nginx的数据结构1——ngx_int_t与ngx_rbtree_t
面对./src/core子目录中71个源文件,有点无从下手。浏览包含主函数的nginx.c文件,发现nginx使用了很多自行封装的数据结构,不弄清楚这是些什么样的数据结构就很难理解主函数中操作的意义。于是我们挑看起来基础的数据结构开始研究。组织nginx所有数据结构的是ngx_core.h文件。它首先包含了ngx_config.h,我们在ngx_config.h中发现了三个类型定义。
1、ngx_int_t、ngx_uint_t、ngx_flag_t
nginx.c中看到的第一个陌生数据类型是ngx_int_t,在nginx_config.h中找到了它的定义。
typedef intptr_t ngx_int_t; typedef uintptr_t ngx_uint_t; typedef intptr_t ngx_flag_t;
/* Types for `void *' pointers. */ #if __WORDSIZE == 64 # ifndef __intptr_t_defined typedef long int intptr_t; # define __intptr_t_defined # endif typedef unsigned long int uintptr_t; #else # ifndef __intptr_t_defined typedef int intptr_t; # define __intptr_t_defined # endif typedef unsigned int uintptr_t; #endif
2、ngx_rbtree_t
2.1、什么是红黑树
作为一个曾经常年在ACM比赛里划水的退役队员,对红黑树这样的有名数据结构还是比较敏感的。红黑树是一种特殊约束形式下的平衡二叉查找树实现。学过数据结构课的同学应该知道,课本上的最早的自平衡二叉树AVL树严格的要求子树的高度差不超过2,以获得根结点到所有叶结点距离基本相同(平衡)的特性。
红黑树不追求严格的平衡,而是通过5个约束实现基本平衡:
①结点是红色或黑色;
②根是黑色;
③叶结点是黑色;
④红色结点的子结点都是黑色;
⑤任一结点到其叶结点的简单路径中黑色结点数相同。
AVL树根到叶结点最长距离与最短距离的比不超过2。红黑树的约束也保证了这一特性(最长路径是红黑相间,最短路径是全黑,这种情况下最长路径刚好是最短路径的2倍长)。
既然是平衡二叉查找树的一种实现,那么红黑树自然是内部有序的,同时跟AVL树一样支持O(log2n)时间复杂度的查找、插入和删除。
相比AVL树,红黑可以保证在每次插入或删除操作之后的重平衡过程中,全树拓扑结构的更新仅涉及常数个结点。尽管最坏情况下需对O(log2n)个结点重染色,但就分摊意义(平均效率)而言,仅为O(1)个。但是因为没有严格约束树的平衡特性,红黑树的左右子树高度差比AVL树要大。
2.2、ngx_rbtree.h
机会难得,我们就把nginx的源码作为素材来深入了解一下红黑树的实现。首先是结点的结构:
typedef ngx_uint_t ngx_rbtree_key_t;
typedef ngx_int_t ngx_rbtree_key_int_t;
typedef struct ngx_rbtree_node_s ngx_rbtree_node_t;
struct ngx_rbtree_node_s {
ngx_rbtree_key_t key;//平台相关的无符号整型关键字
ngx_rbtree_node_t *left;//左子结点指针
ngx_rbtree_node_t *right;//<span style="font-family:宋体;">右</span>子结点指针
ngx_rbtree_node_t *parent;//父结点指针
u_char color;//结点颜色
u_char data;//结点数据
};然后是红黑树的结构定义:
typedef struct ngx_rbtree_s ngx_rbtree_t; //“_s”是结构体“_t”是类型
//下面是一个函数指针变量类型的定义,是红黑树插入函数的指针
//参数有树根结点、插入结点和哨兵结点的指针
typedef void (*ngx_rbtree_insert_pt) (ngx_rbtree_node_t *root,
ngx_rbtree_node_t *node, ngx_rbtree_node_t *sentinel);
struct ngx_rbtree_s {
ngx_rbtree_node_t *root; //根节点指针
ngx_rbtree_node_t *sentinel; //哨兵结点指针
ngx_rbtree_insert_pt insert; //插入函数指针
};
#define ngx_rbtree_init(tree, s, i) \
ngx_rbtree_sentinel_init(s); \
(tree)->root = s; \
(tree)->sentinel = s; \
(tree)->insert = i//这里insert函数指针的赋值实现了多态
借助宏来达成内联函数的效果(函数实现如果比较简单,就干脆把实现过程整个搬到类中),令人费解的是,C不是没有内联关键字,甚至同一个头文件中就有一个内联函数的定义。研究内联函数之前,下面还有几个宏要看一看:
#define ngx_rbt_red(node) ((node)->color = 1) #define ngx_rbt_black(node) ((node)->color = 0) #define ngx_rbt_is_red(node) ((node)->color) #define ngx_rbt_is_black(node) (!ngx_rbt_is_red(node)) #define ngx_rbt_copy_color(n1, n2) (n1->color = n2->color) /* a sentinel must be black */ #define ngx_rbtree_sentinel_init(node) ngx_rbt_black(node)
nginx源码中的变量都很容易看懂以至于我们不怎么需要查资料或找注释。color置1染红置0染黑,color为1则结点为红色,不为红色的则为黑色,复制结点颜色即复制color值,哨兵结点一定要染成黑色。
static ngx_inline ngx_rbtree_node_t *
ngx_rbtree_min(ngx_rbtree_node_t *node, ngx_rbtree_node_t *sentinel)
{
while (node->left != sentinel) {
node = node->left;
}
return node;
}
ngx_inline是一个宏,实际值就是关键字inline。这个内联函数非常好懂,目的看起来是寻找以任意结点为根结点的子树中结点值最小的结点。实现方法是找到红黑树子树最边缘的左子结点。那么我们有理由猜测,哨兵结点是空结点或边缘标识。
2.3、红黑树的结点插入
接下来我们来深入ngx_rbtree.c看看nginx如何实现几个关键的红黑树方法。
void
ngx_rbtree_insert(ngx_rbtree_t *tree, ngx_rbtree_node_t *node)
{
//根结点指针的指针,或者根结点指针数组,会有多个根结点吗,令人费解
//临时结点指针
//哨兵结点指针,推测哨兵在每次查询时可能都不一样,也许指待插位置
//变量不分行,我写注释都很不方便
ngx_rbtree_node_t **root, *temp, *sentinel;
/* a binary tree insert */
root = (ngx_rbtree_node_t **) &tree->root;//树根指针的指针赋给了root
sentinel = tree->sentinel;//哨兵指针赋给了哨兵指针
if (*root == sentinel) {//特判,如果根是哨兵,即树是空的
node->parent = NULL;//新插入的结点变成了根
node->left = sentinel;//新结点的左子结点是哨兵
node->right = sentinel;//新结点的右子结点也是哨兵
ngx_rbt_black(node);//新根染黑
*root = node;//确认新结点为新根
return;//插入结束
}
//树初始化时给了insert指针一个函数地址
//查看前面的宏ngx_rbtree_init(tree, s, i)
//发现只是把指定结点染黑,同时赋为根和哨兵,给insert指针指定一个函数
//ngx_rbtree.c中有两个参数表符合的可选函数:插入值、插入计时器值
//稍后来看两种插入分别如何实现又有什么区别
tree->insert(*root, node, sentinel);
/* re-balance tree */
//如果新结点不是根且其父结点是红的,循环
while (node != *root && ngx_rbt_is_red(node->parent)) {
//如果父结点是左子结点,获得父结点的右兄弟
if (node->parent == node->parent->parent->left) {
temp = node->parent->parent->right;
//如果父结点的右兄弟是红的
if (ngx_rbt_is_red(temp)) {
ngx_rbt_black(node->parent);//父结点染黑
ngx_rbt_black(temp);//父结点的右兄弟染黑
ngx_rbt_red(node->parent->parent);//父结点的父结点染红
node = node->parent->parent;//父结点的父结点成为当前结点
} else {//如果父结点的右兄弟是黑的
if (node == node->parent->right) {//如果新结点是右子结点
node = node->parent;//父结点成为新node
ngx_rbtree_left_rotate(root, sentinel, node);//node左旋
}
ngx_rbt_black(node->parent);//node的父结点染黑
//node的父结点的父结点染红
ngx_rbt_red(node->parent->parent);
ngx_rbtree_right_rotate(root, sentinel, node->parent->parent);//node的父结点的父结点右旋
}
} else {//如果父结点是右子结点,获得父结点的左兄弟
temp = node->parent->parent->left;
//如果父结点的左兄弟是红的
if (ngx_rbt_is_red(temp)) {
ngx_rbt_black(node->parent);//父结点染黑
ngx_rbt_black(temp);//父结点的左兄弟染黑
ngx_rbt_red(node->parent->parent);//父结点的父结点染红
