
Kelas WeightedGraph melanjutkan AbstractGraph.
Bab sebelumnya mereka bentuk antara muka Graf, kelas Graf Abstrak dan kelas Graf Tanpa Warat untuk memodelkan graf. Mengikut corak ini, kami mereka bentuk WeightedGraph sebagai subkelas AbstractGraph, seperti ditunjukkan dalam Rajah di bawah.
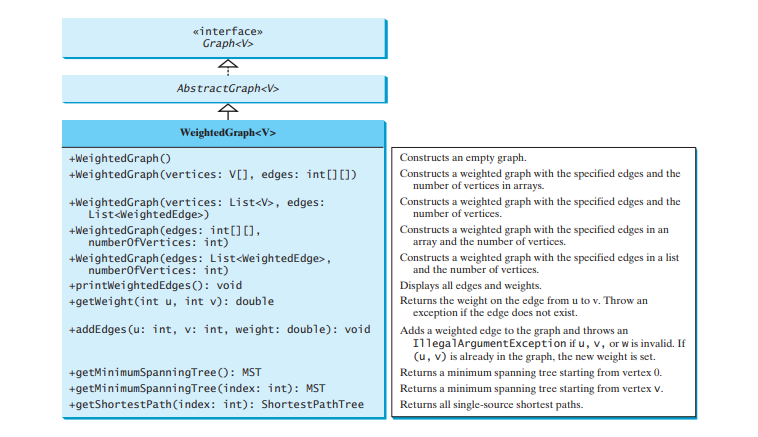
WeightedGraph hanya memanjangkan AbstractGraph dengan lima pembina untuk mencipta konkrit WeightedGraph contoh. WeightedGraph mewarisi semua kaedah daripada AbstractGraph, mengatasi kaedah clear dan addVertex, melaksanakan kaedah addEdge baharu untuk menambah kelebihan berwajaran, dan juga memperkenalkan kaedah baharu untuk mendapatkan pokok rentang minimum dan untuk mencari semua laluan terpendek sumber tunggal. Pokok rentang minimum dan laluan terpendek masing-masing akan diperkenalkan di Bahagian Pokok rentang minimum dan laluan terpendek.
Kod di bawah melaksanakan WeightedGraph. Senarai bersebelahan tepi (baris 38–63) digunakan secara dalaman untuk menyimpan tepi bersebelahan untuk bucu. Apabila WeightedGraph dibina, senarai bersebelahan tepinya dicipta (baris 47 dan 57). Kaedah getMinimumSpanningTree() (baris 99–138) dan getShortestPath() (baris 156–197) akan diperkenalkan dalam bahagian akan datang.
package demo;
import java.util.*;
public class WeightedGraph<V> extends AbstractGraph<V> {
/** Construct an empty */
public WeightedGraph() {}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edged in arrays */
public WeightedGraph(V[] vertices, int[][] edges) {
createWeightedGraph(java.util.Arrays.asList(vertices), edges);
}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edges in list */
public WeightedGraph(int[][] edges, int numberOfVertices) {
List<V> vertices = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfVertices; i++)
vertices.add((V)(new Integer(i)));
createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph for vertices 0, 1, 2 and edge list */
public WeightedGraph(List<V> vertices, List<WeightedEdge> edges) {
createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
}
/** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices 0, 1, and edge array */
public WeightedGraph(List<WeightedEdge> edges, int numberOfVertices) {
List<V> vertices = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfVertices; i++)
vertices.add((V)(new Integer(i)));
createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges);
}
/** Create adjacency lists from edge arrays */
private void createWeightedGraph(List<V> vertices, int[][] edges) {
this.vertices = vertices;
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) {
neighbors.add(new ArrayList<Edge>()); // Create a list for vertices
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
neighbors.get(edges[i][0]).add(new WeightedEdge(edges[i][0], edges[i][1], edges[i][2]));
}
}
/** Create adjacency lists from edge lists */
