New Hash-based Sharding Feature in MongoDB 2.4
Lots of MongoDB users enjoy the flexibility of custom shard keys in organizing a sharded collection’s documents. For certain common workloads though, like key/value lookup, using the natural choice of _id as a shard key isn’t optimal bec
Lots of MongoDB users enjoy the flexibility of custom shard keys in organizing a sharded collection’s documents. For certain common workloads though, like key/value lookup, using the natural choice of _id as a shard key isn’t optimal because default ObjectId’s are ascending, resulting in poor write distribution. ?Creating randomized _ids or choosing another well-distributed field is always possible, but this adds complexity to an app and is another place where something could go wrong.
To help keep these simple workloads simple, in 2.4 MongoDB added the new Hash-based shard key feature. ?The idea behind Hash-based shard keys is that MongoDB will do the work to randomize data distribution for you, based on whatever kind of document identifier you like. ?So long as the identifier has a high cardinality, the documents in your collection will be spread evenly across the shards of your cluster. ?For heavy workloads with lots of individual document writes or reads (e.g. key/value), this is usually the best choice. ?For workloads where getting ranges of documents is more important (i.e. find recent documents from all users), other choices of shard key may be better suited.
Hash-based sharding in an existing collection
To start off with Hash-based sharding, you need the name of the collection you’d like to shard and the name of the hashed “identifier" field for the documents in the collection. ?For example, we might want to create a sharded “mydb.webcrawler" collection, where each document is usually found by a “url" field. ?We can populate the collection with sample data using:
shell$ wget http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_crawler -O web_crawler.html
shell$ mongo
connecting to: /test
> use mydb
switched to db mydb
> cat("web_crawler.html").split("\n").forEach( function(line){
... var regex = /a href="http://blog.mongodb.org/post/\""([^\"]*)\"/; if (regex.test(line)) { db.webcrawler.insert({ "url" : regex.exec(line)[1] }); }})
> db.webcrawler.find()
...
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5162fba3ad5a8e56b7b36020"), "url" : "/wiki/OWASP" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5162fba3ad5a8e56b7b3603d"), "url" : "/wiki/Image_retrieval" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5162fba3ad5a8e56b7b3603e"), "url" : "/wiki/Video_search_engine" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5162fba3ad5a8e56b7b3603f"), "url" : "/wiki/Enterprise_search" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5162fba3ad5a8e56b7b36040"), "url" : "/wiki/Semantic_search" }
...
Just for this example, we multiply this data ~x2000 (otherwise we won’t get any pre-splitting in the collection because it’s too small):
> for (var i = 0; i
<p><span>Next, we create a hashed index on this field:</span></p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">> db.webcrawler.ensureIndex({ url : "hashed" })As usual, the creation of the hashed index doesn’t prevent other types of indices from being created as well.
Then we shard the “mydb.webcrawler" collection using the same field as a Hash-based shard key:
> db.printShardingStatus(true)
--- Sharding Status ---
sharding version: {
"_id" : 1,
"version" : 3,
"minCompatibleVersion" : 3,
"currentVersion" : 4,
"clusterId" : ObjectId("5163032a622c051263c7b8ce")
}
shards:
{ "_id" : "test-rs0", "host" : "test-rs0/nuwen:31100,nuwen:31101" }
{ "_id" : "test-rs1", "host" : "test-rs1/nuwen:31200,nuwen:31201" }
{ "_id" : "test-rs2", "host" : "test-rs2/nuwen:31300,nuwen:31301" }
{ "_id" : "test-rs3", "host" : "test-rs3/nuwen:31400,nuwen:31401" }
databases:
{ "_id" : "admin", "partitioned" : false, "primary" : "config" }
{ "_id" : "mydb", "partitioned" : true, "primary" : "test-rs0" }
mydb.webcrawler
shard key: { "url" : "hashed" }
chunks:
test-rs0 4
{ "url" : { "$minKey" : 1 } } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-4837773290201122847") } on : test-rs0 { "t" : 1, "i" : 3 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-4837773290201122847") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-2329535691089872938") } on : test-rs0 { "t" : 1, "i" : 4 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-2329535691089872938") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("3244151849123193853") } on : test-rs0 { "t" : 1, "i" : 1 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("3244151849123193853") } -->> { "url" : { "$maxKey" : 1 } } on : test-rs0 { "t" : 1, "i" : 2 }
you can see that the chunk boundaries are 64-bit integers (generated by hashing the “url" field). ?When inserts or queries target particular urls, the query can get routed using the url hash to the correct chunk.
