Python의 RegEx 정규식을 사용하는 방법
RegEx 또는 정규식은 검색 패턴을 형성하는 일련의 문자입니다.
RegEx를 사용하면 문자열에 지정된 검색 패턴이 포함되어 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
RegEx 모듈
Python은 정규식을 처리하는 데 사용할 수 있는 re라는 내장 패키지를 제공합니다.
re 모듈 가져오기:
import re
RegEx in Python
re 모듈을 가져온 후에는 정규식을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example
문자열을 검색하여 "China"로 시작하는지 확인하고 "country"로 끝남:
import re
txt = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("^China.*country$", txt)실행 중인 인스턴스
import re
txt = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("^China.*country$", txt)
if (x):
print("YES! We have a match!")
else:
print("No match")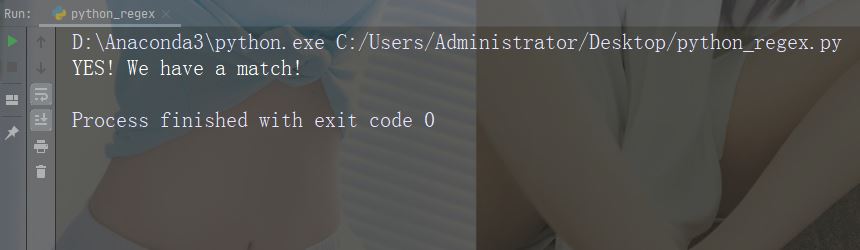
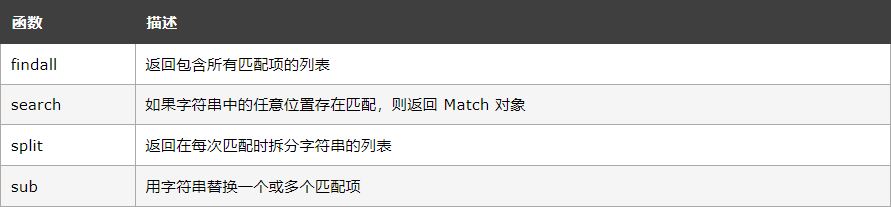
RegEx 함수
re 모듈은 일치를 위해 문자열을 검색할 수 있는 함수 세트를 제공합니다.
메타 문자
메타 문자는 다음과 같습니다.
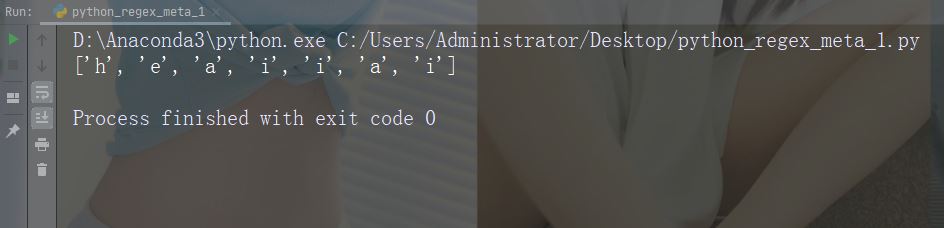
문자: [] 설명: 문자 예 세트: "[a-m]"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Find all lower case characters alphabetically between "a" and "m":
x = re.findall("[a-m]", str)
print(x)예제 실행
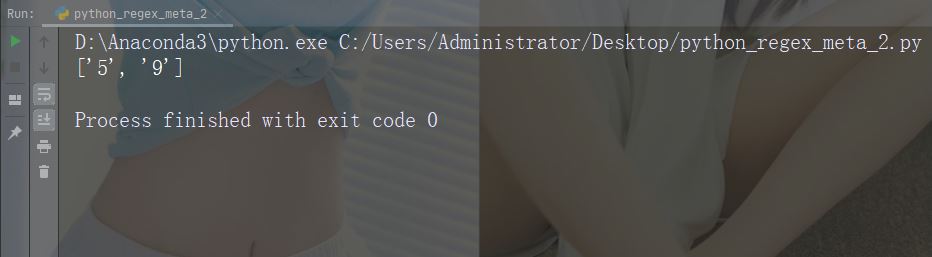
문자: 설명: 특수 시퀀스를 나타냅니다(이스케이프에도 사용할 수 있음) 특수 문자) 예: "d"
import re
str = "That will be 59 dollars"
#Find all digit characters:
x = re.findall("\d", str)
print(x)Run 예
문자: . 설명: 모든 문자(줄 바꿈 제외) 예: "he…o"
import re
str = "hello world"
#Search for a sequence that starts with "he", followed by two (any) characters, and an "o":
x = re.findall("he..o", str)
print(x)Run 예
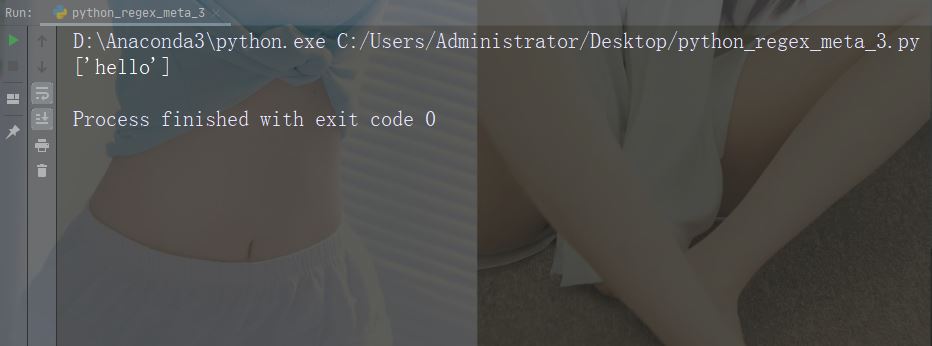
문자: ^ 설명 : 시작 예: "^hello"
import re
str = "hello world"
#Check if the string starts with 'hello':
