
ASP.NET MVC是一个极具可扩展开发框架,在这篇文章中我将通过它的扩展实现与EntLib的集成,并提供一个完整的解决异常处理解决方案。
EntLib的异常处理应用块(Exception Handling Application Block)是一个不错的异常处理框架,它使我们可以采用配置的方式来定义异常处理策略。而ASP.NET MVC是一个极具可扩展开发框架,在这篇文章中我将通过它的扩展实现与EntLib的集成,并提供一个完整的解决异常处理解决方案。
一、基本异常处理策略
我们首先来讨论我们的解决方案具体采用的异常处理策略:
对于执行Controller的某个Action方法抛出的异常,我们会按照指定配置策略进行处理。我们可以采取日志记录、异常替换和封装这些常用的异常处理方式;
对于处理后的异常,如果异常处理策略规定需要将其抛出,则会自动重定向到与异常类型匹配的出错页面。我们会维护一个异常类型和Error View的匹配关系;
对于处理后的异常,如果异常处理策略规定不需要将其抛出,则会执行与当前Action操作相匹配的错误处理Action进行处理。异常处理Action方法默认采用“On{Action}Error”这样的命名规则,而当前上下文会与异常处理操作方法的参数进行绑定。除次之外,我们会设置当前ModelState的错误信息;
如果用户不曾定义相应的异常处理Action,依然采用“错误页面重定向”方式进行异常处理。
二、通过自定义Action处理异常
为了让读者对上面介绍的异常处理页面有一个深刻的理解,我们来进行一个实例演示。该实例用于模拟用户登录,我们定义了如下一个只包含用户名和密码两个属性的Model:LoginInfoModel。
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models
{
public class LoginInfo
{
[Display(Name ="User Name")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "User Name is manadatory!")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Password")]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password is manadatory!")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}我们定义了如下一个AccountController,它是我们自定义的BaseController的子类。AccountController在构造的时候调用基类构造函数指定的参数代表异常处理策略的配置名称。SignIn方法代表用于进行“登录”的操作,而OnSignInError就表示该操作对应的异常处理操作。如果在SignIn操作中抛出的异常经过处理后无需再抛出,则会通过调用OnSignInError,而此时ModelState已经被设置了相应的错误消息。
public class AccountController BaseController
{
public AccountController()
base("myPolicy")
{ }
public ActionResult SignIn()
{
return View(new LoginInfo());
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult SignIn(LoginInfo loginInfo)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = loginInfo.UserName });
}
if (loginInfo.UserName != "Foo")
{
throw new InvalidUserNameException();
}
if (loginInfo.Password != "password")
{
throw new UserNamePasswordNotMatchException();
}
ViewBag.Message = "Authentication Succeeds!";
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = loginInfo.UserName });
}
public ActionResult OnSignInError(string userName)
{
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = userName });
}
}具体定义在SignIn操作方法中的认证逻辑是这样的:如果用户名不是“Foo”则抛出InvalidUserNameException异常;如果密码不是“password”则抛出UserNamePasswordNotMatchException异常。下面是SignIn操作对应的View的定义:
@model Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.LoginInfo
@{
ViewBag.Title = "SignIn";
}
@Html.ValidationSummary()
@if (ViewBag.Messages != null)
{
@ViewBag.Messages
}
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.EditorForModel()
<input type="submit" value="SignIn" />
}在AccountController初始化时指定的异常处理策略“myPolicy”定义在如下的配置中。我们专门针对SignIn操作方法抛出的InvalidUserNameException和UserNamePasswordNotMatchException进行了处理,而ErrorMessageSettingHandler是我们自定义的异常处理器,它仅仅用于设置错误消息。如下面的代码片断所示,如果上述的这两种类型的异常被抛出,最终的错误消息会被指定为“User name does not exist!”和“User name does not match password!”。
<exceptionHandling>
<exceptionPolicies>
<add name="myPolicy">
<exceptionTypes>
<add name="InvalidUserNameException"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="None">
<exceptionHandlers>
<add name="ErrorMessageSettingHandler"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.ErrorMessageSettingHandler, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorMessage="User name does not exist!"/>
</exceptionHandlers>
</add>
<add name="UserNamePasswordNotMatchException"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="None">
<exceptionHandlers>
<add name="ErrorMessageSettingHandler"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.ErrorMessageSettingHandler, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorMessage="User name does not match password!"/>
</exceptionHandlers>
</add>
</exceptionTypes>
</add>
</exceptionPolicies>
</exceptionHandling>现在我们通过路由映射将AccountController和Sign设置为默认Controller和Action后,开启我们的应用程序。在输入错误的用户名和错误明码的情况下在ValidationSummary中将自动得到相应的错误消息。
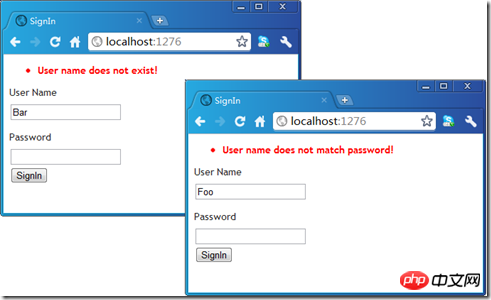
三、通过配置的Error View处理异常
在上面的配置中,针对InvalidUserNameException和UserNamePasswordNotMatchException这两种异常类型的配置策略都将PostHandlingAction属性设置为“None”,意味着不会将原来的异常和处理后的异常进行重新抛出。现在我们将该属性设置为“ThrowNewException”,意味着我们会将处理后的异常重新抛出来。
<exceptionHandling>
<exceptionPolicies>
<add name="myPolicy">
<exceptionTypes>
<add name="InvalidUserNameException" type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="ThrowNewException">
...
