es6의 새로운 연산자는 무엇입니까?
ES6 새 연산자에는 다음이 포함됩니다. 1. 연산자 앞의 속성이 유효한지 여부를 결정하여 체인에 있는 개체의 속성을 읽거나 정의되지 않은 값을 반환할 수 있는 선택적 체인 연산자 "?." ", 지수 연산에 사용되는 중위 연산자, 구문 "x ** y"; 3. 널값 병합 연산자 "??"; 4. 논리 할당 연산자 "&&=", "||=", " ??=", 주로 자체적으로 논리 연산을 수행한 후 후속 값을 할당한 후 5. 확장 연산자 "...".

이 튜토리얼의 운영 환경: Windows 7 시스템, ECMAScript 버전 6, Dell G3 컴퓨터.
Question
인터뷰어: es6의 새로운 연산자에 대해 말씀해주실 수 있나요?
인터뷰어: 어. . .
인터뷰어: 선택적 연결 연산자를 좋아하시나요?
인터뷰어: 어. . .
인터뷰어: 자, 오늘 인터뷰는 여기까지입니다.
인터뷰어: 음. . .
위 장면은 순전히 허구이며 유사점이 있을 수 있습니다. 하하하?.
오늘은 es6의 몇 가지 새로운 연산자를 배우고 통합해 보겠습니다.
Operator
선택적 체인 연산자
이 속성이 객체인 경우 이 하위 속성에도 액세스할 수 있습니다(예:
var obj = {a: {key: 'val'}}
console.log(obj.a.key) // val). 존재하면 오류가 보고될 수 있습니다.
var obj = {key: 'val'}
console.log(obj.a.key) // error: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'key')이 상황과 호환되려면 기본값을 추가해야 호환됩니다
var obj = {key: 'val'}
console.log((obj.a || {}).key) // undefined레벨이 너무 깊어지면 읽기 어려울 수 있습니다.
(((obj.a || {}).b || {}).c || {}).d
// 或者
obj.a && obj.a.b && obj.a.b.c && obj.a.b.c.d이 쓰기 방법을 개선하기 위해 선택적 체인 연산자가 사용되었습니다. ?.를 사용하여 표현됩니다. ?.表示。
上面的例子可以用可选链运算符来改写
obj.a?.key obj.a?.b?.c?.d
效果是一样的,是不是可读性增加,也节省了代码?
如果发现没有该属性的时候,则不会进行后面的点运算。
它也可以写在函数执行的时候。兼容该函数可能不是函数的情况。这种情况需要该函数名先定义好或者有值,不然还是会报错。
var fn fn?.() // 不会报错 fn1?.() // 报错
可选链不能用在super关键字上,模版字符串,实例化构造函数, 赋值运算符的左侧等。
super?.fn() // error
new Fn?.a() // error
obj.a?.`${b}` // error
obj?.a = obj指数运算符
以前我们算幂次方是这样算的
Math.pow(2,3) // 8
现在可以通过指数运算符来计算, 用**表示
2 ** 3 // 8
也可以连写
2** 3 ** 3 // 134217728
可能你会疑惑,为什么这么大,因为它是从右边计算的。 等同于2**(3 ** 3)。
空值合并运算符(也称Null判断运算符)
这个运算符是用??表示。只有当左侧的值是undefined或者null才会执行默认值。
结合例子来看看:
var a = '' ?? 'default' console.log(a) // '' var a = 0 ?? 'default' console.log(a) // 0 var a = 123 ?? 'default' console.log(a) // 123 var a = undefined ?? 'default' console.log(a) // default var a = undefined ?? 'default' console.log(a) // default
如果和&&或者||混用的时候,需要加上()显示表明优先级,不然会报错。
var a = undefined ?? 'default' && 'a' // error
逻辑赋值运算符
有三种逻辑赋值运算符:
- 逻辑并赋值运算符(&&=)
- 逻辑或赋值运算符(||=)
- 空值合并赋值运算符(??=)
主要是对本身进行逻辑操作后,然后对它赋值后面的值。
通过例子来看一下:
var a,b,c a &&= 1 // undefined //等同于 a && (a = 1) b ||= 1 // 1 //等同于 b || (b = 1) c ??= 1 // 1 //等同于 c ?? (c = 1)
扩展操作符 …
扩展操作符 … 是ES6中引入的,将可迭代对象展开到其单独的元素中,所谓的可迭代对象就是任何能用for of循环进行遍历的对象,例如:数组、字符串、Map 、Set 、DOM节点等。
1. 拷贝数组对象
使用扩展符拷贝数组是ES6中常用的操作:
const years = [2018, 2019, 2020, 2021]; const copyYears = [...years]; console.log(copyYears); // [ 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021 ]
扩展运算符拷贝数组,只有第一层是深拷贝,即对一维数组使用扩展运算符拷贝就属于深拷贝,看下面的代码:
const miniCalendar = [2021, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], 1]; const copyArray = [...miniCalendar]; console.log(copyArray); // [ 2021, [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ], 1 ] copyArray[1][0] = 0; copyArray[1].push(8); copyArray[2] = 2; console.log(copyArray); // [ 2021, [ 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ], 2 ] console.log(miniCalendar); // [ 2021, [ 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ], 1 ]
把打印的结果放在一起便于更加清楚进行对比,如下:
