Springboot 통합 타일 클라이언트의 Set 명령을 구현하는 방법
set 명령 구문
SET 키 id [FIELD 이름 값 ...] [EX 초] [NX|XX] (OBJECT geojson)|(POINT lat lon z)|(BOUNDS minlat minlon maxlat maxlon) |(HASH geohash)|(STRING 값)
set 명령은 redis의 hash 명령 사용과 동일하며 키이기도 합니다. 및 id이지만 차이점은 Tile38의 set 명령이 FIELD 필드 사용자 정의와 같은 더 많은 다른 속성도 전달할 수 있다는 것입니다. EX 유효 기간 등을 설정할 수도 있습니다. 그런 다음 개발자가 Tile38을 더 잘 사용할 수 있도록 이 구문에 유용한 java api를 설계해야 합니다. set命令就相当于redis中的hash命令的使用,也是一个key和id的组合,但是不同的是,Tile38的set命令还可以携带更多的其他属性,比如可以自定义FIELD字段,还可以设置EX有效期等等,那么我们需要给这个语法设计一套好用的java api,以便开发人员可以更好地使用Tile38。
语法分析
首先,根据上面提供的语法,我们可以分为三部分:
1.第一部分就是命令的启示关键字SET,我们把这个关键字单独作为一部分;
2.第二部分就是key id [FIELD name value ...] [EX seconds] [NX|XX],我们把这些都作为参数;
3.第三部分就是最后的目标数据对象:
(OBJECT geojson)|(POINT lat lon z)|(BOUNDS minlat minlon maxlat maxlon)|(HASH geohash)|(STRING value)
代码设计
1.我们把第一部分的命令关键字通过枚举的方式来管理:
enum Tile38Command implements ProtocolKeyword {
SET;
public final byte[] bytes;
static final String UNDERSCORE = "_";
static final String SPACE = " ";
Tile38Command() {
String name = StringUtils.replace(this.name(), UNDERSCORE, SPACE);
this.bytes = name.getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
}
@Override
public byte[] getBytes() {
return this.bytes;
}
}因为redis客户端工具在发送命令前需要对所有命令进行编码,所以要求所有的命令都必须实现ProtocolKeyword接口。如果命令的起始关键字是两个或多个单词,那么我们会使用下划线连接,转换成bytes的时候我们可以使用空格把下划线替换。
2.我们把命令的第二部分抽象成一个具体的class,通过相关的字段来进行描述:
public class SetOpts {
private String key;
private String id;
//字段值必须是双精度浮点型
private Map<String, Double> fields;
// 单位秒
private int ex;
// 创建方式:
// NX 不存在的时候创建
// XX 存在的时候更新
private NxXx nxXx;
private SetOpts(Builder builder) {
this.key = builder.key;
this.id = builder.id;
this.fields = builder.fields;
this.ex = builder.ex;
this.nxXx = builder.nxXx;
}
// 把所有的参数按顺序放到列表中
public List<String> commandLine() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add(this.key);
result.add(this.id);
// 添加所有的FIELD
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(this.fields)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Double> entry : this.fields.entrySet()) {
result.add("FIELD");
result.add(entry.getKey());
result.add(entry.getValue().toString());
}
}
// 添加`EX`
if (this.ex >= 0) {
result.add("EX");
result.add(String.valueOf(this.ex));
}
// 添加NX或XX
if (Objects.nonNull(this.nxXx)) {
result.add(this.nxXx.name());
}
// 返回结果
return result;
}
public enum NxXx {
NX,
XX
}
// 建造者模式
public static class Builder {
private String key;
private String id;
//字段值必须是双精度浮点型
private Map<String, Double> fields;
// 单位秒
private int ex = -1;
// 创建方式:
// NX 不存在的时候创建
// XX 存在的时候更新
private NxXx nxXx;
public Builder key(String key) {
this.key = key;
return this;
}
public Builder id(String id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public Builder field(String field, double value) {
if (Objects.isNull(this.fields)) {
this.fields = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
this.fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder ex(int seconds) {
this.ex = seconds;
return this;
}
public Builder nxXx(NxXx nxXx) {
this.nxXx = nxXx;
return this;
}
public SetOpts build() throws AwesomeException {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(this.key)) {
throw new AwesomeException(500, "key is empty");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(this.id)) {
throw new AwesomeException(500, "id is empty");
}
// 创建SetOpts对象
return new SetOpts(this);
}
}
}我们上面通过建造者的设计模式,把所有的参数都转换成了SetOpts这个类当中,开发人员就可以通过SetOpts对象的构建来灵活地控制命令中的参数了。
3.我们需要把第三部分当中的不同数据对象转换成不同的类型:
POINT数据类型
Point关键的字段就是经纬度,除此之外,还有一个额外的字段z
SET 명령의 계시 키워드입니다. 이 키워드를 별도의 부분으로 ;2. 두 번째 부분은 key id [FIELD 이름 값 ...] [EX 초] [NX|XX]이며 이를 매개변수로 사용합니다. 3. 세 번째 부분 최종 대상 데이터 객체입니다: (OBJECT geojson)|(POINT lat lon z)|(BOUNDS minlat minlon maxlat maxlon)|(HASH geohash)|(STRING value)
코드 디자인 1. 첫 번째 부분에 있는 명령 키워드는 열거를 통해 관리됩니다.public class Point extends Element implements Serializable {
// 经度
private double lng;
// 维度
private double lat;
// 额外的数据
private double z;
public Point(double lng, double lat, double z) {
this.lat = lat;
