jQuery常用工具方法
前面的话
jQuery提供一些与元素无关的工具方法,不必选中元素,就可以直接使用这些方法。如果理解原生javascript的继承原理,那么就能理解工具方法的实质。它是定义在jQuery构造函数上的方法,即jQuery.method(),所以可以直接使用。而那些操作元素的方法,是定义在构造函数的prototype对象上的方法,即jQuery.prototype.method(),所以必须生成实例(即选中元素)后使用。把工具方法理解成像javascript原生函数那样可以直接使用的方法就行了。下面将详细介绍jQuery的常用工具方法
元素相关
【each()】
它是一个通用的迭代函数,可以用来无缝迭代对象和数组。数组和类似数组的对象通过一个长度属性(如一个函数的参数对象)来迭代数字索引,从0到 length - 1。其他对象通过其属性名进行迭代
jQuery.each( collection, callback(indexInArray, valueOfElement) )
jQuery.each()函数和 jQuery(selector).each()不一样,后者专门用来遍历一个jQuery对象。jQuery.each()函数可用于迭代任何集合,无论是“名/值”对象(JavaScript对象)或数组。在迭代数组的情况下,回调函数每次传递一个数组索引和相应的数组值作为参数。(该值也可以通过访问this关键字得到,但是JavaScript将始终将this值作为一个Object ,即使它是一个简单的字符串或数字值。)该方法返回其第一个参数,这是迭代的对象
$.each( ['a','b','c'], function(index,value){//Index #0: a//Index #1: b//Index #2: cconsole.log( "Index #" + index + ": " + value );
});$.each( { name: "John", lang: "JS" }, function(index,value){//Index #name: John//Index #lang: JSconsole.log( "Index #" + index + ": " + value );
});【contains()】
检查一个DOM元素是另一个DOM元素的后代
jQuery.contains( container, contained )
$.contains( document.documentElement, document.body ); // true
【extend()】
将两个或更多对象的内容合并到第一个对象
jQuery.extend( target [, object1 ] [, objectN ] ) target: Object 一个对象,如果附加的对象被传递给这个方法将那么它将接收新的属性,如果它是唯一的参数将扩展jQuery的命名空间。 object1: Object 一个对象,它包含额外的属性合并到第一个参数 objectN: Object 包含额外的属性合并到第一个参数
$.extend({}, object1, object2);jQuery.extend( [deep ], target, object1 [, objectN ] ) deep: Boolean 如果是true,合并成为递归(又叫做深拷贝)。 target: Object 对象扩展。这将接收新的属性。 object1: Object 一个对象,它包含额外的属性合并到第一个参数. objectN: Object 包含额外的属性合并到第一个参数
$.extend(true, object1, object2);
数据相关
【data()】
存储任意数据到指定的元素并且/或者返回设置的值
jQuery.data( element )
element:Element 要关联数据的DOM对象 key: String 存储的数据名 value:Object 新数据值
$.data(document.body, 'foo', 52);
$.data(document.body, 'bar', 'test');
console.log($.data( document.body, 'foo' ));//52console.log($.data( document.body ));//{foo: 52, bar: "test"}【removeData()】
删除一个先前存储的数据片段
jQuery.removeData( element [, name ] )
var div = $("div");
$.data(div, "test1", "VALUE-1");
$.data(div, "test2", "VALUE-2");
console.log($.data(div));//{test1: "VALUE-1", test2: "VALUE-2"}$.removeData(div, "test1");
console.log($.data(div));//{test2: "VALUE-2"}
类型检测
【type()】
type()方法用于检测javascript对象的类型
如果对象是undefined或null,则返回相应的“undefined”或“null”
jQuery.type( undefined ) === "undefined"jQuery.type() === "undefined"jQuery.type( window.notDefined ) === "undefined"jQuery.type( null ) === "null"
如果对象有一个内部的[[Class]]和一个浏览器的内置对象的 [[Class]] 相同,返回相应的 [[Class]] 名字
jQuery.type( true ) === "boolean"jQuery.type( 3 ) === "number"jQuery.type( "test" ) === "string"jQuery.type( function(){} ) === "function"jQuery.type( [] ) === "array"jQuery.type( new Date() ) === "date"jQuery.type( new Error() ) === "error" jQuery.type( /test/ ) === "regexp"所以该方法类似于原生javascript中经过封装的Object.prototype.toString()方法
function type(obj){return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).slice(8,-1).toLowerCase();
}【isArray()】
在原生javascript中,数组检测是一个经典问题,当出现网页中包含多个框架的场景时,数组检测就不再容易
jQuery提供了isArray()方法用来检测数组
console.log($.isArray([]));//true