node = node->parent->parent;
} else {//如果父结点的左兄弟是黑的
if (node == node->parent->left) {//如果新结点是左子结点
node = node->parent;//父结点成为当前结点
ngx_rbtree_right_rotate(root, sentinel, node);
//当前结点右旋
}
ngx_rbt_black(node->parent);//当前结点染黑
//当前结点父结点的父结点染红
ngx_rbt_red(node->parent->parent);
ngx_rbtree_left_rotate(root, sentinel, node->parent->parent);//当前结点的父结点的父结点左旋
}
}
}
ngx_rbt_black(*root);//根结点染黑
}然后是对应ngx_rbtree_insert_pt指针的基础的结点插入函数:
void
ngx_rbtree_insert_value(ngx_rbtree_node_t *temp, ngx_rbtree_node_t *node,
ngx_rbtree_node_t *sentinel)
{
ngx_rbtree_node_t **p;//虽然无关紧要,但两层指针令人费解
for ( ;; ) {//无条件循环或者说死循环,等同于while(1)但节省了一个字符
p = (node->key key) ? &temp->left : &temp->right;
if (*p == sentinel) {//在二叉树中查找新结点合适的叶结点位置
break;
}
temp = *p;
}
//令新结点占据合适的哨兵位置成为新的叶结点,染红,产生新哨兵
*p = node;
node->parent = temp;
node->left = sentinel;
node->right = sentinel;
ngx_rbt_red(node);
}
ngx_rbtree_insert_timer_value函数跟ngx_rbtree_insert_value函数唯一区别就是判断大小时,采用了两个值相减,避免溢出。
以上是插入结点涉及的函数,老实说我不太喜欢这么长的函数实现,换我自己写肯定分块了。分支操作太多,看代码逻辑已经乱了,我们需要画几个图。首先,如果树为空:

如果树中只有一个根结点:

如果C>A:

如果C,C染红,B染黑A染红,A右旋。右旋函数如下:
static ngx_inline void
ngx_rbtree_right_rotate(ngx_rbtree_node_t **root, ngx_rbtree_node_t *sentinel,
ngx_rbtree_node_t *node)
{
ngx_rbtree_node_t *temp;
temp = node->left;
node->left = temp->right;//左子结点指向原左子结点的右结点
if (temp->right != sentinel) {//如果左子结点的右结点不为哨兵
temp->right->parent = node;//左子结点的右子结点挂在右旋结点上
}
temp->parent = node->parent;//左子结点挂在右旋结点的父结点上
if (node == *root) {//如果右旋结点为根节点
*root = temp;//根节点赋为左子结点
} else if (node == node->parent->right) {//如果右旋结点为右子结点
node->parent->right = temp;//左子结点挂父结点右边
} else {//否则左子结点挂父结点左边
node->parent->left = temp;
}
temp->right = node;//右旋结点挂左子结点右边
node->parent = temp;
}
显然B将成为新的根,左C右A:

如果B

其他的插入情景要么与以上几个对称,要么发生在树的其他子树中,实际过程完全一样。LL型右旋,RR型左旋,LR型先右旋后左旋,RL型先左旋后右旋。与AVL树不同的是,插入结点时红黑树左旋或右旋的判定条件明确为附近一两个结点的颜色,其他过程没有任何区别。
2.4、红黑树的结点删除
据说红黑树和AVL树的区别主要体现在删除节点时,我们就来看一看。我刚说什么来着,删除结点的函数体更长了,足足165行,我决定分段研究,先看第一部分:
if (node->left == sentinel) {//如果左子结点是哨兵或左右子结点都是哨兵
temp = node->right;//获得右子结点,后面让它接替node位置
subst = node;//node赋给subst
} else if (node->right == sentinel) {//如果右子结点是哨兵
temp = node->left;//获得左子结点,后面让它接替node位置
subst = node;//node赋给subst
} else {//如果左右子结点都不是哨兵
subst = ngx_rbtree_min(node->right, sentinel);//获得右子树中最小的结点
if (subst->left != sentinel) {//如果右子树的最小结点的左子结点不是哨兵
temp = subst->left;//获得右子树的最小结点的左子结点
} else {//否则获得右子树最小结点的右子结点
temp = subst->right;
}//看起来subst将被从原位置删掉然后接替node的位置