this.lng = lng;
this.z = z;
}
public Point(double lng, double lat) {
this(lng, lat, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("POINT");
result.add(String.valueOf(this.lng));
result.add(String.valueOf(this.lat));
if (this.z != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
result.add(String.valueOf(this.z));
}
return result;
}
}ProtocolKeyword 인터페이스를 구현해야 합니다. 명령의 시작 키워드가 두 단어 이상인 경우 밑줄을 사용하여 연결합니다. 바이트로 변환할 때 밑줄을 대체하기 위해 공백을 사용할 수 있습니다. 2. 명령의 두 번째 부분을 특정 클래스로 추상화하고 관련 필드를 통해 설명합니다. @AllArgsConstructor
public class Bounds extends Element {
private double[] coordinate1;
private double[] coordinate2;
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("BOUNDS");
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate1[0]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate1[1]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate2[0]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate2[1]));
return result;
}
}로그인 후 복사
빌더 디자인 패턴을 사용하여 모든 매개변수를 SetOpts 클래스로 변환했습니다. 개발자는 명령에서 매개변수를 유연하게 제어할 수 있습니다. SetOpts 객체의 구성을 통해. 3. 세 번째 부분의 다양한 데이터 개체를 다양한 유형으로 변환해야 합니다. 🎜🎜POINT 데이터 유형 🎜🎜Point의 핵심 필드는 위도와 경도입니다. 또한 추가 필드 @AllArgsConstructor
public class Bounds extends Element {
private double[] coordinate1;
private double[] coordinate2;
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("BOUNDS");
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate1[0]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate1[1]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate2[0]));
result.add(String.valueOf(coordinate2[1]));
return result;
}
}z가 있습니다. 추가 비즈니스 매개변수를 저장하는 데 사용되는 는 비워둘 수 있습니다. 🎜@AllArgsConstructor
public class Geohash extends Element {
private String hash;
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("HASH");
result.add(this.hash);
return result;
}
}
@AllArgsConstructor
public class RawString extends Element {
private String raw;
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("STRING");
result.add(this.raw);
return result;
}
}Point, LineString, Polygon, MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon
@Data
public class GeoJson {
public static class Builder {
public Point.Builder point() {
return new Point.Builder();
}
public MultiPoint.Builder multPoint() {
return new MultiPoint.Builder();
}
public LineString.Builder lineString() {
return new LineString.Builder();
}
public MultiLineString.Builder multiLineString() {
return new MultiLineString.Builder();
}
public Polygon.Builder polygon() {
return new Polygon.Builder();
}
public MultiPolygon.Builder multiPolygon() {
return new MultiPolygon.Builder();
}
}
}// Point类型
public static class Point extends BaseGeoJson {
// 坐标点
private double[] coordinates;
Point(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.Point;
this.coordinates = builder.coordinates;
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private double[] coordinates;
public Builder coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
coordinates = new double[]{lat, lon};
return this;
}
public Point build() {
return new Point(this);
}
}
}
// MultiPoint类型
public static class MultiPoint extends BaseGeoJson {
private double[][] coordinates;
MultiPoint(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.MultiPoint;
this.coordinates = builder.convert2Array();
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private List<Coordinate> coordinates;
public Builder coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.coordinates)) {
this.coordinates = new LinkedList<>();
}
this.coordinates.add(new Coordinate(lat, lon));
return this;
}
protected double[][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.coordinates.size();
double[][] result = new double[length][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.coordinates.get(i).convertToArray();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public MultiPoint build() {
return new MultiPoint(this);
}
}
}
// LineString类型
public static class LineString extends MultiPoint {
private double[][] coordinates;
