Cglib는 SpringBoot 2.x AOP에서 기본적으로 사용되지만, Spring5에서는 여전히 jdk 동적 프록시가 기본적으로 사용됩니다. Spring AOP는 기본적으로 JDK 동적 프록시를 사용합니다. 객체가 인터페이스를 구현하지 않으면 CGLIB 프록시가 사용됩니다. 물론 CGLIB 프록시를 강제로 사용하는 것도 가능합니다.
SpringBoot에서 AOP는 AopAutoConfiguration을 통해 자동으로 어셈블됩니다.
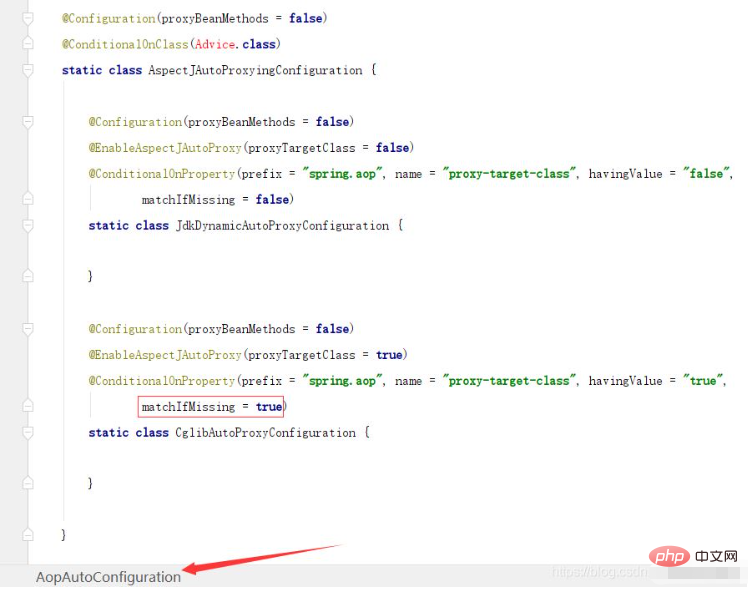
Springboot 1.x AOP는 여전히 기본적으로 JDK 동적 프록시를 사용합니다.
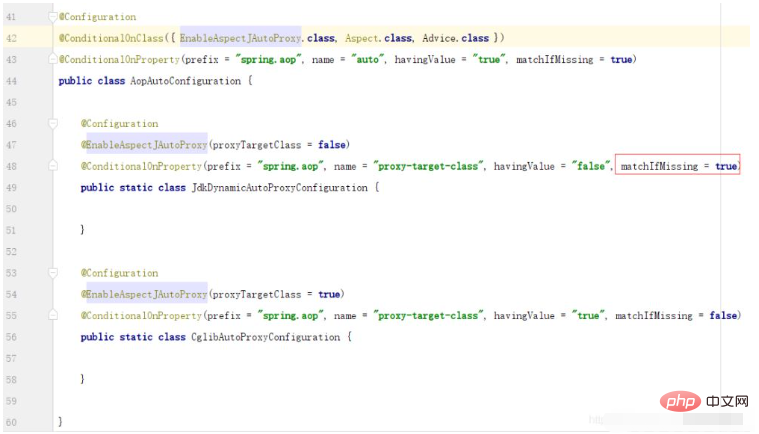
Proxy.newProxyInstance(iCustomerInstance.getClass().getClassLoader(), iCustomerInstance.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
CGLIB에는 이 문제가 없습니다. CGLIB는 서브클래스를 생성하여 구현되기 때문에 프록시 객체가 인터페이스에 할당되거나 구현 클래스에 할당되거나 둘 다 프록시 객체의 상위 클래스입니다.
그래서 버전 2.x 이상에서는 AOP의 기본 구현이 CGLIB 프록시로 변경되었습니다.
새 인터페이스 만들기
public interface ICustomService {
void printf();
}ICustomService의 새 구현 클래스 만들기
@Service
public class CustomServiceImpl implements ICustomService {
public void printf() {
}
}인터페이스를 구현하지 않는 다른 클래스 추가
@Service
public class CustomNoImpl {
public void hello() {
}
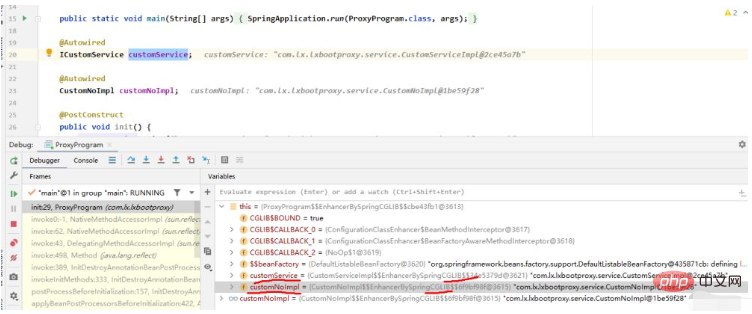
}그런 다음 시작하면 ICustomService 및 CustomNoImpl에서 AOP 에이전트가 CGLIB의 동적 에이전트를 사용하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다
 그런 다음 application.properties 구성을 통해 기본적으로 프록시를 JDK 프록시로 설정합니다.
그런 다음 application.properties 구성을 통해 기본적으로 프록시를 JDK 프록시로 설정합니다.
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false
그런 다음 디버깅을 시작하고 CustomNoImpl이 인터페이스를 구현하지 않기 때문에 CGLIB에서 생성된 프록시를 사용하는 반면
customService에는 인터페이스 구현이 있으므로 JDK
의 동적 프록시를 사용한다는 것을 발견했습니다.
위 내용은 SpringBoot/Spring AOP의 기본 동적 프록시 방법은 무엇입니까?의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!