
Isih Buih ialah salah satu algoritma pengisihan paling mudah dalam sains komputer. Dinamakan untuk cara elemen yang lebih kecil "gelembung" ke bahagian atas senarai dengan setiap lelaran, ia merupakan alat yang sangat baik untuk mengajar asas-asas algoritma pengisihan. Walaupun bukan yang paling cekap untuk set data yang besar, kesederhanaannya menjadikannya titik permulaan yang bagus untuk memahami cara algoritma pengisihan berfungsi.
Isih Buih berfungsi dengan berulang kali melangkah melalui senarai, membandingkan elemen bersebelahan dan menukarnya jika tertib tersalah. Proses ini diulang sehingga tiada lagi pertukaran diperlukan, menunjukkan bahawa senarai itu diisih.
Berikut ialah pecahan langkah demi langkah:
Mari kita bayangkan proses ini:
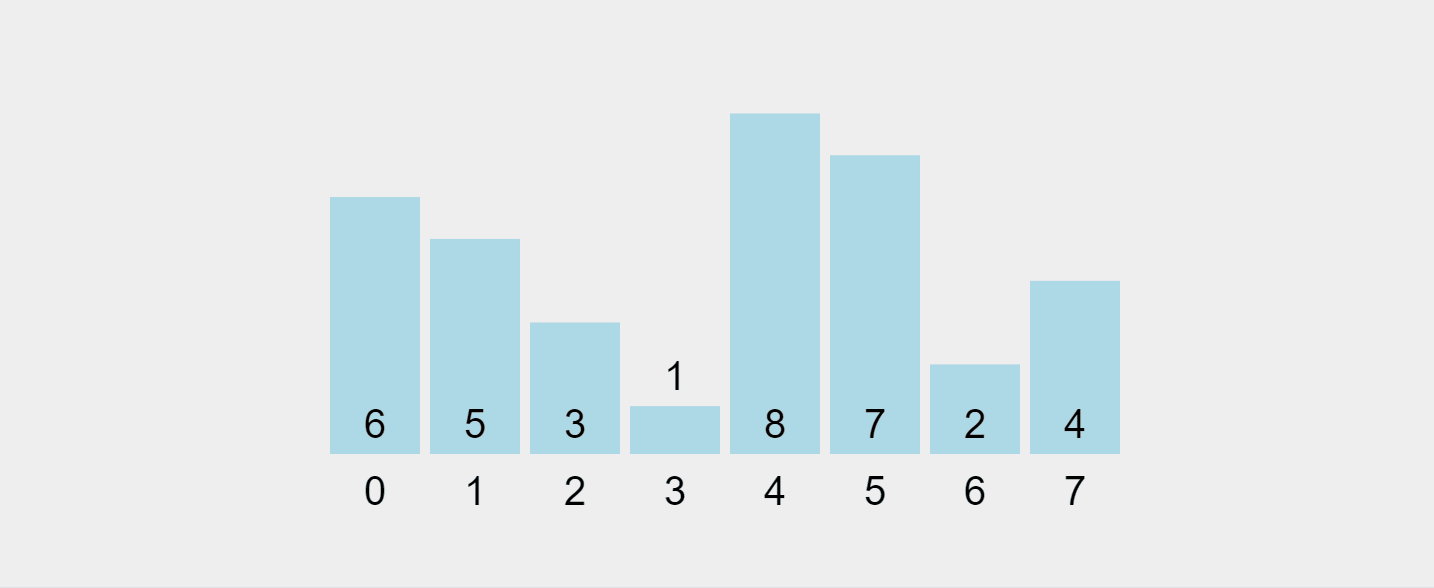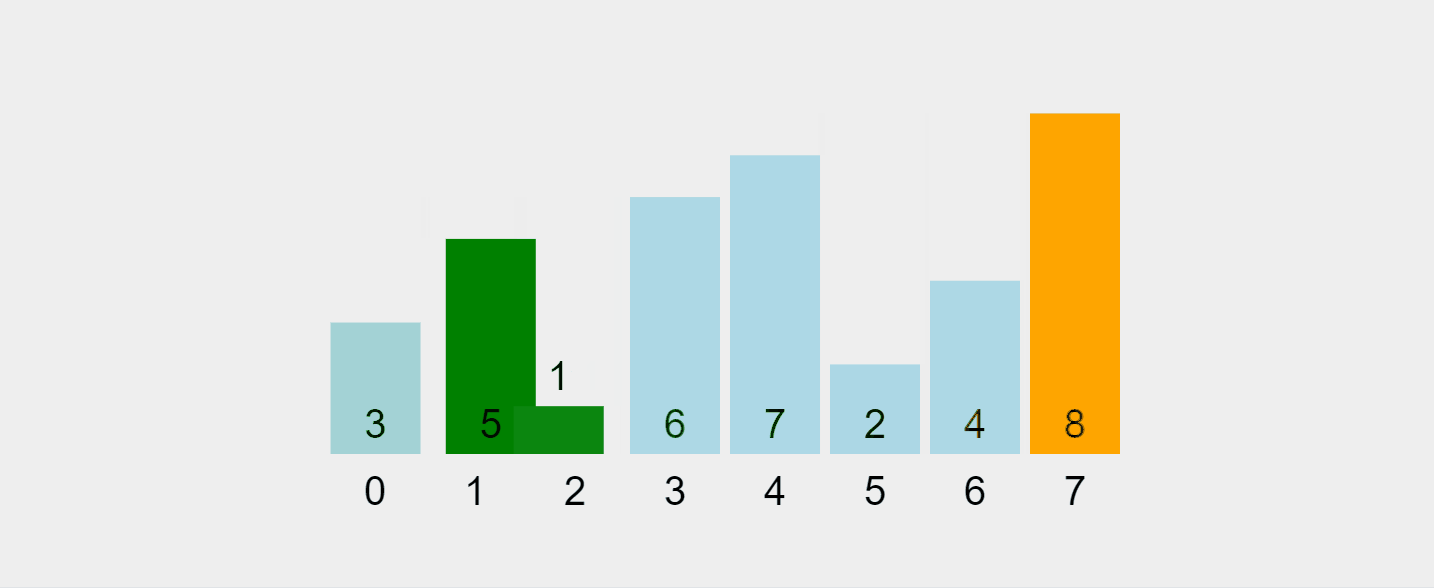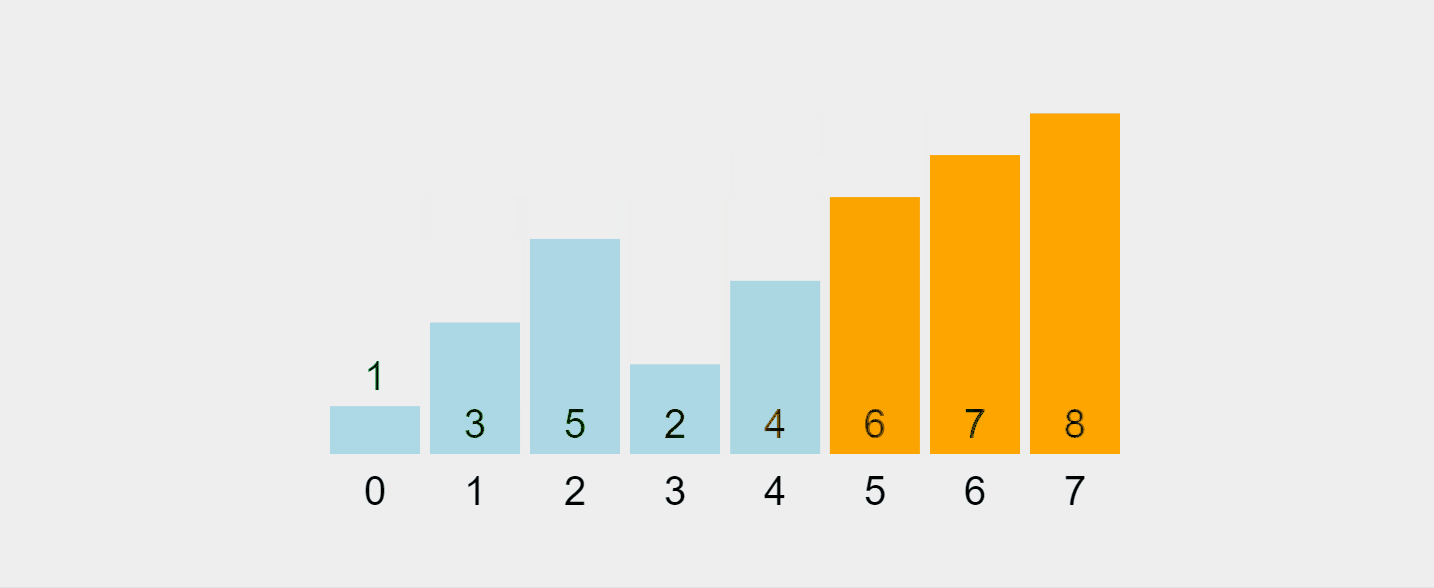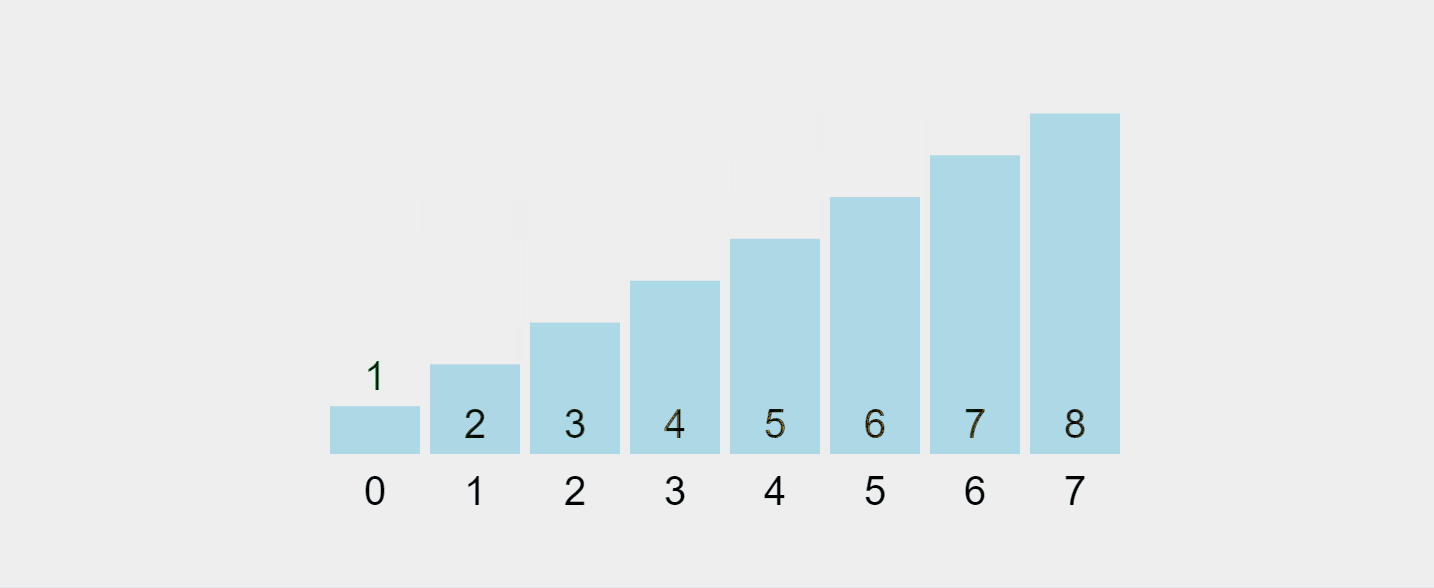
Gif yang dirakam daripada https://visualgo.net/en/sorting
Mari kita periksa tiga pelaksanaan Isih Buih dalam JavaScript, setiap satu dengan tahap pengoptimuman yang semakin meningkat.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
}
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Pelaksanaan asas ini menggunakan gelung bersarang untuk membandingkan dan menukar elemen bersebelahan. Gelung luar memastikan kami membuat hantaran yang mencukupi melalui tatasusunan, manakala gelung dalam melakukan perbandingan dan pertukaran.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Versi ini memperkenalkan bendera bertukar untuk menyemak sama ada sebarang pertukaran dibuat dalam pas. Jika tiada pertukaran berlaku, senarai sudah diisih dan kita boleh keluar dari gelung lebih awal.
