
这篇文章主要介绍了关于React-Reflux的基础介绍,有着一定的参考价值,现在分享给大家,有需要的朋友可以参考一下
因工作需要使用 React + Reflux 开发,最近几天都在努力学习着,特别是 Reflux,在网上查找的许多资料和 github 上的文档年代都有点久远,JavaScript 按照目前的节奏,更新得太快,旧文档的一些语法跟不上更新,对广大初学者来说,确实存在许多困惑。本文是仅适于初学者或对 React 感兴趣的朋友,大神请绕道!!!
废话不多说,进入正题~
引用俗话:“学语言用 hello world,学框架用 todolist”,今天咱们就用 todolist 来做说明。
作为一个对比 todolist-raw 是没有用 Reflux 实现 todolist 的增加和删除的,react-reflux 使用 Reflux 实现 todolist 的增加和删除,react-reflux 又分基本关联和简便法关联 Component。
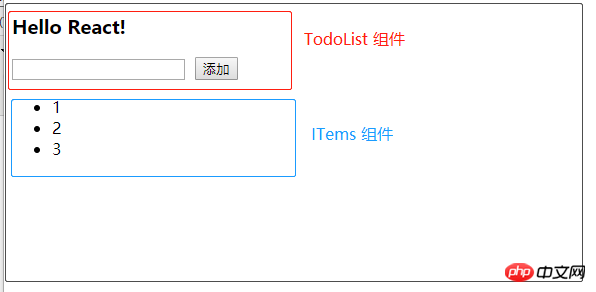
先看下组件的效果图:
电脑需要准备好环境,我用的是 create-react-app 和 yarn ,请自行百度安装好这两个工具,项目目录精简如下图:
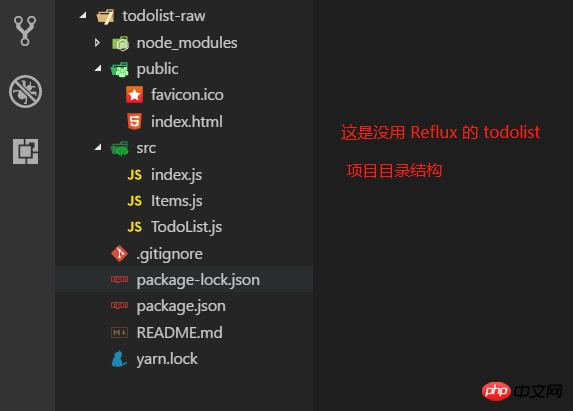
1. todolist-raw 就几个文件,里面的代码都比较简单,相信各道友一看就懂了。
package.json 的配置如下:
{
"name": "todolist-raw",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"react": "^16.4.1",
"react-dom": "^16.4.1",
"react-scripts": "1.1.4"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start",
"build": "react-scripts build",
"test": "react-scripts test --env=jsdom",
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
}
}这里注意一下版本,版本不对应我也不知道会出现什么样的问题,比如我用的是 yarn 安装了 Rflux 之后, 提示 "react-scripts" 不是内部命令,yarn start 启动不了,反复试验都不行,后来打扣了 yarn -h 然后接着 yarn -autoclean 就好了。讲了那么多,其实我遇到的这个问题也不算版本不对称的问题吧,建议出现一些莫名其妙的 bug 就整理下 yarn。痒?痒就挠呗!!!
index.html 如下:与自动生成的没什么改变,就是删了一些注释!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico">
<title>TodoList-raw</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
You need to enable JavaScript to run this app.
</noscript>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>index.js 如下:
1 import React from 'react'; 2 import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; 3 import TodoList from './TodoList'; 4 5 ReactDOM.render(<TodoList />, document.getElementById('root'));
View Code
TodoList.js 如下:
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
import Items from './Items';
class TodoList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
items: [1, 2, 3],
isC: false
};
this.handlerClick = this.handlerClick.bind(this);
}
// 添加一个 item 项
handlerClick() {
const val = this.refs.inputEl.value;
this.refs.inputEl.value = '';
const items = [...this.state.items, val]; // 最好不要直接操作 state
this.setState({items}); // es6 语法,等价于 {items: items}
}
// 删除某一个 item 项,点击就删除
handlerDelete(index) {
const items = [...this.state.items];
items.splice(index, 1);
this.setState({items});
}
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<h3>Hello React!</h3>
<input
ref="inputEl"
style={{marginRight: "10px"}}
/>
<button onClick={this.handlerClick}>添加</button>
<Items
msg={this.state.items}
func={this.handlerDelete.bind(this)} />
</Fragment>
);
}
}
export default TodoList;说明几点:
a. this.handlerClick = this.handlerClick.bind(this); 是用来绑定 this 的,React 用的是 jsx 语法糖,整个 js 就是一个组件,在标签上绑定事件是不能带括号的,如果像传统的 HTML 事件绑定那样绑事件不行,因为这个标签就是在 js 文件中的,像传统的 HTML 绑定事件就会直接调用了!所以 jsx 中的标签绑定事件绑的是引用。而且需要绑定在这个 js 文件(组件)上。所以 jsx 中的标签的事件就是 .这只是我的理解,不知道对不对,如果不正确,请指正!