}
下面我们来看看temp和subst要干什么用:
if (subst == *root) {//如果subst是根
*root = temp;//temp接替根
ngx_rbt_black(temp);//染黑temp
/* DEBUG stuff */
node->left = NULL;//清空了待删结点
node->right = NULL;
node->parent = NULL;
node->key = 0;
return;
}
red = ngx_rbt_is_red(subst);//获得subst是否是红色
if (subst == subst->parent->left) {//如果subst是左子结点
subst->parent->left = temp;//把接替结点挂到subst位置
} else {//如果subst是右子结点
subst->parent->right = temp;//把接替结点挂到subst位置
}
if (subst == node) {//如果subst是待删结点
temp->parent = subst->parent;//接替结点直接接替,删除完成
} else {//如果subst不是待删结点
if (subst->parent == node) {//如果subst的父结点就是待删结点
temp->parent = subst;//接替结点挂在subst上
} else {//如果待删结点比subst的父结点更高
temp->parent = subst->parent;//把接替结点挂在subst的父结点上
}
//subst接替待删结点node的位置,复制待删结点跟周围结点的关系
subst->left = node->left;
subst->right = node->right;
subst->parent = node->parent;
ngx_rbt_copy_color(subst, node);//复制颜色
if (node == *root) {//如果待删结点是根
*root = subst;//subst接替根
} else {//如果待删结点不是根,subst接替它
if (node == node->parent->left) {
node->parent->left = subst;
} else {
node->parent->right = subst;
}
}
if (subst->left != sentinel) {//如果subst左子结点不是哨兵
subst->left->parent = subst;//subst的左子结点放弃node,挂上来
}
if (subst->right != sentinel) {//如果subst右子结点不是哨兵
subst->right->parent = subst;//subst右子结点放弃node,挂上来
}
}
//清空待删结点node
/* DEBUG stuff */
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
node->parent = NULL;
node->key = 0;
//如果subst是红色,红黑树约束依然被遵守,删除工作就可以结束了
if (red) {
return;
}
看起来结点的删除过程已经顺利完成了,但是如果subst是黑色,我们需要修复红黑树的约束。下面这一段代码的主角是接替subst位置的temp结点:
//当subst的接替结点不是根且为黑色,循环
while (temp != *root && ngx_rbt_is_black(temp)) {
if (temp == temp->parent->left) {//如果temp是左子结点
w = temp->parent->right;//获得其右兄弟
if (ngx_rbt_is_red(w)) {//如果temp的右兄弟是红色
ngx_rbt_black(w);//染黑temp的右兄弟
ngx_rbt_red(temp->parent);//染红temp的父结点
//temp的父结点左旋
ngx_rbtree_left_rotate(root, sentinel, temp->parent);
w = temp->parent->right;//获得temp的新右兄弟
}
//如果temp右兄弟的左右子结点都是黑的
if (ngx_rbt_is_black(w->left) && ngx_rbt_is_black(w->right)) {
ngx_rbt_red(w);//染红temp的右兄弟
temp = temp->parent;//获得temp的父结点为新temp
} else {//如果temp右兄弟的子结点不全为黑
if (ngx_rbt_is_black(w->right)) {//如果其右子结点是黑色
ngx_rbt_black(w->left);//染黑左子结点
ngx_rbt_red(w);//染红temp的右兄弟
ngx_rbtree_right_rotate(root, sentinel, w);//右兄弟右旋
w = temp->parent->right;//获得temp的新右兄弟
}
//temp右兄弟复制temp父结点颜色
ngx_rbt_copy_color(w, temp->parent);
ngx_rbt_black(temp->parent);//染黑temp父结点
ngx_rbt_black(w->right);//染黑temp右兄弟的右子结点
//temp父结点左旋
