Analisis contoh konfigurasi lokasi dalam pelayan Nginx
Mula-mula, izinkan saya memperkenalkan secara ringkas jenis lokasi dan peraturan padanan, menggunakan contoh wiki nginx sebagai contoh:
location = / {
# matches the query / only.
[ configuration a ]
}
location / {
# matches any query, since all queries begin with /, but regular
# expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be
# matched first.
[ configuration b ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
# matches any query beginning with /images/ and halts searching,
# so regular expressions will not be checked.
[ configuration c ]
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
# matches any request ending in gif, jpg, or jpeg. however, all
# requests to the /images/ directory will be handled by
# configuration c.
[ configuration d ]
}
location @named {
# such locations are not used during normal processing of requests,
# they are intended only to process internally redirected requests (for example error_page, try_files).
[ configuration e ]
}Anda dapat melihat bahawa terdapat 5 jenis lokasi yang berbeza dalam contoh di atas. Yang keempat diawali dengan "~" ialah lokasi yang memerlukan padanan biasa nginx mempunyai peraturan keutamaan yang berbeza untuk lima jenis lokasi yang berbeza ini apabila menghuraikan URL adalah seperti berikut:
1. Jika rentetan itu sepadan dengan lokasi yang diawali dengan "=", ia akan berhenti dan menggunakan konfigurasi lokasi ini
2 Jika rentetan itu sepadan dengan lokasi bukan biasa dan bukan khas yang tinggal, jika ia sepadan Berhenti apabila sampai ke lokasi yang diawali dengan "^~";
3, padanan biasa, susunan padanan ialah susunan lokasi muncul dalam fail konfigurasi. Jika lokasi biasa dipadankan, hentikan dan gunakan konfigurasi lokasi ini jika tidak, gunakan konfigurasi lokasi dengan padanan rentetan terbesar yang diperoleh dalam langkah 2.
Contohnya, untuk permintaan berikut:
1, / -> url -> Pertama, bahagian awalan rentetan sepadan dengan lokasi kedua, dan kemudian melakukan pemadanan biasa Jelas sekali tiada padanan, jadi konfigurasi konfigurasi lokasi keduab
3,/images/1.jpg ->. ; Pertama Bahagian awalan rentetan sepadan dengan lokasi kedua, tetapi kemudian awalan sepadan dengan lokasi ketiga, dan pada masa ini ia sudah menjadi padanan rentetan terbesar untuk URL ini dalam fail konfigurasi, dan lokasi mempunyai awalan "^~" , tiada padanan biasa dilakukan dan konfigurasi c
4 akhirnya digunakan, /some/other/path/to/1.jpg -> Pertama, rentetan yang sama dalam bahagian awalan sepadan dengan lokasi kedua, dan kemudian biasa pemadanan dilakukan , apabila pemadanan biasa berjaya, gunakan congifuration d
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *static_locations; (ngx_pcre) ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **regex_locations; if
location tree和regex_locations数组建立过程在ngx_http_block中:
/* create location trees */
for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) {
clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_conf_error;
}
if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_conf_error;
}
}
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_init_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf,
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
{
...
locations = pclcf->locations;
...
