Python+Pygame을 사용하여 4개 체스 게임을 구현하는 방법
1. 게임 설명
"Zou Si Er"은 주로 산둥성 지난, 요청, 허쩌 및 기타 지역에서 활동하며 특히 어린이들이 시도하기에 적합합니다.
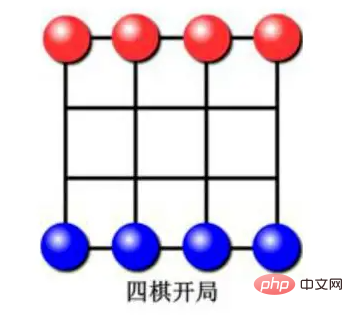
4×4 체스판에서는 각 변에 4개의 말이 있고, 체스판의 상단 두 줄의 네 위치에 배치됩니다. 아래 사진
은 "Go Four" 게임의 초기 모습입니다.
2. 게임 규칙
"Go Four"의 게임 규칙은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 양측이 교대로 이동하며, 각 단계는 상하좌우 중 한 방향으로 한 칸만 이동할 수 있으며 대각선으로는 이동할 수 없습니다. 한 쪽이 움직일 수 없으면 다른 쪽이 이동합니다.
2. A파티의 피스 중 하나가 한 줄로 이동하면 이 라인에는 A파티의 피스 2개와 B의 피스 중 1개만 있고 A파티의 피스 2개가 연결되고, A의 피스 2개 중 1개의 피스가 연결됩니다. 조각이 연결되면 파티 B의 조각이 먹히게 됩니다.
아래 사진은 먹을 수 있는 스타일의 예시입니다:
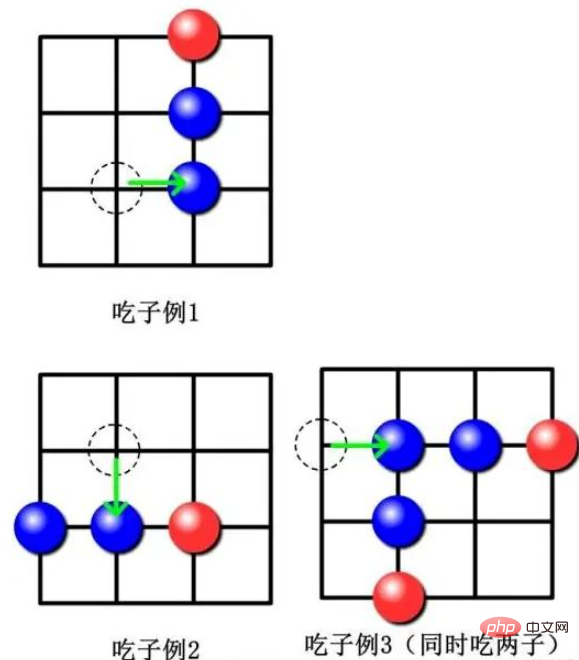
3. 2개 미만의 조각이 있는 쪽이 패자입니다. 어느 쪽도 다른 쪽을 이길 수 없으면 무승부로 간주될 수 있습니다.
3. 환경 설치
1) 재료(사진)
2) 실행 환경 에디터에서 사용하는 환경 : Python3, Pycharm Community Edition, Pygame, numpy 모듈 부분이 포함되어 있으므로 보여주지 않겠습니다. 그것들을 하나씩.
