深入php面向对象、模式与实践_PHP
1 语法
1.1 基础语法
clone
需要操作原对象,但又不想影响原对象.
代码如下:
$K_back = clone $K;
基本数据类型和数组都为真复制,即为真副本,当属性为对象时,为假复制,改变副本仍会影响原对象.解决方案:
//在原对象中添加
function __clone(){
$this->对象 = clone $this->对象
} __clone在clone前自动触发,可以执行一些在备份前的属性操作.
2、&传递引用
方法引用传递,改变源对象
代码如下:
function set_K(& $K){...}
function & get_K(){...}
3、static延迟静态绑定
应用场景:Dog类和Person类都需要一个返回实例化的方法,Dog类和Person类都继承于Animal抽象类.
abstract class Animal{
public static function create(){
//实例化调用类
return new static();
}
}
class Person extends Animal{...}
//返回Person实例化类
Person::create();4、拦截器
__get($property),访问未定义的属性时调用.
__set($property,$value),给未定义的属性赋值时被调用.
__isset($property),对未定义属性调用isset()方法时调用.
__unset($property),对未定义属性调用unset()方法时调用.
__call($method,$arg_array),调用未定义方法时调用.
__call很有用,但要慎用,因为太灵活.
应用场景:有一个专门打印Person类信息的Person_Writer类,如果通过Person类调用Person_Writer类.
//Person委托Person_Writer类处理打印事务.
class Person {
private $writer;
...
function __call($method_name,$args){
if(methood_exists($this->wirter,$method_name)){
return $this->writer->method_name($this);
}
}
//高级__call写法,当委托方法参数不确定时使用.
function __call($method_name,$args){
//当然这里这样写法意义不大,但是call一般都是用call_user_func_array调用
$args = $this ;
if(methood_exists($this->wirter,$method_name)){
return call_user_func_array(
array($this->writer,$method_name),$args);
)
}
}
} 5、回调函数
应用场景: 3个类,Product类,Product_Sale类,Product_Totalizer类,要实现:当卖出Product总共价格超过指定金额时,输出警告.
//Product
class Product {
public $name;
public $price;
}
//Product_Sale
class Product_Sale {
private $callbacks;
//记录回调函数
function register_callback ($callback) {
if(! is_callback($callback)){
thow new Exception('callback not callable');
}
$this->callbacks[] = $callback;
}
//执行回调函数
function sale ($product){
print "{$product->name} : 处理中 \n";
foreach($this->callbacks as $callback){
call_user_func($callback , $product);
}
}
}
//Produce_Totalizer
class Produce_Totalizer {
static function warn_amount ($amt) {
$count = 0;
return function ($produce) use ($amt , &count) {
$count += $produce->price;
print " count : {count}\n"
if($count>$amt){
print "超过指定金额{$amt}啦~";
}
};
}
}
//模拟场景
$product_sale = new Produce_Sale();
//指定报警金额为8块
$product_sale = register_callback(Produce_Totalizer::warn_amount(8));
//卖商品
$product_sale->sale(new Product("Durex",6));
$product_sale->sale(new Produce("Jissbon",5));
//输出结果
Durex : 处理中
count :6
Jissbon : 处理中
count: 11
超过指定金额8块啦~6、get_class()和instanceof
get_class(类)用于判断是否精准等于类名;
instanceof 可以判断是否其本身或继承于某父类.
7、类中的方法和类中的属性
代码如下:
get_class_methods('类名'):获取类中所有方法.
get_class_vars('类名'):获取类中所有public参数;
8、反射API
2 模式
2.1 组合
问题:课堂类被演讲类和研讨会类继承着.但是演讲类和研讨类都要实现一次性计费和上N次课计费的方法.和输出计算的方式.
解决方案1: 在课堂类中添加计算一次性付费的方法,上N次课的计费方法和输出计算方式的方法.
解决方案2: 运用组合,将处理计费和输出计算方式单独封装为一个计费策略类.