LineString(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.LineString;
}
public static class Builder extends MultiPoint.Builder {
@Override
public LineString build() {
return new LineString(this);
}
}
}
// MultiLineString类型
public static class MultiLineString extends BaseGeoJson {
private double[][][] coordinates;
MultiLineString(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.MultiLineString;
this.coordinates = builder.convertToArray();
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private List<Line> lines = new LinkedList<>();
public Line line() {
return new Line(this);
}
void addLine(Line line) {
lines.add(line);
}
double[][][] convertToArray() {
int length = this.lines.size();
double[][][] result = new double[length][][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Line line = this.lines.get(i);
result[i] = line.convert2Array();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public BaseGeoJson build() {
return new MultiLineString(this);
}
}
static class Line {
private List<Coordinate> coordinates;
private Builder builder;
Line(Builder builder) {
this.builder = builder;
this.builder.addLine(this);
}
private double[][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.coordinates.size();
double[][] result = new double[length][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.coordinates.get(i).convertToArray();
}
return result;
}
public Line coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.coordinates)) {
this.coordinates = new LinkedList<>();
}
this.coordinates.add(new Coordinate(lat, lon));
return this;
}
public Line nextLine() {
return new Line(this.builder);
}
public Builder end() {
return this.builder;
}
}
}
// Polygon类型
public static class Polygon extends MultiPoint {
private double[][][] coordinates;
Polygon(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.Polygon;
this.coordinates = new double[][][]{builder.convert2Array()};
}
public static class Builder extends MultiPoint.Builder {
@Override
public Polygon build() {
return new Polygon(this);
}
}
}
// MultiPolygon类型
public static class MultiPolygon extends BaseGeoJson {
private double[][][][] coordinates;
MultiPolygon(Builder builder) {
super(builder);
this.type = GeoJsonType.MultiPolygon;
this.coordinates = new double[][][][]{builder.convert2Array()};
}
@Override
protected Object coordinates() {
return this.coordinates;
}
public static class Builder extends BaseGeoJson.Builder {
private List<Polygon> polygons = new LinkedList<>();
@Override
public BaseGeoJson build() {
return new MultiPolygon(this);
}
void addPolygon(Polygon polygon) {
polygons.add(polygon);
}
private double[][][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.polygons.size();
double[][][] result = new double[length][][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.polygons.get(i).convert2Array();
}
return result;
}
}
static class Polygon {
private List<Coordinate> coordinates;
private Builder builder;
Polygon(Builder builder) {
this.builder = builder;
this.builder.addPolygon(this);
}
private double[][] convert2Array() {
int length = this.coordinates.size();
double[][] result = new double[length][];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
result[i] = this.coordinates.get(i).convertToArray();
}
return result;
}
public Polygon coordinate(double lon, double lat) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.coordinates)) {
this.coordinates = new LinkedList<>();
}
this.coordinates.add(new Coordinate(lat, lon));
return this;
}
public Polygon nextLine() {
return new Polygon(this.builder);
}
public Builder end() {
return this.builder;
}
}
}
// 基类BaseGeoJson
public abstract static class BaseGeoJson extends Element {
// 公共字段type
protected GeoJsonType type;
// 公共字段metadata
private Map<String, String> metadata;
BaseGeoJson(Builder builder) {
this.metadata = builder.metadata;
}
protected abstract Object coordinates();
// 转换成命令参数
@Override
public List<String> commandArgs() {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
