 pembangunan bahagian belakang
pembangunan bahagian belakang
 Tutorial Python
Tutorial Python
 Janus B: Model Bersatu untuk Pemahaman Multimodal dan Tugasan Penjanaan
Janus B: Model Bersatu untuk Pemahaman Multimodal dan Tugasan Penjanaan
Janus B: Model Bersatu untuk Pemahaman Multimodal dan Tugasan Penjanaan
Oct 19, 2024 pm 12:16 PMJanus 1.3B
Janus ialah rangka kerja autoregresif baharu yang menyepadukan pemahaman dan penjanaan pelbagai mod. Tidak seperti model sebelumnya, yang menggunakan pengekod visual tunggal untuk tugas pemahaman dan penjanaan, Janus memperkenalkan dua laluan pengekodan visual yang berasingan untuk fungsi ini.
Perbezaan dalam Pengekodan untuk Pemahaman dan Penjanaan
- Dalam tugas pemahaman multimodal, pengekod visual mengekstrak maklumat semantik peringkat tinggi seperti kategori objek dan atribut visual. Pengekod ini memfokuskan pada menyimpulkan makna yang kompleks, menekankan elemen semantik dimensi lebih tinggi.
- Sebaliknya, dalam tugas penjanaan visual, penekanan diberikan pada penjanaan butiran halus dan mengekalkan konsistensi keseluruhan. Akibatnya, pengekodan dimensi lebih rendah yang boleh menangkap struktur dan tekstur spatial diperlukan.
Menyediakan Persekitaran
Berikut ialah langkah untuk menjalankan Janus dalam Google Colab:
git clone https://github.com/deepseek-ai/Janus cd Janus pip install -e . # If needed, install the following as well # pip install wheel # pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
Tugas Penglihatan
Memuatkan Model
Gunakan kod berikut untuk memuatkan model yang diperlukan untuk tugas penglihatan:
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor from janus.utils.io import load_pil_images # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
Memuatkan dan Menyediakan Imej untuk Pengekodan
Seterusnya, muatkan imej dan tukarkannya kepada format yang boleh difahami oleh model:
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "<image_placeholder>\nDescribe this chart.",
"images": ["images/pie_chart.png"],
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Load the image and prepare input
pil_images = load_pil_images(conversation)
prepare_inputs = vl_chat_processor(
conversations=conversation, images=pil_images, force_batchify=True
).to(vl_gpt.device)
# Run the image encoder and obtain image embeddings
inputs_embeds = vl_gpt.prepare_inputs_embeds(**prepare_inputs)
Menjana Tindak Balas
Akhir sekali, jalankan model untuk menjana respons:
# Run the model and generate a response
outputs = vl_gpt.language_model.generate(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
attention_mask=prepare_inputs.attention_mask,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
bos_token_id=tokenizer.bos_token_id,
eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
max_new_tokens=512,
do_sample=False,
use_cache=True,
)
answer = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0].cpu().tolist(), skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"{prepare_inputs['sft_format'][0]}", answer)
Contoh Output

