
Mysql data control language
1. Data control language
User management:
Storage location of user information:
Users in mysql are stored in the system database "mysql" of the mysql system.
##2. Create user:
create user 'Username'@'Location allowed to log in' identified by 'Password'
Example:
3. Delete user:
drop user ' Username '@' Allowed login location';Modify user password:Modify own password:set password = password(‘新密码’);
set password for ‘用户名’@’允许登录的位置’ = password(‘新密码’);
4. Permission management:
What are permissions? Permission is the right to do something, such as "insert", create, update, and delete. . . . "all" means "all permissions"In fact, in the mysql system, permissions are the above-mentioned "words";What permissions are there?
5. Refined to:
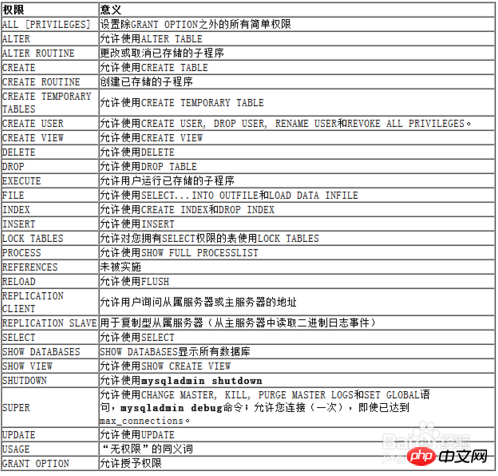
grant permission 1, permission 2, .... on a certain library. A subordinate unit to ' User name '@' allows login location' [identified by 'password']
Description:
1, permission names include: insert, update, select, delete, create, drop. .....
2, "A certain subordinate unit" refers to the subordinate data elements in a library. Currently we have only learned 2: table, view;
For example: php44. The student table or php44.int_test
has two special writing methods:
*.*: indicates all subordinate units in all databases;
a certain library.*: indicates the All subordinate units in the database
3. If permissions are granted to existing users, the identified part can be omitted. If not omitted, it means changing their password;
And for a new user (That is, 'username'@'location where login is allowed' does not actually exist yet), the identified part cannot be omitted, and the grant statement actually creates a new user!

grant all privileges on php44.* to 'user1'@'192.168.44.64';
The above is the detailed content of Mysql data control language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