<add name="UserNamePasswordNotMatchException" type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="ThrowNewException">
...
</add>
</exceptionTypes>
</add>
</exceptionPolicies>
</exceptionHandling>按照我们上面的异常处理策略,在这种情况下我们将采用“错误页面”的方式来进行异常处理。也HandleErrorAttribute的处理方式类似,我们支持异常类型和Error View之间的匹配关系,而这是通过类似于如下的配置来定义的。值得一提的是,这里的异常类型是经过处理后重新抛出的异常。
<artech.exceptionHandling>
<add exceptionType="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorView="InvalideUserNameError"/>
<add exceptionType="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorView="UserNamePasswordNotMatchError"/>
</artech.exceptionHandling>如上面的配置所示,我们为InvalidUserNameException和UserNamePasswordNotMatchException这两种异常类型定义了不同的Error View,分别是“InvalideUserNameError”和“UserNamePasswordNotMatchError”,详细定义如下所示:
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="colorRed; font-weightbold">Sorry,the user name you specify does not exist!</p>
</body>
</html>
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="colorRed; font-weightbold">Sorry, The password does not match the given user name!</p>
</body>
</html>现在我们按照上面的方式运行我们的程序,在分别输入错误的用户名和密码的情况下会自动显现相应的错误页面。
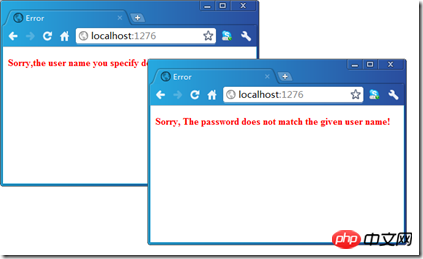
四、自定义ActionInvoker:ExceptionActionInvoker
对于上述的两种不同的异常处理方式最终是通过自定义的ActionInvoker来实现的,我们将其命名为ExceptionActionInvoker。如下面的代码片断所式,ExceptionActionInvoker直接继承自ControllerActionInvoker。属性ExceptionPolicy是一个基于指定的异常策略名称创建的ExceptionPolicyImpl 对象,用于针对EntLib进行的异常处理。而属性GetErrorView是一个用于获得作为错误页面的ViewResult对象的委托。整个异常处理的核心定义在InvokeAction方法中,该方法中指定的handleErrorActionName参数代表的是“异常处理操作名称”,整个方法就是按照上述的异常处理策略实现的。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Common.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.ExceptionHandling;
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling
{
public class ExceptionActionInvoker ControllerActionInvoker
{
protected ExceptionHandlingSettings ExceptionHandlingSettings{get; private set;}
protected virtual Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> GetErrorView { get; private set; }
public ExceptionPolicyImpl ExceptionPolicy { get; private set; }
public ExceptionActionInvoker(string exceptionPolicy,Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> getErrorView)
{
this.ExceptionPolicy = EnterpriseLibraryContainer.Current.GetInstance<ExceptionPolicyImpl>(exceptionPolicy);
this.GetErrorView = getErrorView;
this.ExceptionHandlingSettings = ExceptionHandlingSettings.GetSection();
}
public override bool InvokeAction(ControllerContext controllerContext, string handleErrorActionName)
{
ExceptionContext exceptionContext = controllerContext as ExceptionContext;
if (null == exceptionContext)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The controllerContext must be ExceptionContext!", "controllerContext");
}
try
{
exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled = true;
if (this.ExceptionPolicy.HandleException(exceptionContext.Exception))
{
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
}
else
{
if (ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors.Count == 0)
{
ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors.Add(exceptionContext.Exception.Message);
}
ControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor = this.GetControllerDescriptor(exceptionContext);
ActionDescriptor handleErrorAction = FindAction(exceptionContext, controllerDescriptor, handleErrorActionName);
if (null != handleErrorAction)
{
IDictionary<string, object> parameters = GetParameterValues(controllerContext, handleErrorAction);
exceptionContext.Result = this.InvokeActionMethod(exceptionContext, handleErrorAction, parameters);
}
else
{
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
}
}
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
exceptionContext.Exception = ex;
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
return true;
}
}
protected virtual void HandleRethrownException(ExceptionContext exceptionContext)
{
string errorViewName = this.GetErrorViewName(exceptionContext.Exception.GetType());
string controllerName = (string)exceptionContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller");
string action = (string)exceptionContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
HandleErrorInfo handleErrorInfo = new HandleErrorInfo(exceptionContext.Exception, controllerName, action);
exceptionContext.Result = this.GetErrorView(errorViewName, handleErrorInfo);