x = re.findall("^hello", str)
if (x):
print("Yes, the string starts with 'hello'")
else:
print("No match")Run the example
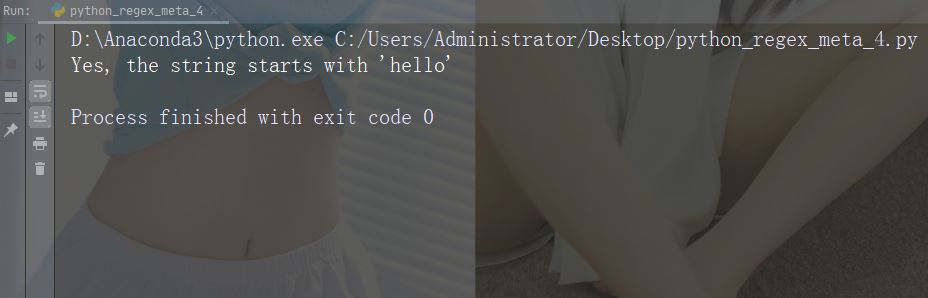
문자: $ 설명: 끝 예: "world$"
import re
str = "hello world"
#Check if the string ends with 'world':
x = re.findall("world$", str)
if (x):
print("Yes, the string ends with 'world'")
else:
print("No match")Run the example
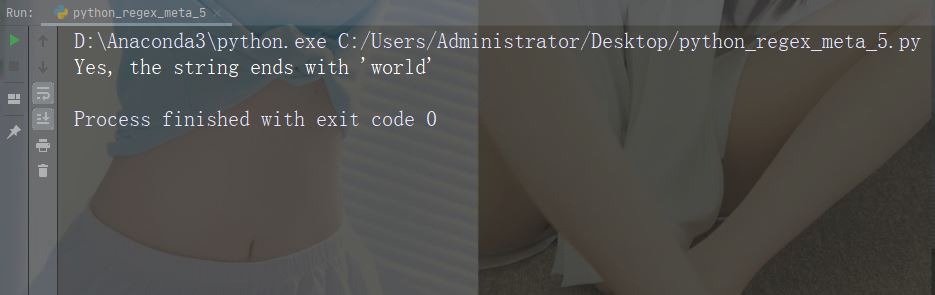
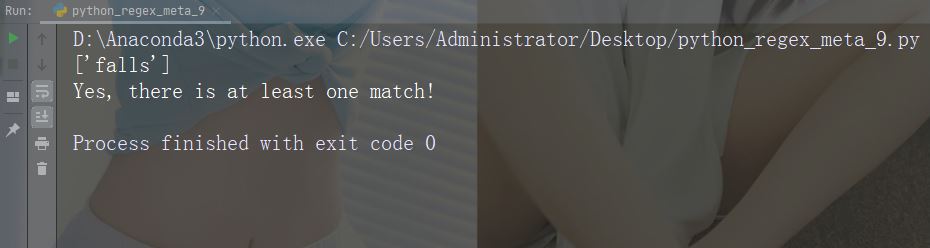
문자: * 설명: 0 이상 발생 예: "aix*"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "ai" followed by 0 or more "x" characters:
x = re.findall("aix*", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
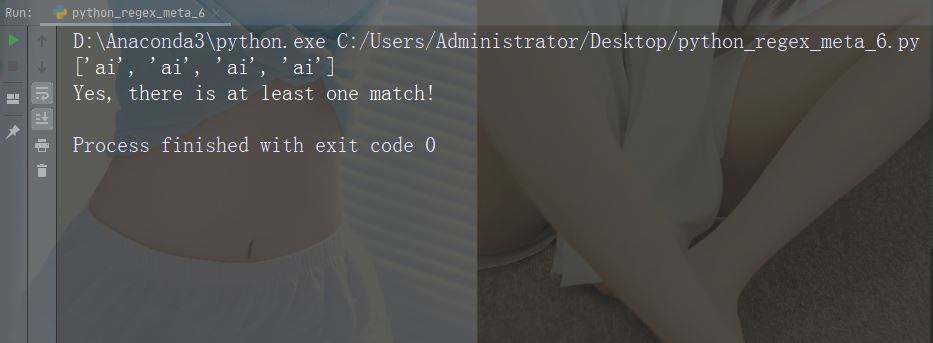
문자: + 설명: 하나 이상의 발생 예: "aix+"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "ai" followed by 1 or more "x" characters:
x = re.findall("aix+", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
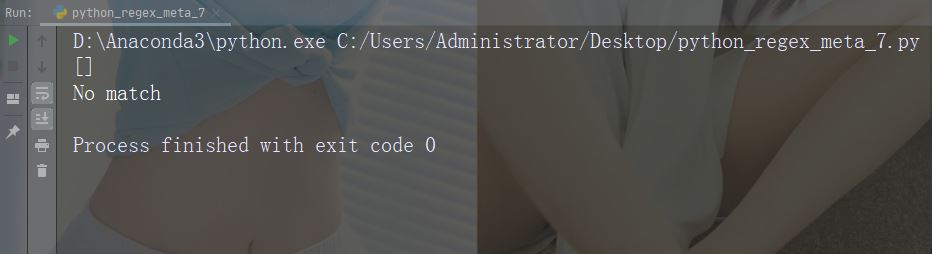
문자: {} 설명 : 발생 횟수를 정확하게 지정 예: "al{2}"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains "a" followed by exactly two "l" characters:
x = re.findall("al{2}", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
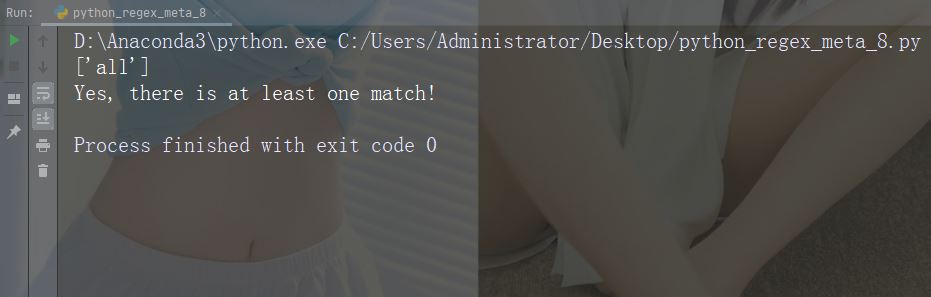
문자: | 설명: 둘 중 하나 예: "falls|stays"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain falls mainly in the plain!"
#Check if the string contains either "falls" or "stays":
x = re.findall("falls|stays", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
문자 : ( ) 설명 : 캡처 및 그룹화
특수 시퀀스
특수 시퀀스는 아래 표의 문자 중 하나가 뒤에 오는 문자를 말하며 특별한 의미를 갖습니다.
