 Operasi dan penyelenggaraan
Operasi dan penyelenggaraan
 Nginx
Nginx
 Bagaimana untuk membina dan mengkonfigurasi perkhidmatan Nginx di bawah Ubuntu
Bagaimana untuk membina dan mengkonfigurasi perkhidmatan Nginx di bawah Ubuntu
Bagaimana untuk membina dan mengkonfigurasi perkhidmatan Nginx di bawah Ubuntu
1. Nginx
Nginx ("enjin x") ialah pelayan proksi Web berprestasi tinggi yang dibangunkan oleh pengaturcara Rusia Igor Sysoev. Ia juga merupakan pelayan proksi IMAP/POP3/SMTP.
Salah satu daripada tiga pelayan WEB utama: apache, Nginx, lighttpd. Nginx ialah alternatif yang baik dan lebih sesuai daripada pelayan Apache apabila anda perlu mengendalikan sambungan serentak yang tinggi.
senario aplikasi nginx
Pelayan statik. (Perkhidmatan gambar, video) Satu lagi ialah lighttpd. Berpuluh-puluh ribu operasi serentak, html, js, css, flv, jpg, gif, dll.
Perkhidmatan dinamik, nginx——fastcgi menjalankan PHP, jsp. (Konkurensi PHP ialah 500-1500, konkurensi MySQL ialah 300-1500).
Proksi songsang, imbangan beban. Jika pv harian di bawah 2000W, anda boleh terus menggunakan nginx sebagai proksi.
Perkhidmatan cache. Sama seperti SOtong, VARNISH.
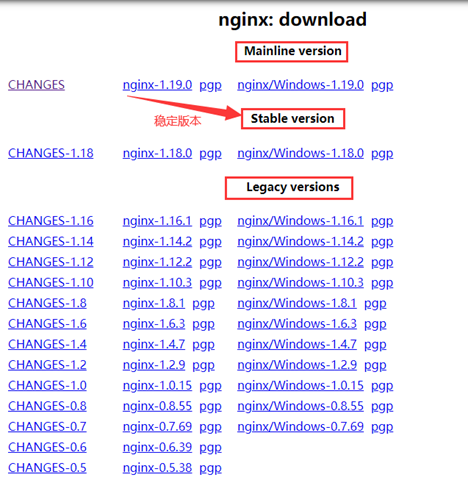
Laman web rasmi menyediakan tiga versi:
Laman web rasmi Nginx menyediakan tiga jenis versi
Versi Mainline: Mainline ialah versi yang sedang diusahakan oleh Nginx . Anda boleh Ia dikatakan sebagai versi pembangunan
Versi stabil: versi stabil terkini, versi disyorkan untuk persekitaran pengeluaran
Versi warisan: versi stabil versi lama warisan
2 , pembinaan perkhidmatan nginx
1 Gunakan apt untuk memasang
sudo apt install nginx
2 Lokasi selepas pemasangan:
/. usr/sbin/nginx: program utama
/etc/nginx: menyimpan fail konfigurasi
/usr/share/nginx: menyimpan fail statik
/var/log/nginx: menyimpan log
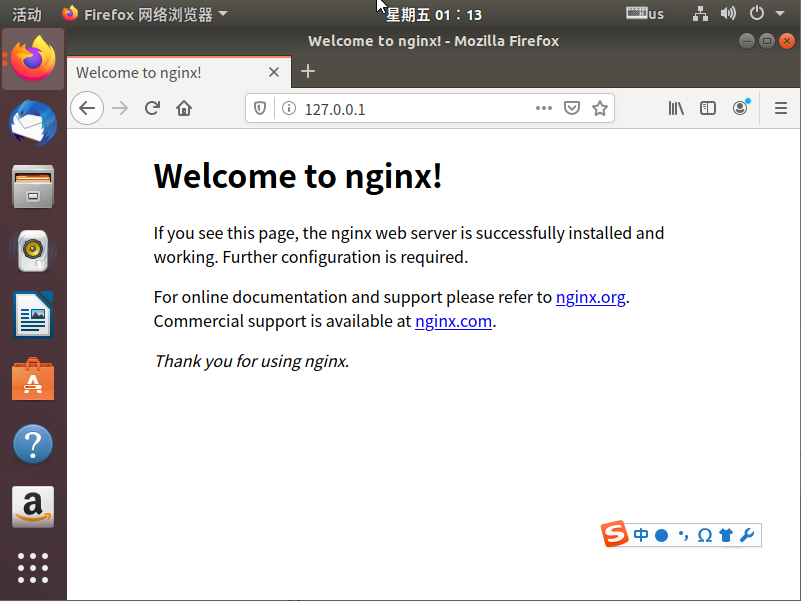
3 Mulakan dan sahkan kesannya
service nginx start # 启动nginx service nginx reload # 重新加载nginx配置文件
Masukkan IP anda alamat dalam penyemak imbas, jika Wellcome kelihatan nginx maka konfigurasi berjaya.