abstract class Cost_Strategy {
protected $duration;
abstract function cost ();
abstract function charge_type();
public __construct($duration){
$this->duration = $duration;
}
}
class Timed_Const_Strategy extends Cost_Stratedy {
function cost () {
//上一次课给5块钱- -.
return $this->duration * 5;
}
function charge_type(){
return "多次课结算";
}
}
class Fixed_Const_Strategy extends Cost_Stratedy {
function cost (){
return 30 ;
}
function charge_type(){
return "一次性课结算";
}
}
abstract class Leason {
private $cost_strategy;
public __construct(Const_Strategy $cost_strategy){
$this->cost_strategy = $cost_strategy;
}
function __call($method_name,$args){
$args = $cost_strategy ;
if(methood_exists($this->cost_strategy,$method_name)){
return call_user_func_array(
array($this->writer,$method_name),$args);
)
}
}
}
//运用
$leasons[] = new Seminar(new Timed_Const_Strategy(4));
$leasons[] = new Lecture(new Fixed_Const_Strategy(null));
foreach ($leasons as $leason){
print "leason charge : {$leason->const()}";
print "charge_type : {$leason->charge_type()}"
}
leason charge 20. charge_type : 多次课结算;
leason charge 30. charge_type : 一次课结算;组合既委托.同级委托.
继承既父子关系.
3 生成对象
3.1 单例模式
确保系统中只有唯一一个用例.例如系统配置文件.
重点
1: 构造方法私有.
2: 类本身包含自己的实例化属性.

class Preferences {
private static $instance;
private function __construct(){ ... }
public static function get_instance(){
if(empty(self::$instance)){
self::$instance = new Preferences();
}
return self::$instance;
}
...
}
//使用
$preferences = Preferences::get_instance();3.2 工厂模式
通过一个父类,生产处多个不同功能的子类.
特点:产品方(新浪微博)和需求方(显示新浪微博)一一对应.
问题:印象笔记中,来源可能为新浪微博,或者开发者头条,在印象笔记显示的时候,两者的页眉和页尾是不一样的.

3.3 抽象模式
RLGL!!!.印象笔记不只要显示新浪微博内容!!!还要显示我的新浪账号,还要该微博啊!!卧槽~憋着急,吻我.
工厂模式主要用于生产一一对应的产品方和需求方,而抽象模式要做的是一个需求方(印象笔记_显示新浪微博),要多个工厂(把需求方抽象为多个需求方),例如提供新浪内容的工厂,提供新浪账号的工厂.提供微博内容的评论的工厂等.

代码:
abstract class Show_Evernote {
abstract function get_header_text();
abstract function get_context();
abstract function get_footer_text();
abstract function get_user();
abstract function get_comment();
}
class 显示新浪微博 extends Show_Evernote{
function get_header_text(){...};
function get_context(){new 新浪微博_内容;}
function get_footer_text(){...};
function get_user(){new 新浪微博_账号 ;}
function get_comment(){new 新浪微博_评论;}
}
//使用
印象笔记控件类->内容 = 显示新浪微博->get_context;
印象笔记控件类->账号 = 显示新浪微博->get_context;
...3.4 平行模式
当使用工厂/抽象模式必须要制定具体的创建者(需求方).
平行模式和抽象模式的模型图一致,但代码实现不一样.
抽象模式中父类均为抽象类,而平行模式中,所以类都为普通类,方便父类的实例化.
在这里列出显示印象笔记类的实现代码
class Show_Evernote{
private $内容;
private $账号;
private $评论;
function __construct(内容,账号,评论){
$this->内容 = 内容;
$this->账号 = 账号;
$this->评论 = 评论;
}
function get_内容(){
return clone $this->内容);
}
function get_账号(){
return clone $this->账号);
}
function get_评论(){
return clone $this->评论;
}
}
//使用
$factory = new Show_Evernote(
new 新浪微博内容(),
new 新浪微博账号(),
new 新浪微博评论()
);
印象笔记控件类->显示印象笔记 = $factory;其实大家可以发现,原型模式只不过只在最顶层类中包装了一下各组件子类而已,然而这样可以轻松的组合他们,例如实现一个显示新浪微博内容,但要显示开发者头条账号的需求?
