

相关免费学习推荐:mysql视频教程
通过我自己的一番实战,可以确定的是,只要创建表,这个rowid一定是存在的,唯一区别就是显示和隐士的区别,也就是是否可以通过select _rowid from table查询出来 那么问题来了,哪些情况下rowid是显示的? 1 、当表中有主键并且是数值型的时候才是显示的 2、当表中没有主键的时候,但是表中有唯一非空并且是数值型的时候才是显示的 接下来,创建表来实战看下,是否是这样的
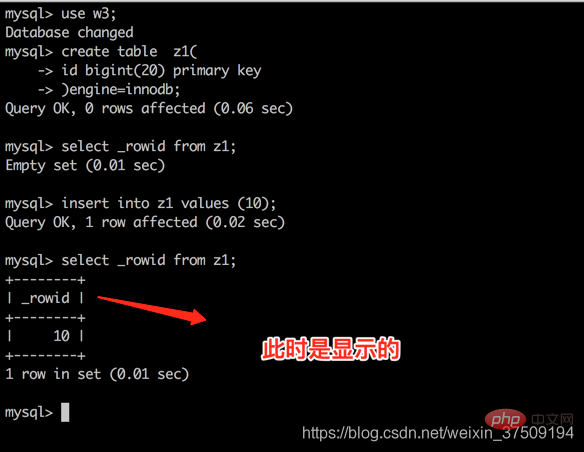
先创建一个带有主键并且是数值型的表 create table z1( id bigint(20) primary key )engine=innodb;
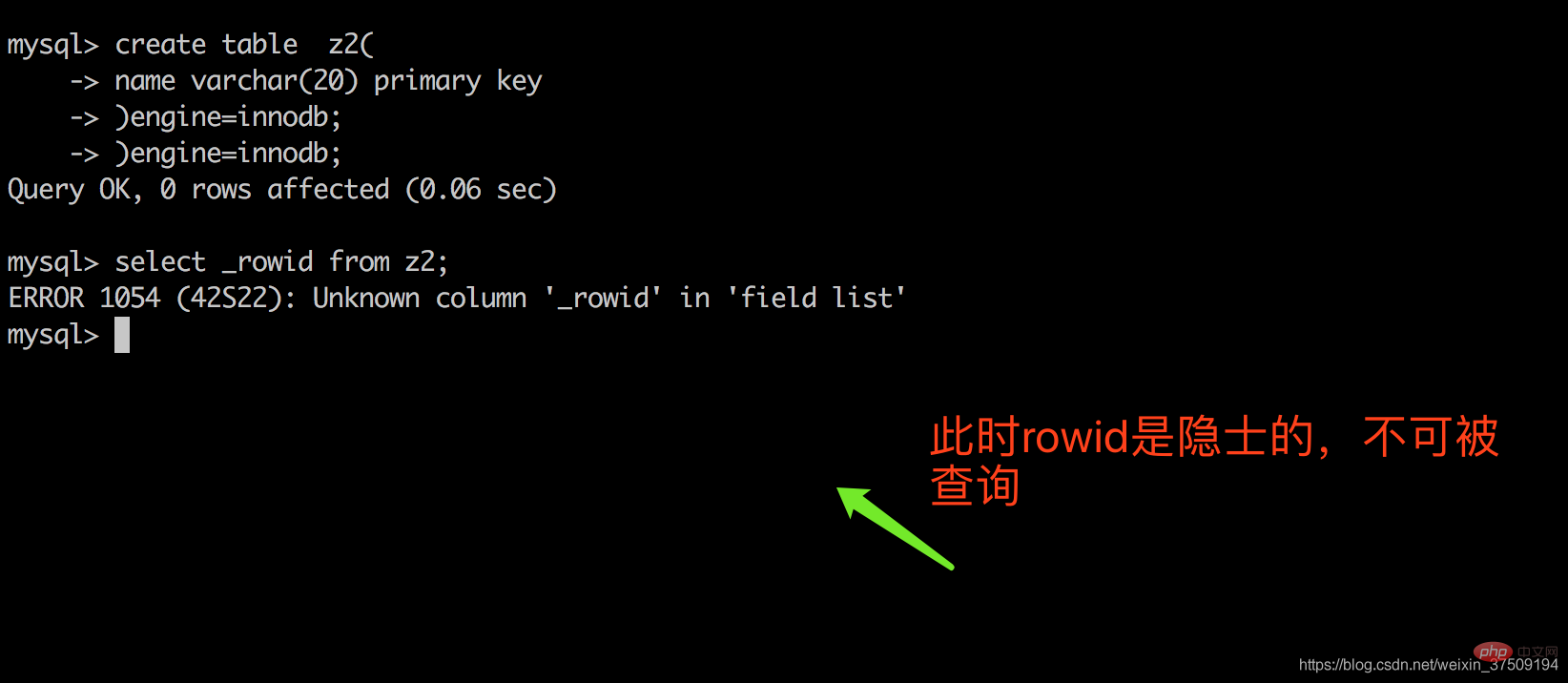
再创建一个带有主键不是数值型的表(虽然业务不会这样创建,只是为了证明rowid) create table z2( name varchar(20) primary key )engine=innodb;
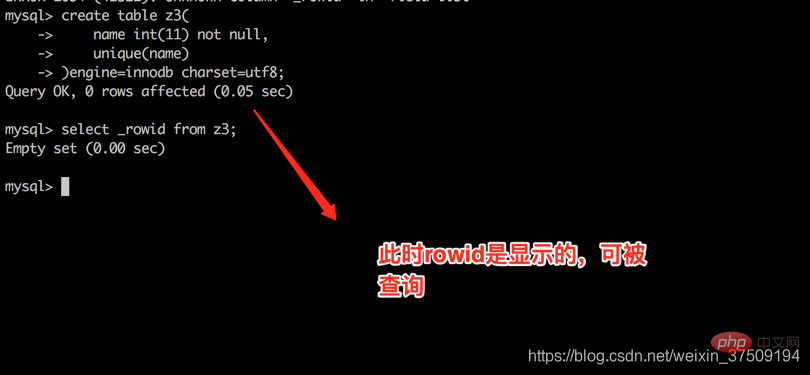