모듈 설치: pip install -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple/+모듈 이름
4. 코드 표시
import pygame as pg
from pygame.locals import *
import sys
import time
import numpy as np
pg.init()
size = width, height = 600, 400
screen = pg.display.set_mode(size)
f_clock = pg.time.Clock()
fps = 30
pg.display.set_caption("走四棋儿")
background = pg.image.load("background.png").convert_alpha()
glb_pos = [[(90, 40), (190, 40), (290, 40), (390, 40)],
[(90, 140), (190, 140), (290, 140), (390, 140)],
[(90, 240), (190, 240), (290, 240), (390, 240)],
[(90, 340), (190, 340), (290, 340), (390, 340)]]
class ChessPieces():
def __init__(self, img_name):
self.name = img_name
self.id = None
if self.name == 'heart':
self.id = 2
elif self.name == 'spade':
self.id = 3
self.img = pg.image.load(img_name + ".png").convert_alpha()
self.rect = self.img.get_rect()
self.pos_x, self.pos_y = 0, 0
self.alive_state = True
def get_rect(self):
return (self.rect[0], self.rect[1])
def get_pos(self):
return (self.pos_x, self.pos_y)
def update(self):
if self.alive_state == True:
self.rect[0] = glb_pos[self.pos_y][self.pos_x][0]
self.rect[1] = glb_pos[self.pos_y][self.pos_x][1]
screen.blit(self.img, self.rect)
class Pointer():
def __init__(self):
self.img = pg.image.load("pointer.png").convert_alpha()
self.rect = self.img.get_rect()
self.show = False
self.selecting_item = False
def point_to(self, Heart_Blade_class):
if Heart_Blade_class.alive_state:
self.pointing_to_item = Heart_Blade_class
self.item_pos = Heart_Blade_class.get_rect()
self.rect[0], self.rect[1] = self.item_pos[0], self.item_pos[1] - 24
def update(self):
screen.blit(self.img, self.rect)
class GlobalSituation():
def __init__(self):
self.glb_situation = np.array([[2, 2, 2, 2],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[3, 3, 3, 3]], dtype=np.uint8)
self.spade_turn = None
def refresh_situation(self):
self.glb_situation = np.zeros([4, 4], np.uint8)
for i in range(4):
if heart[i].alive_state:
self.glb_situation[heart[i].pos_y, heart[i].pos_x] = heart[i].id
for i in range(4):
if spade[i].alive_state:
self.glb_situation[spade[i].pos_y, spade[i].pos_x] = spade[i].id
for i in range(4):
print(self.glb_situation[i][:])
print('=' * 12)
if self.spade_turn != None:
self.spade_turn = not self.spade_turn
def check_situation(self, moved_item):
curr_pos_x, curr_pos_y = moved_item.get_pos()
curr_pos_col = self.glb_situation[:, curr_pos_x]
curr_pos_raw = self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, :]
enemy_die = False
if moved_item.id == 2:
if np.sum(curr_pos_col) == 7:
if (curr_pos_col == np.array([0, 2, 2, 3])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[3, curr_pos_x] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and spade_i.pos_y == 3:
spade_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_col == np.array([2, 2, 3, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[2, curr_pos_x] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and spade_i.pos_y == 2:
spade_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_col == np.array([0, 3, 2, 2])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[1, curr_pos_x] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and spade_i.pos_y == 1:
spade_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_col == np.array([3, 2, 2, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[0, curr_pos_x] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and spade_i.pos_y == 0:
spade_i.alive_state = False
if np.sum(curr_pos_raw) == 7:
if (curr_pos_raw == np.array([0, 2, 2, 3])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 3] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == 3 and spade_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