result.add("OBJECT");
result.add(toJson());
return result;
}
// 提供统一的转json方法
protected String toJson() {
Map<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("type", this.type);
map.put("coordinates", coordinates());
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.metadata)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : this.metadata.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
return JsonUtil.obj2String(map);
}
abstract static class Builder {
private Map<String, String> metadata;
public Builder meta(String key, String value) {
if (MapUtils.isEmpty(this.metadata)) {
this.metadata = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
this.metadata.put(key, value);
return this;
}
public abstract BaseGeoJson build();
}
static class Coordinate {
private double lat;
private double lon;
Coordinate(double lat, double lon) {
this.lat = lat;
this.lon = lon;
}
public double[] convertToArray() {
return new double[]{this.lat, this.lon};
}
}
// GeoJSON所有的数据类型
enum GeoJsonType {
Point,
LineString,
Polygon,
MultiPoint,
MultiLineString,
MultiPolygon
}
}public abstract class Element implements Serializable {
public abstract List<String> commandArgs();
}private String setElement(SetOpts setOpts, Element element) {
List<String> args1 = setOpts.commandLine();
List<String> commandArgs = element.commandArgs();
return execute(Tile38Command.SET, args1, commandArgs);
}
/**
* 设置点位
*
* @param setOpts
* @param point
* @return
*/
public String setPoint(SetOpts setOpts, Point point) {
return setElement(setOpts, point);
}
/**
* 设置对象
*
* @param setOpts
* @param geoJson
* @return
*/
public String setObject(SetOpts setOpts, GeoJson.BaseGeoJson geoJson) {
return setElement(setOpts, geoJson);
}
/**
* 设置矩形边界
*
* @param setOpts
* @param bounds
* @return
*/
public String setBounds(SetOpts setOpts, Bounds bounds) {
return setElement(setOpts, bounds);
}
/**
* 设置geohash
*
* @param setOpts
* @param geohash
* @return
*/
public String setGeohash(SetOpts setOpts, Geohash geohash) {
return setElement(setOpts, geohash);
}
/**
* 设置String
*
* @param setOpts
* @param string
* @return
*/
public String setString(SetOpts setOpts, RawString string) {
return setElement(setOpts, string);
}위 내용은 Springboot 통합 타일 클라이언트의 Set 명령을 구현하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7500
7500
 15
15
 1377
1377
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 52
52
 19
19
 19
19
 52
52
 Springboot가 Jasypt를 통합하여 구성 파일 암호화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Springboot가 Jasypt를 통합하여 구성 파일 암호화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Jasypt 소개 Jasypt는 개발자가 최소한의 노력으로 프로젝트에 기본 암호화 기능을 추가할 수 있게 해주며 암호화 작동 방식에 대한 깊은 이해가 필요하지 않은 단방향 및 양방향 암호화에 대한 높은 보안을 제공합니다. 표준 기반 암호화 기술. 비밀번호, 텍스트, 숫자, 바이너리 암호화... Spring 기반 애플리케이션, 개방형 API와의 통합에 적합하며 모든 JCE 공급자와 함께 사용할 수 있습니다... 다음 종속성을 추가합니다: com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2. Jasypt의 이점은 코드가 유출되더라도 데이터 소스를 보장할 수 있어 시스템 보안을 보호합니다.
 MyBatis 동적 SQL 태그의 Set 태그 기능에 대한 자세한 설명
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
MyBatis 동적 SQL 태그의 Set 태그 기능에 대한 자세한 설명
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
MyBatis 동적 SQL 태그 해석: Set 태그 사용법에 대한 자세한 설명 MyBatis는 풍부한 동적 SQL 태그를 제공하고 데이터베이스 작업 명령문을 유연하게 구성할 수 있는 탁월한 지속성 계층 프레임워크입니다. 그 중 Set 태그는 업데이트 작업에서 매우 일반적으로 사용되는 UPDATE 문에서 SET 절을 생성하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 기사에서는 MyBatis에서 Set 태그의 사용법을 자세히 설명하고 특정 코드 예제를 통해 해당 기능을 보여줍니다. Set 태그란 무엇입니까? Set 태그는 MyBati에서 사용됩니다.
 SpringBoot가 Redisson을 통합하여 지연 대기열을 구현하는 방법
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
SpringBoot가 Redisson을 통합하여 지연 대기열을 구현하는 방법
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
사용 시나리오 1. 주문이 성공적으로 이루어졌으나 30분 이내에 결제가 이루어지지 않았습니다. 결제 시간이 초과되어 주문이 자동으로 취소되었습니다. 2. 주문이 서명되었으며 서명 후 7일 동안 평가가 수행되지 않았습니다. 주문 시간이 초과되어 평가되지 않으면 시스템은 기본적으로 긍정적 평가로 설정됩니다. 3. 판매자가 5분 동안 주문을 받지 않으면 주문이 취소됩니다. 문자 메시지 알림이 전송됩니다... 지연이 길고 실시간 성능이 낮은 시나리오의 경우 작업 예약을 사용하여 정기적인 폴링 처리를 수행할 수 있습니다. 예: xxl-job 오늘은 다음을 선택하겠습니다.