再创建一个没有主键但是有唯一键并且是数值型非空的表 create table z3( name int(11) not null, unique(name) )engine=innodb charset=utf8
此时再创建一个没有主键,并且有唯一键,但是可以为空或者不是数值型的表 create table z4( name varchar(11) not null, unique(name) )engine=innodb charset=utf8; create table z5( name int(11) , unique(name) )engine=innodb charset=utf8;
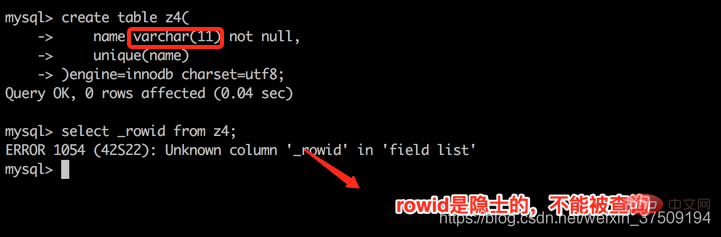
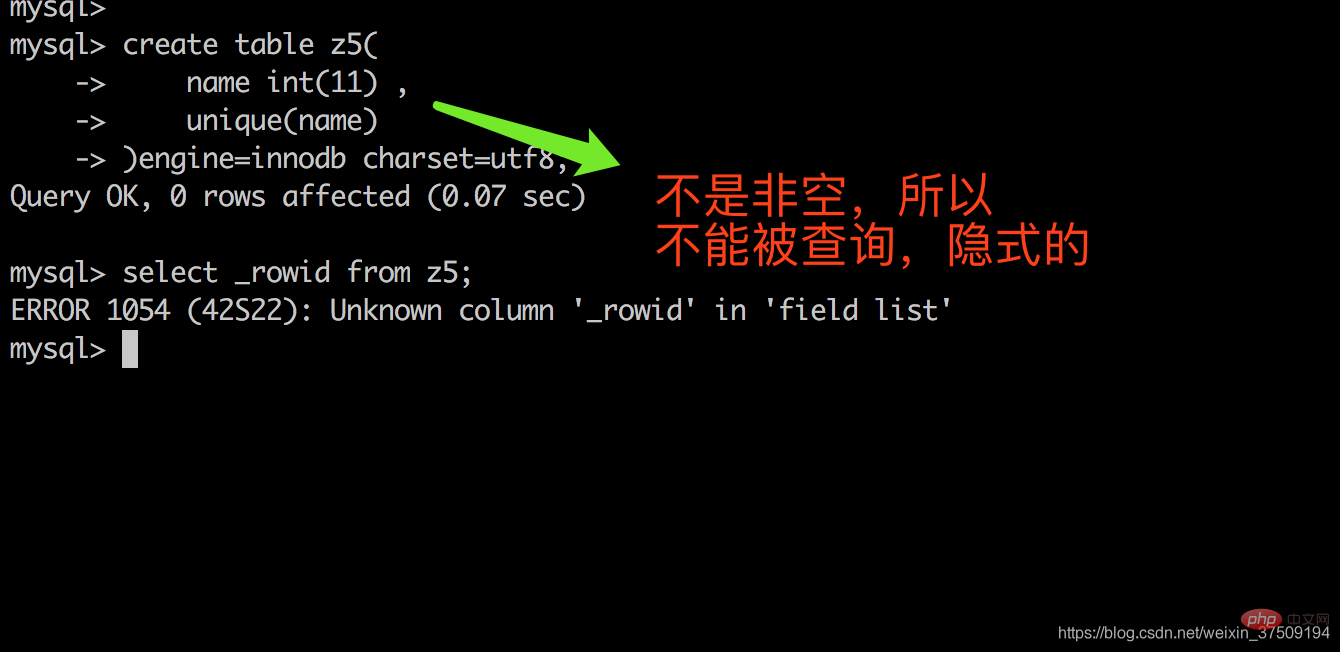
再来看看官网咋说的,再理解下 官网连接:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/create-index.html If a table has a PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE NOT NULL index that consists of a single column that has an integer type, you can use _rowid to refer to the indexed column in SELECT statements, as follows: _rowid refers to the PRIMARY KEY column if there is a PRIMARY KEY consisting of a single integer column. If there is a PRIMARY KEY but it does not consist of a single integer column, _rowid cannot be used. Otherwise, _rowid refers to the column in the first UNIQUE NOT NULL index if that index consists of a single integer column. If the first UNIQUE NOT NULL index does not consist of a single integer column, _rowid cannot be used.
