详解webpack模块及webpack3新特性
本文从简单的例子入手,从打包文件去分析以下三个问题:webpack打包文件是怎样的?如何做到兼容各大模块化方案的?webpack3带来的新特性又是什么?webpack是一个强大的模块打包工具,在处理依赖、模块上都很优秀,本文从bundle.js文件分析出发去探索了不同模块方案的加载机制,初步去理解webpack,并且对webpack3特性进行阐述。
一个简单的例子
webpack配置
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
};简单的js文件
// src/index.js
console.log('hello world');webpack打包后的代码
一看你就会想,我就一行代码,你给我打包那么多???(黑人问号)
// dist/bundle.js
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
console.log('hello world');
/***/ })
/******/ ]);我们来分析一下这部分代码,先精简一下,其实整体就是一个自执行函数,然后传入一个模块数组
(function(modules) {
//...
})([function(module, exports) {
//..
}])好了,传入模块数组做了什么(其实注释都很明显了,我只是大概翻译一下)
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache 缓存已经load过的模块
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function 引用的函数
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache 假如在缓存里就直接返回
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) 构造一个模块并放入缓存
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId, //模块id
/******/ l: false, // 是否已经加载完毕
/******/ exports: {} // 对外暴露的内容
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function 传入模块参数,并执行模块
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded 标记模块已经加载完毕
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module 返回模块暴露的内容
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__) 暴露模块数组
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache 暴露缓存数组
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports 为ES6 exports定义getter
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) { // 假如exports本身不含有name这个属性
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules 解决ES module和Common js module的冲突,ES则返回module['default']
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__ webpack配置下的公共路径
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports 最后执行entry模块并且返回它的暴露内容
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
console.log('hello world');
/***/ })
/******/ ]);整体流程是怎样的呢
传入module数组
调用__webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0)
构造module对象,放入缓存
调用module,传入相应参数modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); (这里exports会被函数内部的东西修改)
标记module对象已经加载完毕
返回模块暴露的内容(注意到上面函数传入了module.exports,可以对引用进行修改)
模块函数中传入module, module.exports, __webpack_require__
执行过程中通过对上面三者的引用修改,完成变量暴露和引用
webpack模块机制是怎样的
我们可以去官网看下webpack模块
doc.webpack-china.org/concepts/mo…
webpack 模块能够以各种方式表达它们的依赖关系,几个例子如下:
ES2015 import 语句
CommonJS require() 语句
AMD define 和 require 语句
css/sass/less 文件中的 @import 语句。
样式(url(...))或 HTML 文件()中的图片链接(image url)
强大的webpack模块可以兼容各种模块化方案,并且无侵入性(non-opinionated)
我们可以再编写例子一探究竟
CommonJS
修改src/index.js
var cj = require('./cj.js');
console.log('hello world');
cj();新增src/cj.js,保持前面例子其他不变
// src/cj.js
function a() {
console.log("CommonJS");
}
module.exports = a;再次运行webpack
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
//... 省略代码
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
let cj = __webpack_require__(1);
console.log('hello world');
cj();
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
function a() {
console.log("CommonJS");
}
module.exports = a;
/***/ })
/******/ ]);我们可以看到模块数组多了个引入的文件,然后index.js模块函数多了个参数__webpack_require__,去引用文件(__webpack_require__在上一节有介绍),整体上就是依赖的模块修改了module.exports,然后主模块执行依赖模块,获取exports即可
ES2015 import
新增src/es.js
// src/es.js
export default function b() {
console.log('ES Modules');
}修改src/index.js
// src/index.js
import es from './es.js';
console.log('hello world');
es();
webpack.config.js不变,执行webpack
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
// ... 省略代码
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });
/* harmony import */ var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__es_js__ = __webpack_require__(1);
console.log('hello world');
Object(__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__es_js__["a" /* default */])();
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
/* harmony export (immutable) */ __webpack_exports__["a"] = b;
function b() {
console.log('ES Modules');
}
/***/ })
/******/ ]);我们可以看到它们都变成了严格模式,webpack自动采用的
表现其实跟CommonJS相似,也是传入export然后修改,在主模块再require进来,
我们可以看到这个
Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });这个干嘛用的?其实就是标记当前的exports是es模块,还记得之前的__webpack_require__.n吗,我们再拿出来看看
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules 解决ES module和Common js module的冲突,ES则返回module['default']
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };为了避免跟非ES Modules冲突?冲突在哪里呢?