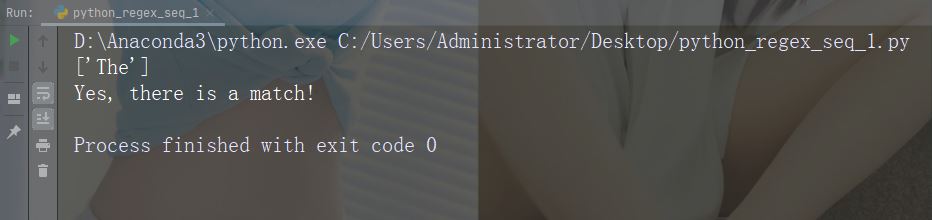
Character: A 설명: 지정된 문자가 문자열의 시작 부분에 있으면 일치 항목을 반환합니다. 예: "AThe"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string starts with "The":
x = re.findall("\AThe", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is a match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
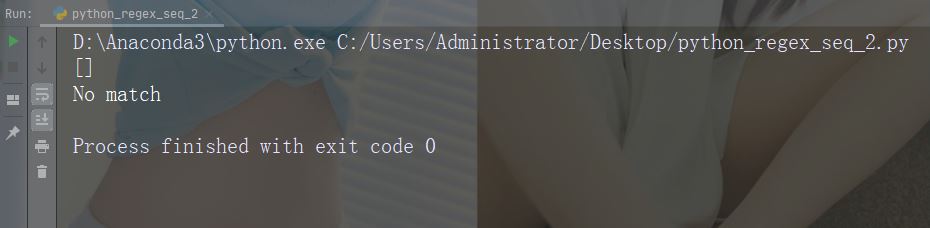
Character: b
설명: 지정된 문자가 있는 경우 해당 문자를 반환합니다. 단어의 시작 부분에 있거나 끝 부분에 일치
예: r"bain"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present at the beginning of a WORD:
x = re.findall(r"\bain", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
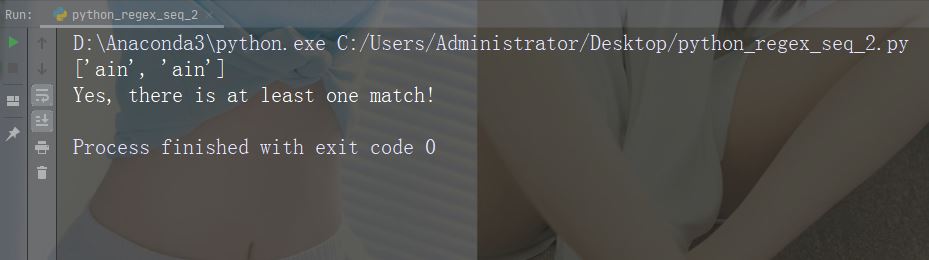
예: r"ainb"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present at the end of a WORD:
x = re.findall(r"ain\b", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
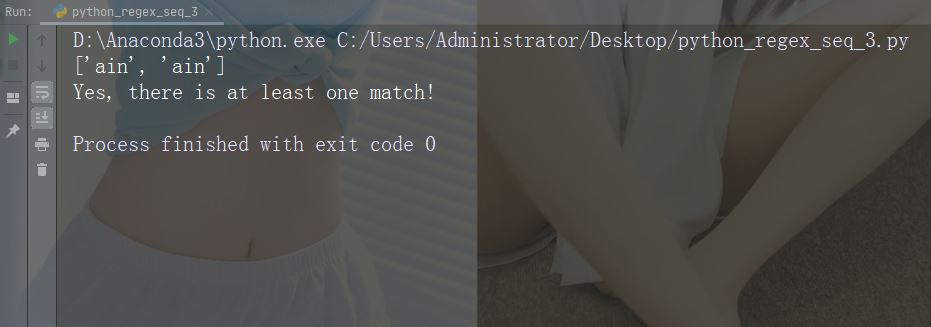
문자 : B
설명: 일치하는 문자가 있으면 지정된 문자를 반환하지만 단어의 시작(또는 끝)에는 반환하지 않습니다.
예: r"Bain"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present, but NOT at the beginning of a word:
x = re.findall(r"\Bain", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
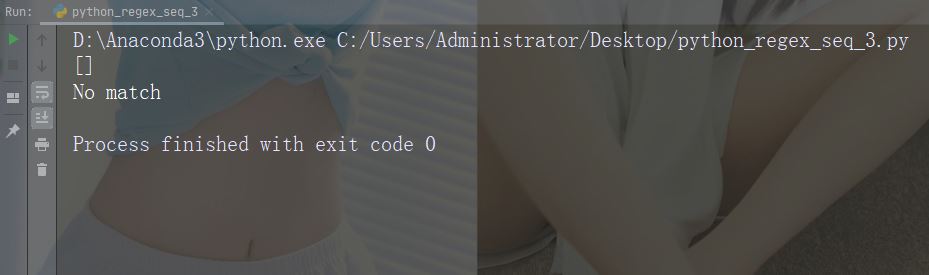
예:r" ainB"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if "ain" is present, but NOT at the end of a word:
x = re.findall(r"ain\B", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
문자: d
설명: 문자열에 숫자(0-9)가 포함된 일치 항목을 반환합니다.