4 使用对象
4.1 组合模式
组合模式,可以理解为单一对象管理组合对象(聚合组件),最终组合体下的各个组合部件最好类型一致.不然特殊性越多,需要判断就越多.
假设捶背男,洗脚男,洗发男,用来服务一个人(妹子).
假设妹子的几个部位可用的服务男均为无限个.

//创建一个妹子 $妹子 = new 人(); //添加洗脚男、捶背男 $妹子->add_man(new 洗脚男); $妹子->add_man(new 捶背男); //循环所有男的给予舒服的方法. $妹子->计算舒服程度();
这是一个很理想的组合模式,在现实情况,我们使用组合模式,可能不得不创建多种类型的洗脚男,需要添加许多判断条件.
4.2 装饰模式
装饰模式,首先洗脚男,洗发男,捶背男都是人,但是如果,一个男的又捶背,又洗发,这怎么玩?.add_man两次?这不科学吧,来给这些男的装饰一下吧~

abstract class 人{
...
abstract function get_well();
}
class 男 extends 人 {
//无论你是神马男,服务你,你就能获得10点舒服度.
private $well = 10;
function get_well(){
return $this->well();
}
}
abstract class 装饰男类型 extends 人 {
protected $人;
function __construct(人 $人){
$this->人 = $人;
}
}
class 捶背装饰 extends 类型男装饰{
function get_well(){
return $this->人->get_well()+30;
}
}
class 洗发装饰 extends 类型男装饰{
function get_well(){
return $this->人->get_well()+20;
}
}
class 洗褪装饰 extends 类型男装饰{
//老子不喜欢别人碰我的毛裤.
function get_well(){
return $this->人->get_well()-20;
}
}
//创建捶背,能给予的舒服指数 - -嘻嘻.
$人 = new 捶背装饰(new 男);
$人->get_well(); // 10+30 = 40
//来来来,全能选手,捶背、洗发、洗腿一起来
$人 = new 洗脚装饰(new 洗发装饰(new 捶背装饰(new 男()))); //10+30+20-20 = 40,注意顺序,由里到外执行.装饰模式,既(组合+继承),基类方法一定要尽量少,不然子类可能有它不该有的方法.直接类继承,她只可能是一种形态,而她的多种形态可能一并拥有的时候,应该运用组合.
继承即单一多态,组合既多种多态.
这个例子中,你可以添加女,然后把装饰男类型改为装饰通用类型,但每个get_well()都要多一个判断是男还是女(如果给予的舒服程度不一样).
这只是确保不可能出现在男,女之外的第三种人,如果基类为动物,给予服务的可能是鸡,鹅,鸭,那么装饰类型应该运用工厂模式,动物形态和装饰形态一一对应.方便拓展.
除了服务类型,服务男的样子也很重要,这就多了一种装饰,现在有装饰男类型和相貌男类型,这种情况怎么破,其实类似.
代码如下:
//如何获取捶背的帅哥麦?,
$人 =new 男类型(new 捶背(new 帅哥麦(new 男())));
4.3 外观模式
即给外部系统提供清晰接口
例如当Model层写得很混乱,但是里面的方法还能用,那我们的Controller层应该列举一些清晰的访问方法来供View层访问.外观模式,强调的是清晰的访问接口.
5 执行任务
5.1 策略模式
给类添加功能.对象要显式的调用它.
继续刚才的洗脚男和人的故事吧...你丫的爽完了要给钱吧?支付宝?微信?现金?
这个付款方式有多种,实现方法不应该放在人类中,而是应该委托给别的类
abstract class 人 {
protectd $支付方式;
function set_支付方式(){...}
function 付款(金额){
return $支付方式->付款($金额);
}
}
abstract class 付款{
abstract function 付款($金额);
}
class 支付宝付款 extends 付款{
function 付款($金额){
return 外接支付宝付款流程($金额);
}
}
...