【isFunction()】
isFunction()方法用来检测传入的参数是否为函数
console.log($.isFunction(function(){}));//true如果使用原生javascript,使用typeof即可实现
console.log(typeof function(){});//"function"【isNumeric()】
isNumeric()方法用来检测传入的参数是否为数字
[注意]参数为纯数字或数字字符串都可以
$.isNumeric("-10"); // true$.isNumeric(-10); // true如果使用原生javascript,使用typeof即可实现,但结果稍有不同
console.log(typeof 10);//"number"console.log(typeof '10');//"string"
【isEmptyObject()】
isEmptyObject()方法用来检测一个对象是否为空对象
jQuery.isEmptyObject({}) // truejQuery.isEmptyObject({ foo: "bar" }) // false【isPlainObject()】
isPlainObject()方法用来检测一个对象是否是原生对象,即通过 "{}" 或者 "new Object" 创建的对象
console.log($.isPlainObject({}));//trueconsole.log($.isPlainObject(document.documentElement));//falseconsole.log($.isPlainObject(new Boolean(true)));//falseconsole.log($.isPlainObject(true));//false
数组相关
【inArray()】
inArray(value, array [, fromIndex ])方法类似于原生javascript的indexOf()方法,没有找到匹配元素时它返回-1。如果数组第一个元素匹配参数,那么$.inArray()返回0
参数fromIndex是数组索引值,表示从哪里在开始查找。默认值是0
var arr = [1,2,3,'1','2','3'];
console.log(arr.indexOf('2'));//4console.log(arr.indexOf(3));//2console.log(arr.indexOf(0));//-1var arr = [1,2,3,'1','2','3'];
console.log($.inArray('2',arr));//4console.log($.inArray(3,arr));//2console.log($.inArray(0,arr));//-1【makeArray()】
makeArray()方法用于将一个类数组对象转换为真正的javascript数组
console.log($.isArray({ 0: 'a', 1: 'b', length: 2 }));//falseconsole.log($.isArray($.makeArray({ 0: 'a', 1: 'b', length: 2 })));//true如果使用原生javascript,可以使用slice()方法将类数组对象变成真正的数组
var arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(arrayLike);
Array.prototype.slice.call({ 0: 'a', 1: 'b', length: 2 })// ['a', 'b']Array.prototype.slice.call(document.querySelectorAll("div"));
Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);【unique()】
unique()方法用于数组去重
var $arr = [document.body,document.body]; console.log($.unique($arr));//[body]var $arr = [1,2,1]; console.log($.unique($arr));//[2,1]
使用原生javascript实现如下
Array.prototype.norepeat = function(){var result = [];for(var i = 0; i < this.length; i++){if(result.indexOf(this[i]) == -1){
result.push(this[i]);
}
}return result;
}var arr = [1,2,1]; console.log(arr.norepeat());//[1,2]var arr = [document.body,document.body]; console.log(arr.norepeat());//[body]
【grep()】
查找满足过滤函数的数组元素。原始数组不受影响
jQuery.grep( array, function(elementOfArray, indexInArray) [, invert ] ) array: Array 用于查询元素的数组。function: Function() 该函数来处理每项元素的比对。第一个参数是正在被检查的数组的元素,第二个参数是该元素的索引值。该函数应返回一个布尔值。this将是全局的window对象。 invert: Boolean 如果“invert”为false,或没有提供,函数返回一个“callback”中返回true的所有元素组成的数组,。如果“invert”为true,函数返回一个“callback”中返回false的所有元素组成的数组。
$.grep()方法会删除数组必要的元素,以使所有剩余元素通过过滤函数的检查。该测试是一个函数传递一个数组元素和该数组内这个的索引值。只有当测试返回true,该数组元素将返回到结果数组中。
该过滤器的函数将被传递两个参数:当前正在被检查的数组中的元素,及该元素的索引值。该过滤器函数必须返回'true'以包含在结果数组项
var result = $.grep( [0,1,2], function(n,i){ return n > 0;
});
console.log(result);//[1, 2]var result = $.grep( [0,1,2], function(n,i){ return n > 0;
},true);
console.log(result);//[0]【merge()】
合并两个数组内容到第一个数组
jQuery.merge( first, second )
console.log($.merge( [0,1,2], [2,3,4] ));//[0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4]