其实这部分如果你看到babel转换ES Modules源码就知道了,为了兼容模块,会把ES Modules直接挂在exports.default上,然后加上__esModule属性,引入的时候判断一次是否是转换模块,是则引入module['default'],不是则引入module
我们再多引入几个ES Modules看看效果
// src/es.js
export function es() {
console.log('ES Modules');
}
export function esTwo() {
console.log('ES Modules Two');
}
export function esThree() {
console.log('ES Modules Three');
}
export function esFour() {
console.log('ES Modules Four');
}我们多引入esTwo和esFour,但是不使用esFour
// src/index.js
import { es, esTwo, esFour} from './es.js';
console.log('hello world');
es();
esTwo();得出
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
// ...
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });
/* harmony import */ var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__es_js__ = __webpack_require__(1);
console.log('hello world');
Object(__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__es_js__["a" /* es */])();
Object(__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__es_js__["b" /* esTwo */])();
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
/* harmony export (immutable) */ __webpack_exports__["a"] = es;
/* harmony export (immutable) */ __webpack_exports__["b"] = esTwo;
/* unused harmony export esThree */
/* unused harmony export esFour */
function es() {
console.log('ES Modules');
}
function esTwo() {
console.log('ES Modules Two');
}
function esThree() {
console.log('ES Modules Three');
}
function esFour() {
console.log('ES Modules Four');
}
/***/ })
/******/ ]);嗯嗯其实跟前面是一样的,举出这个例子重点在哪里呢,有没有注意到注释中
/* unused harmony export esThree */ /* unused harmony export esFour */
esThree是我们没有引入的模块,esFour是我们引用但是没有使用的模块,webpack均对它们做了unused的标记,其实这个如果你使用了webpack插件uglify,通过标记,就会把esThree和esFour这两个未使用的代码消除(其实它就是tree-shaking)
AMD
我们再来看看webpack怎么支持AMD
新增src/amd.js
// src/amd.js
define([
],function(){
return {
amd:function(){
console.log('AMD');
}
};
});修改index.js
// src/index.js
define([
'./amd.js'
],function(amdModule){
amdModule.amd();
});得到
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
// ... 省略代码
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
var __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__;!(__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__ = [
__webpack_require__(1)
], __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ = function(amdModule){
amdModule.amd();
}.apply(exports, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__),
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ !== undefined && (module.exports = __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__));
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
var __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__;!(__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__ = [
], __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ = function(){
return {
amd:function(){
console.log('AMD');
}
};
}.apply(exports, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__),
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ !== undefined && (module.exports = __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__));
/***/ })
/******/ ]);先看amd.js整理一下代码
function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
var __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__,
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__;
!(
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__ = [],
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ = function() {
return {
amd: function() {
console.log('AMD');
}
};
}.apply(exports, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__),
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ !== undefined &&
(module.exports = __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__)
);
})简单来讲收集define Array然后置入返回函数,根据参数获取依赖
apply对数组拆解成一个一个参数
再看index.js模块部分
function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
var __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__,
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__;
!(
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__ = [__webpack_require__(1)],
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ = function(amdModule) {
amdModule.amd();
}.apply(exports, __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_ARRAY__),
__WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__ !== undefined &&
(module.exports = __WEBPACK_AMD_DEFINE_RESULT__)
);
}其实就是引入了amd.js暴露的{amd:[Function: amd]}
css/image?
css和image也可以成为webpack的模块,这是令人震惊的,这就不能通过普通的hack commonjs或者函数调用简单去调用了,这就是anything to JS,它就需要借助webpack loader去实现了
像css就是转换成一段js代码,通过处理,调用时就是可以用js将这段css插入到style中,image也类似,这部分就不详细阐述了,有兴趣的读者可以深入去研究
webpack3新特性
我们可以再顺便看下webpack3新特性的表现
具体可以看这里medium.com/webpack/web…
Scope Hoisting
我们可以发现模块数组是一个一个独立的函数然后闭包引用webpack主函数的相应内容,每个模块都是独立的,然后带来的结果是在浏览器中执行速度变慢,然后webpack3学习了Closure Compiler和RollupJS这两个工具,连接所有闭包到一个闭包里,放入一个函数,让执行速度更快,并且整体代码体积也会有所缩小
我们可以实际看一下效果(要注意的是这个特性只支持ES Modules,是不支持CommonJs和AMD的)
使用上面的例子,配置webpack.config.js,增加new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin()
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
module: {
},
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
]
};打包
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
// ... 省略代码
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });
// CONCATENATED MODULE: ./src/es.js
function es() {
console.log('ES Modules');
}
function esTwo() {
console.log('ES Modules Two');
}
function esThree() {
console.log('ES Modules Three');
}
function esFour() {
console.log('ES Modules Four');
}
// CONCATENATED MODULE: ./src/index.js
// src/index.js
console.log('hello world');
es();
/***/ })
/******/ ]);我们可以惊喜的发现没有什么require了,它们拼接成了一个函数,good!
