 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Bagaimanakah SpringBoot menggunakan RateLimiter untuk mengehadkan arus melalui AOP?
Bagaimanakah SpringBoot menggunakan RateLimiter untuk mengehadkan arus melalui AOP?
Bagaimanakah SpringBoot menggunakan RateLimiter untuk mengehadkan arus melalui AOP?
Gunakan RateLimiter untuk mengehadkan arus melalui AOP
1 Perkenalkan dependensi
<!-- guava 限流 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>25.1-jre</version>
</dependency>2 anotasi tersuai
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ServiceLimit {
String description() default "";
}3 4. Gunakan
@Component
@Scope
@Aspect
public class LimitAspect {
每秒只发出5个令牌,此处是单进程服务的限流,内部采用令牌捅算法实现
private static RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(5.0);
//Service层切点 限流
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.itstyle.seckill.common.aop.ServiceLimit)")
public void ServiceAspect() {
}
@Around("ServiceAspect()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Boolean flag = rateLimiter.tryAcquire();
Object obj = null;
try {
if(flag){
obj = joinPoint.proceed();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
}Had semasa SpringBoot
Algoritma asas had semasa
Badi token dan baldi bocor
- Pelaksanaan algoritma baldi bocor selalunya bergantung pada baris gilir Jika permintaan tiba dan baris gilir tidak penuh, ia terus dimasukkan ke dalam baris gilir, dan kemudian pemproses mengeluarkan permintaan daripada ketua baris gilir. frekuensi tetap untuk pemprosesan. Jika volum permintaan adalah besar, baris gilir akan penuh dan permintaan baharu akan dibuang.
- Algoritma baldi token ialah baldi yang menyimpan token dengan kapasiti tetap dan token ditambahkan pada baldi pada kadar tetap. Terdapat had maksimum untuk bilangan token yang disimpan dalam baldi Setelah melebihi, ia akan dibuang atau ditolak. Apabila permintaan trafik atau rangkaian tiba, setiap permintaan mesti mendapatkan token Jika ia boleh diperolehi, ia akan diproses terus dan token akan dipadamkan daripada baldi token. Jika ia tidak dapat diperoleh, permintaan akan dihadkan aliran dan sama ada dibuang terus atau menunggu dalam penimbal.
- Timba token menambah token pada baldi pada kadar tetap , sama ada permintaan diproses bergantung pada sama ada terdapat cukup token dalam baldi Apabila bilangan token berkurangan kepada sifar, permintaan aliran keluar baldi bocor pada kadar tetap yang tetap, dan kadar permintaan masuk adalah sewenang-wenangnya permintaan masuk terkumpul Apabila kapasiti baldi bocor tercapai, permintaan masuk baharu akan ditolak selagi ada token, ia boleh diproses Sokongan Ambil 3 token dan 4 token pada satu masa; baldi bocor mengehadkan kadar aliran keluar yang berterusan, iaitu, kadar aliran keluar adalah nilai tetap, contohnya, ia sentiasa mengalir keluar pada kadar 1, tetapi ia tidak boleh menjadi 1 sekali dan 2 kali seterusnya melancarkan kadar aliran masuk pecah; adalah untuk melancarkan kadar aliran keluar;
- Penghad Kadar Jambu
1 Kebergantungan
@Override @ServiceLimit @Transactional public Result startSeckil(long seckillId,long userId) { //todo 操作 }Salin selepas log masuk- Kod sampel
<dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>28.1-jre</version> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>Salin selepas log masuk
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RequestInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
// 根据字符串分不同的令牌桶, 每天自动清理缓存
private static LoadingCache<String, RateLimiter> cachesRateLimiter = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000) //设置缓存个数
/**
* expireAfterWrite是在指定项在一定时间内没有创建/覆盖时,会移除该key,下次取的时候从loading中取
* expireAfterAccess是指定项在一定时间内没有读写,会移除该key,下次取的时候从loading中取
* refreshAfterWrite是在指定时间内没有被创建/覆盖,则指定时间过后,再次访问时,会去刷新该缓存,在新值没有到来之前,始终返回旧值
* 跟expire的区别是,指定时间过后,expire是remove该key,下次访问是同步去获取返回新值;
* 而refresh则是指定时间后,不会remove该key,下次访问会触发刷新,新值没有回来时返回旧值
*/
.expireAfterAccess(1, TimeUnit.HOURS)
.build(new CacheLoader<String, RateLimiter>() {
@Override
public RateLimiter load(String key) throws Exception {
// 新的字符串初始化 (限流每秒2个令牌响应)
return RateLimiter.create(2);
}
});
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
log.info("request请求地址path[{}] uri[{}]", request.getServletPath(), request.getRequestURI());
try {
String str = "hello";
// 令牌桶
RateLimiter rateLimiter = cachesRateLimiter.get(str);
if (!rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
System.out.println("too many requests.");
return false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 解决拦截器的异常,全局异常处理器捕获不到的问题
request.setAttribute("exception", e);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/error").forward(request, response);
}
return true;
}
}http://localhost:8080/user/
Jika tiada kelas hasil, anda boleh mengembalikan rentetan sesuka hati
4. Keputusan ujianLain-lain
Buat
RateLimiter menyediakan dua kaedah kilang: Satu adalah letusan lancar Mengehadkan arus
Satu adalah letusan lancar Mengehadkan arus
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
public Result test2(){
System.out.println("1111");
return new Result(true,200,"");
}
}Satu adalah menghadkan arus prapanas lancar
RateLimiter r = RateLimiter.create(5); //项目启动,直接允许5个令牌
Keburukan
RateLimiter hanya boleh digunakan untuk pengehadan arus mesin tunggal, jika anda mahukan kluster Untuk pengehadan semasa, anda perlu memperkenalkan redis atau perisian tengah sentinel sumber terbuka Alibaba.
