Cetak paparan kiri pokok binari dalam bahasa C
Tugasnya adalah untuk mencetak nod kiri pokok binari yang diberikan. Mula-mula, pengguna akan memasukkan data, dengan itu menjana pokok binari, dan kemudian mencetak pandangan kiri pokok yang terhasil.
Setiap nod boleh mempunyai maksimum 2 nod anak jadi program ini mesti mengulangi hanya penunjuk kiri yang dikaitkan dengan nod
Jika penunjuk kiri tidak batal bermakna ia akan mempunyai beberapa data atau penuding yang dikaitkan dengannya jika tidak, ia akan menjadi kiri kanak-kanak untuk dicetak dan dipaparkan sebagai output.
ContohInput : 1 0 3 2 4
Output : 1 0 2
Salin selepas log masuk
Input : 1 0 3 2 4 Output : 1 0 2
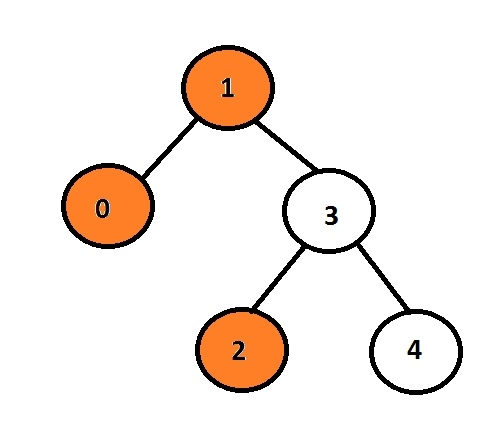
Di sini, nod oren mewakili pandangan kiri pokok binari.
Dalam graf yang diberikan, nod dengan data 1 ialah nod akar, jadi ia akan dicetak, bukannya pergi ke nod anak kiri, ia akan mencetak 0, kemudian ia akan pergi ke 3 dan mencetak nod anak kirinya, Iaitu 2.
Kita boleh menggunakan kaedah rekursif untuk menyimpan tahap nod dan berulang kali dipindahkan ke
Kod di bawah menunjukkan pelaksanaan C bagi algoritma yang diberikan
algoritma
START
Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure
Declare int data
Declare pointer of type node using *left, *right
Step 2 -> create function for inserting node with parameter as new_data
Declare temp variable of node using malloc
Set temp->data = new_data
Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL
return temp
Step 3 -> declare function void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level)
IF root = NULL
Exit
End
IF *highest_level < level
Print root->data
Set *highest_level = level
End
Recursively call left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level)
Recursively call left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level)
Step 4 -> Declare Function void left(struct node* root)
Set int highest_level = 0
Call left_view(root, 1, &highest_level)
Step 5-> In main()
Call New passing value user want to insert as struct node* root = New(1)
Call left(root)
STOPContoh
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//create a structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right; //this pointer will point to the nodes attached with a node
};
struct node* New(int new_data) {
struct node* temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
//allocating memory to a pointer dynamically
temp->data = new_data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) {
if (root == NULL) //if there is no node that means no data
return;
// this function will retrun the root node if there is only root node in a tree
if (*highest_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*highest_level = level;
}
// Recursive function
left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level);
left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level);
}
void left(struct node* root) {
int highest_level = 0;
left_view(root, 1, &highest_level);
}
int main() {
printf("left view of a binary tree is : ");
struct node* root = New(1);
root->left = New(0);
root->right = New(3);
root->right->left = New(2);
root->right->right = New(4);
left(root);
return 0;
}Output
Jika kita menjalankan program di atas ia Output berikut akan dihasilkan. rreeee🎜Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Cetak paparan kiri pokok binari dalam bahasa C. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Notepad++7.3.1
Editor kod yang mudah digunakan dan percuma

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

SublimeText3 versi Mac
Perisian penyuntingan kod peringkat Tuhan (SublimeText3)

Topik panas
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Apakah yang perlu saya lakukan jika garis bingkai hilang semasa mencetak dalam Excel?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Apakah yang perlu saya lakukan jika garis bingkai hilang semasa mencetak dalam Excel?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:50 AM