Dua arahan lain
nginx -s reopen # 重启 Nginx nginx -s stop # 停止 Nginx
4. Semak nombor versi:
~$ nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 (Ubuntu)
3
Blok global: konfigurasikan arahan yang mempengaruhi nginx secara global. Secara amnya, terdapat kumpulan pengguna untuk menjalankan pelayan nginx, laluan penyimpanan pid proses nginx, laluan storan log, pengenalan fail konfigurasi, bilangan proses pekerja yang dibenarkan untuk dihasilkan, dsb.
sekat acara : Konfigurasi yang mempengaruhi pelayan nginx atau sambungan rangkaian kepada pengguna. Terdapat bilangan maksimum sambungan bagi setiap proses, yang model dipacu peristiwa untuk dipilih untuk mengendalikan permintaan sambungan, sama ada membenarkan berbilang sambungan rangkaian diterima pada masa yang sama, membolehkan bersiri berbilang sambungan rangkaian, dsb.
blok http: Anda boleh menyusun berbilang pelayan, mengkonfigurasi proksi, cache, definisi log dan kebanyakan fungsi lain serta konfigurasi modul pihak ketiga. Seperti pengenalan fail, definisi jenis mime, penyesuaian log, sama ada menggunakan fail hantar untuk memindahkan fail, tamat masa sambungan, bilangan permintaan sambungan tunggal, dsb.
blok pelayan : Konfigurasikan parameter berkaitan hos maya Terdapat berbilang pelayan dalam satu http.
blok lokasi : Konfigurasikan penghalaan permintaan dan pemprosesan pelbagai halaman.
... # 全局块。配置影响nginx全局的指令。
events { # events块。配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。
...
}
http # http块。可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。
{
... # http全局块
server # server块。配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。
{
... # server全局块
location [PATTERN] # location块。配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
{
...
}
location [PATTERN]
{
...
}
}
server
{
...
}
... # http全局块
}##
# You should look at the following URL's in order to grasp a solid understanding
# of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx.
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/
# https://wiki.debian.org/Nginx/DirectoryStructure
#
# In most cases, administrators will remove this file from sites-enabled/ and
# leave it as reference inside of sites-available where it will continue to be
# updated by the nginx packaging team.
#
# This file will automatically load configuration files provided by other
# applications, such as Drupal or Wordpress. These applications will be made
# available underneath a path with that package name, such as /drupal8.
#
# Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples.
##
# Default server configuration
#
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
# SSL configuration
#
# listen 443 ssl default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl default_server;
#
# Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332
#
# Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782
#
# Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package
# Don't use them in a production server!
#
# include snippets/snakeoil.conf;
root /var/www/html;
# Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location / {
# First attempt to serve request as file, then
# as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404.
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
# pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets):
# fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
# # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets):
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# Virtual Host configuration for example.com
#
# You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that
# to sites-enabled/ to enable it.
#
#server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80;
#
# server_name example.com;
#
# root /var/www/example.com;
# index index.html;
#
# location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# }
#}Salin selepas log masuk
3. Konfigurasi asas nginx##
# You should look at the following URL's in order to grasp a solid understanding
# of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx.
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/
# https://wiki.debian.org/Nginx/DirectoryStructure
#
# In most cases, administrators will remove this file from sites-enabled/ and
# leave it as reference inside of sites-available where it will continue to be
# updated by the nginx packaging team.
#
# This file will automatically load configuration files provided by other
# applications, such as Drupal or Wordpress. These applications will be made
# available underneath a path with that package name, such as /drupal8.
#
# Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples.