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
// Note: We reduce the upper bound by i in each pass
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1 - i; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
Pengoptimuman akhir ini mengurangkan julat gelung dalam sebanyak i dalam setiap hantaran. Ini kerana selepas setiap hantaran, elemen terbesar yang tidak diisih "bergelembung" ke kedudukannya yang betul di penghujung tatasusunan.
Ciri prestasi Bubble Sort adalah seperti berikut:
Kerumitan Masa:
Kerumitan Ruang: O(1) - Isih Buih ialah algoritma pengisihan di tempat, hanya memerlukan jumlah memori tambahan yang tetap.
Berbanding dengan algoritma yang lebih maju seperti Isih Pantas (purata O(n log n)) atau Isih Gabung (O(n log n)), kerumitan masa kuadratik Isih Buih menjadikannya tidak cekap untuk set data yang besar.
Kelebihan:
Kelemahan:
Isih Koktel, juga dikenali sebagai Isih Kocok Koktel atau Isih Buih Dwi Arah, ialah versi Isih Buih yang dipertingkat. Ia merentasi senarai dalam kedua-dua arah, membantu mengalihkan elemen ke kedudukan yang betul dengan lebih cekap.
Cocktail Sort is particularly useful in cases where the array has elements that are initially large at the beginning and small at the end, as it can reduce the total number of passes needed compared to traditional Bubble Sort.
Here's a visualization of Cocktail Sort:
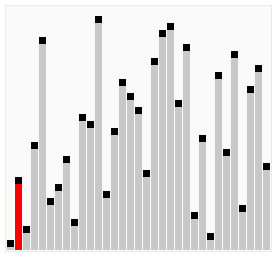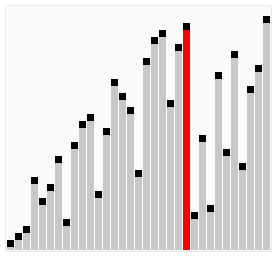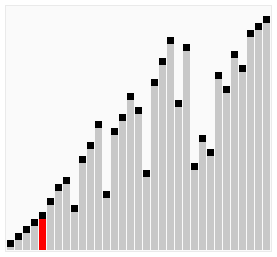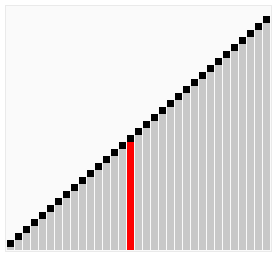
Visual from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cocktail_shaker_sort
function cocktailSort(list) {
let swapped;
// The do...while loop ensures the sorting continues until no swaps are needed
do {
// Reset the swapped flag at the beginning of each complete iteration
swapped = false;
// First pass: left to right (like standard bubble sort)
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in the first pass, the array is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the do...while loop early
}
// Reset the swapped flag for the second pass
swapped = false;
// Second pass: right to left (this is what makes it "cocktail" sort)
for (let i = list.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// The loop will continue if any swaps occurred in either pass
} while (swapped);
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
This implementation alternates between forward and backward passes through the list, potentially reducing the number of iterations needed to sort the array.
While Bubble Sort isn't typically used in production environments for large-scale applications, it can still find use in certain scenarios:
Bubble Sort, despite its inefficiencies with large datasets, offers valuable insights into the world of sorting algorithms and algorithm analysis. Its straightforward approach makes it an excellent teaching tool for beginners in computer science.
Key takeaways are:
While you're unlikely to use Bubble Sort in production code for large-scale applications, the principles behind it are fundamental to many algorithms. The process of optimizing Bubble Sort teaches valuable lessons about algorithm improvement, serving as a stepping stone to more advanced computational problem-solving.
When it comes to algorithms, there's rarely a one-size-fits-all solution. The best algorithm for a given task depends on the specific requirements, constraints, and characteristics of your data. Bubble Sort, with all its limitations, still has its place in this diverse algorithmic ecosystem.
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Pelayaran melalui Algoritma menggunakan Javascript - Bubble Sort. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!




