중앙 집중식 상태 관리 Vuex 사용에 대한 간략한 분석
중앙 집중식 상태 관리와 함께 Vuex를 어떻게 사용하나요? 다음 기사에서는 vuex를 이해하고 vuex 사용 방법에 대해 간략하게 설명하겠습니다. 도움이 되기를 바랍니다.

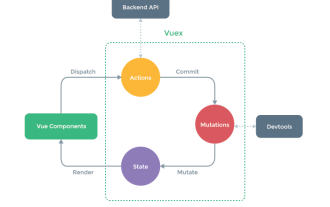
1. vuex란?
Vue 애플리케이션에서 여러 구성 요소의 공유 상태를 중앙에서 관리할 수 있는 Vue의 중앙 집중식 상태 관리를 구체적으로 구현하는 Vue 플러그인입니다. 또한 구성 요소 간 통신 방법이며 모든 구성 요소 간 통신에 적합합니다
2. Vuex를 사용하는 경우
1. 여러 구성 요소가 동일한 상태에 의존합니다
2. 의 구성 요소 중 동일한 상태를 변경해야 합니다
2.1 Vuex 사용 방법
우선 Vuex를 사용하는 경우 두 개 이상의 구성 요소를 공유해야 할 확률이 높다는 점을 알아야 합니다. 데이터/상태 집합이므로 먼저 두 개의 구성 요소(각각 Count, Person)를 준비해야 하며 Vuex는 일련의 준비 작업을 수행하기 위해 저장소에 의존하기 때문에 src 디렉터리에 저장소 파일을 추가해야 합니다
2.2 Count 컴포넌트
이 컴포넌트에서는 map... 다양한 것들을 볼 수 있습니다. 여기서는 vuex의 4가지 map에 대해 이야기해야 합니다. 여기서는 이 구성요소의 기능만 소개하겠습니다. Count는 "강력한" 컴퓨팅 기능을 갖춘 A 구성요소로, 최종 숫자를 10배로 증폭할 수 있고, 홀수 연산을 수행할 수 있으며, 연산을 지연시킬 수 있다고 할 수 있습니다. 극도로 "강력하다"
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前和为:{{sum}}</h3>
<h3>当前和为:放大10倍:{{bigSum}}</h3>
<h3>我在{{school}},学习{{subject}}</h3>
<h3>下方组件的总人数{{personList.length}}</h3>
<select v-model.number="num">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment(num)">+</button>
<button @click="decrement(num)">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(num)">奇数+</button>
<button @click="incrementWait(num)">500ms后再+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入mapState等
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
num: 1 // 用户选择的数字
};
},
computed: {
// 使用mapState生成计算属性,从state种读取数据(...mapstate()的意思是将其内的对象全部展开的计算属性里面)
// ...mapState({ sum: "sum", school: "school", subject: "subject" }), // 对象写法
...mapState(["sum", "school", "subject", "personList"]), // 数组写法
// 使用mapGetters生成计算属性,从getters种读取数据
// ...mapGetters(["bigSum"]), // 数组写法
...mapGetters({ bigSum: "bigSum" }) // 数组写法
},
methods: {
// 借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法种会调用相应的commit去联系mutations
...mapMutations({ increment: "JIA", decrement: "JIAN" }), // 对象式
...mapActions({ incrementOdd: "jiaodd", incrementWait: "jiaWait" }) //数组式
// ...mapActions(["jiaodd", "jiaWait"]) //数组式简写
},
mounted() {
}
};
</script>
<style>
button {
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>2.3Person 컴포넌트
Person 컴포넌트에는 사람을 추가하는 "강력한" 기능이 있으며, 자신의 희망에 따라 친척과 친구를 추가할 수 있습니다
<template>
<div>
<h3>人员列表</h3>
<h3>Count组件的求和为{{sum}}</h3>
<input type="text" placehodler="请输入名字" v-model="name">
<button @click="add">添加</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="p in personList" :key="p.id">{{p.name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from "nanoid";
export default {
name: "Person",
data() {
return {
name: ""
};
},
computed: {
personList() {
return this.$store.state.personList;
},
sum() {
return this.$store.state.sum;
}
},
methods: {
add() {
const personObj = { id: nanoid(), name: this.name };
this.$store.commit("ADD_PERSON", personObj);
this.name = "";
}
}
};
</script>2.4 컴포넌트 소개
이 두 구성 요소를 각각 앱에 도입하세요
<template>
<div class="container">
<Count></Count>
<Person/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Count from "./components/Count";
import Person from "./components/Person";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Count, Person }
};
</script>2.5 폴더 아래에 store index.js 구성
store 폴더 아래에 새 index.js 파일을 만들고 다음을 작성하세요. 먼저 vue 및 vuex를 도입한 다음 action을 사용하여 해당 작업에 응답합니다. 여기서는 각각 전달된 컨텍스트와 값을 나타내는 두 개의 매개변수 context 및 value를 받을 수 있습니다. 컨텍스트에서 구성한 상태에서 모든 것을 찾을 수 있으며, 여기서 value의 값은 1

// 创建VUex种的store核心
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 使用vuex插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 准备actions——用于组件内的动作响应
const actions = {
// 奇数加法
jiaodd(context, value) {
if (context.state.sum % 2) {
context.commit('JIA', value)
}
},
// 延迟加
jiaWait(context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit("JIA", value)
}, 500);
},
}
// 准备mutations——用于数据操作
const mutations = {
JIA(state, value) {
state.sum += value
},
JIAN(state, value) {
state.sum -= value
},
ADD_PERSON(state, value) {
console.log('mustations种的ADD_PERSON被调用',state.personList);
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
}
// 准备state——用于数据的储存
const state = {
sum: 0, // 当前和
school: '山鱼小学',
subject: '前端',
personList:[{id:'001',name:'张三'}]
}
// 用于加工state种的数据
const getters = {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10
}
}
// 创建store并且暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
// actions: actions,// 前后名称一样所以可以触发简写模式
actions,
mutations,
state,
getters
});2입니다. 1.