b. 代码很少阅读起来应该没难度,而且上面也有一些注释了。不过还是要啰嗦一下。React 是用数据(data)基于状态(state)来驱动视图(view),也就是搞来搞去都是在搞数据,用数据改变状态来达到渲染视图的目的,大多是在虚拟内存处理,通过什么 diff 比较算法,层层计较然后达到提高性能,加快视图渲染的目的。额,我只能用“非常快”来形容 React 的性能,当然,性能的事还是跟实际代码复杂度相关,我只想说 React 确实出众!扯远了...,既然是基于状态(state),所以要有 state,在 constructor 中定义了,而且处理业务时改变 state,比如 handlerClick,deleteClick 中都是先用变量保存下来,通过 this.setState() 方法在设置回去!
c. 父子关系的组件,父组件可通过属性来给子组件传参,就像这样:<Items msg={this.state.items} />,子组件可通过 this.props.msg 拿到 items。
Items.js 代码如下:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Items extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.func = this.props.func;
}
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.msg.map((item, index) => <li
key={index}
onClick={this.func.bind(this, index)}
>{item}</li>
)}
</ul>
);
}
}
export default Items;注意,父组件传递方法给子组件时,this 指向的是子组件,所以通过属性传递时,需要用函数绑定 bind() 绑定父组件的 this。
最后,通过 cmd 命令行,yarn start 运行任务即可实现一个简单的 TodoList 功能。
2. react-reflux: 通过 Reflux 来实现简单的 TodoList (基本法关联 Component)。
2.1 简单地说明下为什么要 Reflux 架构,如图(自己画的组件树结构!),不存在父子关系的组件(如 B 和 E)通讯势必会很困难而且麻烦,需要一个中间件(Store)来存储数据,类似于订阅者和发布者(中间人模式)一样,大家都往 Store 中存取数据就好,不需要层层走关系了,避免了层层传递数据的灾难!
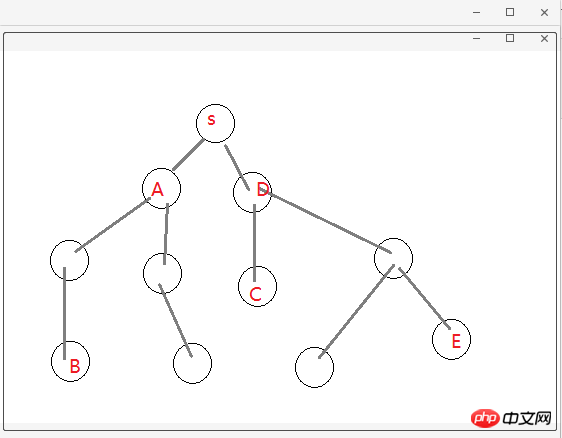
2.2 关于 Actions、Store 和 Component 的关系,可以这么理解:Store 作为一个中间人有订阅和发布的功能,Actions 就是 Component 触发的动作,Actions 被 Store 监听着,组件有新动作了, Store 就会做出相应的处理(回调函数)更改 Store 中的数据通过 this.trigger(this.items) 发布消息[就相当于更新 items], Component 监听着 Store,用一些手段(mixin 或回调函数)关联起 Component 中的状态信息(state.items)和 Store 中的信息(items),这就是所谓的单向数据流,单向表示一个方向流动,不能反向。
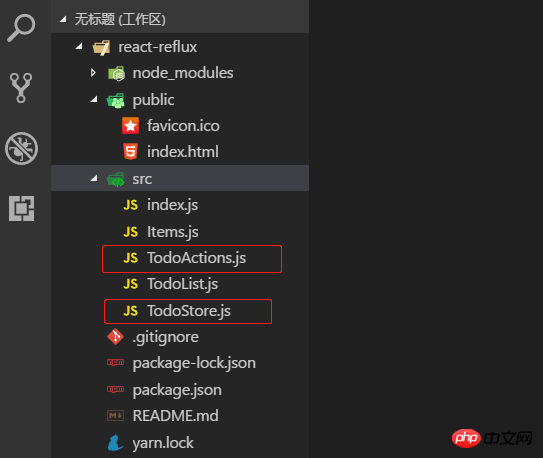
2.3 目录结构和前面的 todolist-raw 没多大区别,就是多了 TodoActions.js 和 TodoStore.js 两个文件。如图:
2.4 一言不合就贴代码。首先 index.js 代码没变化,就不贴了,TodoActions.js 代码如下:
import Reflux from 'reflux';
const TodoActions = Reflux.createActions([
'getAll',
'addItem',
'deleteItem'
]);
export default TodoActions;TodoStore.js 代码如下:
import Reflux from 'reflux';
import Actions from './TodoActions';
const TodoStore = Reflux.createStore({
// items: [1, 2, 3],
// listenables: Actions,
init() {
console.log('TodoStore init method~');
this.items = [1, 2, 3]; // 给个初始值
this.listenables = Actions; // 监听 TodoActions.js
// this.listenTo(addItem, 'addItem');
},
onGetAll() {
console.log('onGetAll');
this.trigger(this.items);
},
onAddItem(model) {
console.log('onAddItem---', model);
this.items.unshift(model);
this.trigger(this.items);
},
onDeleteItem(index) {
console.log('onDeleteItem---', index);
this.items.splice(index, 1);
this.trigger(this.items);
}
})
export default TodoStore;说明:多个监听用 listenables,单个监听 this.listenTo(addItem, 'addItem'); 多个监听的时候定义处理函数是 on + ActionName 驼峰式命名。定义初始值和监听可以写在 init 方法外面,就像上面那样(已注释)。