//使用
$男 =new 男();
///爽爽爽
...
//结账
$支付宝支付账单 = new 支付宝付款($金额);
$人 = new 男();
$人->set_支付方式(new 支付宝付款());
$人->付款();5.2 观察者模式
当被观察者发生变化,观察者需要被通知.
当数据发生变化,页面需要被通知.
使用步骤:
观察者加载到被观察者中.
被观察者通知观察者.

例如登陆类(被观察)状态改变,要出发邮件系统和日志系统(观察者)
interface 被观察者{
function attach(观察者);
function detatch(观察者);
function notify();
}
class Login implements 被观察者{
private $观察者;
function __construct(){
$this->观察者 = array();
}
function attach($观察者){
$this->观察者 = $观察者;
}
function detach($观察者){
//删除某个观察者的操作;
}
function notify(){
foreach ($this->观察者 as $单个观察者){
$单个观察者->update($this);
}
}
}
interface 观察者{
function update(被观察者);
}
abstract class Login_观察者 implements 观察者{
private $login;
function __construct (Login $login){
$this->login = $login;
$login->attach($this);
}
function update(观察者 $观察者){
if ($观察者 ===$this->login){
$this->do_update($观察者);
}
}
abstract function do_update(Login $login);
}
class 邮件观察者 extends 登陆观察者 {
function do_update(Login $login){
//判断条件 发送邮件
}
}
class 日志观察者 extends 登陆观察者 {
function do_update(Login $login){
//判断条件 记录到日志;
}
}
//使用
$login = new Login();
new 邮件观察者 ($login);
new 日志观察者 ($login);PHP有内置的SPL实现上述的观察者模式.
5.3 访问者模式
问题: 在一个军队中,有很多军队,军队下面可能包含军队/步兵/弓箭手,这时我们要显示一个军队的战斗力/需要粮食的各级分配?(遍历对象并设置显示方法).怎么办?.解决办法是军队还是保存自己的基本信息,设置一个访问者,访问者包含总战斗力方法和总粮食的方法.

访问者
abstract class 军队访问者{
abstract function 访问(单元);
function 访问军队($军队){
$this->访问($军队);
}
function 访问弓箭手($弓箭手){
$this->访问($弓箭手);
}
//这里重复定义了大量代码,其实可以用call来替代
function __call($method_name,$args){
if(strrpos($method_name, "访问")){
return call_user_func_array(
array($this,"访问"),$args
);
}
}
}
class 军队战斗力访问者 extends 军队访问者{
private $text="";
function 访问($单元){
$ret = "";
$pad = 4*$单元->getDpth(); //设置显示深一级前面多4个空格.
$ret .= sprintf( "%{$pad}s","");
$ret .= get_class($单元). ": ";
$ret .= "战斗力: " .$单元->bombardStrenth()."\n";
$this->text .=$ret;
}
function get_text(){
return $this->text;
}
}被访问者
abstract class 单元{
function 接受($军队访问者){
$method = "访问_".get_class($this);
$军队访问者->$method($this);
}
private $depth;
protected function set_depath($depth){
$this->depth=$depth;
}
function get_depth(){
return $this->depth;
}
...
}
abstract class 综合单元 extends 单元{
function 接受($军队访问者){
parent::接受($军队访问者)
foreach($this->单元集合 as $this_unit){
$this->unit->接受($军队访问者);
}
}
}
class 军队 extends 综合单元{
function bombardStrenth(){
$ret =0;
foreach($this-units() as $unit){
$ret += $unit->bombardStrenth();
}
return $ret
}
}
class 弓箭手 extends 单元{
function bombardStrenth(){
return 4;
}
}调用
$main_army = new Army(); $main_army->add_unit(new 步兵()); $main_army->add_unit(new 弓箭手()); $军队战斗力访问者_实例 =new 军队战斗力访问者(); $main_army->接受(均分战斗力访问者); print $军队战斗力访问者->get_text();
输出
代码如下:
军队: 战斗力: 50
步兵: 攻击力 :48
弓箭手: 攻击力: 4
5.4 命令模式
例子为Web页面的login和feed_back,假如都需要使用ajax提交,那么问题来了,将表单封装好提交上去,得到了返回结果.如何根据返回结果跳转不同的页面?.