mapState: 계산을 위해 상태의 데이터를 매핑하는 데 사용됩니다. Attributes
computed: {
// 使用mapState生成计算属性,从state种读取数据(...mapstate({})的意思是将其内的对象全部展开的计算属性里面)
...mapState({ sum: "sum", school: "school", subject: "subject" }), // 对象写法
// ...mapState(["sum", "school", "subject"]), // 数组写法
}mapGetters: getter의 데이터를 계산된 속성에 매핑하는 데 사용됩니다.
computed: {
// 使用mapGetters生成计算属性,从getters种读取数据
...mapGetters({bigSum:"bigSum"})
...mapGetters(["bigSum"])
}mapMutations: 생성 및 돌연변이를 돕는 데 사용됩니다. $store.commit()
methods: {
// 借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法种会调用相应的commit去联系mutations
...mapMutations({ increment: "JIA", decrement: "JIAN" }), // 对象式
// ...mapMutations(["JIA", "JIAN"]), // 数组式(button的名字和vuex里面的名字必须统一)
},mapActions 함수를 포함한 통신 방법: 사용됨 $store.commit()
methods: {
// 借助mapActions生成对应的方法,方法种会调用相应的dispath去联系actions
...mapActions({ incrementOdd: "jiaodd", incrementWait: "jiaWait" }), //对象式
// ...mapActions(["jiaodd", "jiaWait"]) //数组式
},(학습 영상 공유: vuejs 입문 튜토리얼,
기본 프로그래밍 영상위 내용은 중앙 집중식 상태 관리 Vuex 사용에 대한 간략한 분석의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7518
7518
 15
15
 1378
1378
 52
52
 81
81
 11
11
 53
53
 19
19
 21
21
 68
68
 Vuex를 사용하여 Vue2.x에서 전역 상태를 관리하는 모범 사례
Jun 09, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
Vuex를 사용하여 Vue2.x에서 전역 상태를 관리하는 모범 사례
Jun 09, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
Vue2.x는 현재 가장 널리 사용되는 프런트 엔드 프레임워크 중 하나이며 전역 상태 관리를 위한 솔루션으로 Vuex를 제공합니다. Vuex를 사용하면 상태 관리가 더욱 명확해지고 유지 관리가 쉬워집니다. 개발자가 Vuex를 더 잘 사용하고 코드 품질을 향상하는 데 도움이 되도록 Vuex의 모범 사례가 아래에 소개됩니다. 1. 모듈식 조직 상태를 사용합니다. Vuex는 단일 상태 트리를 사용하여 애플리케이션의 모든 상태를 관리하고 구성 요소에서 상태를 추출하여 상태 관리를 더 명확하고 이해하기 쉽게 만듭니다. 상태가 많은 애플리케이션에서는 모듈을 사용해야 합니다.
![Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 '오류: [vuex]는 돌연변이 처리기 외부에서 vuex 저장소 상태를 변경하지 않습니다.' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/164/168760467048976.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 '오류: [vuex]는 돌연변이 처리기 외부에서 vuex 저장소 상태를 변경하지 않습니다.' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 07:04 PM
Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 '오류: [vuex]는 돌연변이 처리기 외부에서 vuex 저장소 상태를 변경하지 않습니다.' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 07:04 PM
Vue 애플리케이션에서는 vuex를 사용하는 것이 일반적인 상태 관리 방법입니다. 그러나 vuex를 사용할 때 "오류:[vuex]donotmutatevuexstorestateoutsidemutationhandlers"와 같은 오류 메시지가 나타날 수 있습니다. 이 오류 메시지는 무엇을 의미합니까? 이 오류 메시지가 나타나는 이유는 무엇입니까? 이 오류를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 이 기사에서는 이 문제를 자세히 다룰 것입니다. 오류 메시지에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
 Vue3에서 Vuex를 사용하는 방법
May 14, 2023 pm 08:28 PM
Vue3에서 Vuex를 사용하는 방법
May 14, 2023 pm 08:28 PM
Vuex는 무엇을 하나요? Vue 공식: 상태 관리 도구 상태 관리란 무엇입니까? 상태는 여러 구성 요소 간에 공유되어야 하며 하나의 변경으로 모든 것이 변경됩니다. 예를 들어 사용자 로그인 상태, 사용자 이름, 지리적 위치 정보, 장바구니 항목 등 전역적으로 사용되는 일부 상태 정보가 있습니다. 이때 전역 상태 관리를 위한 도구가 필요하며 Vuex가 그러한 도구입니다. 단일 페이지 상태 관리 View–>Actions–>State 뷰 레이어(view)는 상태(state)를 변경하기 위한 액션(action)을 트리거하고 뷰 레이어(view) vuex(Vue3.0)에 다시 응답합니다.
![Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 '오류: [vuex] 알 수 없는 작업 유형: xxx' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/168766615217161.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 '오류: [vuex] 알 수 없는 작업 유형: xxx' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 '오류: [vuex] 알 수 없는 작업 유형: xxx' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Vue.js 프로젝트에서 vuex는 매우 유용한 상태 관리 도구입니다. 이는 여러 구성 요소 간에 상태를 공유하는 데 도움이 되며 상태 변경을 관리하는 안정적인 방법을 제공합니다. 그러나 vuex를 사용할 때 가끔 "Error:[vuex]unknownactiontype:xxx" 오류가 발생합니다. 이 기사에서는 이 오류의 원인과 해결 방법을 설명합니다. 1. 오류 원인 vuex를 사용할 때 몇 가지 액션과 뮤를 정의해야 합니다.
 vuex의 구현 원칙에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
Mar 20, 2023 pm 06:14 PM
vuex의 구현 원칙에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
Mar 20, 2023 pm 06:14 PM
인터뷰에서 vuex의 구현 원리에 대한 질문을 받았을 때 어떻게 답해야 할까요? 다음 기사는 vuex의 구현 원리에 대한 심층적인 이해를 제공할 것입니다. 도움이 되기를 바랍니다.
 Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 'TypeError: 정의되지 않은 'xxx' 속성을 읽을 수 없습니다' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Aug 18, 2023 pm 09:24 PM
Vue 애플리케이션에서 vuex를 사용할 때 'TypeError: 정의되지 않은 'xxx' 속성을 읽을 수 없습니다' 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Aug 18, 2023 pm 09:24 PM
Vue 애플리케이션에서 Vuex를 사용하는 것은 매우 일반적인 작업입니다. 그러나 Vuex를 사용할 때 가끔 "TypeError: Cannotreadproperty'xxx'ofundefine" 오류 메시지가 표시됩니다. 이 오류 메시지는 정의되지 않은 속성 "xxx"를 읽을 수 없어 프로그램 오류가 발생함을 의미합니다. 이 문제의 원인은 실제로 매우 분명합니다. Vuex의 특정 속성을 호출할 때 이 속성이 올바르게 설정되지 않았기 때문입니다.
 vue3+vite에서 vuex를 사용하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 09:10 AM
vue3+vite에서 vuex를 사용하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 09:10 AM
구체적인 단계: 1. vuex(vue3 권장 4.0 이상) pnpmivuex-S2를 설치하고, main.js에서 importstorefrom'@/store'//hx-app의 전역 구성을 구성합니다. constapp=createApp(App)app.use(store) 3 .새 관련 폴더 및 파일을 생성합니다. 여기에서는 vuex 모듈을 사용하여 다른 페이지와 파일을 배치한 다음 여기에서 Import.meta.glob을 사용합니다. ~의
 Vue에서 컴포넌트 통신을 위해 vuex를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jul 19, 2023 pm 06:16 PM
Vue에서 컴포넌트 통신을 위해 vuex를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Jul 19, 2023 pm 06:16 PM
Vue에서 컴포넌트 통신을 위해 vuex를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까? Vue는 컴포넌트 기반 개발 모델을 채택하여 복잡한 애플리케이션을 보다 쉽게 구축할 수 있는 인기 있는 JavaScript 프레임워크입니다. Vue의 컴포넌트 개발 과정에서 우리는 종종 서로 다른 컴포넌트 간의 통신이 필요한 상황에 직면합니다. Vuex는 Vue에서 공식적으로 권장하는 상태 관리 도구입니다. 중앙 집중식 저장소 관리자를 제공하고 구성 요소 간의 통신 문제를 해결합니다. 이 글에서는 Vue에서 컴포넌트 통신을 위해 Vuex를 사용하는 방법을 소개합니다.




