Python에서 np.random.permutation 함수를 사용하는 방법
1: 함수 소개
데이터 세트를 처리할 때 일반적으로 이 기능을 사용하여 데이터 내부를 뒤섞을 수 있습니다. 순서를 설정하고 동일한 순서로 라벨 순서를 섞습니다. 둘: 예2.1 배열 또는 목록 번호를 직접 처리np.random.permutation() 일반적으로 입력 데이터를 무작위로 배열하는 임의 순열 함수입니다. 공식 문서에서는 이 함수를 사용할 수 있는 경우에만 사용할 수 있다고 명시하고 있습니다. 1차원 데이터는 무작위로 배열됩니다. 다차원 데이터의 경우 첫 번째 차원의 데이터만 무작위로 배열될 수 있습니다.
간단히 말하면 np.random.permutation 함수의 기능은 주어진 목록에 따라 뒤섞인 무작위 목록을 생성하는 것입니다.
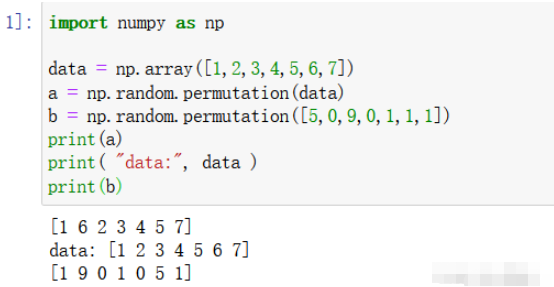
import numpy as np
data = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
a = np.random.permutation(data)
b = np.random.permutation([5,0,9,0,1,1,1])
print(a)
print( "data:", data )
print(b)
로그인 후 복사
import numpy as np data = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7]) a = np.random.permutation(data) b = np.random.permutation([5,0,9,0,1,1,1]) print(a) print( "data:", data ) print(b)
label = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
a = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(label)))
print("Label[a] :" ,label[a] )로그인 후 복사
label = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
a = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(label)))
print("Label[a] :" ,label[a] )
보충: 일반적으로 다음과 같이만 가능합니다. N 차원 배열에 사용되는 것은 정수 스칼라 배열을 스칼라 인덱스로만 변환할 수 있습니다
왜?label1[a1] label1은 목록이고, a1은 목록 첨자의 무작위 순열이지만! 목록 구조에 스칼라 인덱스 label1[a1] 오류
label1=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
print(len(label1))
a1 = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(label1)))#有结果
print(a1)
print("Label1[a1] :" ,label1[a1] )#这列表结构没有标量索引 所以会报错
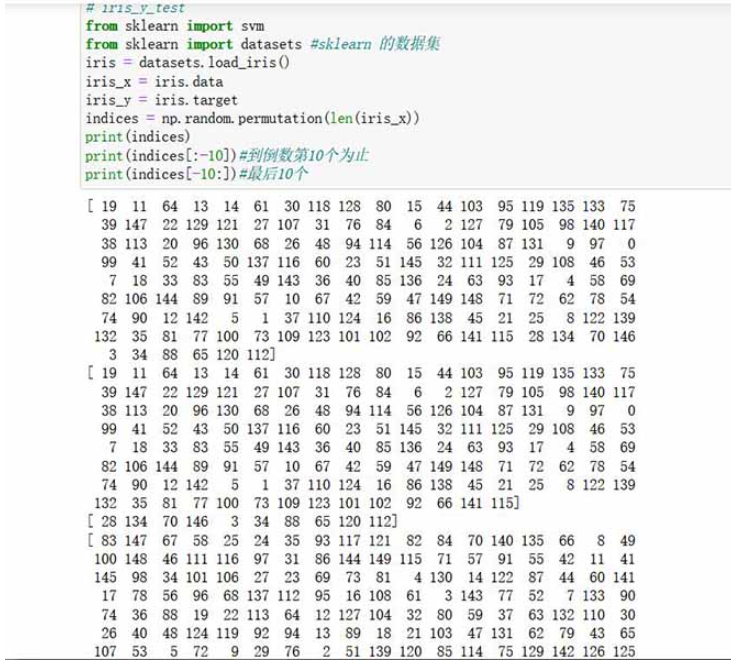
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets #sklearn 的数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris_x = iris.data
iris_y = iris.target
indices = np.random.permutation(len(iris_x))
#此时 打乱的是数组的下标的排序
print(indices)
print(indices[:-10])#到倒数第10个为止
print(indices[-10:])#最后10个
# print(type(iris_x)) <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
#9:1分类
#iris_x_train = iris_x[indices[:-10]]#使用的数组打乱后的下标
#iris_y_train = iris_y[indices[:-10]]
#iris_x_test= iris_x[indices[-10:]]
#iris_y_test= iris_y[indices[-10:]]
로그인 후 복사
배열 첨자 재배포, 즉 스칼라 인덱스: 다음 마크는 0
from sklearn import svm from sklearn import datasets #sklearn 的数据集 iris = datasets.load_iris() iris_x = iris.data iris_y = iris.target indices = np.random.permutation(len(iris_x)) #此时 打乱的是数组的下标的排序 print(indices) print(indices[:-10])#到倒数第10个为止 print(indices[-10:])#最后10个 # print(type(iris_x)) <class 'numpy.ndarray'> #9:1分类 #iris_x_train = iris_x[indices[:-10]]#使用的数组打乱后的下标 #iris_y_train = iris_y[indices[:-10]] #iris_x_test= iris_x[indices[-10:]] #iris_y_test= iris_y[indices[-10:]]
 부터 시작합니다.