##
# Default server configuration
#
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
# SSL configuration
#
# listen 443 ssl default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl default_server;
#
# Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332
#
# Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782
#
# Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package
# Don't use them in a production server!
#
# include snippets/snakeoil.conf;
root /var/www/html;
# Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location / {
# First attempt to serve request as file, then
# as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404.
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
# pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets):
# fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
# # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets):
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# Virtual Host configuration for example.com
#
# You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that
# to sites-enabled/ to enable it.
#
#server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80;
#
# server_name example.com;
#
# root /var/www/example.com;
# index index.html;
#
# location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# }
#}########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。#################
#user administrator administrators; #配置用户或者组,默认为nobody nobody。
#worker_processes 2; #允许生成的进程数,默认为1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #指定nginx进程运行文件存放地址
error_log log/error.log debug; #制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块,级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on
multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off
#use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512
}
http {
include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain
#access_log off; #取消服务日志
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #自定义格式
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined为日志格式的默认值
sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块。
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。
keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; #错误页
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。
listen 80; #监听端口
server_name 127.0.0.1; #监听地址
location ~*^.+$ { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。
#root path; #根目录
#index vv.txt; #设置默认页
proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表
deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip
allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip
}
}
}Salin selepas log masuk
4 Sahkan fail konfigurasi: ########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。#################
#user administrator administrators; #配置用户或者组,默认为nobody nobody。
#worker_processes 2; #允许生成的进程数,默认为1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #指定nginx进程运行文件存放地址
error_log log/error.log debug; #制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块,级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on
multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off
#use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512
}
http {
include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain
#access_log off; #取消服务日志
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #自定义格式
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined为日志格式的默认值
sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块。
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。
keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; #错误页
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。
listen 80; #监听端口
server_name 127.0.0.1; #监听地址
location ~*^.+$ { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。
#root path; #根目录
#index vv.txt; #设置默认页
proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表
deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip
allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip
}
}
}#下面是server虚拟主机的配置段
server
{
listen 80;#监听端口
server_name localhost;#域名
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /usr/local/webserver/nginx/html;#站点目录
location ~ .*\.(php|php5)?$
{
#fastcgi_pass unix:/tmp/php-cgi.sock;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ico)$
{
expires 30d;
#access_log off;
}
location ~ .*\.(js|css)?$
{
expires 15d;
#access_log off;
}
access_log off;
}Salin selepas log masuk
5. pembolehubah global nginx Untuk merekodkan alamat IP pelanggan, anda boleh menggunakan $remote_addr dan $http_x_forwarded_for#下面是server虚拟主机的配置段
server
{
listen 80;#监听端口
server_name localhost;#域名
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /usr/local/webserver/nginx/html;#站点目录
location ~ .*\.(php|php5)?$
{
#fastcgi_pass unix:/tmp/php-cgi.sock;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ico)$
{
expires 30d;
#access_log off;
}
location ~ .*\.(js|css)?$
{
expires 15d;
#access_log off;
}
access_log off;
}- $remote_user: digunakan untuk merekodkan nama pengguna klien; 🎜> $request: digunakan untuk merekodkan URL dan protokol http bagi permintaan itu; 🎜>
$body_bytes_s ent: merekodkan saiz kandungan kandungan fail yang dihantar kepada klien
$http_referer: digunakan untuk merekodkan pautan halaman yang diakses daripada; ;
-
$http_user_agent: Rekod maklumat yang berkaitan pelayar klien; Konfigurasi pelayan HTTP statik
Pertama sekali, Nginx ialah pelayan HTTP yang boleh memaparkan fail statik (seperti HTML dan gambar) pada pelayan kepada klien melalui protokol HTTP. - Konfigurasi: 2. Konfigurasi pelayan proksi terbalik
root@ubuntu: nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Salin selepas log masuk - Apakah proksi terbalik?