예: "d"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string contains any digits (numbers from 0-9):
x = re.findall("\d", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
문자: D
설명: 문자열에 숫자가 포함되지 않은 일치 항목을 반환합니다. 일치
예: "D"
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every no-digit character:
x = re.findall("\D", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")예제 실행
문자: s
描述:返回字符串包含空白字符的匹配项
示例:“\s”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every white-space character:
x = re.findall("\s", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
字符:\S
描述:返回字符串不包含空白字符的匹配项
示例:“\S”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every NON white-space character:
x = re.findall("\S", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
字符:\w
描述: 返回一个匹配项,其中字符串包含任何单词字符 (从 a 到 Z 的字符,从 0 到 9 的数字和下划线 _ 字符)
示例:“\w”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every word character (characters from a to Z, digits from 0-9, and the underscore _ character):
x = re.findall("\w", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
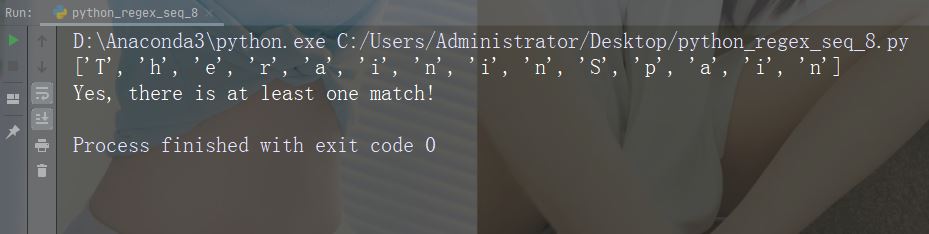
字符:\W
描述:返回一个匹配项,其中字符串不包含任何单词字符
示例:“\W”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Return a match at every NON word character (characters NOT between a and Z. Like "!", "?" white-space etc.):
x = re.findall("\W", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
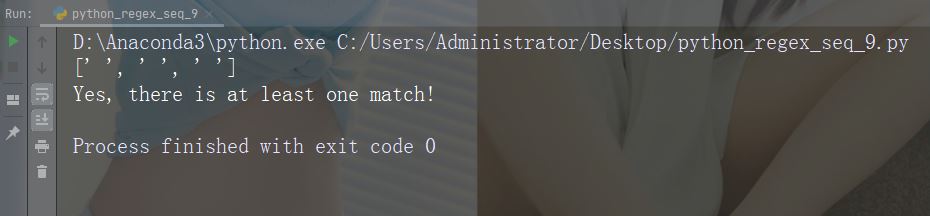
字符:\Z
描述:如果指定的字符位于字符串的末尾,则返回匹配项 。
示例:“Spain\Z”
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string ends with "Spain":
x = re.findall("Spain\Z", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is a match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
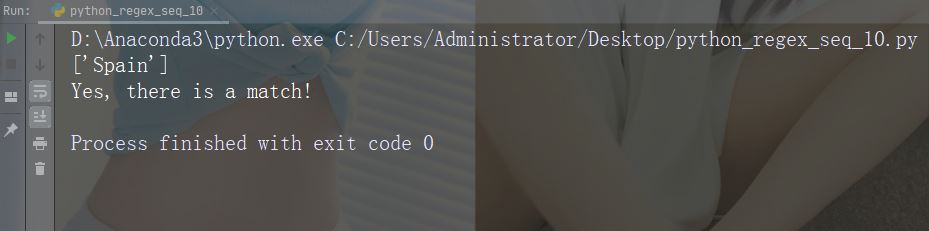
集合(Set)
集合(Set)是一对方括号 [] 内的一组字符,具有特殊含义。
