
뉴스 읽기, 이메일 보내기, 날씨 확인, 폴더 정리 등 매일 반복적인 작업을 많이 수행할 수 있습니다. 자동화된 스크립트를 사용하면 이러한 작업을 수동으로 반복해서 완료할 필요가 없습니다. 매우 편리합니다. 어느 정도 Python은 자동화와 동의어입니다.
오늘 저는 8가지 매우 유용한 Python 자동화 스크립트를 공유합니다. 마음에 드신다면 수집, 팔로우, 좋아요 꼭 눌러주세요.
이 스크립트는 웹 페이지에서 텍스트를 캡처한 다음 자동으로 음성으로 읽을 수 있습니다.
코드는 두 부분으로 나누어져 있습니다. 첫 번째는 웹페이지 텍스트를 크롤링하는 것이고, 두 번째는 읽기 도구를 통해 텍스트를 소리내어 읽는 것입니다.
필수 타사 라이브러리:
Beautiful Soup - 크롤링된 웹 페이지 정보를 추출하는 데 사용되는 클래식 HTML/XML 텍스트 파서입니다.
requests - 데이터를 얻기 위해 웹 페이지에 요청을 보내는 데 사용되는 매우 사용하기 쉬운 HTTP 도구입니다.
Pyttsx3 - 텍스트를 음성으로 변환하고 속도, 주파수 및 음성을 제어합니다.
import pyttsx3
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
engine = pyttsx3.init('sapi5')
voices = engine.getProperty('voices')
newVoiceRate = 130 ## Reduce The Speech Rate
engine.setProperty('rate',newVoiceRate)
engine.setProperty('voice', voices[1].id)
def speak(audio):
engine.say(audio)
engine.runAndWait()
text = str(input("Paste articlen"))
res = requests.get(text)
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text,'html.parser')
articles = []
for i in range(len(soup.select('.p'))):
article = soup.select('.p')[i].getText().strip()
articles.append(article)
text = " ".join(articles)
speak(text)
# engine.save_to_file(text, 'test.mp3') ## If you want to save the speech as a audio file
engine.runAndWait()데이터 탐색은 데이터 과학 프로젝트의 첫 번째 단계로, 더 깊은 가치를 분석하기 위해서는 데이터의 기본 정보를 이해해야 합니다.
일반적으로 우리는 데이터 탐색을 위해 pandas, matplotlib 및 기타 도구를 사용하지만, 효율성을 높이고 싶다면 직접 많은 코드를 작성해야 합니다. Dtale이 좋은 선택입니다.
Dtale은 한 줄의 코드로 자동화된 분석 보고서를 생성하는 것이 특징입니다. Flask 백엔드와 React 프론트엔드를 결합하여 Pandas 데이터 구조를 쉽게 보고 분석할 수 있는 방법을 제공합니다.
Jupyter에서 Dtale을 사용할 수 있습니다.
필수 타사 라이브러리:
Dtale - 자동으로 분석 보고서를 생성합니다.
### Importing Seaborn Library For Some Datasets
import seaborn as sns
### Printing Inbuilt Datasets of Seaborn Library
print(sns.get_dataset_names())
### Loading Titanic Dataset
df=sns.load_dataset('titanic')
### Importing The Library
import dtale
#### Generating Quick Summary
dtale.show(df)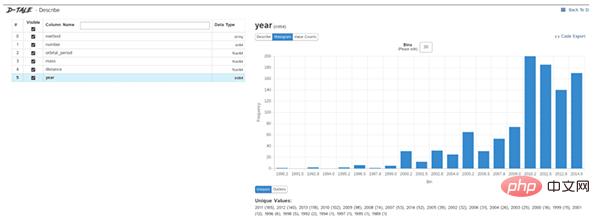
이 스크립트를 사용하면 이메일 내용과 첨부 파일을 사용자 정의하고 조정할 수 있어 매우 실용적입니다.
이메일 클라이언트와 비교할 때 Python 스크립트의 장점은 이메일 서비스를 지능적으로, 일괄적으로, 높은 수준의 사용자 정의로 배포할 수 있다는 것입니다.
필수 타사 라이브러리:
Email - 이메일 메시지 관리용
Smtlib - 이메일을 SMTP 서버로 보내기 위해 SMTP가 있는 모든 컴퓨터에서 인터넷으로 이메일을 보내는 SMTP 클라이언트 세션 개체를 정의합니다. ESMTP 수신기
Pandas - 데이터 분석 및 정리 도구입니다.
import smtplib
from email.message import EmailMessage
import pandas as pd
def send_email(remail, rsubject, rcontent):
email = EmailMessage()## Creating a object for EmailMessage
email['from'] = 'The Pythoneer Here'## Person who is sending
email['to'] = remail## Whom we are sending
email['subject'] = rsubject ## Subject of email
email.set_content(rcontent) ## content of email
with smtplib.SMTP(host='smtp.gmail.com',port=587)as smtp:
smtp.ehlo() ## server object
smtp.starttls() ## used to send data between server and client
smtp.login("deltadelta371@gmail.com","delta@371") ## login id and password of gmail
smtp.send_message(email)## Sending email
print("email send to ",remail)## Printing success message
if __name__ == '__main__':
df = pd.read_excel('list.xlsx')
length = len(df)+1
for index, item in df.iterrows():
email = item[0]
subject = item[1]
content = item[2]
send_email(email,subject,content)이 스크립트는 PDF를 오디오 파일로 변환할 수 있습니다. 원리도 매우 간단합니다. 먼저 PyPDF를 사용하여 PDF의 텍스트를 추출한 다음 Pyttsx3을 사용하여 텍스트를 음성으로 변환합니다. .