Jika semasa membuka fail yang perlu dicetak, kami akan mendapati bahawa garis bingkai jadual telah hilang atas sebab tertentu dalam pratonton cetak Apabila menghadapi situasi sedemikian, kami mesti menanganinya dalam masa Jika ini juga muncul dalam cetakan anda fail Jika anda mempunyai soalan seperti ini, kemudian sertai editor untuk mempelajari kursus berikut: Apakah yang perlu saya lakukan jika garis bingkai hilang semasa mencetak jadual dalam Excel? 1. Buka fail yang perlu dicetak, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah di bawah. 2. Pilih semua kawasan kandungan yang diperlukan, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah di bawah. 3. Klik kanan tetikus dan pilih pilihan "Format Sel", seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah di bawah. 4. Klik pilihan "Sempadan" di bahagian atas tetingkap, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah di bawah. 5. Pilih corak garisan pepejal nipis dalam gaya garisan di sebelah kiri, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah di bawah. 6. Pilih "Sempadan Luar"
 Memori atau ruang cakera tidak mencukupi untuk mengepa semula atau mencetak dokumen ini Ralat Word
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:15 PM
Memori atau ruang cakera tidak mencukupi untuk mengepa semula atau mencetak dokumen ini Ralat Word
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:15 PM
Artikel ini akan memperkenalkan cara menyelesaikan masalah memori yang tidak mencukupi atau ruang cakera untuk halaman semula atau mencetak dokumen dalam Microsoft Word. Ralat ini biasanya berlaku apabila pengguna cuba mencetak dokumen Word. Jika anda menghadapi ralat yang serupa, sila rujuk cadangan yang diberikan dalam artikel ini untuk menyelesaikannya. Memori atau ruang cakera tidak mencukupi untuk halaman semula atau mencetak dokumen ini Ralat Word Bagaimana untuk menyelesaikan ralat pencetakan Microsoft Word "Tidak ada memori atau ruang cakera yang mencukupi untuk halaman semula atau mencetak dokumen." Kemas kini Microsoft Office Tutup aplikasi penyamaran memori Tukar pencetak lalai anda Mulakan Word dalam mod selamat Namakan semula fail NorMal.dotm Simpan fail Word sebagai yang lain
 4 Cara Mencetak daripada iPhone
Feb 02, 2024 pm 04:10 PM
4 Cara Mencetak daripada iPhone
Feb 02, 2024 pm 04:10 PM
Dalam dunia digital ini, keperluan untuk halaman bercetak tidak hilang. Walaupun anda mungkin berpendapat lebih mudah untuk menyimpan kandungan pada komputer anda dan menghantarnya terus ke pencetak, anda boleh melakukan perkara yang sama pada iPhone anda. Dengan kamera iPhone anda, anda boleh mengambil foto atau dokumen, dan anda juga boleh menyimpan fail terus untuk dicetak pada bila-bila masa. Dengan cara ini anda boleh merealisasikan maklumat yang anda perlukan dengan cepat dan mudah dan menyimpannya dalam dokumen kertas. Sama ada di tempat kerja atau dalam kehidupan seharian, iPhone memberikan anda penyelesaian percetakan mudah alih. Siaran berikut akan membantu anda memahami semua yang anda perlu tahu jika anda ingin menggunakan iPhone anda untuk mencetak halaman pada pencetak. Cetak dari iPhone: Tanya Apple
 Tidak dapat mencetak daripada alat snipping dalam Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:39 AM
Tidak dapat mencetak daripada alat snipping dalam Windows 11/10
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:39 AM
Jika anda tidak dapat mencetak menggunakan Alat Snipping dalam Windows 11/10, ia mungkin disebabkan oleh fail sistem yang rosak atau isu pemacu. Artikel ini akan memberi anda penyelesaian kepada masalah ini. Tidak boleh mencetak daripada Snipping Tool dalam Windows 11/10 Jika anda tidak boleh mencetak daripada Snipping Tool dalam Windows 11/10, gunakan pembetulan ini: Mulakan semula Pencetak PC Kosongkan baris gilir cetakan Kemas kini pencetak dan pemacu grafik Betulkan atau tetapkan semula Snipping Tool Jalankan SFC dan DISM Scan menggunakan arahan PowerShell untuk menyahpasang dan memasang semula Alat Snipping. mari kita mulakan. 1] Mulakan semula PC dan pencetak anda Memulakan semula PC dan pencetak anda membantu menghapuskan gangguan sementara
