
事件冒泡:事件促发的最深层元素首先接收事件。然后是它的父元素,依次向上,直到document对象最终接收到事件。尽管相对于html元素来说,document没有独立的视觉表现,他仍然是html元素的父元素并且事件能冒泡到document元素。
随便也说一下事件捕获。
事件捕获:事件首先发生在DOM树的最高层对象(document)然后往最深层的元素传播。(注意IE6只有冒泡,没有捕获)
事件委托:我认为事件委托是利用冒泡原理,把事件的监听转换到其父元素上,也就是把事件绑定到父元素上,然后在事件中获取子元素对象,对其进行相应的操作。优点:1.提高性能2.减少代码量
事件默认是在冒泡阶段执行
首先看下面代码:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
var oId1=document.getElementById('id1');
var oId2=document.getElementById('id2');
var oId3=document.getElementById('id3');
oId1.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id1");
});
oId2.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id2");
});
oId3.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id3");
});
}</script><style type="text/css">
*{margin: 0;padding: 0;}</style>
<p id="box" style="background-color:#669;widht:600px; height:400px;">
<p id="id1" style="background-color:#F00;widht:500px;height:300px;">
<p id="id2" style="background-color:#6F9;widht:400px; height:200px;">
<p id="id3" style="background-color:#000;widht:300px; height:100px;">
</p>
</p></p></p>我依次点击id1、id2、id3,执行效果如下图: 
解析:因为点击id3时候,先从id3开始冒泡,执行id3上绑定的事件,在冒泡到id2,执行id2,上面的事件,最后执行id1上面的事件。
现在开始阻止id2的冒泡,修改JS如下
window.onload=function(){
var oId1=document.getElementById('id1');
var oId2=document.getElementById('id2');
var oId3=document.getElementById('id3');
oId1.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id1");
});
oId2.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id2");
e.stopPropagation();
});
oId3.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id3");
});
}
</script>此时,我依次点击id1、id2、id3,执行效果如下图: 
因为事件执行到id2,不在冒泡,故点击id2,id3的时候,不会执行id1绑定的事件。
为了验证事件在捕获阶段执行,我将JS代码改为如下:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
var oId1=document.getElementById('id1');
var oId2=document.getElementById('id2');
var oId3=document.getElementById('id3');
oId1.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id1");
},true);
oId2.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id2");
},true);
oId3.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id3");
},true);
}</script>此时,我依次点击id1、id2、id3,执行效果如下图: 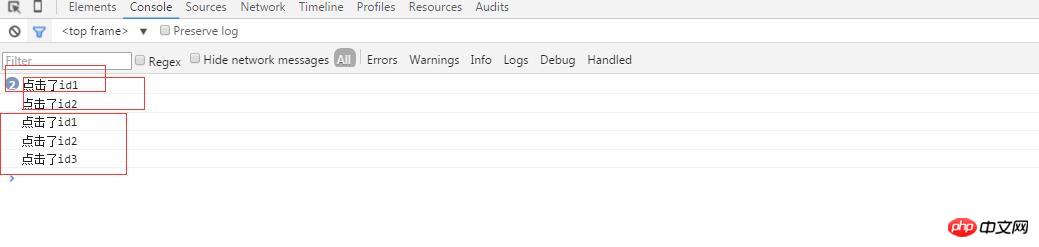
解析:每次点击,事件都会从根元素开始开始执行,即捕获到,如果有事件,就执行。
此时,我将JS代码改为如下:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
var oId1=document.getElementById('id1');
var oId2=document.getElementById('id2');
var oId3=document.getElementById('id3');
oId1.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id1");
},true);
oId2.addEventListener('click',function(e){
e.stopPropagation();
console.log("点击了id2");
},true);
oId3.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id3");
},true);
}</script>此时,我依次点击id1、id2、id3,执行效果如下图: 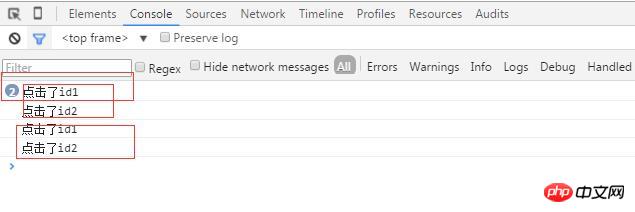
从中发现了,一个现象,我点击id3的时候,发现执行了id1和id2上面绑定的事件,为什么不执行id3上面的事件呢?原来是因为取消冒泡e.stopPropagation();,也阻止了事件的捕获。
现在我将JS修改为如下:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
var oId1=document.getElementById('id1');
var oId2=document.getElementById('id2');
var oId3=document.getElementById('id3');
oId1.onclick=function(){ //该事件在冒泡阶段执行
console.log("点击了id1");
}
oId2.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id2");
},true);
oId3.addEventListener('click',function(e){
console.log("点击了id3");
},true);
}</script>此时,我依次点击id1、id2、id3,执行效果如下图: 
下面代码,当我在box绑定click事件的时候,通过e.srcElement,可以获取点击的是哪个元素。
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
var oBox=document.getElementById('box');
oBox.onclick=function(e){
var curObj=e.srcElement;
console.log(curObj.id);
}
}</script><style type="text/css">
*{margin: 0;padding: 0;}</style>
<p id="box" style="background-color:#669;widht:600px; height:400px;">
<p id="id1" style="background-color:#F00;widht:500px;height:300px;">
<p id="id2" style="background-color:#6F9;widht:400px; height:200px;">
<p id="id3" style="background-color:#000;widht:300px; height:100px;">
</p>
</p></p></p>
可以看出,我们在box绑定click事件里面能获取点击的元素。
验证事件委托中冒泡
将上面的JS改为如下:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
var oBox=document.getElementById('box');
var oId2=document.getElementById('id2');
oId2.onclick=function(e){
e.stopPropagation();
}
oBox.onclick=function(e){
var curObj=e.srcElement;
console.log(curObj.id);
}
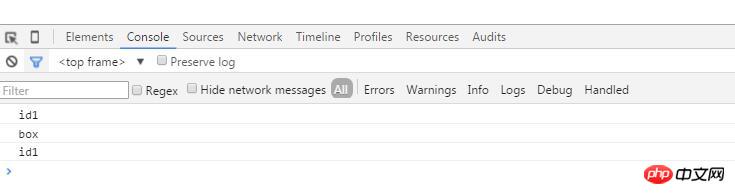
}</script>此时点击,会发现,id2,id3的时候,没法通过e.srcElement获取到。因为我阻止了id2的冒泡。
以上就是Javascript中事件捕获、事件冒泡以及事件委托机制的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!