ngx_rbtree_left_rotate(root, sentinel, temp->parent);
temp = *root;//获得根
}
} else {//如果temp是右子结点,做对称的事
w = temp->parent->left;
if (ngx_rbt_is_red(w)) {
ngx_rbt_black(w);
ngx_rbt_red(temp->parent);
ngx_rbtree_right_rotate(root, sentinel, temp->parent);
w = temp->parent->left;
}
if (ngx_rbt_is_black(w->left) && ngx_rbt_is_black(w->right)) {
ngx_rbt_red(w);
temp = temp->parent;
} else {
if (ngx_rbt_is_black(w->left)) {
ngx_rbt_black(w->right);
ngx_rbt_red(w);
ngx_rbtree_left_rotate(root, sentinel, w);
w = temp->parent->left;
}
ngx_rbt_copy_color(w, temp->parent);
ngx_rbt_black(temp->parent);
ngx_rbt_black(w->left);
ngx_rbtree_right_rotate(root, sentinel, temp->parent);
temp = *root;
}
}
}
ngx_rbt_black(temp);//染黑当前temp跟插入结点时一样乱,我们梳理一下。
首先忽略红黑树的约束进行删除:
①如果删除的是一个叶结点,即没有后继或后继全为哨兵的结点,直接删除即可;
②如果只有一个后继,让其替换待删除结点即可;
③如果有两个后继,需要从树的边缘选择一个结点,有两种等价的选择,待删结点左子树的最大结点和右子树的最小结点,nginx选择的是后者,以这个结点的键与值(key与value/data)替换待删结点的键与值,然后删除这个替身。
不论是①、②情景中的待删结点还是③情景中替身,在源码中都是subst。下面要围绕着它来进行讨论。
以上是不考虑红黑树平衡性的纯拓扑结构变动。下面要考虑是否调整树的拓扑结构使树重新平衡,是否调整结点的颜色使树重新符合红黑树的约束条件。我们知道红黑树有一条关键约束是任意结点到其子树中叶结点的简单路径中黑色结点数相同。那么如果subst是一个红色结点,我们不需要对红黑树做任何调整,它仍是一棵红黑树;如果subst是黑色的,所有经过subst的简单路径上都会少一个黑色结点数,所以需要进行调整。
下面来根据不同情景分情况讨论,因为二叉树的情景左右颠倒时调整方式也可以左右颠倒,我们只讨论subst是左子结点的情况。设刚接替subst的temp为X,X的新右兄弟为W。从经过简化的源码来看,关于结点颜色的变化很令人费解,我们不妨先来看一看:
①W为红色:将W染黑,将X与W的父结点X->parent染红,X->parent左旋,W重设为X的新右兄弟,然后转入情景①、②或③;
②W为黑色,W两个后继都是黑色:将W染红,X重设为X->parent;
③W为黑色,W右子结点为黑色:将W左子结点染黑,将W染红,W右旋,W重设为X的新右兄弟,然后将X->parent的颜色赋给W,将X->parent染黑,X->parent左旋,根赋给temp;
④W为黑色,W右子结点为红色:将W左子结点染黑,将W染红,W右旋,W重设为X的新右兄弟,然后将X->parent的颜色赋给W,将X->parent染黑,将W右子结点染黑,X->parent左旋,根赋给temp。
最后还要把temp染黑。我们可以看到情景①中进行了一次左旋,情景②只进行了染色,情景③、④都进行了一次右旋和一次左旋。情景①处理结束时一定还要转入别的情景,情景②、③、④的出现则标志着本次调整的结束。那么,红黑树删除结点后的调整过程中,依情景①循环出现的次数,调整过程中旋转的最多见的次数将是1次、2次、3次,再往上次数越多越罕见(依情景①循环出现的次数),最多旋转次数将可能到达树高即log2n次。生产环境中,删除结点后平均每次调整中旋转的次数就像分析源码之前提到的,将是常数规模的。
接下来我打算以逐步翻新版本的方式重写红黑树,更精细、直观地了解红黑树这一数据结构。而在重写之前,我们需要了解,nginx的红黑中所有的叶结点,都是哨兵(sentinel),这在调整红黑树时达成了对红黑树的一种优化。通过增加一层全黑的子结点,红黑树中实际有值的子树里,就允许在子结点出现红色结点了。虽然我没有证明,但这常数规模地增加了删除结点时的旋转次数,也促进了插入新结点时进行调整的概率(增加了在红色结点下插入新结点的概率),同样增加了旋转的次数。而旋转将压缩红黑树子树的高度,提高查询效率。
在由朴素到精致地重写红黑树的过程中,我将由少到多地考虑使用nginx对红黑树的优化,或者加入我自己的优化。
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
以上就介绍了nginx的数据结构1——ngx_int_t与ngx_rbtree_t,包括了方面的内容,希望对PHP教程有兴趣的朋友有所帮助。

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

Video Face Swap
Tukar muka dalam mana-mana video dengan mudah menggunakan alat tukar muka AI percuma kami!

