SpringBoot 소스코드에서 Bean의 생명주기는 어떻게 되나요?
입력 방법은 SpringApplication#run()
1.SpringApplication#run()SpringApplication#run()
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}2.SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}3.SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof SmartFactoryBean<?> smartFactoryBean && smartFactoryBean.isEagerInit()) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
// 此处就是初始化bean的方法
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 此处就是解决循环依赖的代码
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton) {
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
smartInitialize.end();
}
}
}解决循环依赖的代码如下:
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 尝试从缓存中获取成品的目标对象,如果存在,则直接返回
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果缓存中不存在目标对象,则判断当前对象是否已经处于创建过程中,在前面的讲解中,第一次尝试获取A对象
// 的实例之后,就会将A对象标记为正在创建中,因而最后再尝试获取A对象的时候,这里的if判断就会为true
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 这里的singletonFactories是一个Map,其key是bean的名称,而值是一个ObjectFactory类型的
// 对象,这里对于A和B而言,调用图其getObject()方法返回的就是A和B对象的实例,无论是否是半成品
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// 获取目标对象的实例
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}一级缓存,singletonObjects 单例缓存,存储已经实例化的单例bean。
二级缓存,earlySingletonObjects 提前暴露的单例缓存,这里存储的bean是刚刚构造完成,但还会通过属性注入bean。
三级缓存,singletonFactories 生产单例的工厂缓存,存储工厂。
解决原理如下:
在第一层中,先去获取 A 的 Bean,发现没有就准备去创建一个,然后将 A 的代理工厂放入“三级缓存”(这个 A 其实是一个半成品,还没有对里面的属性进行注入),但是 A 依赖 B 的创建,就必须先去创建 B;
在第二层中,准备创建 B,发现 B 又依赖 A,需要先去创建 A,去创建 A,因为第一层已经创建了 A 的代理工厂,直接从“三级缓存”中拿到 A 的代理工厂,获取 A 的代理对象,放入“二级缓存”,并清除“三级缓存”;
有了 A 的代理对象,对 A 的依赖完美解决(这里的 A 仍然是个半成品),B 初始化成功。在 B 初始化成功,完成 A 对象的属性注入,然后再填充 A 的其它属性,以及 A 的其它步骤(包括 AOP),完成对 A 完整的初始化功能(这里的 A 才是完整的 Bean)。
将 A 放入“一级缓存”。
4.SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>AbstractBeanFactory#getBean() => AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean()=>AbstractBeanFactory#createBean()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class // which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition. Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// 1.调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor# postProcessBeforeInstantiation
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
// 跟进doCreateBean()
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry. throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}SpringApplication#run()=> = >SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 2.创建bean实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.markAsPostProcessed();
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 跟进populateBean()
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 跟进initializeBean()
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException bce && beanName.equals(bce.getBeanName())) {
throw bce;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}SpringApplication#run()=> ) =>SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory #preInstantiateSingletons() < /code><p><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
if (bw.getWrappedClass().isRecord()) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to a record");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for records since they are immutable.
return;
}
}
// 3.调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor# postProcessAfterInstantiation
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
if (hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 4.注入属性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div><br/>순환 종속성을 해결하는 코드는 다음과 같습니다.</p><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 5.设置Aware接口的属性