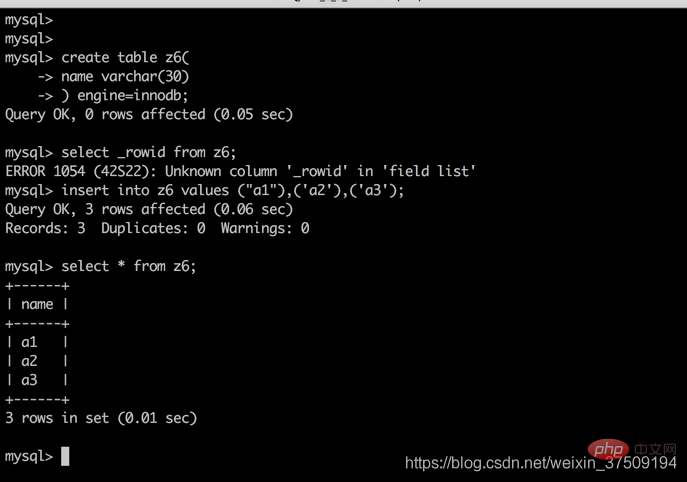
此时我再创建一个表,表中只有一个字段,并且是字符串类型的,看下生成的隐式rowid,达到最大值会发生什么?(注意此时底层会默认生成一个6字节的指针,最大值为2^48 次幂)
此时用gdb工具让rowid达到最大值再插入看看会怎么样? 答:先找到mysqld的进程pid,命令 ps aux | grep mysqld gdb -p 