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
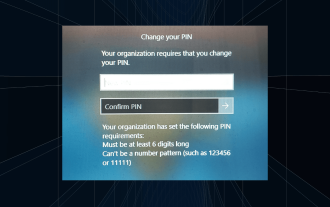 Penyelesaian: Organisasi anda memerlukan anda menukar PIN anda
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
Penyelesaian: Organisasi anda memerlukan anda menukar PIN anda
Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
Mesej "Organisasi anda memerlukan anda menukar PIN anda" akan muncul pada skrin log masuk. Ini berlaku apabila had tamat tempoh PIN dicapai pada komputer menggunakan tetapan akaun berasaskan organisasi, di mana mereka mempunyai kawalan ke atas peranti peribadi. Walau bagaimanapun, jika anda menyediakan Windows menggunakan akaun peribadi, sebaiknya mesej ralat tidak akan muncul. Walaupun ini tidak selalu berlaku. Kebanyakan pengguna yang mengalami ralat melaporkan menggunakan akaun peribadi mereka. Mengapa organisasi saya meminta saya menukar PIN saya pada Windows 11? Ada kemungkinan akaun anda dikaitkan dengan organisasi dan pendekatan utama anda adalah untuk mengesahkan perkara ini. Menghubungi pentadbir domain anda boleh membantu! Selain itu, tetapan dasar tempatan yang salah konfigurasi atau kunci pendaftaran yang salah boleh menyebabkan ralat. Sekarang ni
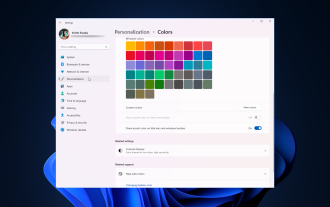 Cara melaraskan tetapan sempadan tetingkap pada Windows 11: Tukar warna dan saiz
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Cara melaraskan tetapan sempadan tetingkap pada Windows 11: Tukar warna dan saiz
Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Windows 11 membawa reka bentuk yang segar dan elegan ke hadapan antara muka moden membolehkan anda memperibadikan dan menukar butiran terbaik, seperti sempadan tingkap. Dalam panduan ini, kami akan membincangkan arahan langkah demi langkah untuk membantu anda mencipta persekitaran yang mencerminkan gaya anda dalam sistem pengendalian Windows. Bagaimana untuk menukar tetapan sempadan tetingkap? Tekan + untuk membuka apl Tetapan. WindowsSaya pergi ke Pemperibadian dan klik Tetapan Warna. Perubahan Warna Tetingkap Sempadan Tetapan Tetingkap 11" Lebar="643" Tinggi="500" > Cari pilihan Tunjukkan warna aksen pada bar tajuk dan sempadan tetingkap, dan togol suis di sebelahnya. Untuk memaparkan warna aksen pada menu Mula dan bar tugas Untuk memaparkan warna tema pada menu Mula dan bar tugas, hidupkan Tunjukkan tema pada menu Mula dan bar tugas
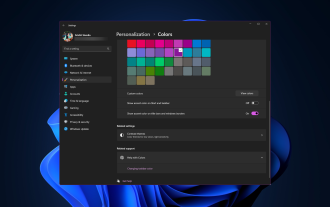 Bagaimana untuk menukar warna bar tajuk pada Windows 11?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Bagaimana untuk menukar warna bar tajuk pada Windows 11?