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 详解webpack模块及webpack3新特性. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1384
1384
 52
52
 Tutorial Bermula VUE3: Membungkus dan Membina dengan Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
Tutorial Bermula VUE3: Membungkus dan Membina dengan Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
Vue ialah rangka kerja JavaScript yang sangat baik yang boleh membantu kami membina aplikasi web yang interaktif dan cekap dengan cepat. Vue3 ialah versi terkini Vue, yang memperkenalkan banyak ciri dan fungsi baharu. Webpack kini merupakan salah satu pembungkus modul JavaScript dan alat binaan yang paling popular, yang boleh membantu kami mengurus pelbagai sumber dalam projek kami. Artikel ini akan memperkenalkan cara menggunakan Webpack untuk membungkus dan membina aplikasi Vue3. 1. Pasang Webpack
 Cara menggunakan kedi pelayan web Nginx
May 30, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
Cara menggunakan kedi pelayan web Nginx
May 30, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
Pengenalan kepada Caddy Caddy ialah pelayan web yang berkuasa dan berskala tinggi yang pada masa ini mempunyai 38K+ bintang di Github. Caddy ditulis dalam bahasa Go dan boleh digunakan untuk pengehosan sumber statik dan proksi terbalik. Caddy mempunyai ciri-ciri utama berikut: Berbanding dengan konfigurasi kompleks Nginx, konfigurasi Caddyfile asalnya adalah sangat mudah secara dinamik melalui AdminAPI yang disediakannya, ia menyokong konfigurasi HTTPS automatik secara lalai, dan boleh memohon sijil HTTPS secara automatik; dan konfigurasikannya; ia boleh dikembangkan kepada data Berpuluh-puluh ribu tapak boleh dilaksanakan di mana-mana tanpa kebergantungan tambahan yang ditulis dalam bahasa Go, keselamatan memori lebih terjamin. Pertama sekali, kami memasangnya terus dalam CentO
 Menggunakan Jetty7 untuk pemprosesan pelayan Web dalam pembangunan API Java
Jun 18, 2023 am 10:42 AM
Menggunakan Jetty7 untuk pemprosesan pelayan Web dalam pembangunan API Java
Jun 18, 2023 am 10:42 AM
Menggunakan Jetty7 untuk Pemprosesan Pelayan Web dalam Pembangunan JavaAPI Dengan pembangunan Internet, pelayan Web telah menjadi bahagian teras pembangunan aplikasi dan juga menjadi tumpuan banyak perusahaan. Untuk memenuhi keperluan perniagaan yang semakin meningkat, ramai pembangun memilih untuk menggunakan Jeti untuk pembangunan pelayan web, dan fleksibiliti dan skalabilitinya diiktiraf secara meluas. Artikel ini akan memperkenalkan cara menggunakan Jetty7 dalam pembangunan JavaAPI untuk We
 Perlindungan masa nyata terhadap rentetan penyekat muka di web (berdasarkan pembelajaran mesin)
Jun 10, 2023 pm 01:03 PM
Perlindungan masa nyata terhadap rentetan penyekat muka di web (berdasarkan pembelajaran mesin)
Jun 10, 2023 pm 01:03 PM
Benteng penghalang muka bermakna sebilangan besar benteng terapung tanpa menyekat orang dalam video, menjadikannya kelihatan seperti terapung dari belakang orang itu. Pembelajaran mesin telah popular selama beberapa tahun, tetapi ramai orang tidak tahu bahawa keupayaan ini juga boleh dijalankan dalam penyemak imbas Artikel ini memperkenalkan proses pengoptimuman praktikal dalam rentetan video penyelesaian ini, dengan harapan dapat membukanya beberapa idea. mediapipeDemo (https://google.github.io/mediapipe/) menunjukkan prinsip pelaksanaan rentetan penyekat muka arus perdana atas permintaan sehingga pengiraan latar belakang pelayan video untuk mengekstrak kawasan potret dalam skrin video dan menukarnya kepada storan svg klien semasa memainkan video Muat turun svg dari pelayan dan gabungkannya dengan rentetan, potret
 Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan pengesahan borang untuk aplikasi web menggunakan Golang
Jun 24, 2023 am 09:08 AM
Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan pengesahan borang untuk aplikasi web menggunakan Golang
Jun 24, 2023 am 09:08 AM
Pengesahan borang adalah pautan yang sangat penting dalam pembangunan aplikasi web Ia boleh menyemak kesahihan data sebelum menyerahkan data borang untuk mengelakkan kelemahan keselamatan dan ralat data dalam aplikasi. Pengesahan borang untuk aplikasi web boleh dilaksanakan dengan mudah menggunakan Golang Artikel ini akan memperkenalkan cara menggunakan Golang untuk melaksanakan pengesahan borang untuk aplikasi web. 1. Elemen asas pengesahan borang Sebelum memperkenalkan cara melaksanakan pengesahan borang, kita perlu mengetahui apakah elemen asas pengesahan borang. Unsur bentuk: unsur bentuk ialah
 Bagaimana untuk mengkonfigurasi nginx untuk memastikan bahawa pelayan frps dan web berkongsi port 80
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:19 AM
Bagaimana untuk mengkonfigurasi nginx untuk memastikan bahawa pelayan frps dan web berkongsi port 80
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:19 AM
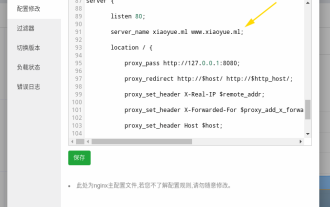
Pertama sekali, anda akan ragu-ragu, apakah itu frp? Ringkasnya, frp ialah alat penembusan intranet Selepas mengkonfigurasi klien, anda boleh mengakses intranet melalui pelayan. Sekarang pelayan saya telah menggunakan nginx sebagai laman web, dan hanya terdapat satu port 80. Jadi apakah yang perlu saya lakukan jika pelayan FRP juga mahu menggunakan port 80? Selepas membuat pertanyaan, ini boleh dicapai dengan menggunakan proksi terbalik nginx. Untuk menambah: frps ialah pelayan, frpc ialah pelanggan. Langkah 1: Ubah suai fail konfigurasi nginx.conf dalam pelayan dan tambahkan parameter berikut pada http{} dalam nginx.conf, server{listen80
 Apakah standard web?
Oct 18, 2023 pm 05:24 PM
Apakah standard web?
Oct 18, 2023 pm 05:24 PM
Piawaian web ialah satu set spesifikasi dan garis panduan yang dibangunkan oleh W3C dan organisasi lain yang berkaitan Ia termasuk penyeragaman HTML, CSS, JavaScript, DOM, kebolehcapaian Web dan pengoptimuman prestasi Dengan mengikut piawaian ini, keserasian halaman boleh dipertingkatkan. kebolehcapaian, kebolehselenggaraan dan prestasi. Matlamat standard web adalah untuk membolehkan kandungan web dipaparkan dan berinteraksi secara konsisten pada platform, pelayar dan peranti yang berbeza, memberikan pengalaman pengguna yang lebih baik dan kecekapan pembangunan.
 Bagaimana untuk mendayakan akses pentadbiran daripada UI web kokpit
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
Bagaimana untuk mendayakan akses pentadbiran daripada UI web kokpit
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
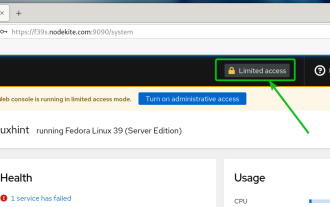
Kokpit ialah antara muka grafik berasaskan web untuk pelayan Linux. Ia bertujuan terutamanya untuk memudahkan pengurusan pelayan Linux untuk pengguna baharu/pengguna pakar. Dalam artikel ini, kami akan membincangkan mod akses Cockpit dan cara menukar akses pentadbiran kepada Cockpit daripada CockpitWebUI. Topik Kandungan: Mod Kemasukan Kokpit Mencari Mod Akses Kokpit Semasa Dayakan Capaian Pentadbiran untuk Kokpit daripada CockpitWebUI Melumpuhkan Capaian Pentadbiran untuk Kokpit daripada CockpitWebUI Kesimpulan Mod Kemasukan Kokpit Kokpit mempunyai dua mod capaian: Capaian Terhad: Ini adalah lalai untuk mod capaian kokpit. Dalam mod akses ini anda tidak boleh mengakses pengguna web dari kokpit