其他
【proxy()】
proxy()方法接受一个函数,然后返回一个新函数,并且这个新函数使用指定的this
proxy()方法类似于bind(),但并不相同。区别在于,bind()方法是改变原函数的this指向,而proxy()方法是新建一个函数,并使用参数中的this指向,原函数的this指向并无变化
var a = 0;function foo(){
console.log(this.a);
}var obj = {
a:2};
foo();//0$.proxy(foo,obj)();//2foo();//0proxy()方法支持多种参数传递方式
function foo(a,b){
console.log(a+b);
}
$.proxy(foo,document)(1,2);//3$.proxy(foo,document,1,2)();//3$.proxy(foo,document,1)(2);//3在绑定事件时一定要合理使用proxy()方法的参数传递方式,否则事件还没有发生,可能函数已经被调用了
$(document).click($.proxy(foo,window,1,2))
【trim()】
jQuery.trim()函数用于去除字符串两端的空白字符
这个函数很简单,没有多余的参数用法
console.log($.trim(" hello, how are you? "));//'hello, how are you?'【noop()】
一个空函数
jQuery.noop() 此方法不接受任何参数
当你仅仅想要传递一个空函数的时候,就用他吧
这对一些插件作者很有用,当插件提供了一个可选的回调函数接口,那么如果调用的时候没有传递这个回调函数,就用jQuery.noop来代替执行
【now()】
返回一个数字,表示当前时间
jQuery.now() 这个方法不接受任何参数
$.now()方法是表达式(new Date).getTime()返回数值的一个简写
【parseHTML()】
将字符串解析到一个DOM节点的数组中
jQuery.parseHTML( data [, context ] [, keepScripts ] ) data : String 用来解析的HTML字符串 context (默认: document): Element DOM元素的上下文,在这个上下文中将创建的HTML片段。 keepScripts (默认: false): Boolean 一个布尔值,表明是否在传递的HTML字符串中包含脚本。
jQuery.parseHTML 使用原生的DOM元素的创建函数将字符串转换为一组DOM元素,然后,可以插入到文档中。
默认情况下,如果没有指定或给定null or undefined,context是当前的document。如果HTML被用在另一个document中,比如一个iframe,该frame的文件可以使用
var result = $.parseHTML( "hello, my name is jQuery");
$('div').append(result);【parseJSON()】
接受一个标准格式的 JSON 字符串,并返回解析后的 JavaScript 对象
jQuery.parseJSON( json )
var obj = jQuery.parseJSON('{"name":"John"}');
console.log(obj.name === "John");//true
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci jQuery常用工具方法. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1377
1377
 52
52
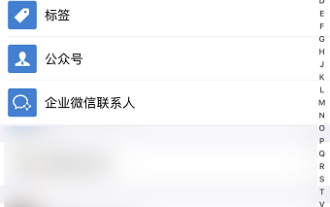 Bagaimana untuk memadam rakan WeChat? Bagaimana untuk memadam rakan WeChat
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
Bagaimana untuk memadam rakan WeChat? Bagaimana untuk memadam rakan WeChat
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
WeChat ialah salah satu alat sembang arus perdana Kami boleh bertemu rakan baru, menghubungi rakan lama dan mengekalkan persahabatan antara rakan melalui WeChat. Sama seperti tidak ada jamuan yang tidak pernah berakhir, perselisihan faham akan berlaku apabila orang ramai bergaul antara satu sama lain. Apabila seseorang sangat mempengaruhi mood anda, atau anda mendapati pandangan anda tidak konsisten apabila anda bergaul, dan anda tidak boleh terus berkomunikasi, maka kami mungkin perlu memadamkan rakan WeChat. Bagaimana untuk memadam rakan WeChat? Langkah pertama untuk memadam rakan WeChat: ketik [Buku Alamat] pada antara muka utama WeChat langkah kedua: klik pada rakan yang ingin anda padamkan dan masukkan [Butiran]; sudut kanan; Langkah 4: Klik [Padam] di bawah Langkah 5: Selepas memahami gesaan halaman, klik [Padam Kenalan];
 Cara menulis novel dalam aplikasi Novel Percuma Tomato Kongsi tutorial cara menulis novel dalam Novel Tomato.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Cara menulis novel dalam aplikasi Novel Percuma Tomato Kongsi tutorial cara menulis novel dalam Novel Tomato.