spade_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_raw == np.array([2, 2, 3, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 2] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == 2 and spade_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
spade_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_raw == np.array([0, 3, 2, 2])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 1] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == 1 and spade_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
spade_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_raw == np.array([3, 2, 2, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 0] = 0
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.pos_x == 0 and spade_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
spade_i.alive_state = False
elif moved_item.id == 3:
if np.sum(curr_pos_col) == 8:
if (curr_pos_col == np.array([0, 3, 3, 2])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[3, curr_pos_x] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and heart_i.pos_y == 3:
heart_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_col == np.array([3, 3, 2, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[2, curr_pos_x] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and heart_i.pos_y == 2:
heart_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_col == np.array([0, 2, 3, 3])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[1, curr_pos_x] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and heart_i.pos_y == 1:
heart_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_col == np.array([2, 3, 3, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[0, curr_pos_x] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == curr_pos_x and heart_i.pos_y == 0:
heart_i.alive_state = False
if np.sum(curr_pos_raw) == 8:
if (curr_pos_raw == np.array([0, 3, 3, 2])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 3] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == 3 and heart_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
heart_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_raw == np.array([3, 3, 2, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 2] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == 2 and heart_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
heart_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_raw == np.array([0, 2, 3, 3])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 1] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == 1 and heart_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
heart_i.alive_state = False
elif (curr_pos_raw == np.array([2, 3, 3, 0])).all():
enemy_die = True
self.glb_situation[curr_pos_y, 0] = 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.pos_x == 0 and heart_i.pos_y == curr_pos_y:
heart_i.alive_state = False
if enemy_die == True:
self.glb_situation = np.zeros([4, 4], np.uint8)
for i in range(4):
if heart[i].alive_state:
self.glb_situation[heart[i].pos_y, heart[i].pos_x] = heart[i].id
for i in range(4):
if spade[i].alive_state:
self.glb_situation[spade[i].pos_y, spade[i].pos_x] = spade[i].id
for i in range(4):
print(self.glb_situation[i][:])
print('=' * 12)
def check_game_over(self):
heart_alive_num, spade_alive_num = 0, 0
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state:
heart_alive_num += 1
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state:
spade_alive_num += 1
if heart_alive_num <= 1:
print('Spades win!')
GlobalSituation.__init__(self)
Pointer.__init__(self)
chess_pieces_init()
if spade_alive_num <= 1:
print('Hearts win!')
GlobalSituation.__init__(self)
Pointer.__init__(self)
chess_pieces_init()
heart, spade = [None] * 4, [None] * 4
for i in range(4):
heart[i] = ChessPieces('heart')