你的mysql的pid -ex 'p dict_sys->row_id=1' -batch
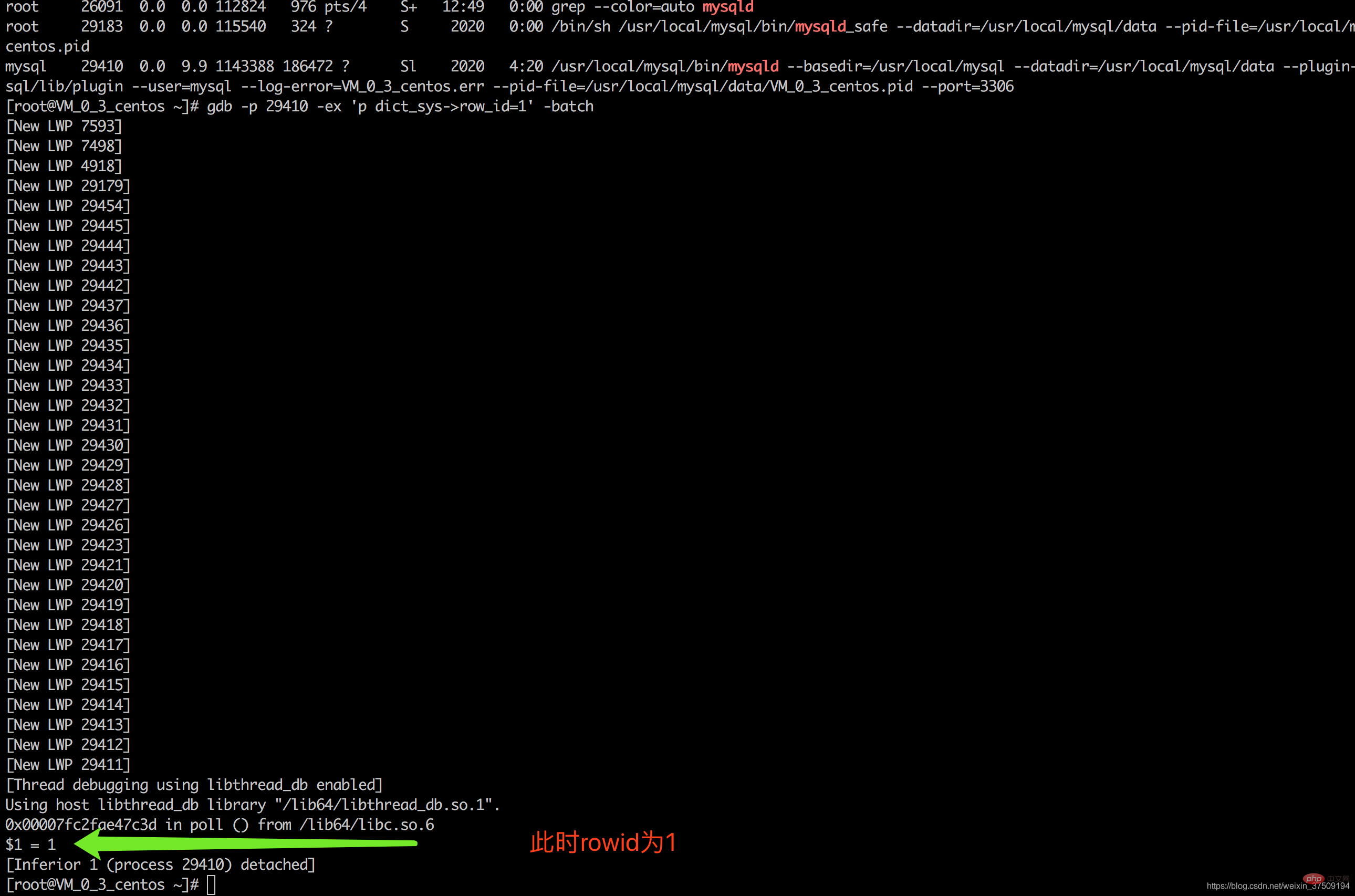
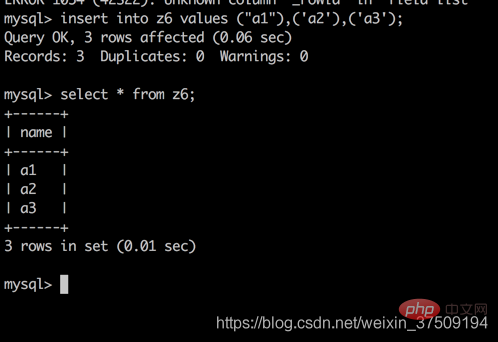
可以看到此时插入了3条数据
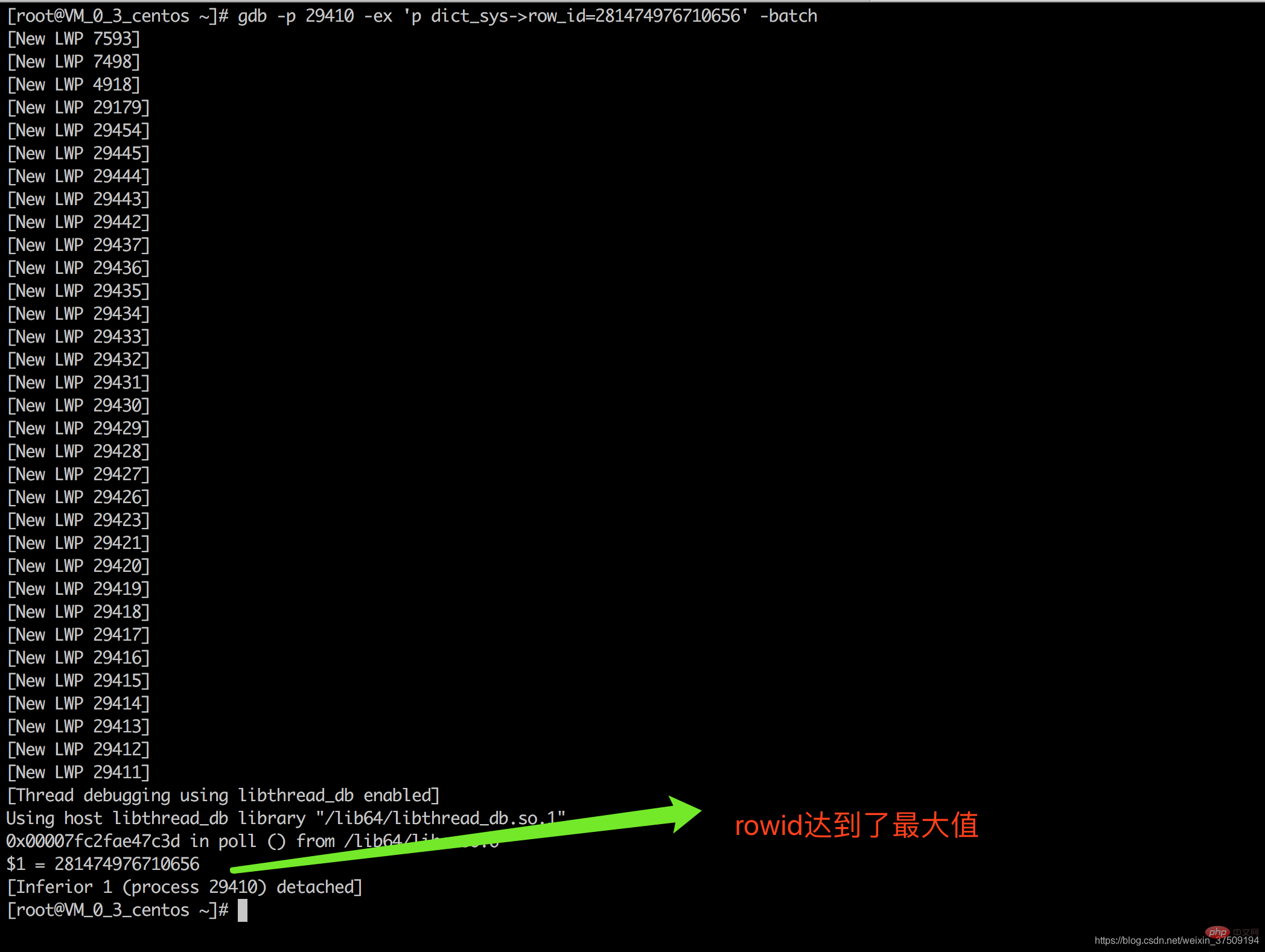
