
This article will introduce in detail how to install JDK, Tomcat and MySQL in Linux after installing a virtual machine on Windows. If you are interested, you can learn more
This article will introduce in detail how to install a virtual machine on Windows. How to install JDK, Tomcat and MySQL in Linux, I hope it can help you.
First of all, these installations are run in xshell, what, no xshell? Well, I'll give you the resources. After installation, there will be xshell inside, just open it and use it.
1. Install JDK
I personally recommend using the rpm package when installing. The rpm in Linux is equivalent to the exe in Windows. There is no need to manually set up using the installation method in this article. environment variables.
Here is a resource for JDK-8.
1.1 Upload the local JDK file to the server (Linux)
Many people will use xftp to drag directly to Linux. Although the same effect can be achieved, But this is what a rookie does. Today we will use another method, which is quite crude: typing commands.
Knocking the command will use a software. In the future, yum will be used first to install software. yum puts some popular Linux packages on some relatively fast domestic servers. It downloads the installation package in rpm format and installs it.
Okay, let’s install this software first, command: yum -y install lrzsz;


1.2 Get the rpm package
Use the command:yum -y install jdk-8u141-linux-x64.rpm;

2. Install Tomcat
2.1 Put the Tomcat installation package into Linux
You can use the command line. To save trouble, there is no need for commands here. Just use xftp to drag it into Linux (forgive me). Here is a resource for Tomcat. (How about various resources, I’m pretty good, haha) It is recommended to put all the software you need to decompress under the /data directory. If there is no such directory, you can directly Create this directory under the root directory. The command to create this directory: mkdir /data Enter the /data directory and copy (cut) the Tomcat compressed package to the /data directory:
2.2 Decompress the Tomcat compressed package
Use the command: tar -xzvf apache-tomcat-8.0.45.tar. gzAmong them:V: represents the display of the decompression process;
Z: represents whether this is a compressed package, Generally speaking, if it ends with gz, it means a compressed package;
F: means recursive decompression;

2.3 Check whether Tomcat is started
Some people may have questions, why don’t you check whether Tomcat is started? Sometimes the Tomcat port is occupied, so Will fail to start. Check whether the command is started: ps aux|grep tomcat
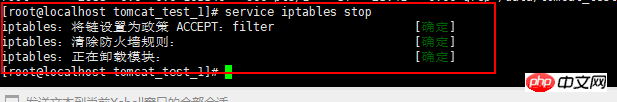
2.4 Stop the firewall
Command:service iptables stop

3. Install the latest version mysql 5.7
On the official website of MySQL, there is a link: A Quick Guide to Using the MySQL Yum Repository.
Now, I will walk you through the installation process according to this address.
3.1 Create yum source
Create yum source. The file name can be chosen casually, but the official website recommends naming it mysql-community.repo, so create a new file with the extension repo and the file content. As follows:
[mysql57-community] name=MySQL 5.7 Community Server baseurl=http://repo.mysql.com/yum/mysql-5.7-community/el/6/$basearch/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-mysql
Upload this file to /etc/yum.repos.d/.
Then use the command: yum search mysql, you will find an extra line at the bottom:

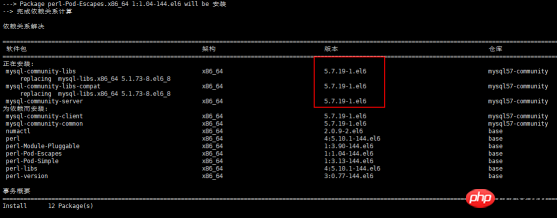
3.2 Install mysql
Use command: yum install mysql-community-server
##3.3 Restart mysql
Use command:service mysqld restart
3.4 View login password
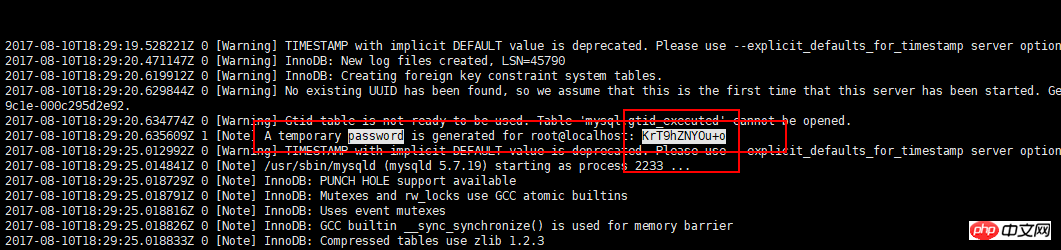
3.5 Log in to the mysql client
Use the command:mysql -u root -p

ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass4!';
uninstall plugin validate_password;
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
Copy code The code is as follows:
grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '123456' with grant option;Then use Navicat under Windows to connect to the database.3.6 Modify the default encoding
After using Navicat to connect to the database, the default encoding format is Latin, so you need to modify the default encoding format. Modify the configuration file /etc/my.cnf. When changing the file again, develop a habit of making a backup copy before modifying it. Use vi /etc/my.cnf, then find mysqld, add a linecharacter_set_server=utf8

The above is the detailed content of Graphic tutorial for installing JDK, Tomcat and MySQL on Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