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Secara lalai, warna bar tajuk pada Windows 11 bergantung pada tema gelap/terang yang anda pilih. Walau bagaimanapun, anda boleh menukarnya kepada mana-mana warna yang anda mahu. Dalam panduan ini, kami akan membincangkan arahan langkah demi langkah untuk tiga cara mengubahnya dan memperibadikan pengalaman desktop anda untuk menjadikannya menarik secara visual. Adakah mungkin untuk menukar warna bar tajuk tetingkap aktif dan tidak aktif? Ya, anda boleh menukar warna bar tajuk tetingkap aktif menggunakan apl Tetapan, atau anda boleh menukar warna bar tajuk tetingkap tidak aktif menggunakan Registry Editor. Untuk mempelajari langkah-langkah ini, pergi ke bahagian seterusnya. Bagaimana untuk menukar warna bar tajuk dalam Windows 11? 1. Tekan + untuk membuka tetingkap tetapan menggunakan apl Tetapan. WindowsSaya pergi ke "Peribadikan" dan kemudian
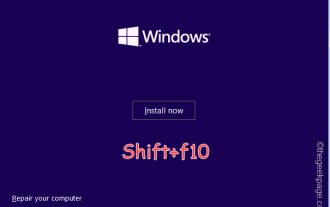 Masalah Ralat OOBELANGUAGE dalam Pembaikan Windows 11/10
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Masalah Ralat OOBELANGUAGE dalam Pembaikan Windows 11/10
Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
Adakah anda melihat "Masalah berlaku" bersama-sama dengan pernyataan "OOBELANGUAGE" pada halaman Pemasang Windows? Pemasangan Windows kadangkala terhenti kerana ralat tersebut. OOBE bermaksud pengalaman di luar kotak. Seperti yang ditunjukkan oleh mesej ralat, ini ialah isu yang berkaitan dengan pemilihan bahasa OOBE. Tiada apa yang perlu dibimbangkan, anda boleh menyelesaikan masalah ini dengan penyuntingan pendaftaran yang bagus dari skrin OOBE itu sendiri. Pembetulan Pantas – 1. Klik butang “Cuba Semula” di bahagian bawah apl OOBE. Ini akan meneruskan proses tanpa gangguan lagi. 2. Gunakan butang kuasa untuk menutup paksa sistem. Selepas sistem dimulakan semula, OOBE harus diteruskan. 3. Putuskan sambungan sistem daripada Internet. Lengkapkan semua aspek OOBE dalam mod luar talian
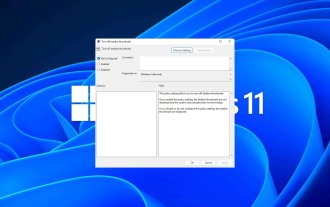 Bagaimana untuk mendayakan atau melumpuhkan pratonton lakaran kecil bar tugas pada Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Bagaimana untuk mendayakan atau melumpuhkan pratonton lakaran kecil bar tugas pada Windows 11
Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Lakaran kecil bar tugas boleh menjadi menyeronokkan, tetapi ia juga boleh mengganggu atau menjengkelkan. Memandangkan kekerapan anda menuding di atas kawasan ini, anda mungkin telah menutup tetingkap penting secara tidak sengaja beberapa kali. Kelemahan lain ialah ia menggunakan lebih banyak sumber sistem, jadi jika anda telah mencari cara untuk menjadi lebih cekap sumber, kami akan menunjukkan kepada anda cara untuk melumpuhkannya. Walau bagaimanapun, jika spesifikasi perkakasan anda boleh mengendalikannya dan anda menyukai pratonton, anda boleh mendayakannya. Bagaimana untuk mendayakan pratonton lakaran kecil bar tugas dalam Windows 11? 1. Menggunakan apl Tetapan ketik kekunci dan klik Tetapan. Windows klik Sistem dan pilih Perihal. Klik Tetapan sistem lanjutan. Navigasi ke tab Lanjutan dan pilih Tetapan di bawah Prestasi. Pilih "Kesan Visual"