字符:[arn]
描述:返回一个匹配项,其中存在指定字符(a,r 或 n)之一
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any a, r, or n characters:
x = re.findall("[arn]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
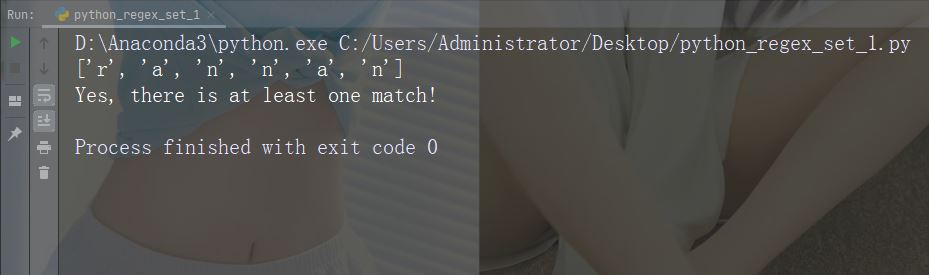
字符:[a-n]
描述:返回字母顺序 a 和 n 之间的任意小写字符匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any characters between a and n:
x = re.findall("[a-n]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
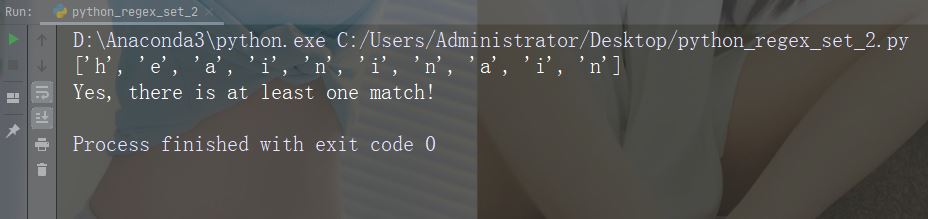
字符:[^arn]
描述:返回除 a、r 和 n 之外的任意字符的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has other characters than a, r, or n:
x = re.findall("[^arn]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
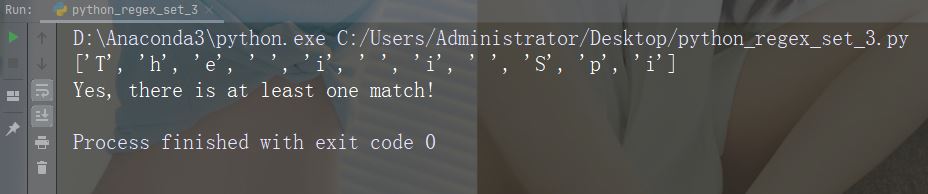
字符:[0123]
描述:返回存在任何指定数字(0、1、2 或 3)的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "The rain in Spain"
#Check if the string has any 0, 1, 2, or 3 digits:
x = re.findall("[0123]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
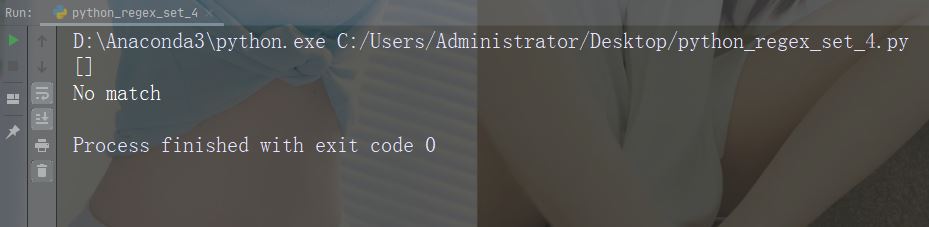
字符:[0-9]
描述:返回 0 与 9 之间任意数字的匹配
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any digits:
x = re.findall("[0-9]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
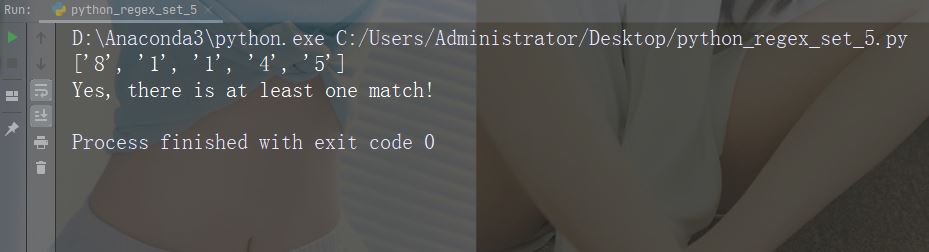
字符:[0-5][0-9]
描述:返回介于 0 到 9 之间的任何数字的匹配项
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any two-digit numbers, from 00 to 59:
x = re.findall("[0-5][0-9]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
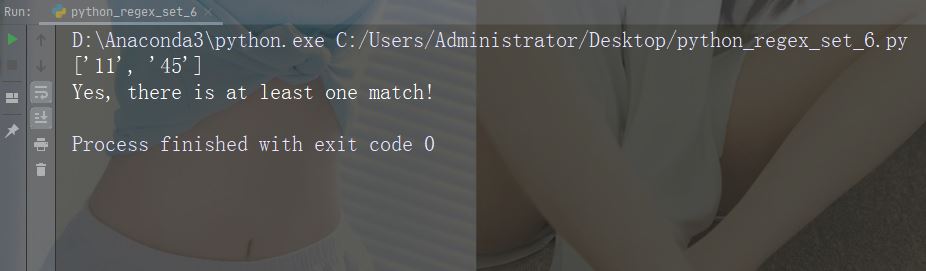
字符:[a-zA-Z]
描述:返回字母顺序 a 和 z 之间的任何字符的匹配,小写或大写
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any characters from a to z lower case, and A to Z upper case:
x = re.findall("[a-zA-Z]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
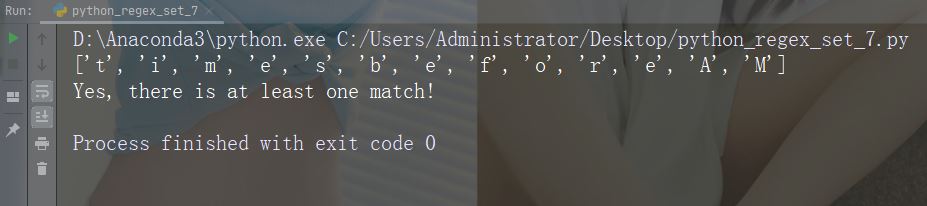
字符:[+]
描述:在集合中,+、*、.、|、()、$、{} 没有特殊含义,因此 [+] 表示:返回字符串中任何 + 字符的匹配项。
