1. Introduction to MySQL
Overview
MySQL is a relational database management system developed by the Swedish MySQL AB company and currently belongs to Oracle.
MySQL is a relational database management system that stores data in different tables instead of putting all data in one big warehouse, which increases speed and improves flexibility.
Mysql is open source, so you don’t need to pay extra.
Mysql supports large databases. Can handle large databases with tens of millions of records.
MySQL uses the standard SQL data language form.
Mysql can be used on multiple systems and supports multiple languages. These programming languages include C, C++, Python, Java, Perl, PHP, Eiffel, Ruby and Tcl, etc.
Mysql has good support for PHP, which is currently the most popular web development language.
MySQL supports large databases and data warehouses with 50 million records. The 32-bit system table file can support a maximum of 4GB, and the 64-bit system supports a maximum table file of 8TB.
Mysql can be customized and adopts the GPL protocol. You can modify the source code to develop your own Mysql system.
Advanced MySQL involves knowledge
mysql kernel
sql optimization siege lion
Optimization of mysql server
Various parameter constant settings
-
Query statement optimization
Master-slave replication
Software and hardware upgrade
- ##Disaster recovery backup
- sql programming
Complete mysql optimization requires a deep foundation. Large companies even have dedicated DBAs to write the above
2. Installation of MySQL Linux version
- This time I installed MySQL 5.5, and the installation environment is CentOS 6.5
- version download Address official website download address
- Check whether MySQL is installed on the current system
##Query command: - rpm -qa|grep -i mysql
Delete command: - rpm -e --nodeps RPM package full name
Install mysql server (- Pay attention to the tips
)
-
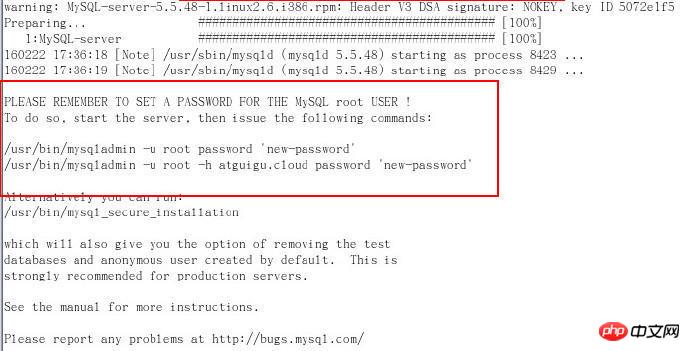
Set password prompt
Install mysql client
- # cat /etc/passwd | grep mysql
- cat /etc/group | grep mysql
Start + stop mysql service
-
Modify the character set and modify the previously copied configuration file. (Detailed follow-up code)
-
MySQL installation location
-
##show variables like 'character%';
-
show variables like '%char%';
- ##Character set
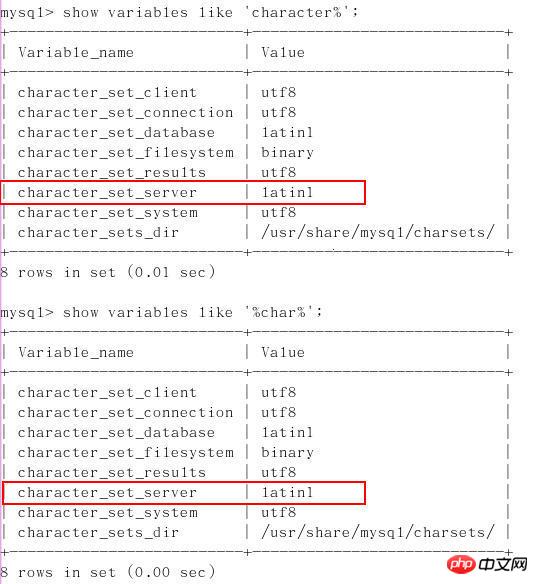
The default is that both the client and the server use latin1, so the characters will be garbled.
- View the installation directory under linux
ps -ef|grep mysql
-
Copy the current 5.5 version
: cp /usr/share/mysql/my-huge.cnf /etc/my.cnf-
##5.6 version
cp /usr/share/mysql/my-default.cnf /etc/my.cnf
chkconfig mysql on Set automatic startup
# chkconfig --list | grep mysql Check whether automatic startup is set
# /etc/init .d/mysql start
# /etc/init.d/mysql stop
or
- #service mysql start
service mysql stop
View MySQL start and stop status: # ps -ef | grep mysql
Start and stop operations:
-
| Path |
Explanation |
Remarks |
##/var/lib/mysql/ | Mysql database file storage path | /var/lib/mysql/atguigu.cloud.pid |
/usr/share/mysql | Configuration file directory | mysql.server command and configuration file |
##/usr/bin | Related command directory |
mysqladmin mysqldump and other commands |
|
/etc/init.d/mysql
| Start and stop related scripts |
|
|

MySQL installation location
[client]
#password = your_password
port = 3306
socket = /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
# 这一行需要设置字符集
default-character-set=utf8
# The MySQL server
[mysqld]
port = 3306
# 还有这三行
character_set_server=utf8
character_set_client=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
socket = /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
skip-external-locking
key_buffer_size = 384M
max_allowed_packet = 1M
table_open_cache = 512
sort_buffer_size = 2M
read_buffer_size = 2M
read_rnd_buffer_size = 8M
myisam_sort_buffer_size = 64M
thread_cache_size = 8
query_cache_size = 32M
# Try number of CPU's*2 for thread_concurrency
thread_concurrency = 8
[mysql]
no-auto-rehash
# 还有这一行
default-character-set=utf8
Copy after login
3. Mysql configuration file
Main configuration file
Binary log log-bin
Master-slave replication
-
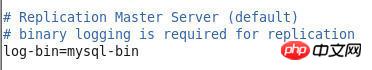
- ##Error log log-error
- The default is turned off, recording serious warnings and error messages, every Startup and shutdown details, etc.
- Query log log
- is turned off by default and records query sql statements. If it is turned on, it will reduce the overall performance of mysql. , because recording logs also consumes system resources
- data files
How to configureWindows: my.ini file
4. Introduction to Mysql logical architecture
Overview
First, the query process of mysql Roughly:
-
There is a series of preprocessing, such as checking whether the statement is written correctly, and then query optimization (such as whether to use index scanning, if it is an impossible condition, terminate early), and generate queries Plan, then the query engine starts, starts executing the query, calls the API from the underlying storage engine to obtain the data, and finally returns it to the client. How to store data and how to retrieve data are all related to the storage engine.
Then, mysql uses the BTREE index by default, and a general direction is that no matter how you toss sql, at least for now, mysql only uses at most one index in the table.
5. Mysql storage engine
View command
show variables like '%storage_engine%';
mysql> show engines;
View What storage engine does the current MySQL provide?
Depends on the current default storage engine of your MySQL:
-

Default storage engine
MyISAM and InnoDB
For Alibaba and Taobao Which
Free mysql online video tutorial
2. MySQL latest manual tutorial
3. Boolean Education Yan Shiba mysql introductory video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of An introduction to database architecture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!







