09.Java 基础 - 注解
基本概念
Annotion (注解)是一个接口,程序可以通过反射来获取指定程序元素的 Annotion 对象,然后通过 Annotion 对象来获取注解里面的元数据。
根据注解的使用方法和用途,我们可以将 Annotation 分为三类:系统注解,元注解,自定义注解。
系统注解
系统注解,即 JDK 内置的注解,主要有:@Override,@Deprecated,@SuppressWarnnings。
1.@Override
修饰方法时表示该方法覆盖了父类的方法,或实现接口的方法
interface Demo{ public void print();
}public class Test implements Demo{
@Override
public void print() {
}
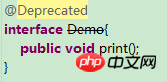
}2.@Deprecated
修饰已经过时的方法
3.@SuppressWarnnings
抑制编译器警告,即去除警告。
常见的参数值有:
| 名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| rawtypes | 表示传参时也要传递带泛型的参数 |
| deprecation | 使用了不赞成使用的类或方法时的警告 |
| unchecked | 执行了未检查的转换时的警告,例如当使用集合时没有用泛型 (Generics) 来指定集合保存的类型 |
| fallthrough | 当 Switch 程序块直接通往下一种情况而没有 Break 时的警告; |
| path | 在类路径、源文件路径等中有不存在的路径时的警告; |
| serial | 当在可序列化的类上缺少 serialVersionUID 定义时的警告; |
| finally | 任何 finally 子句不能正常完成时的警告; |
| all | 关于以上所有情况的警告。 |
实例如下:
// 抑制单类型@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void print() { @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
}// 抑制多类型@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })public void print() {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
}// 抑制所有类型@SuppressWarnings({ "all" })public void print() {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
}元注解
元注解的作用就是负责注解其他注解。Java5.0 定义了4 个标准的 meta-annotation 类型,它们被用来提供对其它 annotation 类型作说明。
定义的元注解如下:@Target,@Retention,@Documented,@Inherited。
1.@Target
@Target 定义了 Annotation所修饰的对象范围,具体的修饰范围如下:
public enum ElementType { // 用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
TYPE, // 用于描述域(即变量)
FIELD, // 用于描述方法
METHOD, // 用于描述参数
PARAMETER, // 用于描述构造器
CONSTRUCTOR, // 用于描述局部变量
LOCAL_VARIABLE, // 用于描述注解类型
ANNOTATION_TYPE, // 用于描述包
PACKAGE
}2.@Retention
@Retention 定义了该 Annotation 被保留的时间长短,即指明了 Annotation 的生命周期。
public enum RetentionPolicy { // 在源文件中有效(编译器要丢弃的注解)
SOURCE, // class 文件中有效(默认,编译器将把注解记录在类文件中,但在运行时 VM 不需要保留注解)
CLASS, // 在运行时有效(编译器将把注解记录在类文件中,在运行时 VM 将保留注解,因此可以反射性地读取)
RUNTIME
}3.@Documented
@Documented 定义 Annotation ,表示某一类型的注解将通过 javadoc 和类似的默认工具进行文档化。
如果类型声明是用 Documented 来注解的,则其注解将成为注解元素的公共 API 的一部分。
4.@Inherited
@Inherited 定义 Annotation ,表示注解类型被自动继承,即一个使用了@Inherited 修饰的annotation 类型被用于一个 class,则这个 annotation 将被用于该class的子类。
使用注解类型注解 class 以外的任何事物,@Inherited 都是无效的。
此元注解仅促成从父类继承注解;对已实现接口的注解无效。
当@Inherited annotation类型标注的annotation的Retention是RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,则反射API增强了这种继承性。如果我们使用java.lang.reflect去查询一个@Inherited annotation类型的annotation时,反射代码检查将展开工作:检查class和其父类,直到发现指定的annotation类型被发现,或者到达类继承结构的顶层
实例如下:
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Inherited@interface MyAnotation{
public String name();
}// 作用在类上@MyAnotation(name="parent")
class Parent{
}// 继承 Parent 类public class Test extends Parent{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> cls = Test.class; // 通过 @Inherited 继承父类的注解
Annotation annotation = cls.getAnnotation(MyAnotation.class);
MyAnotation myAnotation = (MyAnotation) annotation;
System.out.println(myAnotation.name());
}
}// 输出结果:parent(若注释掉注解,返回异常)自定义注解
1.类注解
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@interface MyAnnotation {
public String name(); public String age();
}// 调用注解@MyAnnotation(name="cook",age="100")public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> cls = Test.class; // 1.取得所有注解
Annotation[] annotations =cls.getAnnotations(); // 2.取得指定注解
MyAnnotation annotation =
(MyAnnotation)cls.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
}
}2.方法注解
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 修改作用范围@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@interface MyAnnotation { public String name(); public String age();
}
// 调用注解public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Test.class;
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("print", null); // 1.取得所有注解
Annotation[] annotations = method.getDeclaredAnnotations(); // 2.取得指定注解
MyAnnotation annotation =
(MyAnnotation)method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
}3.参数注解
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 修改作用范围@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)@interface MyAnnotation { public String name(); public String age();
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Test.class;
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod("print", new Class[]{String.class,String.class});
getAllAnnotations(method);
} // 作用在参数上
public void print(@MyAnnotation(name = "cook", age = "100")
String name, String age) { } public static void getAllAnnotations(Method method) {
