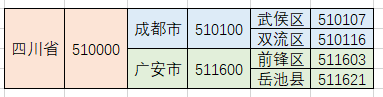
때때로 우리의 데이터는 계층적입니다. 예를 들어 지방과 자치단체의 일반적인 3단계 연결은 아래와 같이 한 계층 안에 다른 계층으로 구성됩니다.
데이터베이스에 데이터를 저장하는 경우도 있습니다. 이는 아래와 같이 목록 형식인 경우가 많습니다.
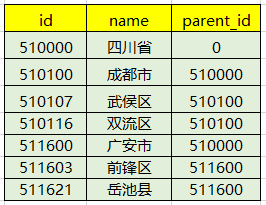
그런 다음 데이터베이스에서 쿼리하여 프런트 엔드로 반환하고 프런트 엔드에서 트리 수준을 제공해야 할 때 이번에는 이를 트리 구조로 재귀적으로 처리해야 하므로 다음 도구가 유용할 수 있습니다.
위와 같이 Place 객체를 정의하고 도구 주석을 추가합니다.
@TreeKey는 고유한
@TreeParentKey가 상위 노드 식별을 식별합니다.
@TreeChildren이 하위 노드 컬렉션을 식별합니다.
@Data
@Data
public class Place {
@TreeKey
private String id;
@TreeParentKey
private String parentId;
private String name;
@TreeChildren
private List<Place> children;
public Place(String id, String name, String parentId) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.parentId = parentId;
}
}테스트:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Place> places = new ArrayList<>();
places.add(new Place("510000", "四川省", "0"));
places.add(new Place("510100", "成都市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("510107", "武侯区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("510116", "双流区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("511600", "广安市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("511603", "前锋区", "511600"));
places.add(new Place("511621", "岳池县", "511600"));
List<Place> treeList = TreeUtils.getTree(places, "0");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(treeList));
}
}최종 효과:

@TreeKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeKey {
}@TreeParentKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeParentKey {
}@Tr eeChildren
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeChildren {
}@TreeUtils
package com.csd.utils.tree;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 递归求树形工具类
*
* @author Yuanqiang.Zhang
* @since 2023/3/8
*/
public class TreeUtils {
/**
* 集合转化为树形
*
* @param list 集合
* @param highestParentKey 最高层父节点值
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 树形
*/
public static <T> List<T> getTree(List<T> list, Object highestParentKey) {
if (Objects.isNull(list) || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Field key = null;
Field parentKey = null;
Field children = null;
Field[] fields = list.get(0).getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (Objects.isNull(key)) {
TreeKey treeKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeKey)) {
key = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(parentKey)) {
TreeParentKey treeParentKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeParentKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeParentKey)) {
parentKey = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(children)) {
TreeChildren treeChildren = field.getAnnotation(TreeChildren.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeChildren)) {
children = field;
continue;
}
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(key) || Objects.isNull(parentKey) || Objects.isNull(children)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
key.setAccessible(true);
parentKey.setAccessible(true);
children.setAccessible(true);
// 获取最高层数据
List<T> highs = new ArrayList<>();
try {
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(pk).equals(getString(highestParentKey))) {
highs.add(t);
}
}
// 获取最高层子孙节点
for (T t : highs) {
setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children);
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return highs;
}
/**
* 获取子孙节点
*
* @param list 集合
* @param parent 父节点对象
* @param key 唯一属性
* @param parentKey 父唯一属性
* @param children 节点
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 带有子孙集合的父节点对象
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
private static <T> T setChildren(List<T> list, T parent, Field key, Field parentKey, Field children) throws IllegalAccessException {
Object k = key.get(parent);
List<T> tempList = new ArrayList<>();
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(k).equals(getString(pk))) {
tempList.add(setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children));
}
}
children.set(parent, tempList);
return parent;
}
/**
* 获取字符串
*
* @param o 值
* @return 字符串
*/
private static String getString(Object o) {
return Objects.isNull(o) ? "" : o.toString();
}
}위 내용은 재귀를 사용하여 Java에서 트리 구조 도구 클래스를 구현하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!