spade[i] = ChessPieces('spade')
def chess_pieces_init():
for i in range(4):
heart[i].pos_y, heart[i].pos_x = 0, i
spade[i].pos_y, spade[i].pos_x = 3, i
heart[i].alive_state = True
spade[i].alive_state = True
chess_pieces_init()
pointer = Pointer()
situation = GlobalSituation()
def check_click_item(c_x, c_y):
selected_item = None
if situation.spade_turn==None:
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.rect.collidepoint(c_x, c_y):
situation.spade_turn = False
selected_item = heart_i
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.rect.collidepoint(c_x, c_y):
situation.spade_turn = True
selected_item = spade_i
else:
if situation.spade_turn:
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.alive_state and spade_i.rect.collidepoint(c_x, c_y):
selected_item = spade_i
else:
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.alive_state and heart_i.rect.collidepoint(c_x, c_y):
selected_item = heart_i
return selected_item
def move_to_dst_pos(selected_item, c_x, c_y):
update_situation = False
enemy_exist = False
if selected_item.name == 'heart':
for spade_i in spade:
if spade_i.rect.collidepoint(c_x, c_y) and spade_i.alive_state:
enemy_exist = True
elif selected_item.name == 'spade':
for heart_i in heart:
if heart_i.rect.collidepoint(c_x, c_y) and heart_i.alive_state:
enemy_exist = True
if enemy_exist == False:
delta_y, delta_x = c_y - selected_item.rect[1], c_x - selected_item.rect[0]
if 80 <= abs(delta_x) <= 120 and abs(delta_y) <= 20:
if delta_x < 0:
if selected_item.pos_x > 0:
selected_item.pos_x -= 1
else:
if selected_item.pos_x < 3:
selected_item.pos_x += 1
update_situation = True
if 80 <= abs(delta_y) <= 120 and abs(delta_x) <= 20:
if delta_y < 0:
if selected_item.pos_y > 0:
selected_item.pos_y -= 1
else:
if selected_item.pos_y < 3:
selected_item.pos_y += 1
update_situation = True
return update_situation
while True:
for event in pg.event.get():
if event.type == pg.QUIT:
sys.exit()
elif event.type == pg.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
cursor_x, cursor_y = pg.mouse.get_pos()
clicked_item = check_click_item(cursor_x, cursor_y)
if clicked_item != None:
pointer.selecting_item = True
pointer.point_to(clicked_item)
else:
if pointer.selecting_item:
update_situation_flag = move_to_dst_pos(pointer.pointing_to_item, cursor_x, cursor_y)
if update_situation_flag:
situation.refresh_situation()
situation.check_situation(pointer.pointing_to_item)
situation.check_game_over()
pointer.selecting_item = False
screen.blit(background, (0, 0))
for heart_i in heart:
heart_i.update()
for spade_i in spade:
spade_i.update()
if pointer.selecting_item:
pointer.update()
f_clock.tick(fps)
pg.display.update()5. 효과 표시
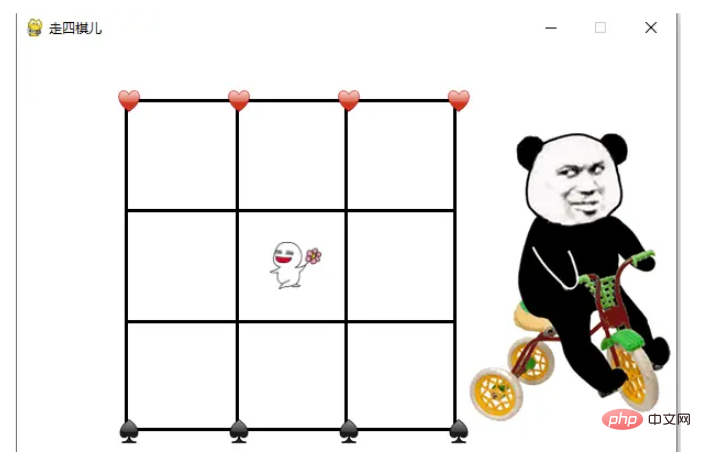
위 내용은 Python+Pygame을 사용하여 4개 체스 게임을 구현하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7433
7433
 15
15
 1359
1359
 52
52
 76
76
 11
11
 29
29
 19
19
 C 언어 합계의 기능은 무엇입니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
C 언어 합계의 기능은 무엇입니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
C 언어에는 내장 합계 기능이 없으므로 직접 작성해야합니다. 합계는 배열 및 축적 요소를 가로 질러 달성 할 수 있습니다. 루프 버전 : 루프 및 배열 길이를 사용하여 계산됩니다. 포인터 버전 : 포인터를 사용하여 배열 요소를 가리키며 효율적인 합계는 자체 증가 포인터를 통해 달성됩니다. 동적으로 배열 버전을 할당 : 배열을 동적으로 할당하고 메모리를 직접 관리하여 메모리 누출을 방지하기 위해 할당 된 메모리가 해제되도록합니다.
 별개의 구별이 관련되어 있습니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
별개의 구별이 관련되어 있습니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
구별되고 구별되는 것은 구별과 관련이 있지만, 다르게 사용됩니다. 뚜렷한 (형용사)는 사물 자체의 독창성을 묘사하고 사물 사이의 차이를 강조하는 데 사용됩니다. 뚜렷한 (동사)는 구별 행동이나 능력을 나타내며 차별 과정을 설명하는 데 사용됩니다. 프로그래밍에서 구별은 종종 중복 제거 작업과 같은 컬렉션에서 요소의 독창성을 나타내는 데 사용됩니다. 홀수 및 짝수 숫자를 구별하는 것과 같은 알고리즘이나 함수의 설계에 별개가 반영됩니다. 최적화 할 때 별도의 작업은 적절한 알고리즘 및 데이터 구조를 선택해야하며, 고유 한 작업은 논리 효율성의 구별을 최적화하고 명확하고 읽을 수있는 코드 작성에주의를 기울여야합니다.