import pyttsx3,PyPDF2
pdfreader = PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(open('story.pdf','rb'))
speaker = pyttsx3.init()
for page_num in range(pdfreader.numPages):
text = pdfreader.getPage(page_num).extractText()## extracting text from the PDF
cleaned_text = text.strip().replace('n',' ')## Removes unnecessary spaces and break lines
print(cleaned_text)## Print the text from PDF
#speaker.say(cleaned_text)## Let The Speaker Speak The Text
speaker.save_to_file(cleaned_text,'story.mp3')## Saving Text In a audio file 'story.mp3'
speaker.runAndWait()
speaker.stop()이 스크립트는 노래 폴더에서 재생할 노래를 무작위로 선택합니다. os.startfile은 Windows 시스템만 지원합니다.
import random, os music_dir = 'G:\new english songs' songs = os.listdir(music_dir) song = random.randint(0,len(songs)) print(songs[song])## Prints The Song Name os.startfile(os.path.join(music_dir, songs[0]))
국립기상청 웹사이트에서는 날씨 데이터를 json 형식으로 직접 반환하는 일기예보 획득 API를 제공합니다. 따라서 json에서 해당 필드만 추출하면 됩니다.
다음은 지정 도시(군,구)의 날씨 URL입니다. 해당 URL을 직접 열면 해당 도시의 날씨 데이터가 반환됩니다. 예:
http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/101021200.html 상하이 쉬후이구에 해당하는 날씨 URL입니다.
구체적인 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
mport requests
import json
import logging as log
def get_weather_wind(url):
r = requests.get(url)
if r.status_code != 200:
log.error("Can't get weather data!")
info = json.loads(r.content.decode())
# get wind data
data = info['weatherinfo']
WD = data['WD']
WS = data['WS']
return "{}({})".format(WD, WS)
def get_weather_city(url):
# open url and get return data
r = requests.get(url)
if r.status_code != 200:
log.error("Can't get weather data!")
# convert string to json
info = json.loads(r.content.decode())
# get useful data
data = info['weatherinfo']
city = data['city']
temp1 = data['temp1']
temp2 = data['temp2']
weather = data['weather']
return "{} {} {}~{}".format(city, weather, temp1, temp2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
msg = """**天气提醒**:
{} {}
{} {}
来源: 国家气象局
""".format(
get_weather_city('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/101021200.html'),
get_weather_wind('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/sk/101021200.html'),
get_weather_city('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/cityinfo/101020900.html'),
get_weather_wind('http://www.weather.com.cn/data/sk/101020900.html')
)
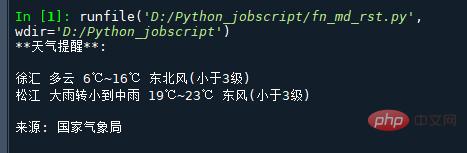
print(msg)실행 결과는 다음과 같습니다.
때로는 큰 URL이 매우 짜증나고 읽기 어려워질 수 있습니다. 공유하면 이 피트는 긴 URL을 짧은 URL로 변환할 수 있습니다.
import contextlib
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from urllib.request import urlopen
import sys
def make_tiny(url):
request_url = ('http://tinyurl.com/api-create.php?' +
urlencode({'url':url}))
with contextlib.closing(urlopen(request_url)) as response:
return response.read().decode('utf-8')
def main():
for tinyurl in map(make_tiny, sys.argv[1:]):
print(tinyurl)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()이 스크립트는 매우 실용적입니다. 예를 들어 공개 계정 기사를 차단하는 콘텐츠 플랫폼이 있는 경우 공개 계정 기사의 링크를 짧은 링크로 변경하고 삽입하여 우회할 수 있습니다.
세상에서 가장 복잡한 것 중 하나는 개발자의 다운로드 폴더입니다. 여기에는 정리되지 않은 파일이 많이 포함되어 있습니다. 이 스크립트는 크기 제한에 따라 제한된 정리로 다운로드 폴더를 정리합니다. 오래된 파일입니다 :
import os
import threading
import time
def get_file_list(file_path):
#文件按最后修改时间排序
dir_list = os.listdir(file_path)
if not dir_list:
return
else:
dir_list = sorted(dir_list, key=lambda x: os.path.getmtime(os.path.join(file_path, x)))
return dir_list
def get_size(file_path):
"""[summary]
Args:
file_path ([type]): [目录]
Returns:
[type]: 返回目录大小,MB
"""
totalsize=0
for filename in os.listdir(file_path):
totalsize=totalsize+os.path.getsize(os.path.join(file_path, filename))
#print(totalsize / 1024 / 1024)
return totalsize / 1024 / 1024
def detect_file_size(file_path, size_Max, size_Del):
"""[summary]
Args:
file_path ([type]): [文件目录]
size_Max ([type]): [文件夹最大大小]
size_Del ([type]): [超过size_Max时要删除的大小]
"""
print(get_size(file_path))
if get_size(file_path) > size_Max:
fileList = get_file_list(file_path)
for i in range(len(fileList)):
if get_size(file_path) > (size_Max - size_Del):
print ("del :%d %s" % (i + 1, fileList[i]))
#os.remove(file_path + fileList[i])위 내용은 즉시 사용할 수 있는 Python 자동화 스크립트 8개!의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!