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotions = method.getParameterAnnotations();
// 通过反射只能取得所有参数类型,不能取得指定参数
Class[] paraemterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
int i = 0;
for (Annotation[] annotations : parameterAnnotions) {
Class paraemterType = paraemterTypes[i++];
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
if (annotation instanceof MyAnnotation) {
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println(paraemterType.getName());
System.out.println(myAnnotation.name());
System.out.println(myAnnotation.age());
}
}
}
}
}4.变量注解
// 定义注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 修改作用范围@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@interface MyAnnotation { public String name(); public String age();
}public class Test {
// 作用在变量上
@MyAnnotation(name = "cook", age = "100")
private String name;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cls = Test.class;
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("name");
Annotation[] fieldAnnotions = field.getDeclaredAnnotations();
MyAnnotation annotation =
(MyAnnotation) field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
}
} 以上就是09.Java 基础 - 注解的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Nombor Sempurna di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Nombor Sempurna di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Panduan Nombor Sempurna di Jawa. Di sini kita membincangkan Definisi, Bagaimana untuk menyemak nombor Perfect dalam Java?, contoh dengan pelaksanaan kod.
 Penjana Nombor Rawak di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Penjana Nombor Rawak di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Panduan untuk Penjana Nombor Rawak di Jawa. Di sini kita membincangkan Fungsi dalam Java dengan contoh dan dua Penjana berbeza dengan contoh lain.
 Weka di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Panduan untuk Weka di Jawa. Di sini kita membincangkan Pengenalan, cara menggunakan weka java, jenis platform, dan kelebihan dengan contoh.
 Nombor Smith di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Nombor Smith di Jawa
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Panduan untuk Nombor Smith di Jawa. Di sini kita membincangkan Definisi, Bagaimana untuk menyemak nombor smith di Jawa? contoh dengan pelaksanaan kod.
 Soalan Temuduga Java Spring
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Soalan Temuduga Java Spring
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Dalam artikel ini, kami telah menyimpan Soalan Temuduga Spring Java yang paling banyak ditanya dengan jawapan terperinci mereka. Supaya anda boleh memecahkan temuduga.
 Cuti atau kembali dari Java 8 Stream Foreach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Cuti atau kembali dari Java 8 Stream Foreach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 memperkenalkan API Stream, menyediakan cara yang kuat dan ekspresif untuk memproses koleksi data. Walau bagaimanapun, soalan biasa apabila menggunakan aliran adalah: bagaimana untuk memecahkan atau kembali dari operasi foreach? Gelung tradisional membolehkan gangguan awal atau pulangan, tetapi kaedah Foreach Stream tidak menyokong secara langsung kaedah ini. Artikel ini akan menerangkan sebab -sebab dan meneroka kaedah alternatif untuk melaksanakan penamatan pramatang dalam sistem pemprosesan aliran. Bacaan Lanjut: Penambahbaikan API Java Stream Memahami aliran aliran Kaedah Foreach adalah operasi terminal yang melakukan satu operasi pada setiap elemen dalam aliran. Niat reka bentuknya adalah
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Panduan untuk TimeStamp to Date di Java. Di sini kita juga membincangkan pengenalan dan cara menukar cap waktu kepada tarikh dalam java bersama-sama dengan contoh.
 Cipta Masa Depan: Pengaturcaraan Java untuk Pemula Mutlak
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Cipta Masa Depan: Pengaturcaraan Java untuk Pemula Mutlak
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java ialah bahasa pengaturcaraan popular yang boleh dipelajari oleh pembangun pemula dan berpengalaman. Tutorial ini bermula dengan konsep asas dan diteruskan melalui topik lanjutan. Selepas memasang Kit Pembangunan Java, anda boleh berlatih pengaturcaraan dengan mencipta program "Hello, World!" Selepas anda memahami kod, gunakan gesaan arahan untuk menyusun dan menjalankan program, dan "Hello, World!" Pembelajaran Java memulakan perjalanan pengaturcaraan anda, dan apabila penguasaan anda semakin mendalam, anda boleh mencipta aplikasi yang lebih kompleks.