Sharding a new collection
Above we’ve sharded an existing collection, which will result in all the chunks of a collection initially living on the same shard. ?The balancer takes care of moving the chunks around, as usual, until we get an even distribution of data.
Much of the time though, it’s better to shard the collection before we add our data - this way MongoDB doesn’t have to worry about moving around existing data. ?Users of sharded collections are familiar with pre-splitting - where empty chunks can be quickly balanced around a cluster before data is added. ?When sharding a new collection using Hash-based shard keys, MongoDB will take care of the presplitting for you. Similarly sized ranges of the Hash-based key are distributed to each existing shard, which means that no initial balancing is needed (unless of course new shards are added).
Let’s see what happens when we shard a new collection webcrawler_empty the same way:
> sh.stopBalancer()
Waiting for active hosts...
Waiting for the balancer lock...
Waiting again for active hosts after balancer is off...
> db.webcrawler_empty.ensureIndex({ url : "hashed" })
> sh.shardCollection("mydb.webcrawler_empty", { url : "hashed" })
{ "collectionsharded" : "mydb.webcrawler_empty", "ok" : 1 }
> db.printShardingStatus(true)
--- Sharding Status ---
...
mydb.webcrawler_empty
shard key: { "url" : "hashed" }
chunks:
test-rs0 2
test-rs1 2
test-rs2 2
test-rs3 2
{ "url" : { "$minKey" : 1 } } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-6917529027641081850") } on : test-rs0 { "t" : 4, "i" : 2 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-6917529027641081850") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-4611686018427387900") } on : test-rs0 { "t" : 4, "i" : 3 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-4611686018427387900") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-2305843009213693950") } on : test-rs1 { "t" : 4, "i" : 4 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-2305843009213693950") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong(0) } on : test-rs1 { "t" : 4, "i" : 5 }
{ "url" : NumberLong(0) } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("2305843009213693950") } on : test-rs2 { "t" : 4, "i" : 6 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("2305843009213693950") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("4611686018427387900") } on : test-rs2 { "t" : 4, "i" : 7 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("4611686018427387900") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("6917529027641081850") } on : test-rs3 { "t" : 4, "i" : 8 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("6917529027641081850") } -->> { "url" : { "$maxKey" : 1 } } on : test-rs3 { "t" : 4, "i" : 9 }
As you can see, the new empty collection is already well-distributed and ready to use. ?Be aware though - any balancing currently in progress can interfere with moving the empty initial chunks off the initial shard, balancing will take priority (hence the initial stopBalancer step). Like before, eventually the balancer will distribute all empty chunks anyway, but if you are preparing for a immediate data load it’s probably best to stop the balancer beforehand.
That’s it - you now have a pre-split collection on four shards using Hash-based shard keys. ?Queries and updates on exact urls go to randomized shards and are balanced across the cluster:
> db.webcrawler_empty.find({ url: "/wiki/OWASP" }).explain()
{
"clusteredType" : "ParallelSort",
"shards" : {
"test-rs2/nuwen:31300,nuwen:31301" : [ ... ]
...
However, the trade-off with Hash-based shard keys is that ranged queries and multi-updates must hit all shards:
> db.webcrawler_empty.find({ url: /^\/wiki\/OWASP/ }).explain()
{
"clusteredType" : "ParallelSort",
"shards" : {
"test-rs0/nuwen:31100,nuwen:31101" : [ ... ],
"test-rs1/nuwen:31200,nuwen:31201" : [ ... ],
"test-rs2/nuwen:31300,nuwen:31301" : [ ... ],
"test-rs3/nuwen:31400,nuwen:31401" : [ ... ]
...
