详解CSS中position属性的用法
本篇文章介绍了CSS中的position属性的用法、分类以及使用效果展示,希望对学习css的朋友有帮助!

详解CSS中position属性的用法
一、position属性有什么作用?
CSS position属性用于指定一个元素在文档中的定位方式。top,right,bottom 和 left属性则决定了该元素的最终位置。(MDN定义)。
( 推荐学习:CSS教程 )
二、position有哪些分类?
1、static
正常的布局行为,元素在文档常规流中当前的布局位置。此时 top, right, bottom, left 和 z-index 属性无效。
位置不变。
2、relative
该关键字下,元素先放置在未添加定位时的位置,再在不改变页面布局的前提下调整元素位置(因此会在此元素未添加定位时所在位置留下空白)。position:relative 对 table-*-group, table-row, table-column, table-cell, table-caption 元素无效。
相对于自身位置的偏移。
3、absolute
不为元素预留空间,通过指定元素相对于最近的非 static 定位祖先元素的偏移,来确定元素位置。绝对定位的元素可以设置外边距(margins),且不会与其他边距合并。
就像从来没有这个元素一样,会根据此元素的非static祖先元素确定元素的偏移。
4、fixed
不为元素预留空间,而是通过指定元素相对于屏幕视口(viewport)的位置来指定元素位置。元素的位置在屏幕滚动时不会改变。打印时,元素会出现在的每页的固定位置。fixed 属性会创建新的层叠上下文。当元素祖先的 transform 属性非 none 时,容器由视口改为该祖先。
低版本ie不兼容。
5、sticky
盒位置根据正常流计算(这称为正常流动中的位置),然后相对于该元素在流中的 flow root(BFC)和 containing block(最近的块级祖先元素)定位。在所有情况下(即便被定位元素为 table 时),该元素定位均不对后续元素造成影响。当元素 B 被粘性定位时,后续元素的位置仍按照 B 未定位时的位置来确定。position: sticky 对 table 元素的效果与 position: relative 相同。
同时sticky还有以下问题:
1、sticky 不会触发 BFC。
2、样式表 z-index 无效。行内 style 写有效。
3、sticky 是容器相关的,也就说 sticky 的特性只会在他所处的容器里生效。强调这一点是因为在实际使用中,碰到 body 设置 height:100% 的时候 sticky 元素停在某一个位置不动了。
三、测试代码
测试代码的公共代码如下:
<html html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>position</title>
</head>
<style>
.main-app{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.app-container {
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
#the-box{
position: static;
/* position: relative;
top:100px;
left:200px; */
}
.sub-box {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="main-app">
<div class="app-container">
<div class="sub-box" style="background: gray;"></div>
<div id="the-box" class="sub-box" style="background: green;"></div>
<div class="sub-box" style="background: yellow;"></div>
<div class="sub-box" style="background: red;"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>我选定第二个元素作为我们本次的测试对象,测试环境为chrome 75版本。
1、static
#the-box{
position: static;
}结果:
正常文档流显示

2、relative
#the-box{
position: relative;
top:100px;
left:200px;
}结果:
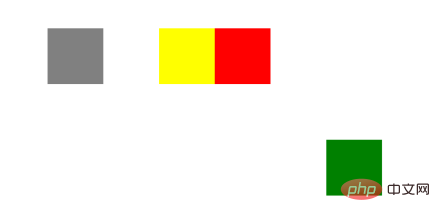
相对于自身原来的位置偏移设定的位置,但是原来的位置被保留下来。
3、absolute
#the-box{
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 200px;
}结果:

原来固定的位置被别的元素占用,由于父元素是非static(flex),所以当前元素相对于父元素偏移设定的位置。
4、sticky
须指定 top, right, bottom 或 left 四个阈值其中之一,才可使粘性定位生效。否则其行为与相对定位相同。
此特性是元素固定在视口的位置,如果页面没有滚动轴,将无法展示特性,此时,我们对它的父元素稍加更改,使页面出现滚动轴。
.app-container {
width: 100%;
height: 3000px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
#the-box{
position: sticky;
top: 100px;
}结果:
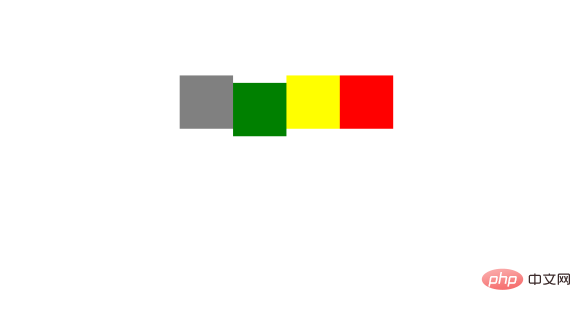
当我们滚动页面当元素距离顶部超过100px时,向下滚动时当前元素位置相对于视口不变,此特性可以用作table固定表头。
5、fixed
对于ie7以下版本不能使用,其实就相当于固定元素在浏览器窗口的位置。
#the-box{
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
left: 200px;
}结果:
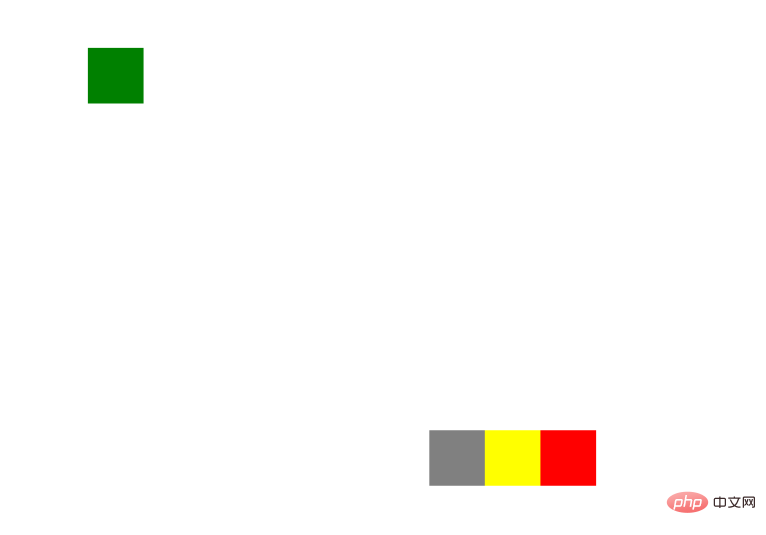