2.5 Actions 和 Store 都写好了,就差最后一步,整合到组件 Component 中,才算有点意义了!TodoList.js 代码如下:
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
import Actions from './TodoActions';
import TodoStore from './TodoStore';
import Items from './Items';
class TodoList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
items: [],
isC: false
};
this.handlerClick = this.handlerClick.bind(this);
}
// 组件挂载
componentDidMount() {
this.unsubscribe = TodoStore.listen(this.onStatusChange, this);
Actions.getAll();
}
// 组件移除
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentWillUnmount');
this.unsubscribe(); // 解除监听
}
// callback
onStatusChange(items) {
this.setState({items});
}
// 添加一个 item 项
handlerClick() {
const val = this.refs.inputEl.value;
this.refs.inputEl.value = '';
Actions.addItem(val);
}
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<h3>Hello React-Reflux!</h3>
<input
ref="inputEl"
style={{marginRight: "10px"}}
/>
<button onClick={this.handlerClick}>添加</button>
<Items msg={this.state.items} />
</Fragment>
);
}
}
export default TodoList;说明:这是基本的添加关联,需要在组件挂载时监听 Store,需要定义一个回调函数 onStatusChange(),组件卸载时解除监听 this.unsubscribe(),Store 源码如下:
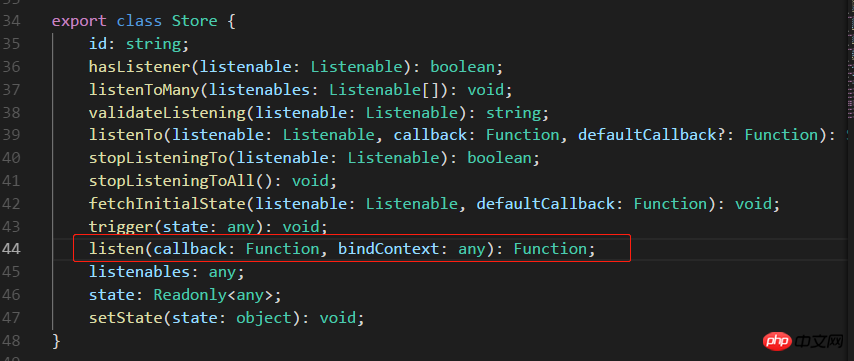
不传 bindContext 更新不了状态,回调函数 onStatusChange 中报异常,传入 this 就好了。如图:

Items.js 代码如下:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Actions from './TodoActions';
class Items extends Component {
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.msg.map((item, index) => <li
key={index}
onClick={this.handlerDelete.bind(this, index)}
>{item}</li>
)}
</ul>
);
}
handlerDelete(index) {
Actions.deleteItem(index);
}
}
export default Items;3. react-reflux: 通过 Reflux 来实现简单的 TodoList (简便法关联 Component)。
3.1 先安装 react-mixin 和 axios: npm install react-mixin,npm install axios。结合异步操作实现简便 Store 关联 Component。
安装两个依赖之后,修改 TodoStore.js 和 TodoList.js 代码如下:
我贴:TodoStore.js:
import Reflux from 'reflux';
import Actions from './TodoActions';
import Axios from 'axios';
const TodoStore = Reflux.createStore({
// items: [3, 2, 1],
// listenables: Actions,
init() {
console.log('TodoStore init method~');
this.items = [3, 2, 1]; // 初始值,此处不是 state, mark-1 -2 -3 都可以直接操作
this.listenables = Actions;
},
onGetAll() {
console.log('onGetAll');
Axios.get('https://api.github.com/')
.then(res => {
const keys = Object.keys(res.data);
console.log('axios-response-keys: ', keys);
this.items = keys; // mark-1
this.trigger(this.items);
})
.catch(err => console.log('axios-error: ', err));
},
onAddItem(model) {
console.log('onAddItem---', model);
this.items.unshift(model); // mark-2