부터 시작합니다.
위 내용은 Python에서 np.random.permutation 함수를 사용하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7664
7664
 15
15
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1205
1205
 24
24
 91
91
 11
11
 73
73
 19
19
 PHP와 Python : 다른 패러다임이 설명되었습니다
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP와 Python : 다른 패러다임이 설명되었습니다
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP는 주로 절차 적 프로그래밍이지만 객체 지향 프로그래밍 (OOP)도 지원합니다. Python은 OOP, 기능 및 절차 프로그래밍을 포함한 다양한 패러다임을 지원합니다. PHP는 웹 개발에 적합하며 Python은 데이터 분석 및 기계 학습과 같은 다양한 응용 프로그램에 적합합니다.
 PHP와 Python 중에서 선택 : 가이드
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP와 Python 중에서 선택 : 가이드
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP는 웹 개발 및 빠른 프로토 타이핑에 적합하며 Python은 데이터 과학 및 기계 학습에 적합합니다. 1.PHP는 간단한 구문과 함께 동적 웹 개발에 사용되며 빠른 개발에 적합합니다. 2. Python은 간결한 구문을 가지고 있으며 여러 분야에 적합하며 강력한 라이브러리 생태계가 있습니다.
 Python에서 비주얼 스튜디오 코드를 사용할 수 있습니다
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Python에서 비주얼 스튜디오 코드를 사용할 수 있습니다
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS 코드는 파이썬을 작성하는 데 사용될 수 있으며 파이썬 애플리케이션을 개발하기에 이상적인 도구가되는 많은 기능을 제공합니다. 사용자는 다음을 수행 할 수 있습니다. Python 확장 기능을 설치하여 코드 완료, 구문 강조 및 디버깅과 같은 기능을 얻습니다. 디버거를 사용하여 코드를 단계별로 추적하고 오류를 찾아 수정하십시오. 버전 제어를 위해 git을 통합합니다. 코드 서식 도구를 사용하여 코드 일관성을 유지하십시오. 라인 도구를 사용하여 잠재적 인 문제를 미리 발견하십시오.
 Windows 8에서 코드를 실행할 수 있습니다
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Windows 8에서 코드를 실행할 수 있습니다
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS 코드는 Windows 8에서 실행될 수 있지만 경험은 크지 않을 수 있습니다. 먼저 시스템이 최신 패치로 업데이트되었는지 확인한 다음 시스템 아키텍처와 일치하는 VS 코드 설치 패키지를 다운로드하여 프롬프트대로 설치하십시오. 설치 후 일부 확장은 Windows 8과 호환되지 않을 수 있으며 대체 확장을 찾거나 가상 시스템에서 새로운 Windows 시스템을 사용해야합니다. 필요한 연장을 설치하여 제대로 작동하는지 확인하십시오. Windows 8에서는 VS 코드가 가능하지만 더 나은 개발 경험과 보안을 위해 새로운 Windows 시스템으로 업그레이드하는 것이 좋습니다.
 VScode 확장자가 악의적입니까?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VScode 확장자가 악의적입니까?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS 코드 확장은 악의적 인 코드 숨기기, 취약성 악용 및 합법적 인 확장으로 자위하는 등 악성 위험을 초래합니다. 악의적 인 확장을 식별하는 방법에는 게시자 확인, 주석 읽기, 코드 확인 및주의해서 설치가 포함됩니다. 보안 조치에는 보안 인식, 좋은 습관, 정기적 인 업데이트 및 바이러스 백신 소프트웨어도 포함됩니다.
 Python vs. JavaScript : 학습 곡선 및 사용 편의성
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript : 학습 곡선 및 사용 편의성
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python은 부드러운 학습 곡선과 간결한 구문으로 초보자에게 더 적합합니다. JavaScript는 가파른 학습 곡선과 유연한 구문으로 프론트 엔드 개발에 적합합니다. 1. Python Syntax는 직관적이며 데이터 과학 및 백엔드 개발에 적합합니다. 2. JavaScript는 유연하며 프론트 엔드 및 서버 측 프로그래밍에서 널리 사용됩니다.
 PHP와 Python : 그들의 역사에 깊은 다이빙
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP와 Python : 그들의 역사에 깊은 다이빙
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP는 1994 년에 시작되었으며 Rasmuslerdorf에 의해 개발되었습니다. 원래 웹 사이트 방문자를 추적하는 데 사용되었으며 점차 서버 측 스크립팅 언어로 진화했으며 웹 개발에 널리 사용되었습니다. Python은 1980 년대 후반 Guidovan Rossum에 의해 개발되었으며 1991 년에 처음 출시되었습니다. 코드 가독성과 단순성을 강조하며 과학 컴퓨팅, 데이터 분석 및 기타 분야에 적합합니다.
 터미널 VSCODE에서 프로그램을 실행하는 방법
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
터미널 VSCODE에서 프로그램을 실행하는 방법
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
vs 코드에서는 다음 단계를 통해 터미널에서 프로그램을 실행할 수 있습니다. 코드를 준비하고 통합 터미널을 열어 코드 디렉토리가 터미널 작업 디렉토리와 일치하는지 확인하십시오. 프로그래밍 언어 (예 : Python의 Python Your_file_name.py)에 따라 실행 명령을 선택하여 성공적으로 실행되는지 여부를 확인하고 오류를 해결하십시오. 디버거를 사용하여 디버깅 효율을 향상시킵니다.