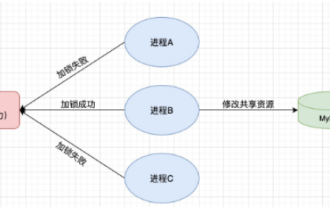 Redis를 사용하여 SpringBoot에서 분산 잠금을 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
Redis를 사용하여 SpringBoot에서 분산 잠금을 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
1. Redis는 분산 잠금 원칙과 분산 잠금이 필요한 이유를 구현합니다. 분산 잠금에 대해 이야기하기 전에 분산 잠금이 필요한 이유를 설명해야 합니다. 분산 잠금의 반대는 독립형 잠금입니다. 다중 스레드 프로그램을 작성할 때 공유 변수를 동시에 작동하여 발생하는 데이터 문제를 방지하기 위해 일반적으로 잠금을 사용하여 공유 변수를 상호 제외합니다. 공유 변수의 사용 범위는 동일한 프로세스에 있습니다. 동시에 공유 리소스를 운영해야 하는 여러 프로세스가 있는 경우 어떻게 상호 배타적일 수 있습니까? 오늘날의 비즈니스 애플리케이션은 일반적으로 마이크로서비스 아키텍처입니다. 이는 하나의 애플리케이션이 여러 프로세스를 배포한다는 의미이기도 합니다. 여러 프로세스가 MySQL에서 동일한 레코드 행을 수정해야 하는 경우 잘못된 작업으로 인해 발생하는 더티 데이터를 방지하려면 배포가 필요합니다. 현재 소개할 스타일은 잠겨 있습니다. 포인트를 얻고 싶다
 springboot가 파일을 jar 패키지로 읽은 후 파일에 액세스할 수 없는 문제를 해결하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
springboot가 파일을 jar 패키지로 읽은 후 파일에 액세스할 수 없는 문제를 해결하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot가 파일을 읽지만 jar 패키지로 패키징한 후 최신 개발에 액세스할 수 없습니다. springboot가 파일을 jar 패키지로 패키징한 후 파일을 읽을 수 없는 상황이 발생합니다. 그 이유는 패키징 후 파일의 가상 경로 때문입니다. 유효하지 않으며 읽기를 통해서만 액세스할 수 있습니다. 파일은 리소스 publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input 아래에 있습니다.
 여러 테이블을 추가하기 위해 SQL 문을 사용하지 않고 Springboot+Mybatis-plus를 구현하는 방법
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
여러 테이블을 추가하기 위해 SQL 문을 사용하지 않고 Springboot+Mybatis-plus를 구현하는 방법
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Springboot+Mybatis-plus가 다중 테이블 추가 작업을 수행하기 위해 SQL 문을 사용하지 않을 때 내가 직면한 문제는 테스트 환경에서 생각을 시뮬레이션하여 분해됩니다. 매개 변수가 있는 BrandDTO 개체를 생성하여 배경으로 매개 변수 전달을 시뮬레이션합니다. Mybatis-plus에서 다중 테이블 작업을 수행하는 것은 매우 어렵다는 것을 Mybatis-plus-join과 같은 도구를 사용하지 않으면 해당 Mapper.xml 파일을 구성하고 냄새나고 긴 ResultMap만 구성하면 됩니다. 해당 SQL 문을 작성합니다. 이 방법은 번거로워 보이지만 매우 유연하며 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다.
 SpringBoot와 SpringMVC의 비교 및 차이점 분석
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot와 SpringMVC의 비교 및 차이점 분석
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot와 SpringMVC는 모두 Java 개발에서 일반적으로 사용되는 프레임워크이지만 둘 사이에는 몇 가지 분명한 차이점이 있습니다. 이 기사에서는 이 두 프레임워크의 기능과 용도를 살펴보고 차이점을 비교할 것입니다. 먼저 SpringBoot에 대해 알아봅시다. SpringBoot는 Spring 프레임워크를 기반으로 하는 애플리케이션의 생성 및 배포를 단순화하기 위해 Pivotal 팀에서 개발되었습니다. 독립 실행형 실행 파일을 구축하는 빠르고 가벼운 방법을 제공합니다.
 SpringBoot가 Redis를 사용자 정의하여 캐시 직렬화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
SpringBoot가 Redis를 사용자 정의하여 캐시 직렬화를 구현하는 방법
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. RedisAPI 기본 직렬화 메커니즘인 RedisTemplate1.1을 사용자 정의합니다. API 기반 Redis 캐시 구현은 데이터 캐싱 작업에 RedisTemplate 템플릿을 사용합니다. 여기서 RedisTemplate 클래스를 열고 클래스의 소스 코드 정보를 봅니다. 키 선언, 값의 다양한 직렬화 방법, 초기 값은 비어 있음 @NullableprivateRedisSe