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 5.调用BeanPostProcessor的初始化前置方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 6.调用init-method方法,进行初始化操作
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 7. 调用BeanPostProcessor的初始化后置方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">로그인 후 복사</div></div><ul class=" list-paddingleft-2">
<li><p>첫 번째 수준 캐시인 SingletonObjects 싱글턴 캐시는 인스턴스화된 싱글턴을 저장합니다. 콩. </p></li>
<li><p>레벨 2 캐시, earlySingletonObjects 싱글턴 캐시가 미리 노출되어 있습니다. 여기에 저장된 Bean은 방금 생성되었지만 속성을 통해 Bean도 주입됩니다. <br></p></li>
<li>레벨 3 캐시, 싱글톤 생산을 위한 SingletonFactories 팩토리 캐시, 스토리지 팩토리. <p></p>
</li>
</ul>해결 원리는 다음과 같습니다. <p></p>
<ul class=" list-paddingleft-2">
<li>첫 번째 레이어에서 먼저 A의 Bean을 얻고, 찾으면 사용할 수 없는 경우 하나를 만들 준비를 한 다음 A의 프록시 팩토리를 "3단계 캐시"에 넣습니다(이 A는 실제로 반제품이고 내부 속성은 아직 주입되지 않았습니다). B의 생성에 따라 B를 먼저 생성해야 합니다. <p> li></p>
</li>
<li>두 번째 레이어에서 B를 생성할 준비를 하고 B가 A에 종속된다는 것을 알아냅니다. 레이어는 이미 "3단계 캐시"에서 직접 A의 프록시 팩토리를 생성했습니다. "A의 프록시 팩토리를 가져오고 A의 프록시 객체를 가져와서 이를 "2단계 캐시"에 넣은 다음 "3단계 캐시"를 지웁니다. <p> </p>
</li>
<li>A의 프록시 객체를 사용하면 A의 종속성이 완벽하게 해결되고(여기서 A는 아직 반제품임) B는 성공적으로 초기화됩니다. B가 성공적으로 초기화된 후 A 객체의 속성 주입이 완료되고 A의 다른 속성과 A의 다른 단계(AOP 포함)가 채워져 A의 완전한 초기화 기능이 완료됩니다(여기서 A는 다음과 같습니다). 완전한 빈). <p></p>
</li>
<li>A를 "레벨 1 캐시"에 넣으세요. <p></p>
</li>
</ul>4.<code>SpringApplication#run()=> SpringApplication#refreshContext(context)=> SpringApplication#refresh(context)=>ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext #refresh()=>AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization()=>ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons()=>AbstractBeanFactory#getBean() => AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean()= > BeanFactory#createBean ()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()=>AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean()🎜🎜Bean 수명 주기: 🎜🎜1. InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor# postProcessBeforeInstantiation🎜doCreateBean()🎜rrreee를 호출하세요. 🎜2. 빈 예시 생성 🎜🎜populateBean()을 따르세요🎜initializationBean()을 따르세요🎜rrreee🎜3. InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor# postProcessAfterInstantiation🎜🎜4. Aware 인터페이스의 속성을 설정하세요🎜🎜6. BeanPostProcessor 메소드 🎜🎜7. 먼저 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(), 그런 다음 초기화 작업을 수행하기 위해 init-method 메소드를 호출합니다. 🎜🎜8 BeanPostProcessor의 초기화 메소드를 호출합니다.위 내용은 SpringBoot 소스코드에서 Bean의 생명주기는 어떻게 되나요?의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7467
7467
 15
15
 1376
1376
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 45
45
 19
19
 18
18
 19
19
 Springboot가 Jasypt를 통합하여 구성 파일 암호화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Springboot가 Jasypt를 통합하여 구성 파일 암호화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Jasypt 소개 Jasypt는 개발자가 최소한의 노력으로 프로젝트에 기본 암호화 기능을 추가할 수 있게 해주며 암호화 작동 방식에 대한 깊은 이해가 필요하지 않은 단방향 및 양방향 암호화에 대한 높은 보안을 제공합니다. 표준 기반 암호화 기술. 비밀번호, 텍스트, 숫자, 바이너리 암호화... Spring 기반 애플리케이션, 개방형 API와의 통합에 적합하며 모든 JCE 공급자와 함께 사용할 수 있습니다... 다음 종속성을 추가합니다: com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2. Jasypt의 이점은 코드가 유출되더라도 데이터 소스를 보장할 수 있어 시스템 보안을 보호합니다.
 SpringBoot가 Redisson을 통합하여 지연 대기열을 구현하는 방법
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
SpringBoot가 Redisson을 통합하여 지연 대기열을 구현하는 방법
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
사용 시나리오 1. 주문이 성공적으로 이루어졌으나 30분 이내에 결제가 이루어지지 않았습니다. 결제 시간이 초과되어 주문이 자동으로 취소되었습니다. 2. 주문이 서명되었으며 서명 후 7일 동안 평가가 수행되지 않았습니다. 주문 시간이 초과되어 평가되지 않으면 시스템은 기본적으로 긍정적 평가로 설정됩니다. 3. 판매자가 5분 동안 주문을 받지 않으면 주문이 취소됩니다. 문자 메시지 알림이 전송됩니다... 지연이 길고 실시간 성능이 낮은 시나리오의 경우 작업 예약을 사용하여 정기적인 폴링 처리를 수행할 수 있습니다. 예: xxl-job 오늘은 다음을 선택하겠습니다.