private void createWeightedGraph(List<V> vertices, List<WeightedEdge> edges) {
this.vertices = vertices;
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) {
neighbors.add(new ArrayList<Edge>()); // Create a list for vertices
}
for (WeightedEdge edge: edges) {
neighbors.get(edge.u).add(edge); // Add an edge into the list
}
}
/** Return the weight on the edge (u, v) */
public double getWeight(int u, int v) throws Exception {
for (Edge edge : neighbors.get(u)) {
if (edge.v == v) {
return ((WeightedEdge)edge).weight;
}
}
throw new Exception("Edge does not exit");
}
/** Display edges with weights */
public void printWeightedEdges() {
for (int i = 0; i < getSize(); i++) {
System.out.print(getVertex(i) + " (" + i + "): ");
for (Edge edge : neighbors.get(i)) {
System.out.print("(" + edge.u + ", " + edge.v + ", " + ((WeightedEdge)edge).weight + ") ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/** Add edges to the weighted graph */
public boolean addEdge(int u, int v, double weight) {
return addEdge(new WeightedEdge(u, v, weight));
}
/** Get a minimum spanning tree rooted at vertex 0 */
public MST getMinimumSpanningTree() {
return getMinimumSpanningTree(0);
}
/** Get a minimum spanning tree rooted at a specified vertex */
public MST getMinimumSpanningTree(int startingVertex) {
// cost[v] stores the cost by adding v to the tree
double[] cost = new double[getSize()];
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
cost[i] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // Initial cost
}
cost[startingVertex] = 0; // Cost of source is 0
int[] parent = new int[getSize()]; // Parent of a vertex
parent[startingVertex] = -1; // startingVertex is the root
double totalWeight = 0; // Total weight of the tree thus far
List<Integer> T = new ArrayList<>();
// Expand T
while (T.size() < getSize()) {
// Find smallest cost v in V - T
int u = -1; // Vertex to be determined
double currentMinCost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < getSize(); i++) {
if (!T.contains(i) && cost[i] < currentMinCost) {
currentMinCost = cost[i];
u = i;
}
}
T.add(u); // Add a new vertex to T
totalWeight += cost[u]; // Add cost[u] to the tree
// Adjust cost[v] for v that is adjacent to u and v in V - T
for (Edge e : neighbors.get(u)) {
if (!T.contains(e.v) && cost[e.v] > ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) {
cost[e.v] = ((WeightedEdge)e).weight;
parent[e.v] = u;
}
}
} // End of while
return new MST(startingVertex, parent, T, totalWeight);
}
/** MST is an inner class in WeightedGraph */
public class MST extends Tree {
private double totalWeight; // Total weight of all edges in the tree
public MST(int root, int[] parent, List<Integer> searchOrder, double totalWeight) {
super(root, parent, searchOrder);
this.totalWeight = totalWeight;
}
public double getTotalWeight() {
return totalWeight;