/* 按照类型排序location,排序完后的队列: (exact_match 或 inclusive) (排序好的,如果某个exact_match名字和inclusive location相同,exact_match排在前面)
| regex(未排序)| named(排序好的) | noname(未排序)*/
ngx_queue_sort(locations, ngx_http_cmp_locations);
named = null;
n = 0;
#if (ngx_pcre)
regex = null;
r = 0;
#endif
for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
/* 由于可能存在nested location,也就是location里面嵌套的location,这里需要递归的处理一下当前location下面的nested location */
if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, null, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_error;
}
#if (ngx_pcre)
if (clcf->regex) {
r++;
if (regex == null) {
regex = q;
}
continue;
}
#endif
if (clcf->named) {
n++;
if (named == null) {
named = q;
}
continue;
}
if (clcf->noname) {
break;
}
}
if (q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations)) {
ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
}
/* 如果有named location,将它们保存在所属server的named_locations数组中 */
if (named) {
clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
(n + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
if (clcfp == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
cscf->named_locations = clcfp;
for (q = named;
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
*(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
}
*clcfp = null;
ngx_queue_split(locations, named, &tail);
}
#if (ngx_pcre)
/* 如果有正则匹配location,将它们保存在所属server的http core模块的loc配置的regex_locations 数组中,
这里和named location保存位置不同的原因是由于named location只能存在server里面,而regex location可以作为nested location */
if (regex) {
clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
(r + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
if (clcfp == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
pclcf->regex_locations = clcfp;
for (q = regex;
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
*(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
}
*clcfp = null;
ngx_queue_split(locations, regex, &tail);
}
#endif
return ngx_ok;
} Langkah di atas dikekalkan dalam Lokasi padanan biasa Pokok Lokasi adalah berdasarkan ngx_http_init_stative_location_trees:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(ngx_conf_t *cf,
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
{
ngx_queue_t *q, *locations;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
ngx_http_location_queue_t *lq;
locations = pclcf->locations;
if (locations == null) {
return ngx_ok;
}
if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
return ngx_ok;
}
/* 这里也是由于nested location,需要递归一下 */
for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_error;
}
}
/* join队列中名字相同的inclusive和exact类型location,也就是如果某个exact_match的location名字和普通字符串匹配的location名字相同的话,
就将它们合到一个节点中,分别保存在节点的exact和inclusive下,这一步的目的实际是去重,为后面的建立排序树做准备 */
if (ngx_http_join_exact_locations(cf, locations) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_error;
}
/* 递归每个location节点,得到当前节点的名字为其前缀的location的列表,保存在当前节点的list字段下 */
ngx_http_create_locations_list(locations, ngx_queue_head(locations));
/* 递归建立location三叉排序树 */
pclcf->static_locations = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, 0);
if (pclcf->static_locations == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
return ngx_ok;
}location /xyz {
}
location = /xyz {
}
location /xyza {
}
location /xyzab {
}
location /xyzb {
}
location /abc {
}
location /efg {
}
location /efgaa {
}
static ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *
ngx_http_create_locations_tree(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations,
size_t prefix)
{
...
/* 根节点为locations队列的中间节点 */
q = ngx_queue_middle(locations);
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
len = lq->name->len - prefix;
node = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
offsetof(ngx_http_location_tree_node_t, name) + len);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
node->left = null;
node->right = null;
node->tree = null;
node->exact = lq->exact;
node->inclusive = lq->inclusive;
node->auto_redirect = (u_char) ((lq->exact && lq->exact->auto_redirect)
|| (lq->inclusive && lq->inclusive->auto_redirect));
node->len = (u_char) len;