示例
import re
str = "8 times before 11:45 AM"
#Check if the string has any + characters:
x = re.findall("[+]", str)
print(x)
if (x):
print("Yes, there is at least one match!")
else:
print("No match")运行示例
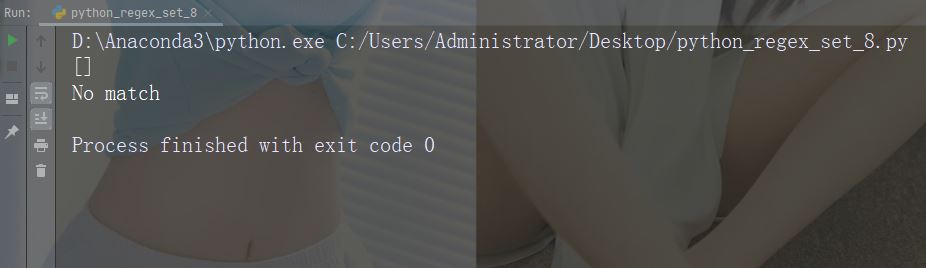
findall() 函数
findall() 函数返回包含所有匹配项的列表。
实例
打印所有匹配的列表
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.findall("a", str)
print(x)运行实例
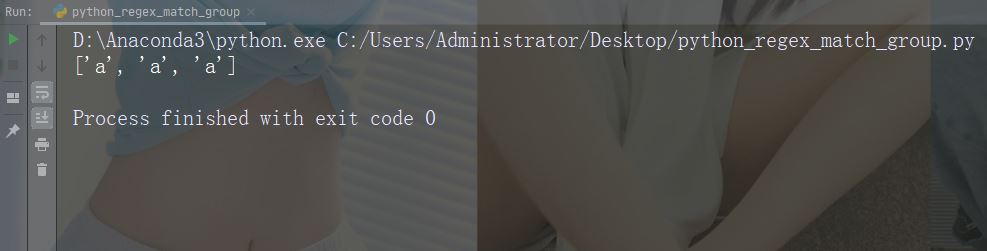
这个列表以被找到的顺序包含匹配项。
如果未找到匹配项,则返回空列表。
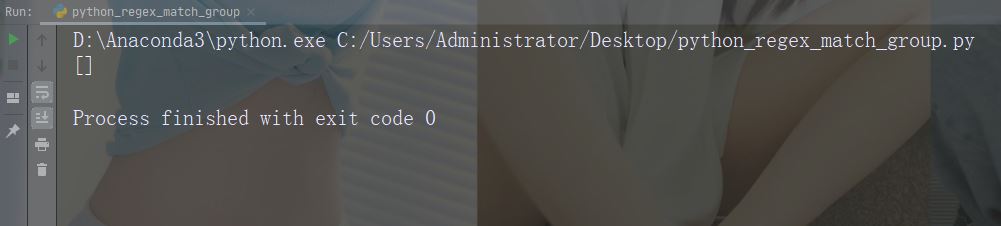
实例
如果未找到匹配,则返回空列表:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.findall("USA", str)
print(x)运行实例
search() 函数
search() 函数搜索字符串中的匹配项,如果存在匹配则返回 Match 对象。
如果有多个匹配,则仅返回首个匹配项。
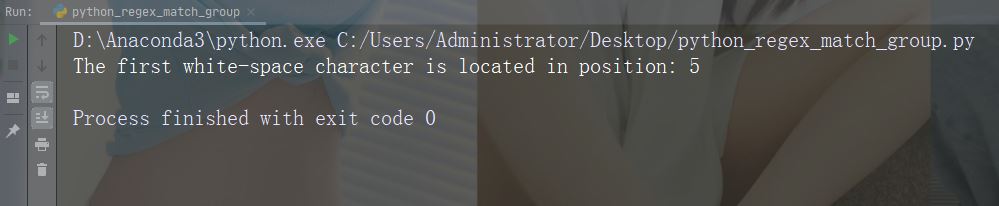
实例
在字符串中搜索第一个空白字符
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("\s", str)
print("The first white-space character is located in position:", x.start())运行实例
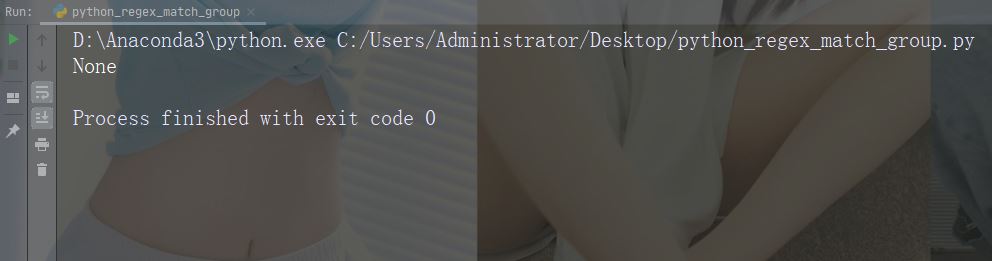
如果未找到匹配,则返回值 None:
实例
进行不返回匹配的检索
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("USA", str)
print(x)运行实例
split() 函数
split() 函数返回一个列表,其中字符串在每次匹配时被拆分。
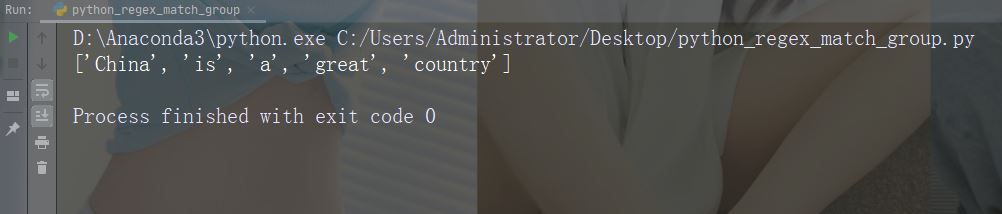
实例
在每个空白字符处进行拆分
import re
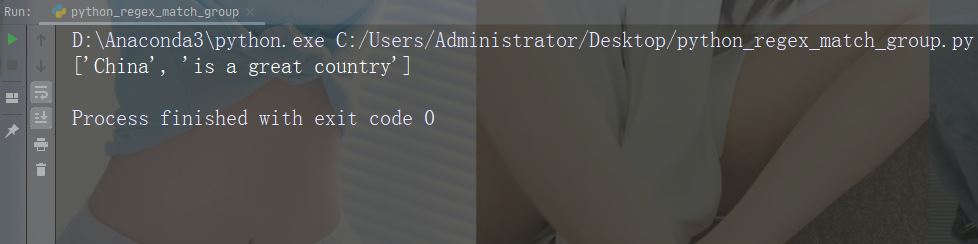
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.split("\s", str)
print(x)运行实例
可以通过指定 maxsplit 参数来控制出现次数:
实例
仅在首次出现时拆分字符串:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.split("\s", str, 1)
print(x)运行实例
sub() 函数
sub() 函数把匹配替换为您选择的文本
实例
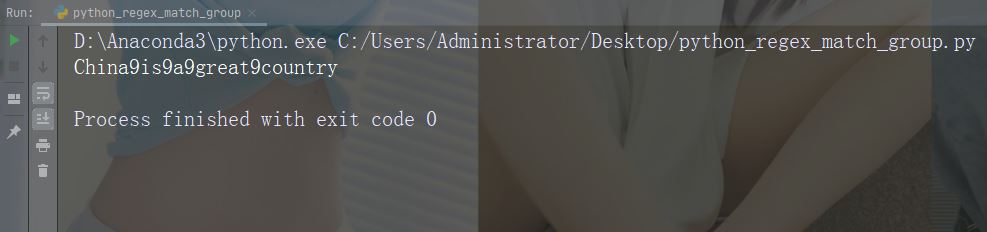
用数字 9 替换每个空白字符
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.sub("\s", "9", str)
print(x)运行实例
可以通过指定 count 参数来控制替换次数:
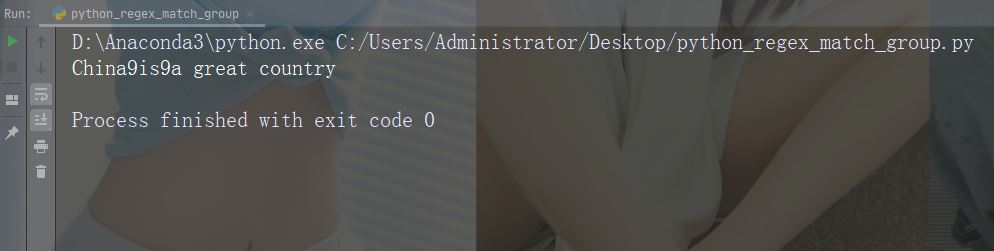
实例
替换前两次出现
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.sub("\s", "9", str, 2)
print(x)运行实例
Match 对象