 Bagaimana untuk menjeda percetakan dalam Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:50 AM
Bagaimana untuk menjeda percetakan dalam Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:50 AM
Tersilap mencetak fail besar? Perlu menghentikan atau menjeda percetakan untuk menjimatkan dakwat dan kertas? Terdapat banyak situasi di mana anda mungkin perlu menjeda kerja cetakan yang sedang berjalan pada peranti Windows 11 anda. Bagaimana untuk menjeda percetakan dalam Windows 11? Dalam Windows 11, menjeda pencetakan akan menjeda kerja cetakan, tetapi ia tidak akan membatalkan tugas cetakan. Ini memberikan pengguna kawalan yang lebih fleksibel. Terdapat tiga cara untuk melakukan ini: Jeda pencetakan menggunakan bar tugas Menjeda pencetakan menggunakan tetapan Windows Mencetak menggunakan panel kawalan Sekarang, mari lihat ini secara terperinci. 1] Cetak menggunakan bar tugas Klik kanan pemberitahuan baris gilir cetakan pada bar tugas. Klik untuk membuka semua pilihan pencetak yang aktif. Di sini, klik kanan pada kerja cetakan dan pilih Jeda Semua
 Bagaimana untuk mencetak semua lampiran dalam Outlook
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Bagaimana untuk mencetak semua lampiran dalam Outlook
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Outlook ialah salah satu pelanggan e-mel yang paling kaya dengan ciri dan telah menjadi alat yang sangat diperlukan untuk komunikasi profesional. Salah satu cabaran ialah mencetak semua lampiran pada masa yang sama dalam Outlook. Biasanya anda perlu memuat turun lampiran satu demi satu sebelum anda boleh mencetaknya, tetapi jika anda ingin mencetak semuanya sekali gus, ini adalah masalah yang dihadapi kebanyakan orang. Cara Mencetak Semua Lampiran dalam Outlook Walaupun kebanyakan maklumat dikekalkan dalam talian dalam aplikasi Outlook, ada kalanya anda perlu mencetak maklumat untuk sandaran. Mesti menandatangani dokumen sendiri untuk memenuhi keperluan undang-undang seperti kontrak, borang kerajaan atau tugasan kerja rumah. Terdapat beberapa kaedah yang membolehkan anda mencetak semua lampiran dalam Outlook dengan satu klik dan bukannya mencetaknya satu demi satu. Mari kita lihat setiap satu secara terperinci. Outloo
 Cantuman mel perkataan mencetak halaman kosong
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Cantuman mel perkataan mencetak halaman kosong
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
Jika anda mendapati halaman kosong muncul apabila anda mencetak dokumen gabungan mel menggunakan Word, artikel ini akan membantu anda. Cantuman mel ialah ciri mudah yang membolehkan anda membuat dokumen diperibadikan dengan mudah dan menghantarnya kepada berbilang penerima. Dalam Microsoft Word, ciri gabungan mel dipandang tinggi kerana ia membantu pengguna menjimatkan masa menyalin kandungan yang sama secara manual untuk setiap penerima. Untuk mencetak dokumen gabungan mel, anda boleh pergi ke tab Mel. Tetapi sesetengah pengguna Word telah melaporkan bahawa apabila cuba mencetak dokumen gabungan mel, pencetak mencetak halaman kosong atau tidak mencetak langsung. Ini mungkin disebabkan oleh pemformatan atau tetapan pencetak yang salah. Cuba semak tetapan dokumen dan pencetak dan pastikan anda pratonton dokumen sebelum mencetak untuk memastikan kandungannya betul. jika
 Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan fungsi percetakan dalam Vue
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
Bagaimana untuk melaksanakan fungsi percetakan dalam Vue
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
Cara melaksanakan fungsi pencetakan dalam Vue memerlukan contoh kod khusus Vue.js ialah rangka kerja JavaScript progresif untuk membina antara muka pengguna. Dalam kebanyakan aplikasi web, fungsi pencetakan adalah bahagian yang sangat penting. Artikel ini akan memperkenalkan cara melaksanakan fungsi pencetakan dalam Vue dan memberikan contoh kod khusus. Untuk melaksanakan fungsi pencetakan dalam Vue, anda mesti terlebih dahulu menjelaskan kandungan yang dicetak. Biasanya, kami akan meletakkan kandungan untuk dicetak dalam elemen HTML, seperti div. Kemudian, melalui Jav