}
}
/** Find single source shortest paths */
public ShortestPathTree getShortestPath(int sourceVertex) {
// cost[v] stores the cost of the path from v to the source
double[] cost = new double[getSize()];
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
cost[i] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // Initial cost set to infinity
}
cost[sourceVertex] = 0; // Cost of source is 0
// parent[v] stores the previous vertex of v in the path
int[] parent = new int[getSize()];
parent[sourceVertex] = -1; // The parent of source is set to -1
// T stores the vertices whose path found so far
List<Integer> T = new ArrayList<>();
// Expand T
while (T.size() < getSize()) {
// Find smallest cost v in V - T
int u = -1; // Vertex to be determined
double currentMinCost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < getSize(); i++) {
if (!T.contains(i) && cost[i] < currentMinCost) {
currentMinCost = cost[i];
u = i;
}
}
T.add(u); // Add a new vertex to T
// Adjust cost[v] for v that is adjacent to u and v in V - T
for (Edge e : neighbors.get(u)) {
if (!T.contains(e.v) && cost[e.v] > cost[u] + ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) {
cost[e.v] = cost[u] + ((WeightedEdge)e).weight;
parent[e.v] = u;
}
}
} // End of while
// Create a ShortestPathTree
return new ShortestPathTree(sourceVertex, parent, T, cost);
}
/** ShortestPathTree is an inner class in WeightedGraph */
public class ShortestPathTree extends Tree {
private double[] cost; // cost[v] is the cost from v to source
/** Construct a path */
public ShortestPathTree(int source, int[] parent, List<Integer> searchOrder, double[] cost) {
super(source, parent, searchOrder);
this.cost = cost;
}
/** Return the cost for a path from the root to vertex v */
public double getCost(int v) {
return cost[v];
}
/** Print paths from all vertices to the source */
public void printAllPaths() {
System.out.println("All shortest paths from " + vertices.get(getRoot()) + " are:");
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
printPath(i); // Print a path from i to the source
System.out.println("(cost: " + cost[i] + ")"); // Path cost
}
}
}
}
Kelas WeightedGraph memanjangkan kelas AbstractGraph (baris 3). Sifat bucu dan jiran dalam Graf Abstrak diwarisi dalam WeightedGraph.jiran ialah senarai. Setiap elemen ialah senarai adalah senarai lain yang mengandungi tepi. Untuk graf tidak berwajaran, setiap tepi ialah contoh Graf Abstrak. Tepi. Untuk graf berwajaran, setiap tepi ialah contoh WeightedEdge. WeightedEdge ialah subjenis Edge. Jadi anda boleh menambah kelebihan berwajaran ke dalam jiran.get(i) untuk graf berwajaran (baris 47).
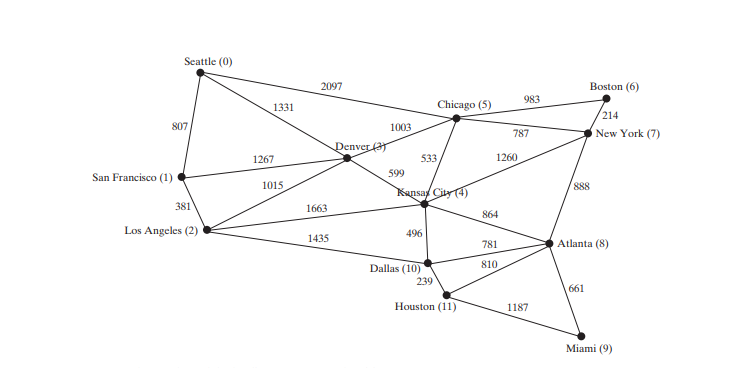
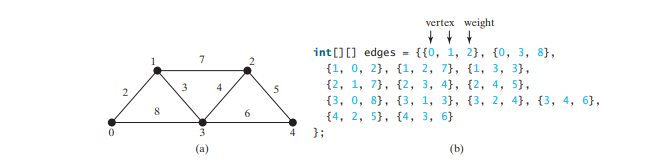
Kod di bawah memberikan program ujian yang mencipta graf untuk yang dalam Rajah di bawah dan graf lain untuk yang dalam Rajah di bawah a.