Match 对象是包含有关搜索和结果信息的对象。
注释:如果没有匹配,则返回值 None,而不是 Match 对象。
实例
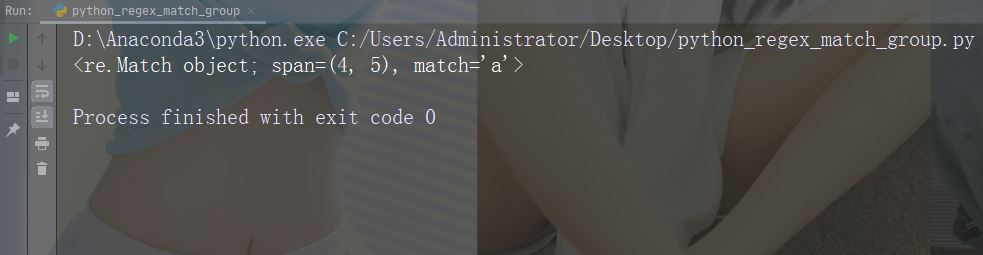
执行会返回 Match 对象的搜索:
import re
str = "China is a great country"
x = re.search("a", str)
print(x) # 将打印一个对象运行实例
Match 对象提供了用于取回有关搜索及结果信息的属性和方法:
span()返回的元组包含了匹配的开始和结束位置.string返回传入函数的字符串group()返回匹配的字符串部分
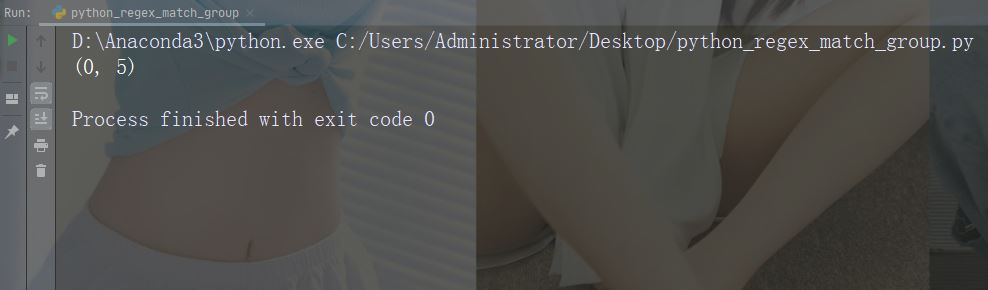
实例
打印首个匹配出现的位置(开始和结束位置)。
正则表达式查找以大写 “C” 开头的任何单词:
import re str = "China is a great country" x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str) print(x.span())
运行实例
实例
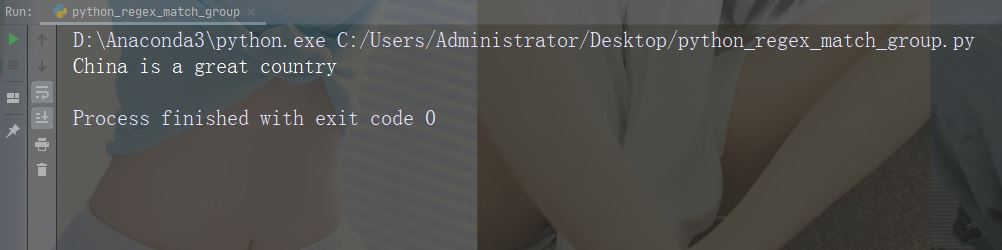
打印传入函数的字符串
import re str = "China is a great country" x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str) print(x.string)
运行实例
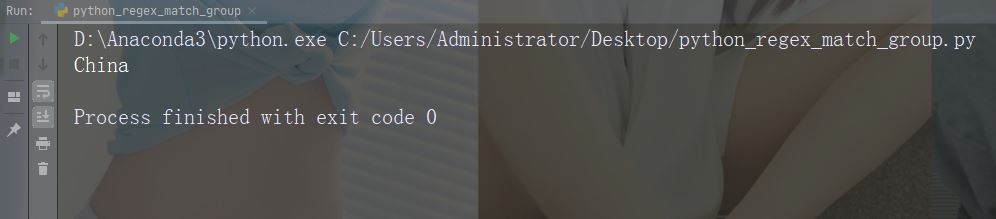
实例
打印匹配的字符串部分
正则表达式查找以大写 “C” 开头的任何单词:
import re str = "China is a great country" x = re.search(r"\bC\w+", str) print(x.group())
运行实例
注释:如果没有匹配项,则返回值 None,而不是 Match 对象。
위 내용은 Python의 RegEx 정규식을 사용하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

AI Hentai Generator
AI Hentai를 무료로 생성하십시오.

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

메모장++7.3.1
사용하기 쉬운 무료 코드 편집기

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

스튜디오 13.0.1 보내기
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

뜨거운 주제
 7469
7469
 15
15
 1376
1376
 52
52
 77
77
 11
11
 48
48
 19
19
 19
19
 29
29
 MySQL은 지불해야합니다
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL은 지불해야합니다
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL에는 무료 커뮤니티 버전과 유료 엔터프라이즈 버전이 있습니다. 커뮤니티 버전은 무료로 사용 및 수정할 수 있지만 지원은 제한되어 있으며 안정성이 낮은 응용 프로그램에 적합하며 기술 기능이 강합니다. Enterprise Edition은 안정적이고 신뢰할 수있는 고성능 데이터베이스가 필요하고 지원 비용을 기꺼이 지불하는 응용 프로그램에 대한 포괄적 인 상업적 지원을 제공합니다. 버전을 선택할 때 고려 된 요소에는 응용 프로그램 중요도, 예산 책정 및 기술 기술이 포함됩니다. 완벽한 옵션은없고 가장 적합한 옵션 만 있으므로 특정 상황에 따라 신중하게 선택해야합니다.
