
ArrayList ialah pelaksanaan antara muka Senarai, yang terdapat di bawah rangka kerja pengumpulan dalam java yang membolehkan kami mengembangkan saiz tatasusunan secara dinamik, iaitu pada masa jalan. Kelas ini tersedia dalam java.util.package secara dalaman, ia menggunakan struktur data tatasusunan. ArrayList membenarkan hanya kelas pembalut dalam java dan pengguna mentakrifkan kelas.
Mulakan Kursus Pembangunan Perisian Percuma Anda
Pembangunan web, bahasa pengaturcaraan, ujian perisian & lain-lain
Sintaks:
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
Kami boleh terus menggunakan contoh ArrayList atau menetapkannya kepada rujukan Senarai.
Pembina:
Dalam senarai tatasusunan, kami mempunyai tiga pembina yang tersedia, iaitu seperti berikut:
Berikut ialah kaedah kelas java ArrayList:
Examples of Java ArrayList Class are given below:
The below example will show how to add an element to an array list.
Code:
package com.cont.article;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArratListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
System.out.println("list is :: " + list);
}
}Output:

Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.addAll(list);
System.out.println("Elements in list one : " + list);
System.out.println("Elements in list two : " + list2);
}
}Output:
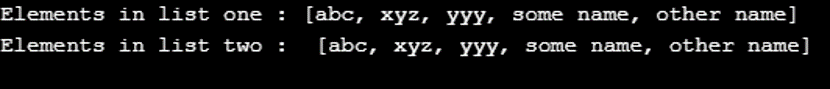
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
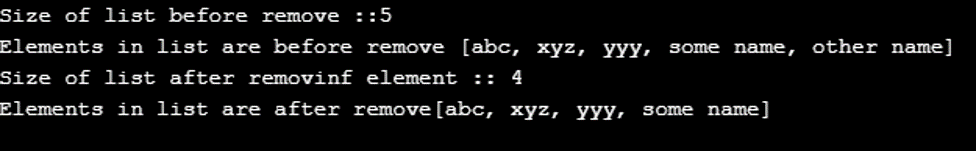
System.out.println("Size of list before remove ::" + list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are before remove " + list);
list.remove(4);
System.out.println("Size of list after removinf element :: " +list.size());
System.out.println("Elements in list are after remove" + list);
}
}Output:
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
list.clear();
System.out.println("Clering all elements of list " +list.size());
}
}Output:

Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("xyz");
list.add("yyy");
list.add("some name");
list.add("other name");
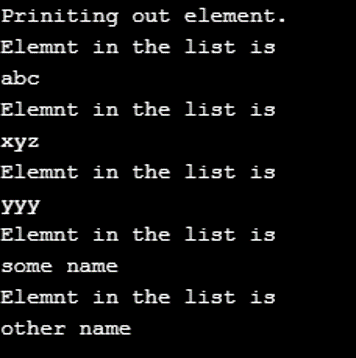
System.out.println("Priniting out element.");
for (String string : list) {
System.out.println("Elemnt in the list is");
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}Output:
The array list in java does not contain duplicate elements. Also, the insertion order is maintained in a list, which means we put over elements that will generate the output in the same sequence. Some detailed points which need to be remembered for the array list in java are as follows:
It implements various interfaces:
The class hierarchy is as follows:
java.lang.Object >> java.util.AbstractCollection<E> >> java.util.AbstractList<E> >> java.util.ArrayList<E>
By default, the array list is not synchronized in nature and is not thread-safe, But we can make them synchronized using the collections class synchronized method. The syntax is described below for reference :
List arrList = Collections.synchronizedList (new ArrayList(...));
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Kelas Java ArrayList. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!