rreeeeAtas ialah kandungan terperinci Bagaimanakah SpringBoot menggunakan RateLimiter untuk mengehadkan arus melalui AOP?. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

Video Face Swap
Tukar muka dalam mana-mana video dengan mudah menggunakan alat tukar muka AI percuma kami!

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1205
1205
 24
24
 Bagaimana Springboot menyepadukan Jasypt untuk melaksanakan penyulitan fail konfigurasi
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Bagaimana Springboot menyepadukan Jasypt untuk melaksanakan penyulitan fail konfigurasi
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Pengenalan kepada Jasypt Jasypt ialah perpustakaan java yang membenarkan pembangun menambah fungsi penyulitan asas pada projeknya dengan usaha yang minimum dan tidak memerlukan pemahaman yang mendalam tentang cara penyulitan berfungsi dengan tinggi untuk penyulitan sehala dan dua hala. teknologi penyulitan berasaskan piawai. Sulitkan kata laluan, teks, nombor, perduaan... Sesuai untuk penyepaduan ke dalam aplikasi berasaskan Spring, API terbuka, untuk digunakan dengan mana-mana pembekal JCE... Tambahkan kebergantungan berikut: com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2 Faedah Jasypt melindungi keselamatan sistem kami Walaupun kod itu bocor, sumber data boleh dijamin.
 Bagaimana SpringBoot menyepadukan Redisson untuk melaksanakan baris gilir kelewatan
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Bagaimana SpringBoot menyepadukan Redisson untuk melaksanakan baris gilir kelewatan
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Senario penggunaan 1. Tempahan berjaya dibuat tetapi pembayaran tidak dibuat dalam masa 30 minit. Pembayaran tamat masa dan pesanan dibatalkan secara automatik 2. Pesanan telah ditandatangani dan tiada penilaian dilakukan selama 7 hari selepas ditandatangani. Jika pesanan tamat dan tidak dinilai, sistem lalai kepada penilaian positif 3. Pesanan dibuat dengan jayanya jika peniaga tidak menerima pesanan selama 5 minit, pesanan itu dibatalkan peringatan mesej teks dihantar... Untuk senario dengan kelewatan yang lama dan prestasi masa nyata yang rendah, kami boleh Gunakan penjadualan tugas untuk melaksanakan pemprosesan undian biasa. Contohnya: xxl-job Hari ini kita akan memilih
 Cara menggunakan Redis untuk melaksanakan kunci teragih dalam SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
Cara menggunakan Redis untuk melaksanakan kunci teragih dalam SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
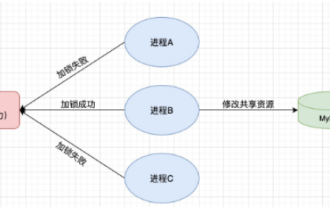
1. Redis melaksanakan prinsip kunci teragih dan mengapa kunci teragih diperlukan Sebelum bercakap tentang kunci teragih, adalah perlu untuk menjelaskan mengapa kunci teragih diperlukan. Lawan daripada kunci yang diedarkan ialah kunci yang berdiri sendiri Apabila kami menulis program berbilang benang, kami mengelakkan masalah data yang disebabkan oleh mengendalikan pembolehubah yang dikongsi pada masa yang sama Kami biasanya menggunakan kunci untuk mengecualikan pembolehubah yang dikongsi bersama untuk memastikan ketepatannya pembolehubah yang dikongsi skop penggunaannya adalah dalam proses yang sama. Jika terdapat berbilang proses yang perlu mengendalikan sumber yang dikongsi pada masa yang sama, bagaimanakah ia boleh saling eksklusif? Aplikasi perniagaan hari ini biasanya merupakan seni bina perkhidmatan mikro, yang juga bermakna bahawa satu aplikasi akan menggunakan berbilang proses Jika berbilang proses perlu mengubah suai baris rekod yang sama dalam MySQL, untuk mengelakkan data kotor yang disebabkan oleh operasi yang tidak teratur, keperluan pengedaran. untuk diperkenalkan pada masa ini. Gaya dikunci. Ingin mencapai mata
 Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikan masalah bahawa springboot tidak boleh mengakses fail selepas membacanya ke dalam pakej balang