Klien boleh terus mengakses pelayan aplikasi laman web melalui protokol HTTP Jika pentadbir tapak web menambah Nginx di tengah, pelanggan meminta Nginx, Nginx meminta pelayan aplikasi, dan kemudian mengembalikan hasilnya kepada klien. Nginx ialah pelayan proksi Songsang.
- Konfigurasi proksi songsang:
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.0.112:8080; # 应用服务器HTTP地址
}
}既然服务器可以直接HTTP访问,为什么要在中间加上一个反向代理,不是多此一举吗?反向代理有什么作用?继续往下看,下面的负载均衡、虚拟主机,都基于反向代理实现,当然反向代理的功能也不仅仅是这些。
3、负载均衡配置
当网站访问量非常大,也摊上事儿了。因为网站越来越慢,一台服务器已经不够用了。因此,可以将同一应用部署在多台服务器上,以将众多用户请求分配至多台机器进行处理。即使其中一台服务器故障,只要其他服务器正常运行,用户仍然可以正常使用,这是多台服务器带来的好处。Nginx可以通过反向代理来实现负载均衡。
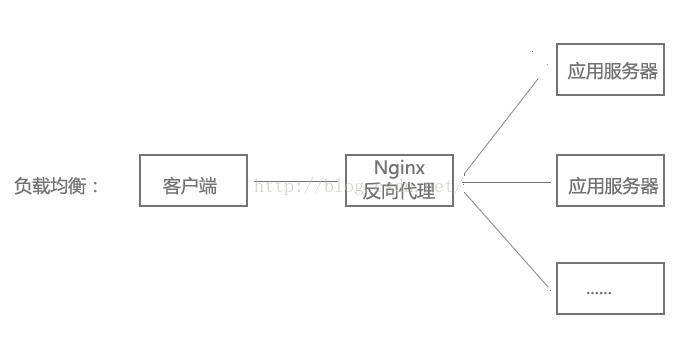
负载均衡配置:
upstream myapp {
server 192.168.0.111:8080; # 应用服务器1
server 192.168.0.112:8080; # 应用服务器2
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myweb;
}
}4、虚拟主机配置
有的网站访问量大,需要负载均衡。然而并不是所有网站都如此出色,有的网站,由于访问量太小,需要节省成本,将多个网站部署在同一台服务器上。
例如将www.aaa.com和www.bbb.com两个网站部署在同一台服务器上,两个域名解析到同一个IP地址,但是用户通过两个域名却可以打开两个完全不同的网站,互相不影响,就像访问两个服务器一样,所以叫两个虚拟主机。
虚拟主机配置:
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
return 444; # 过滤其他域名的请求,返回444状态码
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.aaa.com; # www.aaa.com域名
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080; # 对应端口号8080
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.bbb.com; # www.bbb.com域名
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8081; # 对应端口号8081
}
}在服务器8080和8081分别开了一个应用,客户端通过不同的域名访问,根据server_name可以反向代理到对应的应用服务器。
虚拟主机的原理是通过HTTP请求头中的Host是否匹配server_name来实现的,有兴趣的同学可以研究一下HTTP协议。
另外,server_name配置还可以过滤有人恶意将某些域名指向你的主机服务器。
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Bagaimana untuk membina dan mengkonfigurasi perkhidmatan Nginx di bawah Ubuntu. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 Bagaimana untuk membenarkan akses rangkaian luaran ke pelayan tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Bagaimana untuk membenarkan akses rangkaian luaran ke pelayan tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Untuk membenarkan pelayan Tomcat mengakses rangkaian luaran, anda perlu: mengubah suai fail konfigurasi Tomcat untuk membenarkan sambungan luaran. Tambahkan peraturan tembok api untuk membenarkan akses kepada port pelayan Tomcat. Buat rekod DNS yang menunjukkan nama domain ke IP awam pelayan Tomcat. Pilihan: Gunakan proksi terbalik untuk meningkatkan keselamatan dan prestasi. Pilihan: Sediakan HTTPS untuk meningkatkan keselamatan.