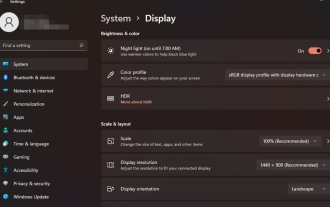 Paparkan panduan penskalaan pada Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Paparkan panduan penskalaan pada Windows 11
Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Kita semua mempunyai pilihan yang berbeza apabila ia berkaitan dengan penskalaan paparan pada Windows 11. Sesetengah orang suka ikon besar, ada yang suka ikon kecil. Walau bagaimanapun, kita semua bersetuju bahawa mempunyai penskalaan yang betul adalah penting. Penskalaan fon yang lemah atau penskalaan berlebihan imej boleh menjadi pembunuh produktiviti sebenar apabila bekerja, jadi anda perlu tahu cara menyesuaikannya untuk memanfaatkan sepenuhnya keupayaan sistem anda. Kelebihan Zum Tersuai: Ini adalah ciri yang berguna untuk orang yang mengalami kesukaran membaca teks pada skrin. Ia membantu anda melihat lebih banyak pada skrin pada satu masa. Anda boleh membuat profil sambungan tersuai yang digunakan hanya pada monitor dan aplikasi tertentu. Boleh membantu meningkatkan prestasi perkakasan kelas rendah. Ia memberi anda lebih kawalan ke atas perkara yang terdapat pada skrin anda. Cara menggunakan Windows 11
 10 Cara untuk Melaraskan Kecerahan pada Windows 11
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
10 Cara untuk Melaraskan Kecerahan pada Windows 11
Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
Kecerahan skrin adalah bahagian penting dalam menggunakan peranti pengkomputeran moden, terutamanya apabila anda melihat skrin untuk jangka masa yang lama. Ia membantu anda mengurangkan ketegangan mata, meningkatkan kebolehbacaan dan melihat kandungan dengan mudah dan cekap. Walau bagaimanapun, bergantung pada tetapan anda, kadangkala sukar untuk mengurus kecerahan, terutamanya pada Windows 11 dengan perubahan UI baharu. Jika anda menghadapi masalah melaraskan kecerahan, berikut ialah semua cara untuk mengurus kecerahan pada Windows 11. Cara Menukar Kecerahan pada Windows 11 [10 Cara Diterangkan] Pengguna monitor tunggal boleh menggunakan kaedah berikut untuk melaraskan kecerahan pada Windows 11. Ini termasuk sistem desktop menggunakan monitor tunggal serta komputer riba. Jom mulakan. Kaedah 1: Gunakan Pusat Tindakan Pusat Tindakan boleh diakses
 Bagaimana untuk Membetulkan Kod Ralat Pengaktifan 0xc004f069 dalam Pelayan Windows
Jul 22, 2023 am 09:49 AM
Bagaimana untuk Membetulkan Kod Ralat Pengaktifan 0xc004f069 dalam Pelayan Windows
Jul 22, 2023 am 09:49 AM
Proses pengaktifan pada Windows kadangkala mengambil giliran secara tiba-tiba untuk memaparkan mesej ralat yang mengandungi kod ralat ini 0xc004f069. Walaupun proses pengaktifan adalah dalam talian, beberapa sistem lama yang menjalankan Windows Server mungkin mengalami masalah ini. Lakukan semakan awal ini dan jika ia tidak membantu anda mengaktifkan sistem anda, lompat ke penyelesaian utama untuk menyelesaikan isu tersebut. Penyelesaian – Tutup mesej ralat dan tetingkap pengaktifan. Kemudian, mulakan semula komputer anda. Cuba semula proses pengaktifan Windows dari awal lagi. Betulkan 1 – Aktifkan dari Terminal Aktifkan sistem Windows Server Edition dari terminal cmd. Peringkat – 1 Semak Versi Pelayan Windows Anda perlu menyemak jenis W yang anda gunakan