无论如何滚动滚动轴,元素位置始终不变。
6、inherit
规定应该从父元素继承 position 属性的值。
7、initial
initial 关键字用于设置 CSS 属性为它的默认值,可作用于任何 CSS 样式。(IE 不支持该关键字)
8、unset
名如其意,unset 关键字我们可以简单理解为不设置。其实,它是关键字 initial 和 inherit 的组合。
当我们给一个 CSS 属性设置了 unset:
如果该属性是默认继承属性,该值等同于 inherit
如果该属性是非继承属性,该值等同于 initial
9、revert
暂时未列入规范。
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 详解CSS中position属性的用法. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Cara menggunakan butang bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
Cara menggunakan butang bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
Bagaimana cara menggunakan butang bootstrap? Perkenalkan CSS bootstrap untuk membuat elemen butang dan tambahkan kelas butang bootstrap untuk menambah teks butang
 Cara mengubah saiz bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
Cara mengubah saiz bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
Untuk menyesuaikan saiz unsur-unsur dalam bootstrap, anda boleh menggunakan kelas dimensi, yang termasuk: menyesuaikan lebar: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust ketinggian: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 Cara Menyiapkan Kerangka untuk Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
Cara Menyiapkan Kerangka untuk Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
Untuk menubuhkan rangka kerja bootstrap, anda perlu mengikuti langkah -langkah ini: 1. Rujuk fail bootstrap melalui CDN; 2. Muat turun dan tuan rumah fail pada pelayan anda sendiri; 3. Sertakan fail bootstrap di HTML; 4. Menyusun sass/kurang seperti yang diperlukan; 5. Import fail tersuai (pilihan). Setelah persediaan selesai, anda boleh menggunakan sistem grid Bootstrap, komponen, dan gaya untuk membuat laman web dan aplikasi yang responsif.
 Cara memasukkan gambar di bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
Cara memasukkan gambar di bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
Terdapat beberapa cara untuk memasukkan imej dalam bootstrap: masukkan imej secara langsung, menggunakan tag HTML IMG. Dengan komponen imej bootstrap, anda boleh memberikan imej yang responsif dan lebih banyak gaya. Tetapkan saiz imej, gunakan kelas IMG-cecair untuk membuat imej boleh disesuaikan. Tetapkan sempadan, menggunakan kelas IMG-Sempadan. Tetapkan sudut bulat dan gunakan kelas IMG-bulat. Tetapkan bayangan, gunakan kelas bayangan. Saiz semula dan letakkan imej, menggunakan gaya CSS. Menggunakan imej latar belakang, gunakan harta CSS imej latar belakang.
 Cara melihat tarikh bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
Cara melihat tarikh bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
Jawapan: Anda boleh menggunakan komponen pemetik tarikh bootstrap untuk melihat tarikh di halaman. Langkah -langkah: Memperkenalkan rangka kerja bootstrap. Buat kotak input pemilih Tarikh dalam HTML. Bootstrap secara automatik akan menambah gaya kepada pemilih. Gunakan JavaScript untuk mendapatkan tarikh yang dipilih.
 Cara Mengesahkan Tarikh Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Cara Mengesahkan Tarikh Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Untuk mengesahkan tarikh dalam bootstrap, ikuti langkah -langkah ini: memperkenalkan skrip dan gaya yang diperlukan; memulakan komponen pemilih tarikh; Tetapkan atribut data-BV-tarikh untuk membolehkan pengesahan; Konfigurasikan peraturan pengesahan (seperti format tarikh, mesej ralat, dll.); Mengintegrasikan rangka kerja pengesahan bootstrap dan mengesahkan input tarikh secara automatik apabila borang dikemukakan.
 Cara Menulis Garis Pecah Di Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Cara Menulis Garis Pecah Di Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Terdapat dua cara untuk membuat garis perpecahan bootstrap: menggunakan tag, yang mewujudkan garis perpecahan mendatar. Gunakan harta sempadan CSS untuk membuat garis perpecahan gaya tersuai.
 Cara menetapkan bar navigasi bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 01:51 PM
Cara menetapkan bar navigasi bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 01:51 PM
Bootstrap Menyediakan panduan mudah untuk menubuhkan bar navigasi: Memperkenalkan Perpustakaan Bootstrap untuk membuat bar navigasi Tambah Identiti Jenama Buat Pautan Navigasi Tambah Elemen Lain (Pilihan) Laraskan Gaya (Pilihan)