这个时候把rowid变为2^48次幂之后,再插入看下效果 gdb -p 29410 -ex 'p dict_sys->row_id=281474976710656' -batch
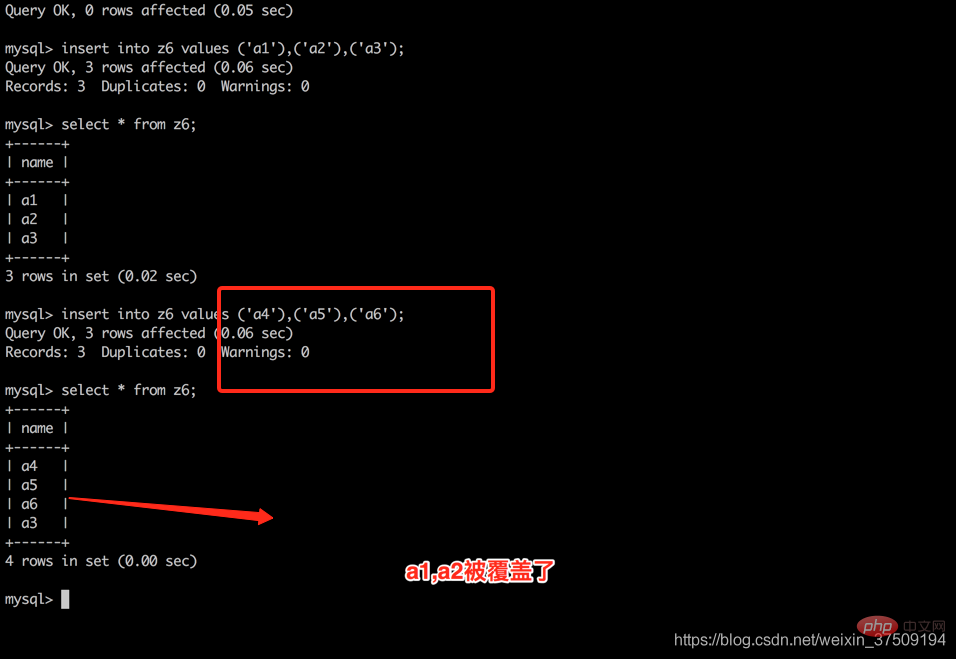
此时再插入三条数据,此时a1 a2被覆盖了,所以在不满足上述二种情况的时候,生成的隐式rowid在用尽之后,之前的记录会被覆盖,所以创建表一定要有主键id,避免发生覆盖,虽然概率比较低,这个只是用主键的其中一个原因哈