 Android TV Box mendapat peningkatan Ubuntu 24.04 tidak rasmi
Sep 05, 2024 am 06:33 AM
Android TV Box mendapat peningkatan Ubuntu 24.04 tidak rasmi
Sep 05, 2024 am 06:33 AM
Bagi kebanyakan pengguna, menggodam kotak TV Android kedengaran menakutkan. Walau bagaimanapun, pemaju Murray R. Van Luyn menghadapi cabaran untuk mencari alternatif yang sesuai untuk Raspberry Pi semasa kekurangan cip Broadcom. Usaha kerjasama beliau dengan Armbia
 Bagaimana untuk menjalankan thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Bagaimana untuk menjalankan thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Langkah-langkah untuk menjalankan ThinkPHP Framework secara setempat: Muat turun dan nyahzip ThinkPHP Framework ke direktori tempatan. Buat hos maya (pilihan) yang menunjuk ke direktori akar ThinkPHP. Konfigurasikan parameter sambungan pangkalan data. Mulakan pelayan web. Mulakan aplikasi ThinkPHP. Akses URL aplikasi ThinkPHP dan jalankannya.
 Selamat datang ke nginx! Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikannya?
Apr 17, 2024 am 05:12 AM
Selamat datang ke nginx! Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikannya?
Apr 17, 2024 am 05:12 AM
Untuk menyelesaikan ralat "Selamat datang ke nginx!", anda perlu menyemak konfigurasi hos maya, dayakan hos maya, muat semula Nginx, jika fail konfigurasi hos maya tidak dapat ditemui, buat halaman lalai dan muat semula Nginx, kemudian mesej ralat akan hilang dan laman web akan menjadi paparan biasa.
 Cara berkomunikasi antara bekas docker
Apr 07, 2024 pm 06:24 PM
Cara berkomunikasi antara bekas docker
Apr 07, 2024 pm 06:24 PM
Terdapat lima kaedah untuk komunikasi kontena dalam persekitaran Docker: rangkaian kongsi, Karang Docker, proksi rangkaian, volum dikongsi dan baris gilir mesej. Bergantung pada keperluan pengasingan dan keselamatan anda, pilih kaedah komunikasi yang paling sesuai, seperti memanfaatkan Docker Compose untuk memudahkan sambungan atau menggunakan proksi rangkaian untuk meningkatkan pengasingan.
 Bagaimana untuk menggunakan projek nodejs ke pelayan
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Bagaimana untuk menggunakan projek nodejs ke pelayan
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Langkah-langkah penggunaan pelayan untuk projek Node.js: Sediakan persekitaran penggunaan: dapatkan akses pelayan, pasang Node.js, sediakan repositori Git. Bina aplikasi: Gunakan npm run build untuk menjana kod dan kebergantungan yang boleh digunakan. Muat naik kod ke pelayan: melalui Git atau Protokol Pemindahan Fail. Pasang kebergantungan: SSH ke dalam pelayan dan gunakan pemasangan npm untuk memasang kebergantungan aplikasi. Mulakan aplikasi: Gunakan arahan seperti node index.js untuk memulakan aplikasi, atau gunakan pengurus proses seperti pm2. Konfigurasikan proksi terbalik (pilihan): Gunakan proksi terbalik seperti Nginx atau Apache untuk menghalakan trafik ke aplikasi anda
 Cara mendaftar phpmyadmin
Apr 07, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
Cara mendaftar phpmyadmin
Apr 07, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
Untuk mendaftar untuk phpMyAdmin, anda perlu terlebih dahulu mencipta pengguna MySQL dan memberikan kebenaran kepadanya, kemudian memuat turun, memasang dan mengkonfigurasi phpMyAdmin, dan akhirnya log masuk ke phpMyAdmin untuk mengurus pangkalan data.
 Bagaimana untuk menjana URL daripada fail html
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
Bagaimana untuk menjana URL daripada fail html
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
Menukar fail HTML kepada URL memerlukan pelayan web, yang melibatkan langkah berikut: Dapatkan pelayan web. Sediakan pelayan web. Muat naik fail HTML. Buat nama domain. Halakan permintaan.





