle
}
})
...
}不过由于 RoundRobinHandle 不会传递 handle 给子进程,所以此时会执行 rr:
function rr(message, {indexesKey, index}, cb) {
...
// Faux handle. Mimics a TCPWrap with just enough fidelity to get away
// with it. Fools net.Server into thinking that it's backed by a real
// handle. Use a noop function for ref() and unref() because the control
// channel is going to keep the worker alive anyway.
const handle = {close, listen, ref: noop, unref: noop}
if (message.sockname) {
handle.getsockname = getsockname // TCP handles only.
}
assert(handles.has(key) === false)
handles.set(key, handle)
debugger
cb(0, handle)
}可以看到,这里构造了一个假的 handle,然后执行 cb 也就是 listenOnPrimaryHandle。最终跟 SharedHandle 一样会调用 setupListenHandle 执行 this._handle.onconnection = onconnection。
RoundRobinHandle 逻辑到此就结束了,好像缺了点什么的样子。回顾下,我们给每个子进程中的 server 上都挂载了一个假的 handle,但它跟绑定了端口的 TCP 对象没有任何关系,如果客户端请求过来了,是不会执行它上面的 onconnection 方法的。之所以要这样写,估计是为了保持跟之前 SharedHandle 代码逻辑的统一。
此时,我们需要回到 RoundRobinHandle,有这样一段代码:
// lib/internal/cluster/round_robin_handle.js
this.server.once('listening', () => {
this.handle = this.server._handle
this.handle.onconnection = (err, handle) => {
this.distribute(err, handle)
}
this.server._handle = null
this.server = null
})在 listen 执行完后,会触发 listening 事件的回调,这里重写了 handle 上面的 onconnection。
所以,当客户端请求过来时,会调用 distribute 在多个子进程中轮询分发,这里又有一个 handle,这里的 handle 姑且理解为 clientHandle,即客户端连接的 handle,别搞混了。总之,最后会将这个 clientHandle 发送给子进程:
// lib/internal/cluster/round_robin_handle.js
RoundRobinHandle.prototype.handoff = function (worker) {
...
const message = { act: 'newconn', key: this.key };
// 这里的 handle 是 clientHandle
sendHelper(worker.process, message, handle, (reply) => {
if (reply.accepted) handle.close();
else this.distribute(0, handle); // Worker is shutting down. Send to another.
this.handoff(worker);
});
};而子进程在 require('cluster') 时,已经监听了该事件:
// lib/internal/cluster/child.js
process.on('internalMessage', internal(worker, onmessage))
send({act: 'online'})
function onmessage(message, handle) {
if (message.act === 'newconn') onconnection(message, handle)
else if (message.act === 'disconnect')
ReflectApply(_disconnect, worker, [true])
}最终也同样会走到 net.js 中的 function onconnection(err, clientHandle) 方法。这个方法第二个参数名就叫 clientHandle,这也是为什么前面的 handle 我想叫这个名字的原因。
还是用图来总结下:
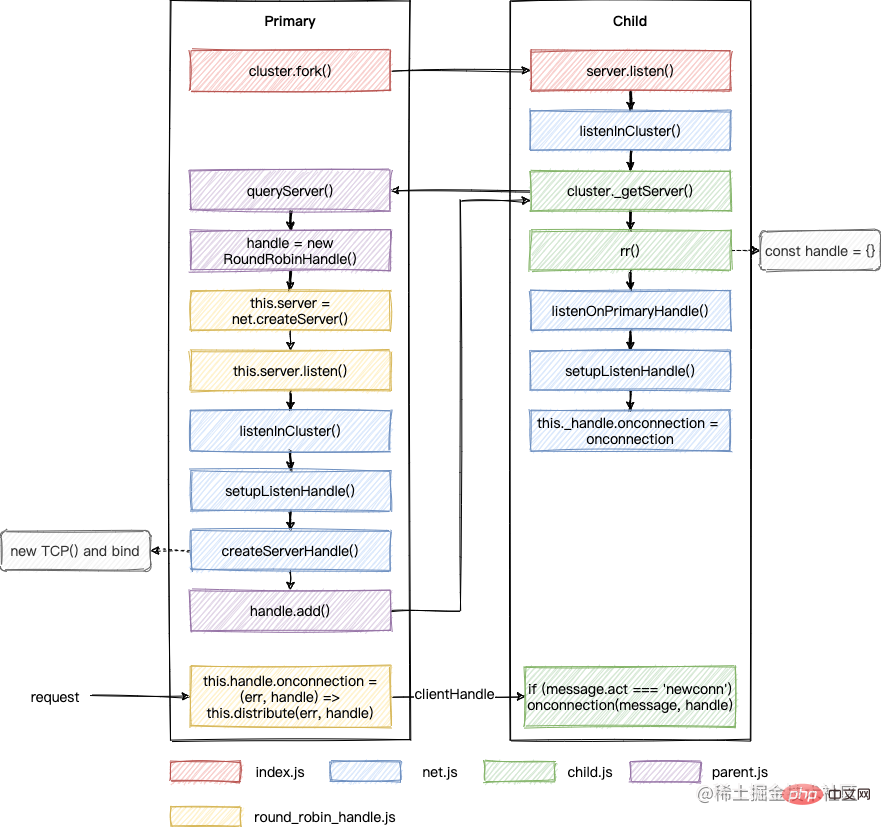
跟 SharedHandle 不同的是,该调度策略中 onconnection 最开始是在主进程中触发的,然后通过轮询算法挑选一个子进程,将 clientHandle 传递给它。
cluster 模块的调试就到此告一段落了,接下来我们来回答一下一开始的问题,为什么多个进程监听同一个端口没有报错?