console.log('TodoStore-items: ', this.items);
this.trigger(this.items);
},
onDeleteItem(index) {
console.log('onDeleteItem---', index);
this.items.splice(index, 1); // mark-3
this.trigger(this.items);
}
})
export default TodoStore;我再贴:TodoList.js:
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
import ReactMixin from 'react-mixin';
import Reflux from 'reflux';
import Actions from './TodoActions';
import TodoStore from './TodoStore';
import Items from './Items';
class TodoList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
items: [],
isC: false
};
this.handlerClick = this.handlerClick.bind(this);
}
// 组件挂载
componentDidMount() {
Actions.getAll();
}
// 添加一个 item 项
handlerClick() {
const val = this.refs.inputEl.value;
this.refs.inputEl.value = '';
if (!val) {
alert('Please enter the data which type of number or string');
return false;
}
Actions.addItem(val);
}
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<h3>Hello React-Reflux!</h3>
<input
ref="inputEl"
style={{marginRight: "10px"}}
/>
<button onClick={this.handlerClick}>添加</button>
<Items msg={this.state.items} />
</Fragment>
);
}
}
// 用 Reflux.connect 将 Store 和 Component 组合在一起
ReactMixin.onClass(TodoList, Reflux.connect(TodoStore, 'items'));
export default TodoList;修改之后 yarn start 启动项目,截图如下:
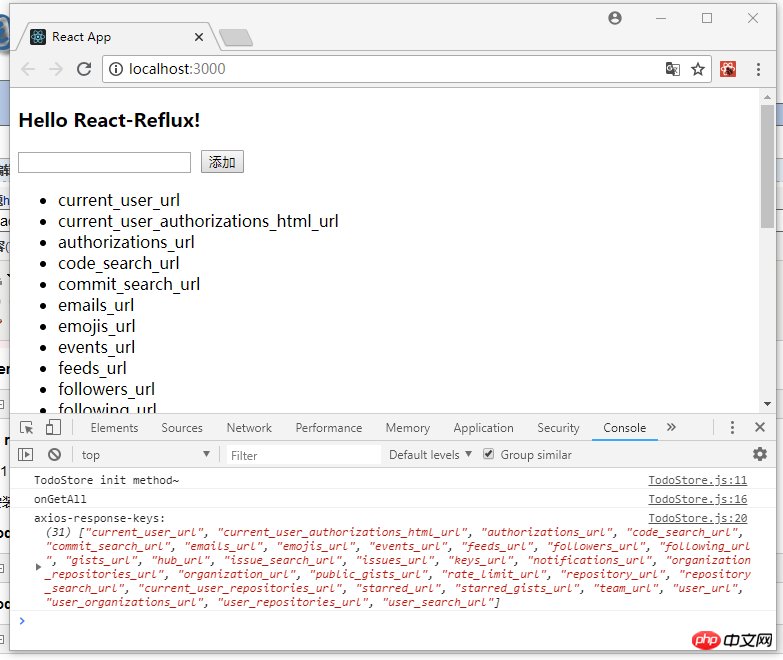
4. 说在后面的话:本篇文章只是关于 React-Reflux 基础入门的一些知识,没有涉及实战应用,读者自酌。对于 React 我也是初学者,难免有许多不准确的地方,有待提高,欢迎各位道友留言指正。
4.1 好了,简单地分享就到此结束了,谢谢阅读~~~
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网!
相关推荐:
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci React-Reflux的基础介绍. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Apakah alat pelayan fail rangkaian?
Apakah alat pelayan fail rangkaian?
 Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan fungsi sembang dalam talian Vue
Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan fungsi sembang dalam talian Vue
 Bagaimana untuk memulihkan video yang telah dialih keluar secara rasmi daripada Douyin
Bagaimana untuk memulihkan video yang telah dialih keluar secara rasmi daripada Douyin
 Mengapa komputer terus dimulakan semula secara automatik
Mengapa komputer terus dimulakan semula secara automatik
 Bagaimana untuk memulihkan fail yang dikosongkan daripada Recycle Bin
Bagaimana untuk memulihkan fail yang dikosongkan daripada Recycle Bin
 Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikan status http 404
Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikan status http 404
 Ungkapan biasa tidak mengandungi
Ungkapan biasa tidak mengandungi
 Apakah kaedah pengisihan?
Apakah kaedah pengisihan?