package demo;
public class TestWeightedGraph {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"};
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097},
{1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267},
{2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435},
{3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003},
{4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496},
{5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787},
{6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214},
{7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888},
{8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810},
{9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187},
{10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239},
{11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239}
};
WeightedGraph<String> graph1 = new WeightedGraph<>(vertices, edges);
System.out.println("The number of vertices in graph1: " + graph1.getSize());
System.out.println("The vertex with index 1 is " + graph1.getVertex(1));
System.out.println("The index for Miami is " + graph1.getIndex("Miami"));
System.out.println("The edges for graph1:");
graph1.printWeightedEdges();
edges = new int[][] {
{0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8},
{1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3},
{2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5},
{3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6},
{4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6}
};
WeightedGraph<Integer> graph2 = new WeightedGraph<>(edges, 5);
System.out.println("\nThe edges for graph2:");
graph2.printWeightedEdges();
}
}
Bilangan bucu dalam graf1: 12
Puncak dengan indeks 1 ialah San Francisco
Indeks untuk Miami ialah 9
Tepi untuk graf1:
Puncak 0: (0, 1, 807) (0, 3, 1331) (0, 5, 2097)
Puncak 1: (1, 2, 381) (1, 0, 807) (1, 3, 1267)
Bucu 2: (2, 1, 381) (2, 3, 1015) (2, 4, 1663) (2, 10, 1435)
Bucu 3: (3, 4, 599) (3, 5, 1003) (3, 1, 1267)
(3, 0, 1331) (3, 2, 1015)
Bucu 4: (4, 10, 496) (4, 8, 864) (4, 5, 533) (4, 2, 1663)
(4, 7, 1260) (4, 3, 599)
Bucu 5: (5, 4, 533) (5, 7, 787) (5, 3, 1003)
(5, 0, 2097) (5, 6, 983)
Bucu 6: (6, 7, 214) (6, 5, 983)
Puncak 7: (7, 6, 214) (7, 8, 888) (7, 5, 787) (7, 4, 1260)
Bucu 8: (8, 9, 661) (8, 10, 781) (8, 4, 864)
(8, 7, 888) (8, 11, 810)
Bucu 9: (9, 8, 661) (9, 11, 1187)
Puncak 10: (10, 11, 239) (10, 4, 496) (10, 8, 781) (10, 2, 1435)
Bucu 11: (11, 10, 239) (11, 9, 1187) (11, 8, 810)
Tepi untuk graf2:
Puncak 0: (0, 1, 2) (0, 3, 8)
Bucu 1: (1, 0, 2) (1, 2, 7) (1, 3, 3)
Bucu 2: (2, 3, 4) (2, 1, 7) (2, 4, 5)
Puncak 3: (3, 1, 3) (3, 4, 6) (3, 2, 4) (3, 0, 8)
Bucu 4: (4, 2, 5) (4, 3, 6)
程序为上图中第 3-27 行的图表创建 graph1。 graph1 的顶点在第 3-5 行中定义。 graph1 的边在第 7-24 行中定义。边缘使用二维数组表示。对于数组中的每一行 i,edges[i][0] 和 edges[i][1] 表示从顶点 edges[i] 有一条边[0] 到顶点 edges[i][1],边的权重为 edges[i][2]。例如,{0, 1, 807}(第 8 行)表示从顶点 0 开始的边 (edges[ 0][0]) 到顶点 1 (边[0][1]),权重 807 (边[0] [2])。 {0, 5, 2097}(第 8 行)表示从顶点 0 开始的边 (edges[2][ 0]) 到顶点 5 (边[2][1]),权重 2097 (边[2][2] )。第 35 行调用 graph1 上的 printWeightedEdges() 方法来显示 graph1 中的所有边。
程序为上图 a 中第 37-44 行中的图形创建 graph2 的边。第 46 行调用 graph2 上的 printWeightedEdges() 方法来显示 graph2 中的所有边。
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Kelas Graf Berwajaran. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikan ralat pangkalan data discuz
Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikan ralat pangkalan data discuz
 penggunaan lateks
penggunaan lateks
 Apakah tapak carian?
Apakah tapak carian?
 Perbezaan antara hibernasi tingkap dan tidur
Perbezaan antara hibernasi tingkap dan tidur
 Rutin permulaan perpustakaan pautan dinamik gagal
Rutin permulaan perpustakaan pautan dinamik gagal
 Bagaimana untuk menyemak port di Linux
Bagaimana untuk menyemak port di Linux
 Mengapa Himalaya tidak boleh menyambung ke Internet?
Mengapa Himalaya tidak boleh menyambung ke Internet?
 Pengenalan kepada kandungan kerja utama bahagian belakang
Pengenalan kepada kandungan kerja utama bahagian belakang
 Cara menutup tetingkap yang dibuka dengan tetingkap.buka
Cara menutup tetingkap yang dibuka dengan tetingkap.buka