ngx_memcpy(node->name, &lq->name->data[prefix], len);
/* 从中间节点开始断开 */
ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
/*
* ngx_queue_split() insures that if left part is empty,
* then right one is empty too
*/
goto inclusive;
}
/* 从locations左半部分得到左子树 */
node->left = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, prefix);
if (node->left == null) {
return null;
}
ngx_queue_remove(q);
if (ngx_queue_empty(&tail)) {
goto inclusive;
}
/* 从locations右半部分得到右子树 */
node->right = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &tail, prefix);
if (node->right == null) {
return null;
}
inclusive:
if (ngx_queue_empty(&lq->list)) {
return node;
}
/* 从list队列得到tree子树 */
node->tree = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &lq->list, prefix + len);
if (node->tree == null) {
return null;
}
return node;
}
location tree节点的ngx_http_location_tree_node_s结构:
struct ngx_http_location_tree_node_s {
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *left;
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *right;
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *tree;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *exact;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *inclusive;
u_char auto_redirect;
u_char len;
u_char name[1];
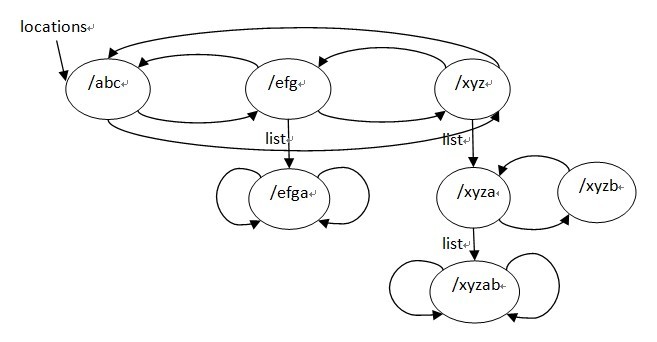
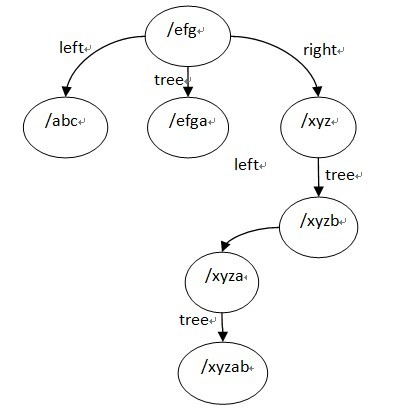
}; location tree结构用到的是left,right,tree 这3个字段, location tree实际上是一个三叉的字符串排序树,而且这里如果某个节点只考虑左,右子树,它是一颗平衡树,它的建立过程有点类似于一颗平衡排序二叉树的建立过程,先排序再用二分查找找到的节点顺序插入,ngx_http_location_tree_node_s的tree节点也是一颗平衡排序树,它是用该节点由ngx_http_create_locations_list()得到的list建立的,也就是该节点的名字是它的tree子树里面的所有节点名字的前缀,所以tree子树里面的所有节点的名字不用保存公共前缀,而且查找的时候,如果是转向tree节点的话,也是不需要再比较父节点的那段字符串了。
ngx_http_create_locations_tree()函数写的很清晰,它有一个参数是队列locations,它返回一颗三叉树,根节点为locations的中间节点,其左子树为locations队列的左半部分建立的location tree,右子树为location队列的右半部分建立的tree,tree节点为该根节点的list队列建立的tree。
最终建立的location tree如下(为了方便阅读,图中列出了tree节点的完整名字):
ps:关于 location modifier
1. =
这会完全匹配指定的 pattern ,且这里的 pattern 被限制成简单的字符串,也就是说这里不能使用正则表达式。
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location = /abcd {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 正好完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 如果运行 nginx server 的系统本身对大小写不敏感,比如 windows ,那么也匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),nginx 不认为这种情况是完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配,因为不是完全匹配
2. (none)
可以不写 location modifier ,nginx 仍然能去匹配 pattern 。这种情况下,匹配那些以指定的 patern 开头的 uri,注意这里的 uri 只能是普通字符串,不能使用正则表达式。
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location /abcd {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 正好完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 如果运行 nginx server 的系统本身对大小写不敏感,比如 windows ,那么也匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash)也属于匹配范围内 http://jb51.net/abcde # 仍然匹配,因为 uri 是以 pattern 开头的
3. ~
这个 location modifier 对大小写敏感,且 pattern 须是正则表达式
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location ~ ^/abcd$ {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 不匹配,~ 对大小写是敏感的 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),并不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$ http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$
注意:对于一些对大小写不敏感的系统,比如 windows ,~ 和 ~* 都是不起作用的,这主要是操作系统的原因。
4. ~*
与 ~ 类似,但这个 location modifier 不区分大小写,pattern 须是正则表达式
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location ~* ^/abcd$ {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 匹配,这就是它不区分大小写的特性 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),并不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$ http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$
5. ^~
匹配情况类似 2. (none) 的情况,以指定匹配模式开头的 uri 被匹配,不同的是,一旦匹配成功,那么 nginx 就停止去寻找其他的 location 块进行匹配了(与 location 匹配顺序有关)
6. @
用于定义一个 location 块,且该块不能被外部 client 所访问,只能被 nginx 内部配置指令所访问,比如 try_files or error_page
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Analisis contoh konfigurasi lokasi dalam pelayan Nginx. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

Video Face Swap
Tukar muka dalam mana-mana video dengan mudah menggunakan alat tukar muka AI percuma kami!