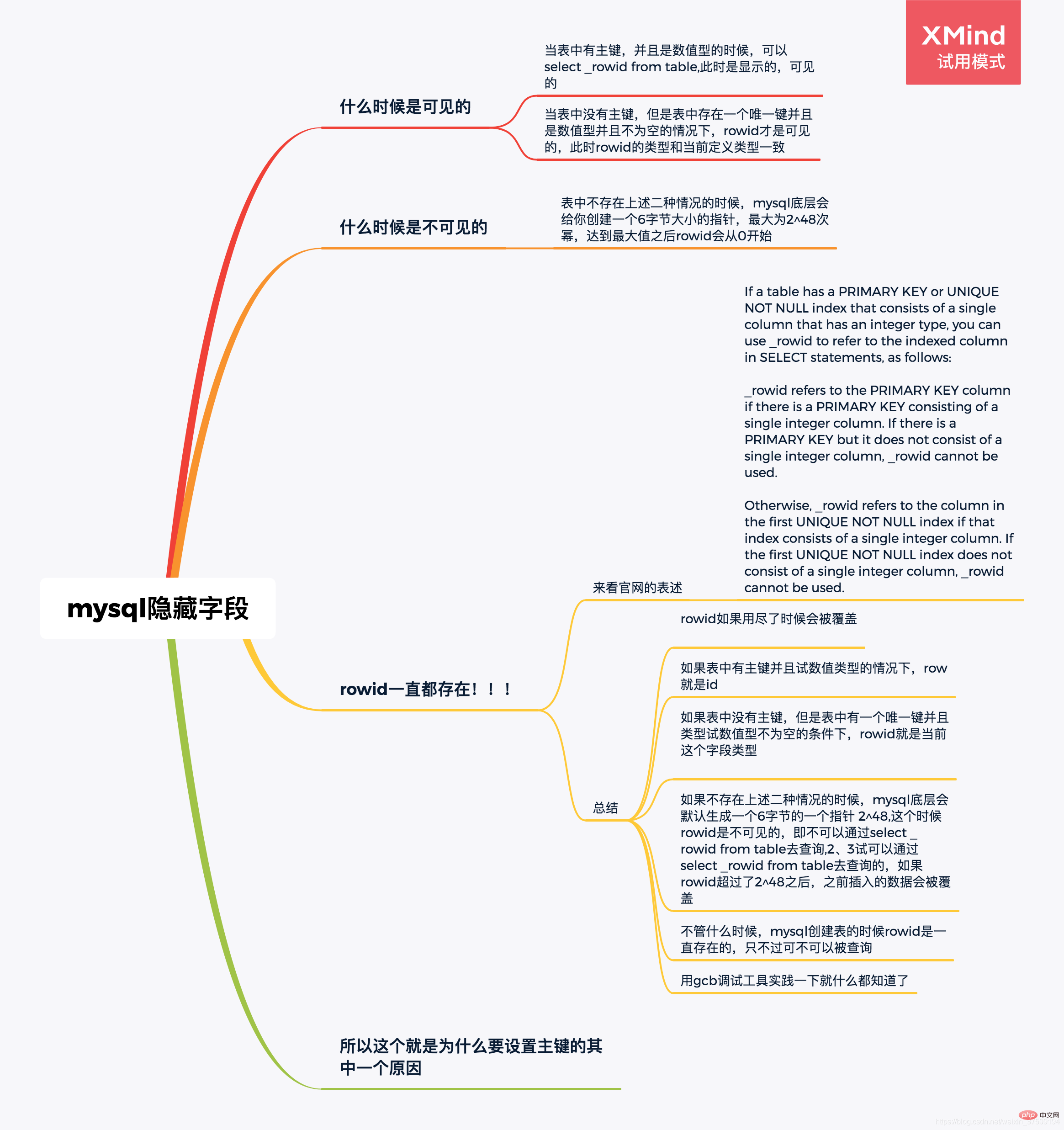
所以综上所述:看我xmind那个总结,自己再理解消化下吧。
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 掌握mysql隐藏字段(rowid)什么时候是可见的. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!