The image depicts a pie chart that illustrates the distribution of four different categories among four distinct groups. The chart is divided into four segments, each representing a category with a specific percentage. The categories and their corresponding percentages are as follows: 1. **Hogs**: This segment is colored in orange and represents 30.0% of the total. 2. **Frog**: This segment is colored in blue and represents 15.0% of the total. 3. **Logs**: This segment is colored in red and represents 10.0% of the total. 4. **Dogs**: This segment is colored in green and represents 45.0% of the total. The pie chart is visually divided into four segments, each with a different color and corresponding percentage. The segments are arranged in a clockwise manner starting from the top-left, moving clockwise. The percentages are clearly labeled next to each segment. The chart is a simple visual representation of data, where the size of each segment corresponds to the percentage of the total category it represents. This type of chart is commonly used to compare the proportions of different categories in a dataset. To summarize, the pie chart shows the following: - Hogs: 30.0% - Frog: 15.0% - Logs: 10.0% - Dogs: 45.0% This chart can be used to understand the relative proportions of each category in the given dataset.
Output menunjukkan pemahaman yang sesuai tentang imej, termasuk warna dan teksnya.
Tugas Penjanaan Imej
Memuatkan Model
Muatkan model yang diperlukan untuk tugas penjanaan imej dengan kod berikut:
import os import PIL.Image import torch import numpy as np from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
Menyediakan Prompt
Seterusnya, sediakan gesaan berdasarkan permintaan pengguna:
# Set up the prompt
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "cute japanese girl, wearing a bikini, in a beach",
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Convert the prompt into the appropriate format
sft_format = vl_chat_processor.apply_sft_template_for_multi_turn_prompts(
conversations=conversation,
sft_format=vl_chat_processor.sft_format,
system_prompt="",
)
prompt = sft_format + vl_chat_processor.image_start_tag
Menjana Imej
Fungsi berikut digunakan untuk menjana imej. Secara lalai, 16 imej dijana:
@torch.inference_mode()
def generate(
mmgpt: MultiModalityCausalLM,
vl_chat_processor: VLChatProcessor,
prompt: str,
temperature: float = 1,
parallel_size: int = 16,
cfg_weight: float = 5,
image_token_num_per_image: int = 576,
img_size: int = 384,
patch_size: int = 16,
):
input_ids = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer.encode(prompt)
input_ids = torch.LongTensor(input_ids)
tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size*2, len(input_ids)), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(parallel_size*2):
tokens[i, :] = input_ids
if i % 2 != 0:
tokens[i, 1:-1] = vl_chat_processor.pad_id
inputs_embeds = mmgpt.language_model.get_input_embeddings()(tokens)
generated_tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size, image_token_num_per_image), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(image_token_num_per_image):
outputs = mmgpt.language_model.model(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=True,
past_key_values=outputs.past_key_values if i != 0 else None,
)
hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
logits = mmgpt.gen_head(hidden_states[:, -1, :])
logit_cond = logits[0::2, :]
logit_uncond = logits[1::2, :]
logits = logit_uncond + cfg_weight * (logit_cond - logit_uncond)
probs = torch.softmax(logits / temperature, dim=-1)
next_token = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)
generated_tokens[:, i] = next_token.squeeze(dim=-1)
next_token = torch.cat([next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1), next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1)], dim=1).view(-1)
img_embeds = mmgpt.prepare_gen_img_embeds(next_token)
inputs_embeds = img_embeds.unsqueeze(dim=1)
dec = mmgpt.gen_vision_model.decode_code(
generated_tokens.to(dtype=torch.int),
shape=[parallel_size, 8, img_size // patch_size, img_size // patch_size],
)
dec = dec.to(torch.float32).cpu().numpy().transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
dec = np.clip((dec + 1) / 2 * 255, 0, 255)
visual_img = np.zeros((parallel_size, img_size, img_size, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
visual_img[:, :, :] = dec
os.makedirs('generated_samples', exist_ok=True)
for i in range(parallel_size):
save_path = os.path.join('generated_samples', f"img_{i}.jpg")
PIL.Image.fromarray(visual_img[i]).save(save_path)
# Run the image generation
generate(vl_gpt, vl_chat_processor, prompt)
Imej yang dijana akan disimpan dalam folder generated_samples.
Contoh Hasil Dijana
Di bawah ialah contoh imej yang dijana:
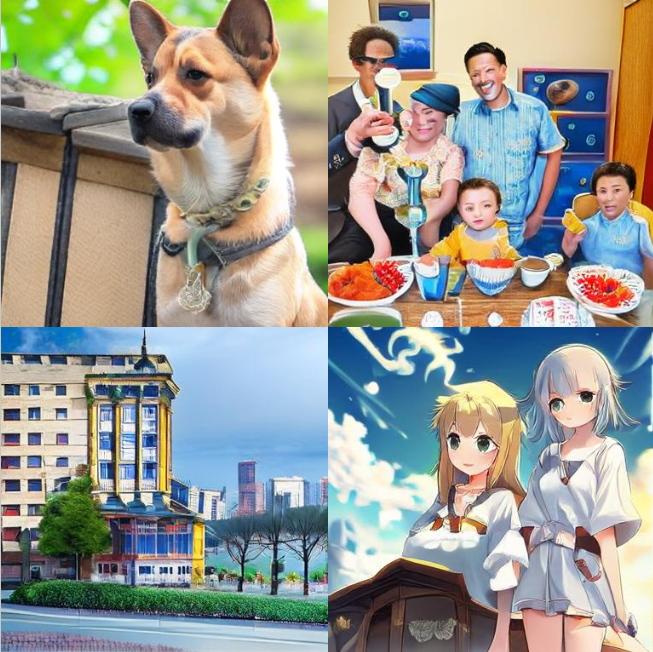

- Anjing digambarkan dengan agak baik.
- Bangunan mengekalkan bentuk keseluruhan, walaupun beberapa butiran, seperti tingkap, mungkin kelihatan tidak realistik.
- Manusia, bagaimanapun, mencabar untuk menjana dengan baik, dengan herotan ketara dalam kedua-dua gaya foto-realistik dan seperti anime.
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Janus B: Model Bersatu untuk Pemahaman Multimodal dan Tugasan Penjanaan. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Artikel Panas

Alat panas Tag

Artikel Panas

Tag artikel panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 Bagaimana saya menggunakan sup yang indah untuk menghuraikan html?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
Bagaimana saya menggunakan sup yang indah untuk menghuraikan html?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
Bagaimana saya menggunakan sup yang indah untuk menghuraikan html?
 Cara Menggunakan Python untuk Mencari Pengagihan Zipf Fail Teks
Mar 05, 2025 am 09:58 AM
Cara Menggunakan Python untuk Mencari Pengagihan Zipf Fail Teks
Mar 05, 2025 am 09:58 AM
Cara Menggunakan Python untuk Mencari Pengagihan Zipf Fail Teks
 Cara Bekerja Dengan Dokumen PDF Menggunakan Python
Mar 02, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Cara Bekerja Dengan Dokumen PDF Menggunakan Python
Mar 02, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Cara Bekerja Dengan Dokumen PDF Menggunakan Python
 Cara Cache Menggunakan Redis dalam Aplikasi Django
Mar 02, 2025 am 10:10 AM
Cara Cache Menggunakan Redis dalam Aplikasi Django
Mar 02, 2025 am 10:10 AM
Cara Cache Menggunakan Redis dalam Aplikasi Django
 Bagaimana untuk melakukan pembelajaran mendalam dengan Tensorflow atau Pytorch?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:52 PM
Bagaimana untuk melakukan pembelajaran mendalam dengan Tensorflow atau Pytorch?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:52 PM
Bagaimana untuk melakukan pembelajaran mendalam dengan Tensorflow atau Pytorch?
 Serialization dan deserialisasi objek python: Bahagian 1
Mar 08, 2025 am 09:39 AM
Serialization dan deserialisasi objek python: Bahagian 1
Mar 08, 2025 am 09:39 AM
Serialization dan deserialisasi objek python: Bahagian 1
 Cara Melaksanakan Struktur Data Anda Sendiri di Python
Mar 03, 2025 am 09:28 AM
Cara Melaksanakan Struktur Data Anda Sendiri di Python
Mar 03, 2025 am 09:28 AM
Cara Melaksanakan Struktur Data Anda Sendiri di Python







