
XML is a popular semi-structured file format that stores data in a database-like format. In practical applications, some simple and low-security data are often stored in XML file format. The advantage of this is that on the one hand, it can improve reading efficiency by reducing interactive operations with the database, and on the other hand, it can effectively utilize the advantages of XML to reduce the difficulty of program writing.
PHP provides a complete set of methods for reading XML files, making it easy to write XML-based scripts. This chapter will introduce the operation methods of PHP and XML, and give a brief introduction to several commonly used XML class libraries.
1 Introduction to XML
XML is the abbreviation of "eXtensible Markup Language" and is a markup language similar to HTML. But unlike HTML, XML is mainly used to describe data and store data, while HTML is mainly used to display data.
XML is a "meta tag" language, developers can create tag names according to their own needs. For example, the following XML code can be used to describe a message.
<thread> <title>Welcome</title> <author>Simon</author> <content>Welcome to XML guestbook!!</content> </thread>
Among them, the
At the top of an XML file, is usually used to identify the beginning of XML data and XML data uses standard version information. When you access an XML file in a browser, you can see clearly layered XML data information, as shown in Figure 1.
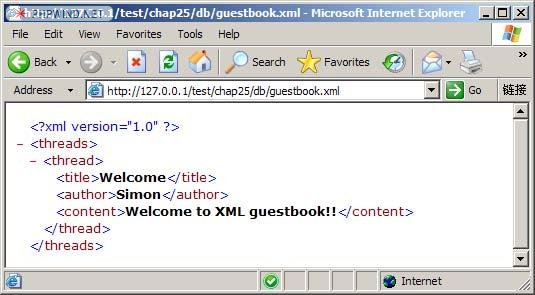
#XML is developing very rapidly. In recent years, many software developers have begun to adopt XML development standards for application development. Moreover, many emerging technologies are built on XML data. This means that XML will become as integral a part of Web technology as HTML.
2 Simple XML operation
In practical applications, the interactive operation between PHP and XML is widely used. The SimpleXML component is a new simple XML operation component added to PHP5. Compared with traditional XML components, the use of SimpleXML components is very simple. This section will give a detailed introduction to the method of using the
SimpleXML component to manipulate XML.
2.1 Create a SimpleXML object
SimpleXML object is a temporary variable used to temporarily store XML data. Operations on XML are completed by operating SimpleXML objects. The SimpleXML component provides two methods for creating SimpleXML objects. The first method is to use the simplexml_load_string function to read the XML data in a string variable to complete the creation. The syntax format is as follows.
simplexml_load_string(string data)
The data variable here is used to store XML data. The following code uses the simplexml_load_string function to create a SimpleXML object
<?php $data = <<<XML //定义 XML数据 <?xml version='1.0′?> <departs> <depart> <name>production support</name> <employees> <employee> <serial_no>100001</serial_no> <name>Simon</name> <age>24</age> <birthday>1982-11-06</birthday> <salary>5000.00</salary> <bonus>1000.00</bonus> </employee> <employee> <serial_no>100002</serial_no> <name>Elaine</name> <age>24</age> <birthday>1982-01-01</birthday> <salary>6000.00</salary> <bonus>2000.00</bonus> </employee> </employees> </depart> <depart> <name>testing center</name> <employees> <employee> <serial_no>110001</serial_no> <name>Helen</name> <age>23</age> <birthday>1983-07-21</birthday> <salary>5000.00</salary> <bonus>1000.00</bonus> </employee> </employees> </depart> </departs> XML; $xml = simplexml_load_string($data); //创建 SimpleXML对象 print_r($xml); //输出 XML ?>
SimpleXMLElement Object ( [depart] => Array ( [0] => SimpleXMLElement Object ( [name] => production support [employees] => SimpleXMLElement Object ( [employee] => Array ( [0] => SimpleXMLElement Object ( [serial_no] => 100001 [name] => Simon [age] => 24 [birthday] => 1982-11-06 [salary] => 5000.00 [bonus] => 1000.00 ) [1] => SimpleXMLElement Object ( [serial_no] => 100002 [name] => Elaine [age] => 24 [birthday] => 1982-01-01 [salary] => 6000.00 [bonus] => 2000.00 ) ) ) ) [1] => SimpleXMLElement Object ( [name] => testing center [employees] => SimpleXMLElement Object ( [employee] => SimpleXMLElement Object ( [serial_no] => 110001 [name] => Helen [age] => 23 [birthday] => 1983-07-21 [salary] => 5000.00 [bonus] => 1000.00 ) ) ) ) )
The second method is to use the simplexml_load_flie function to read an XML file to complete the creation. The syntax format is as follows.
simplexml_load_file(string filename)
The filename variable here is the file name and path used to store the XML data file. The following code uses the simplexml_load_file function to create a SimpleXML object.
