php引用文件有几种方式
php引用文件有4种方式:1、使用include()函数,可以放在PHP脚本的任意位置;2、require()函数,一般放在PHP脚本的最前面;3、include_once()函数;4、require_once()函数。

本教程操作环境:windows7系统、PHP7.1版,DELL G3电脑
PHP中有四个加载文件的语句:include、require、include_once、require_once。
基本语法
require:require函数一般放在PHP脚本的最前面,PHP执行前就会先读入require指定引入的文件,包含并尝试执行引入的脚本文件。require的工作方式是提高PHP的执行效率,当它在同一个网页中解释过一次后,第二次便不会解释。但同样的,正因为它不会重复解释引入文件,所以当PHP中使用循环或条件语句来引入文件时,需要用到include。
include:可以放在PHP脚本的任意位置,一般放在流程控制的处理部分中。当PHP脚本执行到include指定引入的文件时,才将它包含并尝试执行。这种方式可以把程序执行时的流程进行简单化。当第二次遇到相同文件时,PHP还是会重新解释一次,include相对于require的执行效率下降很多,同时在引入文件中包含用户自定义函数时,PHP在解释过程中会发生函数重复定义问题。
require_once / include_once:分别与require / include作用相同,不同的是他们在执行到时会先检查目标内容是不是在之前已经导入过,如果导入过了,那么便不会再次重复引入其同样的内容。
相互区别
include和require:
include有返回值,而require没有返回值
include在加载文件失败时,会生成一个警告(E_WARNING),在错误发生后脚本继续执行。所以include用在希望继续执行并向用户输出结果时。
//test1.php
<?php
include './tsest.php';
echo 'this is test1';
?>
//test2.php
<?php
echo 'this is test2\n';
function test() {
echo 'this is test\n';
}
?>
//结果:
this is test1require在加载失败时会生成一个致命错误(E_COMPILE_ERROR),在错误发生后脚本停止执行。一般用在后续代码依赖于载入的文件的时候。
//test1.php
<?php
require './tsest.php';
echo 'this is test1';
?>
//test2.php
<?php
echo 'this is test2\n';
function test() {
echo 'this is test\n';
}
?>结果:
include和include_once:
include载入的文件不会判断是否重复,只要有include语句,就会载入一次(即使可能出现重复载入)。而include_once载入文件时会有内部判断机制判断前面代码是否已经载入过。这里需要注意的是include_once是根据前面有无引入相同路径的文件为判断的,而不是根据文件中的内容(即两个待引入的文件内容相同,使用include_once还是会引入两个)。
//test1.php <?php include './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1this is test2 //test1.php <?php include './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include_once './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1 //test1.php <?php include_once './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1this is test2 //test1.php <?php include_once './test2.php'; echo 'this is test1'; include_once './test2.php'; ?> //test2.php <?php echo 'this is test2'; ?> //结果: this is test2this is test1
require和require_once:同include和include_once的区别相同。
载入时执行过程
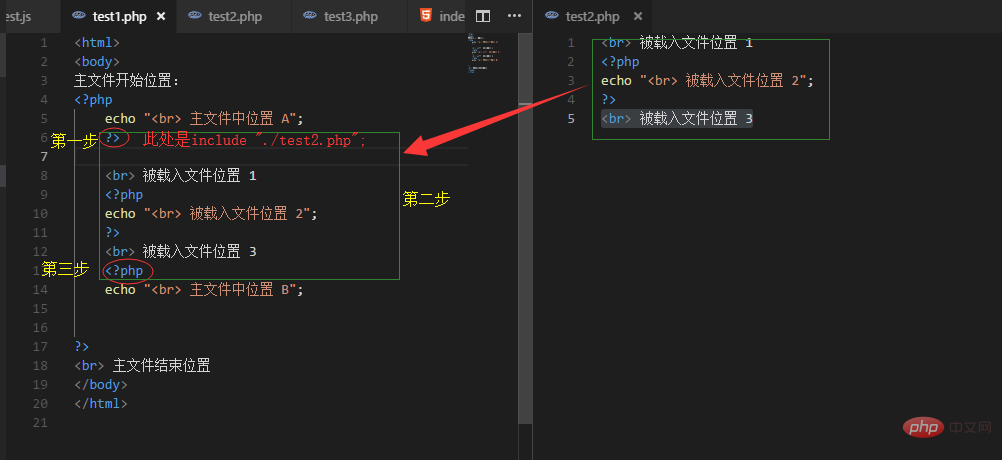
1. 从include(require)语句退出php脚本模式(进入html代码模式)
2. 载入include语句所设定的文件中的代码,并尝试执行
3. 退出html模式,重新进入php脚本模式,继续后面脚本程序的执行
//test1.php
<html>
<body>
主文件开始位置:
<?php
echo "<br> 主文件中位置 A";
include "./test2.php"; //要载入的文件
echo "<br> 主文件中位置 B";
?>
<br> 主文件结束位置
</body>
</html>
//test2.php
<br> 被载入文件位置 1
<?php
echo "<br> 被载入文件位置 2";
?>
<br> 被载入文件位置 3结果:
分析:
返回值的比较
上文说道include有返回值,而require无返回值
对于include,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,则返回false.
对于require,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,无返回值。
//test1.php <?php $a = include "./test2.php"; var_dump($a); echo "<br>"; $b = include "./test2.phps"; var_dump($b); echo "<br>"; $c = require "./test2.php"; var_dump($c); echo "<br>"; $d = require "./test2.phps"; var_dump($d); ?>
输出:

当文件中有return:
当被载入文件中有return语句时,会有另外的机制,此时return语句的作用是终止载入过程,即被载入文件中return语句的后续代码不再载入。return语句也可以用于被载入文件载入时返回一个数据。
//test1.php <?php $a = include "./test2.php"; echo "<br>"; var_dump($a); ?> //test2.php //该文件中有return语句 <?php $b = 'test2'; echo "被载入的文件:A 位置"; return $b; echo "<br 被载入的文件: B 位置"; ?>
结果:

推荐学习:《PHP视频教程》
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci php引用文件有几种方式. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Panduan Pemasangan dan Naik Taraf PHP 8.4 untuk Ubuntu dan Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Panduan Pemasangan dan Naik Taraf PHP 8.4 untuk Ubuntu dan Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 membawa beberapa ciri baharu, peningkatan keselamatan dan peningkatan prestasi dengan jumlah penamatan dan penyingkiran ciri yang sihat. Panduan ini menerangkan cara memasang PHP 8.4 atau naik taraf kepada PHP 8.4 pada Ubuntu, Debian, atau terbitan mereka
 Bincangkan CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Bincangkan CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP ialah rangka kerja sumber terbuka untuk PHP. Ia bertujuan untuk menjadikan pembangunan, penggunaan dan penyelenggaraan aplikasi lebih mudah. CakePHP adalah berdasarkan seni bina seperti MVC yang berkuasa dan mudah difahami. Model, Pandangan dan Pengawal gu
 Muat naik Fail CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
Muat naik Fail CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
Untuk mengusahakan muat naik fail, kami akan menggunakan pembantu borang. Di sini, adalah contoh untuk muat naik fail.
 Cara Menyediakan Kod Visual Studio (Kod VS) untuk Pembangunan PHP
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Cara Menyediakan Kod Visual Studio (Kod VS) untuk Pembangunan PHP
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Kod Visual Studio, juga dikenali sebagai Kod VS, ialah editor kod sumber percuma — atau persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu (IDE) — tersedia untuk semua sistem pengendalian utama. Dengan koleksi sambungan yang besar untuk banyak bahasa pengaturcaraan, Kod VS boleh menjadi c
 Panduan Ringkas CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
Panduan Ringkas CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP ialah rangka kerja MVC sumber terbuka. Ia menjadikan pembangunan, penggunaan dan penyelenggaraan aplikasi lebih mudah. CakePHP mempunyai beberapa perpustakaan untuk mengurangkan beban tugas yang paling biasa.
 Bagaimana anda menghuraikan dan memproses HTML/XML dalam PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Bagaimana anda menghuraikan dan memproses HTML/XML dalam PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Tutorial ini menunjukkan cara memproses dokumen XML dengan cekap menggunakan PHP. XML (bahasa markup extensible) adalah bahasa markup berasaskan teks yang serba boleh yang direka untuk pembacaan manusia dan parsing mesin. Ia biasanya digunakan untuk penyimpanan data
 Jelaskan JSON Web Tokens (JWT) dan kes penggunaannya dalam PHP API.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Jelaskan JSON Web Tokens (JWT) dan kes penggunaannya dalam PHP API.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT adalah standard terbuka berdasarkan JSON, yang digunakan untuk menghantar maklumat secara selamat antara pihak, terutamanya untuk pengesahan identiti dan pertukaran maklumat. 1. JWT terdiri daripada tiga bahagian: header, muatan dan tandatangan. 2. Prinsip kerja JWT termasuk tiga langkah: menjana JWT, mengesahkan JWT dan muatan parsing. 3. Apabila menggunakan JWT untuk pengesahan di PHP, JWT boleh dijana dan disahkan, dan peranan pengguna dan maklumat kebenaran boleh dimasukkan dalam penggunaan lanjutan. 4. Kesilapan umum termasuk kegagalan pengesahan tandatangan, tamat tempoh, dan muatan besar. Kemahiran penyahpepijatan termasuk menggunakan alat debugging dan pembalakan. 5. Pengoptimuman prestasi dan amalan terbaik termasuk menggunakan algoritma tandatangan yang sesuai, menetapkan tempoh kesahihan dengan munasabah,
 Program PHP untuk mengira vokal dalam rentetan
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Program PHP untuk mengira vokal dalam rentetan
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Rentetan adalah urutan aksara, termasuk huruf, nombor, dan simbol. Tutorial ini akan mempelajari cara mengira bilangan vokal dalam rentetan yang diberikan dalam PHP menggunakan kaedah yang berbeza. Vokal dalam bahasa Inggeris adalah a, e, i, o, u, dan mereka boleh menjadi huruf besar atau huruf kecil. Apa itu vokal? Vokal adalah watak abjad yang mewakili sebutan tertentu. Terdapat lima vokal dalam bahasa Inggeris, termasuk huruf besar dan huruf kecil: a, e, i, o, u Contoh 1 Input: String = "TutorialSpoint" Output: 6 menjelaskan Vokal dalam rentetan "TutorialSpoint" adalah u, o, i, a, o, i. Terdapat 6 yuan sebanyak 6