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikan masalah bahawa springboot tidak boleh mengakses fail selepas membacanya ke dalam pakej balang
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot membaca fail, tetapi tidak boleh mengakses perkembangan terkini selepas membungkusnya ke dalam pakej balang Terdapat situasi di mana springboot tidak boleh membaca fail selepas membungkusnya ke dalam pakej balang adalah tidak sah dan hanya boleh diakses melalui strim. Fail berada di bawah resources publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan Springboot+Mybatis-plus tanpa menggunakan pernyataan SQL untuk menambah berbilang jadual
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan Springboot+Mybatis-plus tanpa menggunakan pernyataan SQL untuk menambah berbilang jadual
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Apabila Springboot+Mybatis-plus tidak menggunakan pernyataan SQL untuk melaksanakan operasi penambahan berbilang jadual, masalah yang saya hadapi akan terurai dengan mensimulasikan pemikiran dalam persekitaran ujian: Cipta objek BrandDTO dengan parameter untuk mensimulasikan parameter yang dihantar ke latar belakang bahawa adalah amat sukar untuk melaksanakan operasi berbilang jadual dalam Mybatis-plus Jika anda tidak menggunakan alatan seperti Mybatis-plus-join, anda hanya boleh mengkonfigurasi fail Mapper.xml yang sepadan dan mengkonfigurasi ResultMap yang berbau dan kemudian. tulis pernyataan sql yang sepadan Walaupun kaedah ini kelihatan menyusahkan, ia sangat fleksibel dan membolehkan kita
 Analisis perbandingan dan perbezaan antara SpringBoot dan SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Analisis perbandingan dan perbezaan antara SpringBoot dan SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot dan SpringMVC adalah kedua-dua rangka kerja yang biasa digunakan dalam pembangunan Java, tetapi terdapat beberapa perbezaan yang jelas antara mereka. Artikel ini akan meneroka ciri dan penggunaan kedua-dua rangka kerja ini dan membandingkan perbezaannya. Mula-mula, mari belajar tentang SpringBoot. SpringBoot telah dibangunkan oleh pasukan Pivotal untuk memudahkan penciptaan dan penggunaan aplikasi berdasarkan rangka kerja Spring. Ia menyediakan cara yang pantas dan ringan untuk membina bersendirian, boleh dilaksanakan
 Bagaimana SpringBoot menyesuaikan Redis untuk melaksanakan penyirian cache
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
Bagaimana SpringBoot menyesuaikan Redis untuk melaksanakan penyirian cache
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. Sesuaikan RedisTemplate1.1, mekanisme siri lalai RedisAPI Pelaksanaan cache Redis berasaskan API menggunakan templat RedisTemplate untuk operasi cache data Di sini, buka kelas RedisTemplate dan lihat maklumat kod sumber kelas tersebut. Isytihar kunci, Pelbagai kaedah pesirilan nilai, nilai awal kosong @NullableprivateRedisSe
 Bagaimana untuk mendapatkan nilai dalam application.yml dalam springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
Bagaimana untuk mendapatkan nilai dalam application.yml dalam springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
Dalam projek, beberapa maklumat konfigurasi sering diperlukan Maklumat ini mungkin mempunyai konfigurasi yang berbeza dalam persekitaran ujian dan persekitaran pengeluaran, dan mungkin perlu diubah suai kemudian berdasarkan keadaan perniagaan sebenar. Kami tidak boleh mengekodkan konfigurasi ini dalam kod. Adalah lebih baik untuk menulisnya dalam fail konfigurasi Sebagai contoh, anda boleh menulis maklumat ini dalam fail application.yml. Jadi, bagaimana untuk mendapatkan atau menggunakan alamat ini dalam kod? Terdapat 2 kaedah. Kaedah 1: Kita boleh mendapatkan nilai yang sepadan dengan kunci dalam fail konfigurasi (application.yml) melalui ${key} beranotasi dengan @Value Kaedah ini sesuai untuk situasi di mana terdapat sedikit perkhidmatan mikro projek, Apabila perniagaan adalah rumit, logik