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Novel Tomato adalah perisian membaca novel yang sangat popular Kami sering mempunyai novel dan komik baru untuk dibaca dalam Novel Tomato Setiap novel dan komik sangat menarik ingin menulis ke dalam teks. Jadi bagaimana kita menulis novel di dalamnya? Kongsi tutorial novel Tomato tentang cara menulis novel 1. Mula-mula buka aplikasi novel percuma Tomato pada telefon bimbit anda dan klik pada Pusat Peribadi - Pusat Penulis 2. Lompat ke halaman Pembantu Penulis Tomato - klik pada Buat buku baru di penghujung novel.
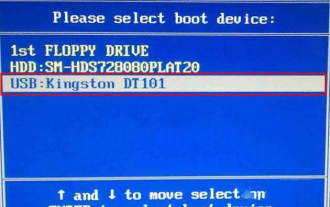 Bagaimana untuk memasukkan bios pada papan induk Berwarna-warni? Ajar anda dua kaedah
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Bagaimana untuk memasukkan bios pada papan induk Berwarna-warni? Ajar anda dua kaedah
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Papan induk berwarna-warni menikmati populariti tinggi dan bahagian pasaran dalam pasaran domestik China, tetapi sesetengah pengguna papan induk Berwarna-warni masih tidak tahu cara memasukkan bios untuk tetapan? Sebagai tindak balas kepada situasi ini, editor telah membawakan anda secara khas dua kaedah untuk memasukkan bios motherboard yang berwarna-warni. Datang dan cuba! Kaedah 1: Gunakan kekunci pintasan permulaan cakera U untuk terus memasuki sistem pemasangan cakera U Kekunci pintasan untuk papan induk Berwarna untuk memulakan cakera U dengan satu klik ialah ESC atau F11 Pertama, gunakan Black Shark Installation Master untuk mencipta Black Cakera but cakera Shark U, dan kemudian hidupkan komputer Apabila anda melihat skrin permulaan, tekan terus kekunci ESC atau F11 pada papan kekunci untuk memasuki tetingkap untuk pemilihan item permulaan secara berurutan ke tempat "USB " dipaparkan, dan kemudian
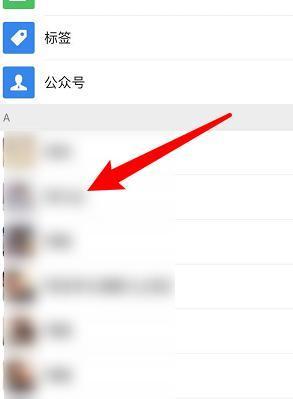 Bagaimana untuk memulihkan kenalan yang dipadam pada WeChat (tutorial mudah memberitahu anda cara memulihkan kenalan yang dipadam)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
Bagaimana untuk memulihkan kenalan yang dipadam pada WeChat (tutorial mudah memberitahu anda cara memulihkan kenalan yang dipadam)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
Malangnya, orang sering memadamkan kenalan tertentu secara tidak sengaja atas sebab tertentu WeChat ialah perisian sosial yang digunakan secara meluas. Untuk membantu pengguna menyelesaikan masalah ini, artikel ini akan memperkenalkan cara mendapatkan semula kenalan yang dipadam dengan cara yang mudah. 1. Fahami mekanisme pemadaman kenalan WeChat Ini memberi kita kemungkinan untuk mendapatkan semula kenalan yang dipadamkan Mekanisme pemadaman kenalan dalam WeChat mengalih keluar mereka daripada buku alamat, tetapi tidak memadamkannya sepenuhnya. 2. Gunakan fungsi "Pemulihan Buku Kenalan" terbina dalam WeChat menyediakan "Pemulihan Buku Kenalan" untuk menjimatkan masa dan tenaga Pengguna boleh mendapatkan semula kenalan yang telah dipadamkan dengan cepat melalui fungsi ini. 3. Masuk ke halaman tetapan WeChat dan klik sudut kanan bawah, buka aplikasi WeChat "Saya" dan klik ikon tetapan di sudut kanan atas untuk memasuki halaman tetapan.
 Ringkasan kaedah untuk mendapatkan hak pentadbir dalam Win11
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Ringkasan kaedah untuk mendapatkan hak pentadbir dalam Win11
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Ringkasan cara mendapatkan hak pentadbir Win11 Dalam sistem pengendalian Windows 11, hak pentadbir adalah salah satu kebenaran yang sangat penting yang membolehkan pengguna melakukan pelbagai operasi pada sistem. Kadangkala, kami mungkin perlu mendapatkan hak pentadbir untuk menyelesaikan beberapa operasi, seperti memasang perisian, mengubah suai tetapan sistem, dsb. Berikut meringkaskan beberapa kaedah untuk mendapatkan hak pentadbir Win11, saya harap ia dapat membantu anda. 1. Gunakan kekunci pintasan Dalam sistem Windows 11, anda boleh membuka gesaan arahan dengan cepat melalui kekunci pintasan.