…
Manual chunk assignment and other caveats
The core benefits of the new Hash-based shard keys are:
-
Easy setup of randomized shard key
-
Automated pre-splitting of empty collections
-
Better distribution of chunks on shards for isolated document writes and reads
The standard split and moveChunk functions do work with Hash-based shard keys, so it’s still possible to balance your collection’s chunks in any way you like. ?However, the usual “find” mechanism used to select chunks can behave a bit unexpectedly since the specifier is a document which is hashed to get the containing chunk. ?To keep things simple, just use the new “bounds” parameter when manually manipulating chunks of hashed collections (or all collections, if you prefer):
> use admin
> db.runCommand({ split : "mydb.webcrawler_empty", bounds : [{ "url" : NumberLong("2305843009213693950") }, { "url" : NumberLong("4611686018427387900") }] })
> db.runCommand({ moveChunk : "mydb.webcrawler_empty", bounds : [{ "url" : NumberLong("2305843009213693950") }, { "url" : NumberLong("4611686018427387900") }], to : "test-rs3" })
There are a few other caveats as well - in particular with tag-aware sharding. ?Tag-aware sharding is a feature we released in MongoDB 2.2, which allows you to attach labels to a subset of shards in a cluster. This is valuable for “pinning" collection data to particular shards (which might be hosted on more powerful hardware, for example). ?You can also tag ranges of a collection differently, such that a collection sharded by { “countryCode" : 1 } would have chunks only on servers in that country.
Hash-based shard keys are compatible with tag-aware sharding. ?As in any sharded collection, you may assign chunks to specific shards, but since the chunk ranges are based on the value of the randomized hash of the shard key instead of the shard key itself, this is usually only useful for tagging the whole range to a specific set of shards:
> sh.addShardTag("test-rs2", "DC1")
sh.addShardTag("test-rs3", "DC1")The above commands assign a hypothetical data center tag “DC1” to shards -rs2 and -rs3, which could indicate that -rs2 and -rs3 are in a particular location. ?Then, by running:
> sh.addTagRange("mydb.webcrawler_empty", { url : MinKey }, { url : MaxKey }, "DC1" )we indicate to the cluster that the mydb.webcrawler_empty collection should only be stored on “DC1” shards. ?After letting the balancer work:
> db.printShardingStatus(true)
--- Sharding Status ---
...
mydb.webcrawler_empty
shard key: { "url" : "hashed" }
chunks:
test-rs2 4
test-rs3 4
{ "url" : { "$minKey" : 1 } } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-6917529027641081850") } on : test-rs2 { "t" : 5, "i" : 0 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-6917529027641081850") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-4611686018427387900") } on : test-rs3 { "t" : 6, "i" : 0 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-4611686018427387900") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("-2305843009213693950") } on : test-rs2 { "t" : 7, "i" : 0 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("-2305843009213693950") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong(0) } on : test-rs3 { "t" : 8, "i" : 0 }
{ "url" : NumberLong(0) } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("2305843009213693950") } on : test-rs2 { "t" : 4, "i" : 6 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("2305843009213693950") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("4611686018427387900") } on : test-rs2 { "t" : 4, "i" : 7 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("4611686018427387900") } -->> { "url" : NumberLong("6917529027641081850") } on : test-rs3 { "t" : 4, "i" : 8 }
{ "url" : NumberLong("6917529027641081850") } -->> { "url" : { "$maxKey" : 1 } } on : test-rs3 { "t" : 4, "i" : 9 }
tag: DC1 { "url" : { "$minKey" : 1 } } -->> { "url" : { "$maxKey" : 1 } }
Again, it doesn’t usually make a lot of sense to tag anything other than the full hashed shard key collection to particular shards - by design, there’s no real way to know or control what data is in what range.