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1205
1205
 24
24
 Cara memeriksa versi nginx
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Cara memeriksa versi nginx
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Kaedah yang boleh menanyakan versi nginx adalah: gunakan perintah nginx -v; Lihat arahan versi dalam fail nginx.conf; Buka halaman ralat Nginx dan lihat tajuk halaman.
 Cara mengkonfigurasi nama domain pelayan awan di nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Cara mengkonfigurasi nama domain pelayan awan di nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Cara mengkonfigurasi nama domain Nginx pada pelayan awan: Buat rekod yang menunjuk ke alamat IP awam pelayan awan. Tambah blok hos maya dalam fail konfigurasi Nginx, menyatakan port pendengaran, nama domain, dan direktori akar laman web. Mulakan semula nginx untuk memohon perubahan. Akses konfigurasi ujian nama domain. Nota Lain: Pasang sijil SSL untuk membolehkan HTTPS, pastikan firewall membenarkan trafik port 80, dan tunggu resolusi DNS berkuatkuasa.
 Cara memeriksa sama ada nginx dimulakan
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Cara memeriksa sama ada nginx dimulakan
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Bagaimana untuk mengesahkan sama ada nginx dimulakan: 1. Gunakan baris arahan: status sistem sistem nginx (linux/unix), netstat -ano | Findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Periksa sama ada port 80 dibuka; 3. Semak mesej permulaan Nginx dalam log sistem; 4. Gunakan alat pihak ketiga, seperti Nagios, Zabbix, dan Icinga.
 Cara memeriksa nama bekas Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Cara memeriksa nama bekas Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Anda boleh menanyakan nama kontena Docker dengan mengikuti langkah -langkah: Senaraikan semua bekas (Docker PS). Tapis senarai kontena (menggunakan arahan grep). Mendapat nama kontena (terletak di lajur "Nama").
 Cara Mengkonfigurasi Nginx di Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Cara Mengkonfigurasi Nginx di Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
Bagaimana cara mengkonfigurasi nginx di Windows? Pasang Nginx dan buat konfigurasi hos maya. Ubah suai fail konfigurasi utama dan sertakan konfigurasi hos maya. Mulakan atau Muat semula Nginx. Uji konfigurasi dan lihat laman web. Selektif membolehkan SSL dan mengkonfigurasi sijil SSL. Selektif tetapkan firewall untuk membolehkan trafik port 80 dan 443.
 Cara memulakan pelayan nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Cara memulakan pelayan nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Memulakan pelayan Nginx memerlukan langkah-langkah yang berbeza mengikut sistem operasi yang berbeza: Sistem Linux/Unix: Pasang pakej Nginx (contohnya, menggunakan apt-get atau yum). Gunakan SystemCTL untuk memulakan perkhidmatan Nginx (contohnya, SUDO SystemCTL Mula Nginx). Sistem Windows: Muat turun dan pasang fail binari Windows. Mula Nginx menggunakan nginx.exe executable (contohnya, nginx.exe -c conf \ nginx.conf). Tidak kira sistem operasi yang anda gunakan, anda boleh mengakses IP pelayan
 Cara membuat bekas untuk Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Cara membuat bekas untuk Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Buat bekas di Docker: 1. Tarik Imej: Docker Pull [Nama Cermin] 2. Buat bekas: Docker Run [Options] [Mirror Name] [Command] 3. Mulailah bekas: Docker Start [Nama Container]
 Cara Memulakan Bekas oleh Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Cara Memulakan Bekas oleh Docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker Container Startup Langkah: Tarik Imej Bekas: Run "Docker Pull [Mirror Name]". Buat bekas: Gunakan "Docker Buat [Pilihan] [Nama Mirror] [Perintah dan Parameter]". Mulakan bekas: Jalankan "Docker Start [Nama Container atau ID]". Semak Status Kontena: Sahkan bahawa bekas sedang berjalan dengan "Docker PS".