 Rahsia penetasan telur naga mudah alih terbongkar (langkah demi langkah untuk mengajar anda cara berjaya menetas telur naga mudah alih)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Rahsia penetasan telur naga mudah alih terbongkar (langkah demi langkah untuk mengajar anda cara berjaya menetas telur naga mudah alih)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Permainan mudah alih telah menjadi sebahagian daripada kehidupan orang ramai dengan perkembangan teknologi. Ia telah menarik perhatian ramai pemain dengan imej telur naga yang comel dan proses penetasan yang menarik, dan salah satu permainan yang telah menarik perhatian ramai ialah versi mudah alih Dragon Egg. Untuk membantu pemain memupuk dan mengembangkan naga mereka sendiri dengan lebih baik dalam permainan, artikel ini akan memperkenalkan kepada anda cara menetas telur naga dalam versi mudah alih. 1. Pilih jenis telur naga yang sesuai Pemain perlu berhati-hati memilih jenis telur naga yang mereka suka dan sesuai dengan diri mereka, berdasarkan pelbagai jenis sifat dan kebolehan telur naga yang disediakan dalam permainan. 2. Tingkatkan tahap mesin pengeraman Pemain perlu meningkatkan tahap mesin pengeraman dengan menyelesaikan tugasan dan mengumpul prop Tahap mesin pengeraman menentukan kelajuan penetasan dan kadar kejayaan penetasan. 3. Kumpul sumber yang diperlukan untuk penetasan Pemain perlu berada dalam permainan
 Bagaimana untuk menetapkan saiz fon pada telefon mudah alih (mudah melaraskan saiz fon pada telefon bimbit)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Bagaimana untuk menetapkan saiz fon pada telefon mudah alih (mudah melaraskan saiz fon pada telefon bimbit)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Menetapkan saiz fon telah menjadi keperluan pemperibadian yang penting kerana telefon mudah alih menjadi alat penting dalam kehidupan seharian manusia. Untuk memenuhi keperluan pengguna yang berbeza, artikel ini akan memperkenalkan cara meningkatkan pengalaman penggunaan telefon mudah alih dan melaraskan saiz fon telefon mudah alih melalui operasi mudah. Mengapa anda perlu melaraskan saiz fon telefon mudah alih anda - Melaraskan saiz fon boleh menjadikan teks lebih jelas dan mudah dibaca - Sesuai untuk keperluan membaca pengguna yang berbeza umur - Mudah untuk pengguna yang kurang penglihatan menggunakan saiz fon fungsi tetapan sistem telefon mudah alih - Cara memasukkan antara muka tetapan sistem - Dalam Cari dan masukkan pilihan "Paparan" dalam antara muka tetapan - cari pilihan "Saiz Fon" dan laraskan saiz fon dengan pihak ketiga aplikasi - muat turun dan pasang aplikasi yang menyokong pelarasan saiz fon - buka aplikasi dan masukkan antara muka tetapan yang berkaitan - mengikut individu
 Kuasai dengan cepat: Bagaimana untuk membuka dua akaun WeChat pada telefon bimbit Huawei didedahkan!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Kuasai dengan cepat: Bagaimana untuk membuka dua akaun WeChat pada telefon bimbit Huawei didedahkan!
Mar 23, 2024 am 10:42 AM
Dalam masyarakat hari ini, telefon bimbit telah menjadi sebahagian daripada kehidupan kita. Sebagai alat penting untuk komunikasi harian, kerja dan kehidupan kita, WeChat sering digunakan. Walau bagaimanapun, mungkin perlu untuk memisahkan dua akaun WeChat apabila mengendalikan transaksi yang berbeza, yang memerlukan telefon mudah alih untuk menyokong log masuk ke dua akaun WeChat pada masa yang sama. Sebagai jenama domestik yang terkenal, telefon bimbit Huawei digunakan oleh ramai orang Jadi apakah kaedah untuk membuka dua akaun WeChat pada telefon bimbit Huawei? Mari kita dedahkan rahsia kaedah ini. Pertama sekali, anda perlu menggunakan dua akaun WeChat pada masa yang sama pada telefon mudah alih Huawei anda Cara paling mudah ialah




