

How to clean up a Linux disk that is full?
1. Check the disk information
df –lh
We can see that the 40G capacity under the mount point /dev/xvda1 under Filesystem has been exhausted. The next step is to delete files that take up a lot of disk space but are useless.
Recommended: "linux tutorial"
2. Locate the largest file directory
cd / #进入根目录。 du -h --max-depth=1 #寻找当前目录,哪个文件夹占用空间最大
You can see that the path /usr occupies a large disk space, occupying 21G. Sharp-eyed students may have seen the last item showing 24G, which means that the total disk space occupied by all files in the current directory is 24G.
Follow the same method, and after several judgments, we located the tomcat log file.
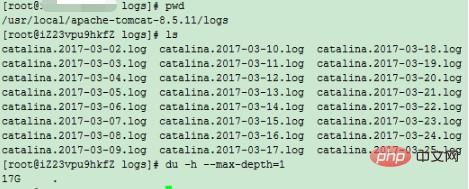
It can be judged from the above figure that the 17G file is in the current directory (tomcat log directory).
3. Locate the largest file
ls –lhS # 将文件以从大到小顺序展现
The final location file is: catalina.out log file.
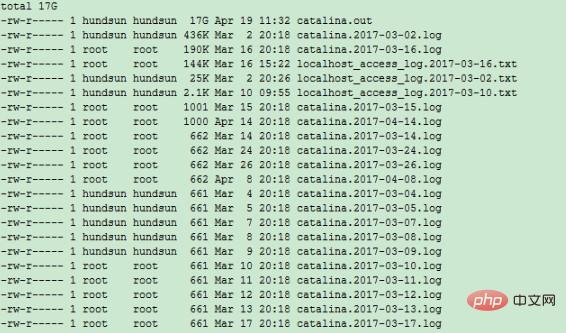
#4. Confirm that the file is not occupied
Anyone can delete a file: rm –f catalina.out However, it is best to confirm Do you want to download it and let developers analyze the logs?
In Linux or Unix systems, deleting a file through rm or the file manager will unlink (unlink) from the file system's directory structure. However, if the file is open (is being used by a process) , then the process will still be able to read the file and the disk space will still be occupied.
/usr/sbin/lsof|grep deleted #确认删除文件是否被占用
is indeed occupied. According to the pid provided in the second column, enter the command: kill -9 13117 Kill the process.

As shown in the figure, the disk space is released. The problem was successfully solved
The above is the detailed content of How to clean up the Linux disk when it is full?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!