Finally, remember that Hash-based shard keys can (right now) only distribute documents based on the value of a single field. ?So, continuing the example above, it isn’t directly possible to use “url" + “timestamp" as a Hash-based shard key without storing the combination in a single field in your application, for example:
url_and_ts : { url : <url>, timestamp : <timestamp> }</timestamp></url>The sub-document will be hashed as a unit.
If you’re interested in learning more about Hash-based sharding, register for the Hash-based sharding feature demo on May 2.
原文地址:New Hash-based Sharding Feature in MongoDB 2.4, 感谢原作者分享。

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

Video Face Swap
Tukar muka dalam mana-mana video dengan mudah menggunakan alat tukar muka AI percuma kami!

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 Apakah perbezaan antara buat dan baharu dalam bahasa go
Jan 09, 2023 am 11:44 AM
Apakah perbezaan antara buat dan baharu dalam bahasa go
Jan 09, 2023 am 11:44 AM
Perbezaan: 1. Make hanya boleh digunakan untuk memperuntukkan dan memulakan data jenis slice, map dan chan manakala baru boleh memperuntukkan sebarang jenis data. 2. Peruntukan baru mengembalikan penunjuk, iaitu jenis "*Jenis" manakala membuat pulangan rujukan, iaitu Jenis. 3. Ruang yang diperuntukkan oleh baru akan dikosongkan selepas membuat memperuntukkan ruang, ia akan dimulakan.
 Bagaimana untuk menggunakan kata kunci baharu dalam java
May 03, 2023 pm 10:16 PM
Bagaimana untuk menggunakan kata kunci baharu dalam java
May 03, 2023 pm 10:16 PM
1. Konsep Dalam bahasa Java, ungkapan "baru" bertanggungjawab untuk mencipta contoh, di mana pembina dipanggil untuk memulakan contoh; jenis nilai pulangan pembina itu sendiri adalah tidak sah, bukan "pembina mengembalikan yang baru dibuat Rujukan objek", tetapi nilai ungkapan baharu ialah rujukan kepada objek yang baru dibuat. 2. Tujuan: Mencipta objek kelas baharu 3. Mekanisme kerja: Peruntukkan ruang memori untuk ahli objek, dan nyatakan nilai lalai secara eksplisit, lakukan pengiraan kaedah pembinaan, dan kembalikan nilai rujukan dengan kerap bermakna membuka yang baru dalam ingatan Ruang memori diperuntukkan dalam kawasan timbunan dalam ingatan Ia dikawal oleh jvm dan menguruskan memori secara automatik. Di sini kita menggunakan kelas String sebagai contoh. Pu
 Penjelasan terperinci tentang pembahagian data (Sharding) yang dilaksanakan oleh Redis
Jun 20, 2023 pm 04:52 PM
Penjelasan terperinci tentang pembahagian data (Sharding) yang dilaksanakan oleh Redis
Jun 20, 2023 pm 04:52 PM
Redis ialah sistem storan nilai kunci berprestasi tinggi, yang sering digunakan dalam senario aplikasi seperti caching dan kedudukan. Apabila jumlah data menjadi lebih besar dan lebih besar, Redis pada satu mesin mungkin menghadapi kesesakan prestasi Pada masa ini, kami boleh mencapai pengembangan mendatar dengan membahagikan data dan menyimpannya pada berbilang nod Redis. Ini ialah pembahagian data Redis (Sharding). Pembahagian data Redis boleh diselesaikan melalui langkah berikut: Untuk menetapkan peraturan sharding, anda perlu menetapkan peraturan sharding terlebih dahulu. Redis sharding boleh berdasarkan nilai utama
 Oukitel melancarkan telefon pintar C50, WP39 dan WP50 baharu pada harga mesra bajet