| 变量说明 | 结果 | 操作 |
|---|---|---|
copyArray | [ 2021, [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ], 1 ] | 复制数组 miniCalendar |
copyArray | [ 2021, [ 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ], 2 ] | 1. 将数组第二个元素的第一个元素重新赋值为 0 ;2. 往数组的第二个元素增加一个元素 8 ;3. 将数组第三个元素重新赋值为2 |
miniCalendar | [ 2021, [ 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ], 1 ] | 위의 예는 선택적 체인 연산자를 사용하여 다시 작성할 수 있습니다.const time = {
year: 2021,
month: 7,
day: {
value: 1,
},
};
const copyTime = { ...time };
console.log(copyTime); // { year: 2021, month: 7, day: { value: 1 } }로그인 후 복사 로그인 후 복사 | 가독성을 높이고 코드를 저장하는 효과는 동일합니까?
copyTime.day.value = 2;
copyTime.month = 6;
console.log(copyTime); // { year: 2021, month: 6, day: { value: 2 } }
console.log(time); // { year: 2021, month: 7, day: { value: 2 } }const halfMonths1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; const halfMonths2 = [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]; const allMonths = [...halfMonths1, ...halfMonths2]; console.log(allMonths); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ]
🎜지수 연산자🎜🎜🎜과거에는 이렇게 거듭제곱을 계산했습니다🎜const time1 = {
month: 7,
day: {
value: 1,
},
};
const time2 = {
year: 2021,
month: 8,
day: {
value: 10,
},
};
const time = { ...time1, ...time2 };
console.log(time); // { month: 8, day: { value: 10 }, year: 2021 }로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사🎜이제 를 사용하여 지수 연산자를 통해 계산할 수 있습니다**< / code>는 🎜<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>const sum = (num1, num2) => num1 + num2;
console.log(sum(...[6, 7])); // 13
console.log(sum(...[6, 7, 8])); // 13</pre><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div>🎜를 🎜<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>const arrayNumbers = [1, 5, 9, 3, 5, 7, 10];
const min = Math.min(...arrayNumbers);
const max = Math.max(...arrayNumbers);
console.log(min); // 1
console.log(max); // 10</pre><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div>🎜와 함께 쓸 수도 있다는 뜻입니다. 오른쪽에서 계산되기 때문에 왜 그렇게 큰지 궁금하실 것입니다. <code>2**(3 ** 3)과 동일합니다. 🎜🎜Null 값 병합 연산자(Null 판단 연산자라고도 함)🎜🎜🎜이 연산자는 ??로 표시됩니다. 기본값은 왼쪽 값이 정의되지 않음 또는 null인 경우에만 실행됩니다. 🎜🎜예제를 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜const arrayNumbers = [1, 5, 9, 3, 5, 7, 10, 4, 5, 2, 5];
const newNumbers = [...new Set(arrayNumbers)];
console.log(newNumbers); // [ 1, 5, 9, 3, 7, 10, 4, 2 ]
로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사🎜&& 또는 ||와 혼합하는 경우 우선순위를 나타내기 위해 ()를 추가해야 합니다. 수준이 아니면 오류가 보고됩니다. 🎜const title = "china";
const charts = [...title];
console.log(charts); // [ 'c', 'h', 'i', 'n', 'a' ]
로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사🎜논리 할당 연산자🎜🎜🎜세 가지 논리 할당 연산자가 있습니다: 🎜- 논리 합집합 할당 연산자(&&=)
< li> 논리 OR 대입 연산자(||=)- 널 값 병합 대입 연산자(??=)
🎜 주로 자신에게 논리 연산을 수행한 후, 다음과 같은 값을 대입합니다. 🎜🎜예를 통해 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜const title = "china";
const short = [...title];
short.length = 2;
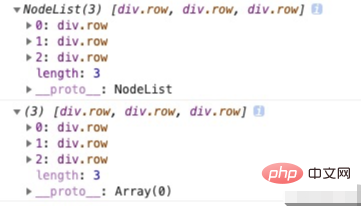