有些同学就说了,login和feed_back各自写一个方法憋,提交的时候调用各自的方法.
然后再来个logout命令..增加..删除..命令怎么办..
命令模式比较适合命令执行例如登陆,反馈等简单只需要判断是否成功的任务

命令:
abstract class Command{
abstract function execute(Conmmand_Context $context);
}
class Login_Command extends Command{
function execute(CommandContext $context){
$managr =Register::getAccessManager();
$user = $context->get("username");
$pass = $context->get('pass');
$user_obj = $manager->login($user,$pass);
if(is_null($user_obj)){
$context->setError($manager->getError());
return false;
}
$context->addParam("user",$user_obj);
return true;
}
}部署命令的调用者
class Command_Facotry{
public function get_command($action){
$class = UCFirst(strtolower($action))."_Command";
$cmd = new $class();
return $cmd;
}
}客户端
class Controller{
private $context;
function __construct(){
//Command_Context主要用来存储request和params
$this->context =new Command_Context();
}
function process(){
$cmd Command_Factory::get_commad($this->context->get('action'));
if(!$cmd-execute($this->context)){
//错误处理
}else{
//成功 分发视图
}
}
}使用
$controller =new Controller();
$context = $controller->get_context();
$context->add_param('action','login');
$context->add_param('username','404_k');
$context->add_param('pass','123456');
$controller->process();
Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Apakah yang dilakukan oleh mod Jangan Ganggu WeChat?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
Apakah yang dilakukan oleh mod Jangan Ganggu WeChat?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
Apakah maksud mod Jangan Ganggu WeChat Pada masa kini, dengan populariti telefon pintar dan perkembangan pesat Internet mudah alih, platform media sosial telah menjadi bahagian yang amat diperlukan dalam kehidupan seharian orang ramai. WeChat ialah salah satu platform media sosial paling popular di China, dan hampir semua orang mempunyai akaun WeChat. Kita boleh berkomunikasi dengan rakan, keluarga dan rakan sekerja dalam masa nyata melalui WeChat, berkongsi detik dalam hidup kita dan memahami situasi semasa satu sama lain. Namun begitu, dalam era ini, sudah pasti kita juga berdepan dengan masalah sarat maklumat dan kebocoran privasi terutamanya bagi mereka yang perlu fokus atau
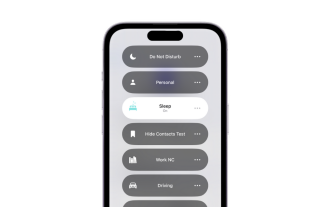 Apakah mod tidur digunakan pada iPhone?
Nov 04, 2023 am 11:13 AM
Apakah mod tidur digunakan pada iPhone?
Nov 04, 2023 am 11:13 AM
Peranti iOS telah lama dapat menjejaki corak tidur anda dan banyak lagi menggunakan apl Kesihatan. Tetapi bukankah ia menjengkelkan apabila anda diganggu oleh pemberitahuan semasa anda sedang tidur? Pemberitahuan ini mungkin tidak relevan dan oleh itu mengganggu corak tidur anda dalam proses. Walaupun mod Jangan Ganggu ialah cara terbaik untuk mengelakkan gangguan semasa tidur, ia boleh menyebabkan anda terlepas panggilan dan mesej penting yang anda terima pada waktu malam. Syukurlah, di sinilah mod tidur masuk. Mari ketahui lebih lanjut mengenainya dan cara menggunakannya pada iPhone. Apakah peranan yang dimainkan oleh mod tidur pada iPhone Mod tidur ialah mod fokus khusus dalam iOS yang diaktifkan secara automatik berdasarkan jadual tidur anda dalam apl "Kesihatan". Ia membantu anda menetapkan penggera dan kemudian
 Apakah maksud mod epc o?