Jun 21, 2024 am 07:10 AM
Oukitel melancarkan telefon pintar C50, WP39 dan WP50 baharu pada harga mesra bajet
Jun 21, 2024 am 07:10 AM
 Bagaimanakah pengendali baharu berfungsi dalam js?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:17 AM
Bagaimanakah pengendali baharu berfungsi dalam js?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:17 AM
Bagaimanakah operator baharu dalam js berfungsi? Contoh kod khusus diperlukan. Fungsinya adalah untuk mencipta objek contoh baharu berdasarkan pembina yang ditentukan dan mengembalikan rujukan kepada objek. Apabila menggunakan operator baharu, langkah berikut sebenarnya dilakukan: buat objek kosong baharu arahkan prototaip objek kosong ke objek prototaip pembina; objek); jalankan kod dalam pembina dan berikan objek baharu
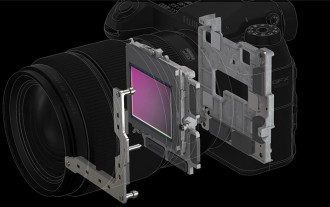 Kamera GFX kanta tetap Fujifilm baharu untuk memperkenalkan sensor format sederhana baharu, boleh memulakan siri serba baharu
Sep 27, 2024 am 06:03 AM
Kamera GFX kanta tetap Fujifilm baharu untuk memperkenalkan sensor format sederhana baharu, boleh memulakan siri serba baharu
Sep 27, 2024 am 06:03 AM
Fujifilm telah melihat banyak kejayaan dalam beberapa tahun kebelakangan ini, sebahagian besarnya disebabkan oleh simulasi filemnya dan populariti kamera gaya jarak jari padatnya di media sosial. Walau bagaimanapun, ia nampaknya tidak berpuas hati dengan kejayaannya, menurut Fujirumors. u
 Bagaimana untuk menggunakan kaedah clone() dalam Java dan bukannya kata kunci baharu?
Apr 22, 2023 pm 07:55 PM
Bagaimana untuk menggunakan kaedah clone() dalam Java dan bukannya kata kunci baharu?
Apr 22, 2023 pm 07:55 PM
Menggunakan clone() dan bukannya new Cara paling biasa untuk mencipta contoh objek baharu dalam Java ialah menggunakan kata kunci baharu. Sokongan JDK untuk baharu sangat baik Apabila menggunakan kata kunci baharu untuk mencipta objek ringan, ia sangat pantas. Walau bagaimanapun, untuk objek berat, masa pelaksanaan pembina mungkin lebih lama kerana objek mungkin melakukan beberapa operasi yang kompleks dan memakan masa dalam pembina. Akibatnya, sistem tidak dapat memperoleh sejumlah besar kejadian dalam jangka pendek. Untuk menyelesaikan masalah ini, anda boleh menggunakan kaedah Object.clone(). Kaedah Object.clone() boleh memintas pembina dan menyalin contoh objek dengan cepat. Walau bagaimanapun, secara lalai, contoh yang dijana oleh kaedah klon() hanyalah salinan cetek objek asal.
 Bagaimana untuk menggunakan instantiasi baru dalam java
May 16, 2023 pm 07:04 PM
Bagaimana untuk menggunakan instantiasi baru dalam java
May 16, 2023 pm 07:04 PM
1. Konsepnya ialah "buat objek Java" ----- peruntukkan memori dan kembalikan rujukan kepada memori tersebut. 2. Nota (1) Kata kunci Java baru ialah operator. Ia mempunyai keutamaan yang sama atau serupa seperti +, -, *, / dan pengendali lain. (2) Mencipta objek Java memerlukan tiga langkah: mengisytiharkan pembolehubah rujukan, membuat instantiate, dan memulakan contoh objek. (3) Sebelum instantiasi, pembina tanpa parameter kelas induk akan dipanggil secara lalai, iaitu objek kelas induk mesti dicipta 3. Dua kaedah instantiasi (1) Nama objek = nama kelas baru (parameter 1,. parameter 2... Parameter n nama objek (); (2) nama kelas baru (parameter 2... parameter n). objek sebenar