 누가 더 많은 파이썬이나 자바 스크립트를 지불합니까?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
누가 더 많은 파이썬이나 자바 스크립트를 지불합니까?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
기술 및 산업 요구에 따라 Python 및 JavaScript 개발자에 대한 절대 급여는 없습니다. 1. 파이썬은 데이터 과학 및 기계 학습에서 더 많은 비용을 지불 할 수 있습니다. 2. JavaScript는 프론트 엔드 및 풀 스택 개발에 큰 수요가 있으며 급여도 상당합니다. 3. 영향 요인에는 경험, 지리적 위치, 회사 규모 및 특정 기술이 포함됩니다.
 이해하는 방법! x는?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
이해하는 방법! x는?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
! x 이해! x는 C 언어로 된 논리적 비 운영자입니다. 그것은 x의 값, 즉 실제 변경, 거짓, 잘못된 변경 사항을 부수합니다. 그러나 C의 진실과 거짓은 부울 유형보다는 숫자 값으로 표시되며, 0이 아닌 것은 참으로 간주되며 0만이 거짓으로 간주됩니다. 따라서! x는 음수를 양수와 동일하게 처리하며 사실로 간주됩니다.
 H5 페이지 생산에는 지속적인 유지 보수가 필요합니까?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
H5 페이지 생산에는 지속적인 유지 보수가 필요합니까?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
코드 취약점, 브라우저 호환성, 성능 최적화, 보안 업데이트 및 사용자 경험 개선과 같은 요소로 인해 H5 페이지를 지속적으로 유지해야합니다. 효과적인 유지 관리 방법에는 완전한 테스트 시스템 설정, 버전 제어 도구 사용, 페이지 성능을 정기적으로 모니터링하고 사용자 피드백 수집 및 유지 관리 계획을 수립하는 것이 포함됩니다.
 C 언어에서 합계는 무엇을 의미합니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
C 언어에서 합계는 무엇을 의미합니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
합에 대한 C에는 내장 합계 기능이 없지만 다음과 같이 구현할 수 있습니다. 루프를 사용하여 요소를 하나씩 축적합니다. 포인터를 사용하여 요소를 하나씩 액세스하고 축적합니다. 큰 데이터 볼륨의 경우 병렬 계산을 고려하십시오.
 사랑 코드 복사 및 붙여 넣기 복사하여 사랑 코드를 무료로 붙여 넣으십시오.
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:48 AM
사랑 코드 복사 및 붙여 넣기 복사하여 사랑 코드를 무료로 붙여 넣으십시오.
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:48 AM
코드 복사 및 붙여 넣기는 불가능하지는 않지만주의해서 처리해야합니다. 코드의 환경, 라이브러리, 버전 등과 같은 종속성은 현재 프로젝트와 일치하지 않으므로 오류 또는 예측할 수없는 결과를 초래할 수 있습니다. 파일 경로, 종속 라이브러리 및 Python 버전을 포함하여 컨텍스트가 일관되게 유지하십시오. 또한 특정 라이브러리의 코드를 복사 및 붙여 넣을 때 라이브러리 및 해당 종속성을 설치해야 할 수도 있습니다. 일반적인 오류에는 경로 오류, 버전 충돌 및 일관되지 않은 코드 스타일이 포함됩니다. 성능 최적화는 코드의 원래 목적 및 제약에 따라 재 설계 또는 리팩토링되어야합니다. 복사 코드를 이해하고 디버그하고 맹목적으로 복사하여 붙여 넣지 않는 것이 중요합니다.
 C 언어에서 합계의 의미는 무엇입니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
C 언어에서 합계의 의미는 무엇입니까?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
C 언어로 배열 요소를 합산하는 방법 : 루프를 사용하여 배열 요소를 하나씩 축적하십시오. 다차원 배열의 경우 중첩 루프를 사용하여 가로 지르고 축적됩니다. 배열 지수를주의 깊게 확인하여 실행되지 않은 액세스를 피하면 프로그램 충돌이 발생합니다.