Nov 09, 2022 am 10:54 AM
Apakah maksud mod epc o?
Nov 09, 2022 am 10:54 AM
Model epc o merujuk kepada rangka kerja kontrak am yang mengintegrasikan reka bentuk, perolehan, dsb. Ia adalah beberapa pautan operasi yang diperolehi daripada epc iaitu, semasa tempoh pembinaan, kontraktor am bukan sahaja perlu menjalankan tugas reka bentuk dalam pengertian tradisional, tetapi juga untuk mengambil alih semua tugas penyelenggaraan sepanjang tempoh operasi. Model ini boleh meningkatkan kecekapan operasi banyak projek dan mengurangkan kos operasi dengan cepat.
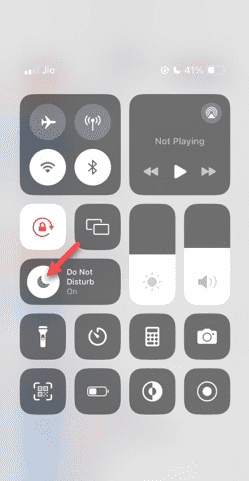 Mod Jangan Ganggu Tidak Berfungsi dalam iPhone: Betulkan
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
Mod Jangan Ganggu Tidak Berfungsi dalam iPhone: Betulkan
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
Malah menjawab panggilan dalam mod Jangan Ganggu boleh menjadi pengalaman yang sangat menjengkelkan. Seperti namanya, mod Jangan Ganggu mematikan semua pemberitahuan panggilan masuk dan makluman daripada e-mel, mesej, dsb. Anda boleh mengikuti set penyelesaian ini untuk membetulkannya. Betulkan 1 – Dayakan Mod Fokus Dayakan mod fokus pada telefon anda. Langkah 1 – Leret ke bawah dari atas untuk mengakses Pusat Kawalan. Langkah 2 – Seterusnya, dayakan “Mod Fokus” pada telefon anda. Mod Fokus mendayakan mod Jangan Ganggu pada telefon anda. Ia tidak akan menyebabkan sebarang makluman panggilan masuk muncul pada telefon anda. Betulkan 2 – Tukar Tetapan Mod Fokus Jika terdapat beberapa isu dalam tetapan mod fokus, anda harus membetulkannya. Langkah 1 – Buka tetingkap tetapan iPhone anda. Langkah 2 – Seterusnya, hidupkan tetapan mod Fokus
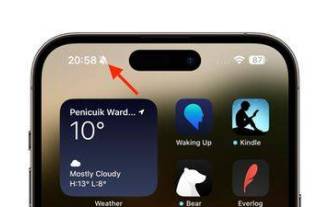 iPhone 15 Pro: Bagaimana untuk membuang simbol mod senyap dalam bar status
Sep 24, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
iPhone 15 Pro: Bagaimana untuk membuang simbol mod senyap dalam bar status
Sep 24, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
Pada model iPhone 15 Pro dan iPhone 15 Pro Max, Apple memperkenalkan butang tindakan boleh atur cara secara fizikal yang menggantikan suis deringan/senyap tradisional di atas butang kelantangan. Butang tindakan boleh diprogramkan untuk melaksanakan beberapa fungsi yang berbeza, tetapi keupayaan untuk bertukar antara mod senyap dan deringan tidak hilang. Secara lalai, tekan lama pada butang tindakan akan menyenyapkan peranti dan maklum balas sentuhan butang akan berdenyut tiga kali. Kedua-dua model iPhone 15 Pro akan memaparkan simbol loceng berpalang di sebelah masa dalam bar status untuk menunjukkan bahawa mod senyap/senyap diaktifkan, dan ia akan kekal sedemikian sehingga anda menekan lama butang Tindakan sekali lagi untuk menyahredam peranti. Jika anda lebih suka meletakkan iPhone anda dalam mod senyap
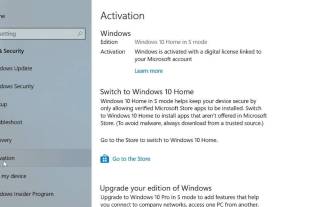 Bagaimana untuk meninggalkan mod S pada Windows 10/11