网上有些文章说是因为设置了 SO_REUSEADDR,但其实跟这个没关系。通过上面的分析知道,不管什么调度策略,最终都只会在主进程中对 TCP 对象 bind 一次。
我们可以修改一下源代码来测试一下:
// deps/uv/src/unix/tcp.c 下面的 SO_REUSEADDR 改成 SO_DEBUG if (setsockopt(tcp->io_watcher.fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &on, sizeof(on)))
编译后执行发现,我们仍然可以正常使用 cluster 模块。
那这个 SO_REUSEADDR 到底影响的是啥呢?我们继续来研究一下。
首先,我们我们知道,下面的代码是会报错的:
const net = require('net') const server1 = net.createServer() const server2 = net.createServer() server1.listen(9999) server2.listen(9999)
但是,如果我稍微修改一下,就不会报错了:
const net = require('net') const server1 = net.createServer() const server2 = net.createServer() server1.listen(9999, '127.0.0.1') server2.listen(9999, '10.53.48.67')
原因在于 listen 时,如果不指定 address,则相当于绑定了所有地址,当两个 server 都这样做时,请求到来就不知道要给谁处理了。
我们可以类比成找对象,port 是对外貌的要求,address 是对城市的要求。现在甲乙都想要一个 port 是 1米7以上 不限城市的对象,那如果有一个 1米7以上 来自 深圳 的对象,就不知道介绍给谁了。而如果两者都指定了城市就好办多了。
那如果一个指定了 address,一个没有呢?就像下面这样:
const net = require('net') const server1 = net.createServer() const server2 = net.createServer() server1.listen(9999, '127.0.0.1') server2.listen(9999)
结果是:设置了 SO_REUSEADDR 可以正常运行,而修改成 SO_DEBUG 的会报错。
还是上面的例子,甲对城市没有限制,乙需要是来自 深圳 的,那当一个对象来自 深圳,我们可以选择优先介绍给乙,非 深圳 的就选择介绍给甲,这个就是 SO_REUSEADDR 的作用。
<span style="font-size: 18px;">SharedHandle</span> 和 <span style="font-size: 18px;">RoundRobinHandle</span> 两种模式的对比
先准备下测试代码:
// cluster.js
const cluster = require('cluster')
const net = require('net')
if (cluster.isMaster) {
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cluster.fork()
}
} else {
const server = net.createServer()
server.on('connection', (socket) => {
console.log(`PID: ${process.pid}!`)
})
server.listen(9997)
}// client.js
const net = require('net')
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
net.connect({port: 9997})
}RoundRobin先执行 node cluster.js,然后执行 node client.js,会看到如下输出,可以看到没有任何一个进程的 PID 是紧挨着的。至于为什么没有一直按照一样的顺序,后面再研究一下。
PID: 42904! PID: 42906! PID: 42905! PID: 42904! PID: 42907! PID: 42905! PID: 42906! PID: 42907! PID: 42904! PID: 42905! PID: 42906! PID: 42907! PID: 42904! PID: 42905! PID: 42906! PID: 42907! PID: 42904! PID: 42905! PID: 42906! PID: 42904!
Shared
先执行 NODE_CLUSTER_SCHED_POLICY=none node cluster.js,则 Node.js 会使用 SharedHandle,然后执行 node client.js,会看到如下输出,可以看到同一个 PID 连续输出了多次,所以这种策略会导致进程任务分配不均的现象。就像公司里有些人忙到 996,有些人天天摸鱼,这显然不是老板愿意看到的现象,所以不推荐使用。
PID: 42561! PID: 42562! PID: 42561! PID: 42562! PID: 42564! PID: 42561! PID: 42562! PID: 42563! PID: 42561! PID: 42562! PID: 42563! PID: 42564! PID: 42564! PID: 42564! PID: 42564! PID: 42564! PID: 42563! PID: 42563! PID: 42564! PID: 42563!
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
위 내용은 Node.js의 클러스터에 대해 이야기하는 기사의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!


![Node.js 전체 입문 튜토리얼 [es6+npm+express+webpack+promise]](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/068/6242b4c8f1a39624.png)