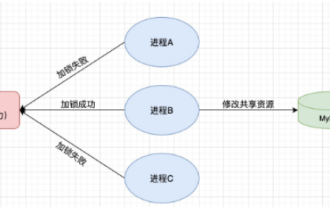 Redis를 사용하여 SpringBoot에서 분산 잠금을 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
Redis를 사용하여 SpringBoot에서 분산 잠금을 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
1. Redis는 분산 잠금 원칙과 분산 잠금이 필요한 이유를 구현합니다. 분산 잠금에 대해 이야기하기 전에 분산 잠금이 필요한 이유를 설명해야 합니다. 분산 잠금의 반대는 독립형 잠금입니다. 다중 스레드 프로그램을 작성할 때 공유 변수를 동시에 작동하여 발생하는 데이터 문제를 방지하기 위해 일반적으로 잠금을 사용하여 공유 변수를 상호 제외합니다. 공유 변수의 사용 범위는 동일한 프로세스에 있습니다. 동시에 공유 리소스를 운영해야 하는 여러 프로세스가 있는 경우 어떻게 상호 배타적일 수 있습니까? 오늘날의 비즈니스 애플리케이션은 일반적으로 마이크로서비스 아키텍처입니다. 이는 하나의 애플리케이션이 여러 프로세스를 배포한다는 의미이기도 합니다. 여러 프로세스가 MySQL에서 동일한 레코드 행을 수정해야 하는 경우 잘못된 작업으로 인해 발생하는 더티 데이터를 방지하려면 배포가 필요합니다. 현재 소개할 스타일은 잠겨 있습니다. 포인트를 얻고 싶다
 springboot가 파일을 jar 패키지로 읽은 후 파일에 액세스할 수 없는 문제를 해결하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot가 파일을 jar 패키지로 읽은 후 파일에 액세스할 수 없는 문제를 해결하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot가 파일을 읽지만 jar 패키지로 패키징한 후 최신 개발에 액세스할 수 없습니다. springboot가 파일을 jar 패키지로 패키징한 후 파일을 읽을 수 없는 상황이 발생합니다. 그 이유는 패키징 후 파일의 가상 경로 때문입니다. 유효하지 않으며 읽기를 통해서만 액세스할 수 있습니다. 파일은 리소스 publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input 아래에 있습니다.
 SpringBoot와 SpringMVC의 비교 및 차이점 분석
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot와 SpringMVC의 비교 및 차이점 분석
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot와 SpringMVC는 모두 Java 개발에서 일반적으로 사용되는 프레임워크이지만 둘 사이에는 몇 가지 분명한 차이점이 있습니다. 이 기사에서는 이 두 프레임워크의 기능과 용도를 살펴보고 차이점을 비교할 것입니다. 먼저 SpringBoot에 대해 알아봅시다. SpringBoot는 Spring 프레임워크를 기반으로 하는 애플리케이션의 생성 및 배포를 단순화하기 위해 Pivotal 팀에서 개발되었습니다. 독립 실행형 실행 파일을 구축하는 빠르고 가벼운 방법을 제공합니다.
 여러 테이블을 추가하기 위해 SQL 문을 사용하지 않고 Springboot+Mybatis-plus를 구현하는 방법
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
여러 테이블을 추가하기 위해 SQL 문을 사용하지 않고 Springboot+Mybatis-plus를 구현하는 방법
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Springboot+Mybatis-plus가 다중 테이블 추가 작업을 수행하기 위해 SQL 문을 사용하지 않을 때 내가 직면한 문제는 테스트 환경에서 생각을 시뮬레이션하여 분해됩니다. 매개 변수가 있는 BrandDTO 개체를 생성하여 배경으로 매개 변수 전달을 시뮬레이션합니다. Mybatis-plus에서 다중 테이블 작업을 수행하는 것은 매우 어렵다는 것을 Mybatis-plus-join과 같은 도구를 사용하지 않으면 해당 Mapper.xml 파일을 구성하고 냄새나고 긴 ResultMap만 구성하면 됩니다. 해당 SQL 문을 작성합니다. 이 방법은 번거로워 보이지만 매우 유연하며 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다.
 SpringBoot가 Redis를 사용자 정의하여 캐시 직렬화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
SpringBoot가 Redis를 사용자 정의하여 캐시 직렬화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. RedisAPI 기본 직렬화 메커니즘인 RedisTemplate1.1을 사용자 정의합니다. API 기반 Redis 캐시 구현은 데이터 캐싱 작업에 RedisTemplate 템플릿을 사용합니다. 여기서 RedisTemplate 클래스를 열고 클래스의 소스 코드 정보를 봅니다. 키 선언, 값의 다양한 직렬화 방법, 초기 값은 비어 있음 @NullableprivateRedisSe
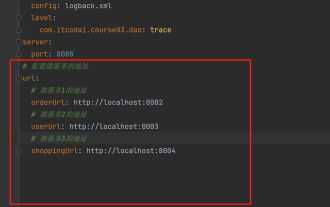 springboot에서 application.yml의 값을 얻는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
springboot에서 application.yml의 값을 얻는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
프로젝트에서는 일부 구성 정보가 필요한 경우가 많습니다. 이 정보는 테스트 환경과 프로덕션 환경에서 구성이 다를 수 있으며 실제 비즈니스 상황에 따라 나중에 수정해야 할 수도 있습니다. 이러한 구성은 코드에 하드 코딩할 수 없습니다. 예를 들어 이 정보를 application.yml 파일에 작성할 수 있습니다. 그렇다면 코드에서 이 주소를 어떻게 얻거나 사용합니까? 2가지 방법이 있습니다. 방법 1: @Value 주석이 달린 ${key}를 통해 구성 파일(application.yml)의 키에 해당하는 값을 가져올 수 있습니다. 이 방법은 마이크로서비스가 상대적으로 적은 상황에 적합합니다. 프로젝트, 업무가 복잡할 때는 논리