}
protected string GetErrorViewName(Type exceptionType)
{
ExceptionErrorViewElement element = ExceptionHandlingSettings.ExceptionErrorViews
.Cast<ExceptionErrorViewElement>().FirstOrDefault(el=>el.ExceptionType == exceptionType);
if(null != element)
{
return element.ErrorView;
}
if(null== element && null != exceptionType.BaseType!= null)
{
return GetErrorViewName(exceptionType.BaseType);
}
else
{
return "Error";
}
}
}
}五、自定义Controller:BaseController
ExceptionActionInvoker最终在我们自定义的Controller基类BaseController中被调用的。ExceptionActionInvoker对象在构造函数中被初始化,并在重写的OnException方法中被调用。
using System;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling
{
public abstract class BaseController Controller
{
public BaseController(string exceptionPolicy)
{
Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> getErrorView = (viewName, handleErrorInfo) => this.View(viewName, handleErrorInfo);
this.ExceptionActionInvoker = new ExceptionActionInvoker(exceptionPolicy,getErrorView);
}
public BaseController(ExceptionActionInvoker actionInvoker)
{
this.ExceptionActionInvoker = actionInvoker;
}
public virtual ExceptionActionInvoker ExceptionActionInvoker { get; private set; }
protected virtual string GetHandleErrorActionName(string actionName)
{
return string.Format("On{0}Error", actionName);
}
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext)
{
using (ExceptionHandlingContextScope contextScope = new ExceptionHandlingContextScope(filterContext))
{
string actionName = RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
string handleErrorActionName = this.GetHandleErrorActionName(actionName);
this.ExceptionActionInvoker.InvokeAction(filterContext, handleErrorActionName);
foreach (var error in ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(Guid.NewGuid().ToString() ,error.ErrorMessage);
}
}
}
}
}值得一提的是:整个OnException方法中的操作都在一个ExceptionHandlingContextScope中进行的。顾名思义, 我们通过ExceptionHandlingContextScope为ExceptionHandlingContext创建了一个范围。ExceptionHandlingContext定义如下,我们可以通过它获得当前的ExceptionContext和ModelErrorCollection,而静态属性Current返回当前的ExceptionHandlingContext对象。
public class ExceptionHandlingContext
{
[ThreadStatic]
private static ExceptionHandlingContext current;
public ExceptionContext ExceptionContext { get; private set; }
public ModelErrorCollection Errors { get; private set; }
public ExceptionHandlingContext(ExceptionContext exceptionContext)
{
this.ExceptionContext = exceptionContext;
this.Errors = new ModelErrorCollection();
}
public static ExceptionHandlingContext Current
{
get { return current; }
set { current = value; }
}
}在BaseController的OnException方法中,当执行了ExceptionActionInvoker的InvokeAction之后,我们会将当前ExceptionHandlingContext的ModelError转移到当前的ModelState中。这就是为什么我们会通过ValidationSummary显示错误信息的原因。对于我们的例子来说,错误消息的指定是通过如下所示的ErrorMessageSettingHandler 实现的,而它仅仅将指定的错误消息添加到当前ExceptionHandlingContext的Errors属性集合中而已。
[ConfigurationElementType(typeof(ErrorMessageSettingHandlerData))]
public class ErrorMessageSettingHandler IExceptionHandler
{
public string ErrorMessage { get; private set; }
public ErrorMessageSettingHandler(string errorMessage)
{
thisErrorMessage = errorMessage;
}
public Exception HandleException(Exception exception, Guid handlingInstanceId)
{
if (null == ExceptionHandlingContextCurrent)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("");
}
if (stringIsNullOrEmpty(thisErrorMessage))
{
ExceptionHandlingContextCurrentErrorsAdd(exceptionMessage);
}
else
{
ExceptionHandlingContextCurrentErrorsAdd(thisErrorMessage);
}
return exception;
}
}【相关推荐】
2.ASP教程
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci ASP.NET下关于EntLib的异常处理的解决方案. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Apakah alat pembangunan asp?
Apakah alat pembangunan asp?
 Bagaimana untuk membuka kunci telefon oppo jika saya terlupa kata laluan
Bagaimana untuk membuka kunci telefon oppo jika saya terlupa kata laluan
 ralat mysql 10060
ralat mysql 10060
 Apakah senario aplikasi mod tunggal PHP?
Apakah senario aplikasi mod tunggal PHP?
 Apakah maksud vram?
Apakah maksud vram?
 Senarai lengkap perintah alter dalam Mysql
Senarai lengkap perintah alter dalam Mysql
 Penjelasan terperinci tentang arahan linux dd
Penjelasan terperinci tentang arahan linux dd
 Bagaimana untuk membeli dan menjual Bitcoin pada platform Ouyi
Bagaimana untuk membeli dan menjual Bitcoin pada platform Ouyi