 설치 후 MySQL을 사용하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
설치 후 MySQL을 사용하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
이 기사는 MySQL 데이터베이스의 작동을 소개합니다. 먼저 MySQLworkBench 또는 명령 줄 클라이언트와 같은 MySQL 클라이언트를 설치해야합니다. 1. MySQL-Uroot-P 명령을 사용하여 서버에 연결하고 루트 계정 암호로 로그인하십시오. 2. CreateABase를 사용하여 데이터베이스를 작성하고 데이터베이스를 선택하십시오. 3. CreateTable을 사용하여 테이블을 만들고 필드 및 데이터 유형을 정의하십시오. 4. InsertInto를 사용하여 데이터를 삽입하고 데이터를 쿼리하고 업데이트를 통해 데이터를 업데이트하고 DELETE를 통해 데이터를 삭제하십시오. 이러한 단계를 마스터하고 일반적인 문제를 처리하는 법을 배우고 데이터베이스 성능을 최적화하면 MySQL을 효율적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
 MySQL 다운로드 파일이 손상되어 설치할 수 없습니다. 수리 솔루션
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:21 AM
MySQL 다운로드 파일이 손상되어 설치할 수 없습니다. 수리 솔루션
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:21 AM
MySQL 다운로드 파일은 손상되었습니다. 어떻게해야합니까? 아아, mySQL을 다운로드하면 파일 손상을 만날 수 있습니다. 요즘 정말 쉽지 않습니다! 이 기사는 모든 사람이 우회를 피할 수 있도록이 문제를 해결하는 방법에 대해 이야기합니다. 읽은 후 손상된 MySQL 설치 패키지를 복구 할 수있을뿐만 아니라 향후에 갇히지 않도록 다운로드 및 설치 프로세스에 대해 더 깊이 이해할 수 있습니다. 파일 다운로드가 손상된 이유에 대해 먼저 이야기합시다. 이에 대한 많은 이유가 있습니다. 네트워크 문제는 범인입니다. 네트워크의 다운로드 프로세스 및 불안정성의 중단으로 인해 파일 손상이 발생할 수 있습니다. 다운로드 소스 자체에도 문제가 있습니다. 서버 파일 자체가 고장 났으며 물론 다운로드하면 고장됩니다. 또한 일부 안티 바이러스 소프트웨어의 과도한 "열정적 인"스캔으로 인해 파일 손상이 발생할 수 있습니다. 진단 문제 : 파일이 실제로 손상되었는지 확인하십시오
 다운로드 후 MySQL을 설치할 수 없습니다
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
다운로드 후 MySQL을 설치할 수 없습니다
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
MySQL 설치 실패의 주된 이유는 다음과 같습니다. 1. 권한 문제, 관리자로 실행하거나 Sudo 명령을 사용해야합니다. 2. 종속성이 누락되었으며 관련 개발 패키지를 설치해야합니다. 3. 포트 충돌, 포트 3306을 차지하는 프로그램을 닫거나 구성 파일을 수정해야합니다. 4. 설치 패키지가 손상되어 무결성을 다운로드하여 확인해야합니다. 5. 환경 변수가 잘못 구성되었으며 운영 체제에 따라 환경 변수를 올바르게 구성해야합니다. 이러한 문제를 해결하고 각 단계를 신중하게 확인하여 MySQL을 성공적으로 설치하십시오.
 MySQL 설치 후 시작할 수없는 서비스에 대한 솔루션
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:18 AM
MySQL 설치 후 시작할 수없는 서비스에 대한 솔루션
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:18 AM
MySQL이 시작을 거부 했습니까? 당황하지 말고 확인합시다! 많은 친구들이 MySQL을 설치 한 후 서비스를 시작할 수 없다는 것을 알았으며 너무 불안했습니다! 걱정하지 마십시오.이 기사는 침착하게 다루고 그 뒤에있는 마스터 마인드를 찾을 수 있습니다! 그것을 읽은 후에는이 문제를 해결할뿐만 아니라 MySQL 서비스에 대한 이해와 문제 해결 문제에 대한 아이디어를 향상시키고보다 강력한 데이터베이스 관리자가 될 수 있습니다! MySQL 서비스는 시작되지 않았으며 간단한 구성 오류에서 복잡한 시스템 문제에 이르기까지 여러 가지 이유가 있습니다. 가장 일반적인 측면부터 시작하겠습니다. 기본 지식 : 서비스 시작 프로세스 MySQL 서비스 시작에 대한 간단한 설명. 간단히 말해서 운영 체제는 MySQL 관련 파일을로드 한 다음 MySQL 데몬을 시작합니다. 여기에는 구성이 포함됩니다
 고로드 애플리케이션의 MySQL 성능을 최적화하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
고로드 애플리케이션의 MySQL 성능을 최적화하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
MySQL 데이터베이스 성능 최적화 안내서 리소스 집약적 응용 프로그램에서 MySQL 데이터베이스는 중요한 역할을 수행하며 대규모 트랜잭션 관리를 담당합니다. 그러나 응용 프로그램 규모가 확장됨에 따라 데이터베이스 성능 병목 현상은 종종 제약이됩니다. 이 기사는 일련의 효과적인 MySQL 성능 최적화 전략을 탐색하여 응용 프로그램이 고 부하에서 효율적이고 반응이 유지되도록합니다. 실제 사례를 결합하여 인덱싱, 쿼리 최적화, 데이터베이스 설계 및 캐싱과 같은 심층적 인 주요 기술을 설명합니다. 1. 데이터베이스 아키텍처 설계 및 최적화 된 데이터베이스 아키텍처는 MySQL 성능 최적화의 초석입니다. 몇 가지 핵심 원칙은 다음과 같습니다. 올바른 데이터 유형을 선택하고 요구 사항을 충족하는 가장 작은 데이터 유형을 선택하면 저장 공간을 절약 할 수있을뿐만 아니라 데이터 처리 속도를 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
 MySQL 설치 후 데이터베이스 성능을 최적화하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL 설치 후 데이터베이스 성능을 최적화하는 방법
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL 성능 최적화는 설치 구성, 인덱싱 및 쿼리 최적화, 모니터링 및 튜닝의 세 가지 측면에서 시작해야합니다. 1. 설치 후 innodb_buffer_pool_size 매개 변수와 같은 서버 구성에 따라 my.cnf 파일을 조정해야합니다. 2. 과도한 인덱스를 피하기 위해 적절한 색인을 작성하고 Execution 명령을 사용하여 실행 계획을 분석하는 것과 같은 쿼리 문을 최적화합니다. 3. MySQL의 자체 모니터링 도구 (showprocesslist, showstatus)를 사용하여 데이터베이스 건강을 모니터링하고 정기적으로 백업 및 데이터베이스를 구성하십시오. 이러한 단계를 지속적으로 최적화함으로써 MySQL 데이터베이스의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
 MySQL은 인터넷이 필요합니까?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
MySQL은 인터넷이 필요합니까?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
MySQL은 기본 데이터 저장 및 관리를위한 네트워크 연결없이 실행할 수 있습니다. 그러나 다른 시스템과의 상호 작용, 원격 액세스 또는 복제 및 클러스터링과 같은 고급 기능을 사용하려면 네트워크 연결이 필요합니다. 또한 보안 측정 (예 : 방화벽), 성능 최적화 (올바른 네트워크 연결 선택) 및 데이터 백업은 인터넷에 연결하는 데 중요합니다.