console.log(short.join("")); // ch로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사 확장 연산자 … 🎜🎜확장 연산자 …는 ES6에 도입되었으며, 이는 반복 가능한 객체를 별도의 요소로 확장합니다. for of 루프가 탐색하는 배열, 문자열, 맵, 세트, DOM 노드 등과 같은 객체입니다. 🎜🎜🎜1. 배열 객체 복사🎜🎜🎜확장기를 사용하여 배열을 복사하는 것은 ES6에서 일반적으로 사용되는 작업입니다. 🎜const nodeList = document.querySelectorAll(".row");
const nodeArray = [...nodeList];
console.log(nodeList);
console.log(nodeArray);로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사🎜확장 연산자는 배열을 복사하며, 🎜첫 번째 레이어만 전체 복사본입니다🎜. 1차원 배열에 대한 확장 작업 사용 문자 복사는 깊은 복사입니다. 다음 코드를 살펴보세요. 🎜const [currentMonth, ...others] = [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12];
console.log(currentMonth); // 7
console.log(others); // [ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ]
로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사🎜보다 명확한 비교를 위해 인쇄된 결과를 다음과 같이 정리합니다. 🎜
const time1 = {
month: 7,
day: {
value: 1,
},
};
const time2 = {
year: 2021,
month: 8,
day: {
value: 10,
},
};
const time = { ...time1, ...time2 };
console.log(time); // { month: 8, day: { value: 10 }, year: 2021 }??로 표시됩니다. 기본값은 왼쪽 값이 정의되지 않음 또는 null인 경우에만 실행됩니다. 🎜🎜예제를 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜const arrayNumbers = [1, 5, 9, 3, 5, 7, 10, 4, 5, 2, 5]; const newNumbers = [...new Set(arrayNumbers)]; console.log(newNumbers); // [ 1, 5, 9, 3, 7, 10, 4, 2 ]
&& 또는 ||와 혼합하는 경우 우선순위를 나타내기 위해 ()를 추가해야 합니다. 수준이 아니면 오류가 보고됩니다. 🎜const title = "china"; const charts = [...title]; console.log(charts); // [ 'c', 'h', 'i', 'n', 'a' ]
🎜논리 할당 연산자🎜🎜🎜세 가지 논리 할당 연산자가 있습니다: 🎜- 논리 합집합 할당 연산자(&&=)
< li> 논리 OR 대입 연산자(||=)- 널 값 병합 대입 연산자(??=)
🎜 주로 자신에게 논리 연산을 수행한 후, 다음과 같은 값을 대입합니다. 🎜🎜예를 통해 살펴보겠습니다. 🎜const title = "china";
const short = [...title];
short.length = 2;
console.log(short.join("")); // ch로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사 확장 연산자 … 🎜🎜확장 연산자 …는 ES6에 도입되었으며, 이는 반복 가능한 객체를 별도의 요소로 확장합니다. for of 루프가 탐색하는 배열, 문자열, 맵, 세트, DOM 노드 등과 같은 객체입니다. 🎜🎜🎜1. 배열 객체 복사🎜🎜🎜확장기를 사용하여 배열을 복사하는 것은 ES6에서 일반적으로 사용되는 작업입니다. 🎜const nodeList = document.querySelectorAll(".row");
const nodeArray = [...nodeList];
console.log(nodeList);
console.log(nodeArray);로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사🎜확장 연산자는 배열을 복사하며, 🎜첫 번째 레이어만 전체 복사본입니다🎜. 1차원 배열에 대한 확장 작업 사용 문자 복사는 깊은 복사입니다. 다음 코드를 살펴보세요. 🎜const [currentMonth, ...others] = [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12];
console.log(currentMonth); // 7
console.log(others); // [ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ]
로그인 후 복사로그인 후 복사🎜보다 명확한 비교를 위해 인쇄된 결과를 다음과 같이 정리합니다. 🎜
const title = "china";
const short = [...title];
short.length = 2;
console.log(short.join("")); // chconst nodeList = document.querySelectorAll(".row");
const nodeArray = [...nodeList];
console.log(nodeList);
console.log(nodeArray);const [currentMonth, ...others] = [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]; console.log(currentMonth); // 7 console.log(others); // [ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ]
| 변수 설명 | 결과 | 작업 | 🎜
|---|---|---|