Aug 03, 2023 pm 08:17 PM
Bagaimana untuk meninggalkan mod S pada Windows 10/11
Aug 03, 2023 pm 08:17 PM
Windows dalam mod S direka untuk menyediakan keselamatan dan prestasi yang dipertingkatkan dengan hanya membenarkan pemasangan apl daripada Gedung Microsoft. Walaupun ciri ini membantu menghalang perisian hasad dan memastikan persekitaran pengkomputeran yang selamat, ciri ini mungkin mengehadkan pengguna yang ingin memasang aplikasi daripada sumber selain daripada Gedung Microsoft. Jika anda mendapati diri anda dalam situasi ini dan terus bertanya kepada diri sendiri bagaimana untuk keluar daripada Mod S dalam Windows 10/11, maka anda telah datang ke tempat yang betul kerana kami akan membimbing anda melalui cara untuk keluar dari Mod S dalam Windows 10/11 menggunakan dua kaedah berbeza Langkah ke Mod S memastikan anda boleh menikmati kebebasan memasang apl dari mana-mana sahaja yang anda pilih. Ketahui cara untuk keluar daripada mod S dalam Windows
 Panduan untuk menggunakan mod siap sedia dalam iOS 17
Aug 22, 2023 pm 04:01 PM
Panduan untuk menggunakan mod siap sedia dalam iOS 17
Aug 22, 2023 pm 04:01 PM
Mod siap sedia akan datang ke iPhone dengan iOS17, dan panduan ini bertujuan untuk menunjukkan kepada anda cara menggunakan ciri ini pada iPhone anda. Mod Siap Sedia ialah ciri terobosan yang mengubah iPhone menjadi paparan pintar yang dinamik dan sentiasa hidup. Apabila iPhone anda diletakkan secara mendatar di sisinya semasa mengecas, ia mengaktifkan mod siap sedia. Mod ini dengan cantik mempamerkan pelbagai widget berguna, termasuk tetapi tidak terhad kepada masa semasa, kemas kini cuaca tempatan, tayangan slaid foto kegemaran anda dan juga kawalan main balik muzik. Kelebihan ketara mod ini ialah keupayaannya untuk memaparkan pemberitahuan, membolehkan pengguna melihat dan berinteraksi dengan mereka tanpa perlu membangunkan iPhone mereka sepenuhnya. Cara Menggunakan Mod Siap Sedia Untuk Mod Siap Sedia berfungsi dengan baik, iPhone anda mesti berjalan i
 Bagaimana untuk mendayakan 'Notepad++ Dark Mode' dan 'Notepad++ Dark Theme'?
Oct 27, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
Bagaimana untuk mendayakan 'Notepad++ Dark Mode' dan 'Notepad++ Dark Theme'?
Oct 27, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
Notepad++ dark mode v8.0 tidak mempunyai parameter, Notepad++ ialah editor teks yang paling berguna. Setiap apl yang dijalankan pada Windows 10 menyokong mod gelap. Anda boleh menamakan penyemak imbas web seperti Chrome, Firefox dan Microsoft Edge. Jika anda menggunakan Notepad++, latar belakang putih lalai mungkin menyakitkan mata anda. Pembangun telah menambahkan mod gelap pada versi 8 Notepad++, berikut ialah cara untuk menghidupkannya. Dayakan Notepad untuk Windows 11/10 ++ Dark Mode Launch Notepad ++ Klik "Settings" > "Preferences" > "Dark Mode" Pilih "Enable Dark Mode" untuk memulakan semula Notepad