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); //创建 SimpleXML对象 print_r($xml); //输出 XML ?>
The above two methods implement the same function, the difference lies in the different data sources of XML. If the XML data source is in a PHP script file, you need to use simplexml_load_string to create it. If the XML data source is in a separate XML file, you need to use simplexml_load_file to create it.
2.2 Read the XML data in the SimpleXML object
We have introduced the use of the print_r function to read the data in the SimpleXML object. The return result is similar to the structure of the array. Obviously, this display method is undesirable in practical applications. Here we will introduce several other methods of reading XML data in SimpleXML objects.
1. The var_dump function displays object detailed information
The var_dump function can be used to display detailed information of SimpleXML objects. Compared with the print_r function, the var_dump function displays more complete information. Its syntax is as follows.
void var_dump(object1, object2…)
The following code uses the var_dump function to output the detailed information of the object in the above example.
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); //创建 SimpleXML对象 var_dump($xml); //输出 XML ?>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#1 (1) { ["depart"]=> array(2) {
[0]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#2 (2) {
["name"]=>
string(18) “production support”
["employees"]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#4 (1) {
["employee"]=>
array(2) {
[0]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#5 (6) {
["serial_no"]=>
string(6) “100001″
["name"]=>
string(5) “Simon”
["age"]=>
string(2) “24″
["birthday"]=>
string(10) “1982-11-06″
["salary"]=>
string(7) “5000.00″
["bonus"]=>
string(7) “1000.00″
}
[1]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#6 (6) {
["serial_no"]=>
string(6) “100002″
["name"]=>
string(6) “Elaine”
["age"]=>
string(2) “24″
["birthday"]=>
string(10) “1982-01-01″
["salary"]=>
string(7) “6000.00″
["bonus"]=>
string(7) “2000.00″
}
}
}
}
[1]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#3 (2) {
["name"]=>
string(14) “testing center”
["employees"]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#7 (1) {
["employee"]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#8 (6) {
["serial_no"]=>
string(6) “110001″
["name"]=>
string(5) “Helen”
["age"]=>
string(2) “23″
["birthday"]=>
string(10) “1983-07-21″
["salary"]=>
string(7) “5000.00″
["bonus"]=>
string(7) “1000.00″
}}}}}与前面 print_r输出的结果相比较,var_dump函数的输出结果的结构更为严谨,并且将对象中的每一个属性的数据类型均作出分析。在实际应用中,var_dump函数往往用于程序调试时的对象检测。
2.读取 XML数据中的标签
与操作数组类型的变量类似,读取 XML也可以通过类似的方法来完成。例如,如果需要读取上面 XML数据中每一个“ depart”标签下的“name”属性,可以通过使用 foreach函数来完成,如以下代码
所示。
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); foreach($xml->depart as $a)
{
echo “$a->name <BR>”;
}
?>运行结果如下所示。
production support
testing center
//读取 XML文件 //循环读取 XML数据中的每一个 depart标签
//输出其中的 name属性
也可以使用方括号“ []”来直接读取 XML数据中指定的标签。以下代码输出了上面 XML数据中的第一个“depart”标签的“name”属性。
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); //读取 XML文件 echo $xml->depart->name[0]; //输出节点 ?>
运行结果如下所示。
production support
对于一个标签下的所有子标签,SimpleXML组件提供了 children方法进行读取。例如,对于上面的 XML数据中的“ depart”标签,其下包括两个子标签:“ name”和“employees”。以下代码实现了对第一个“depart”标签下的子标签的读取。
<?php
$xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml');
foreach ($xml->depart->children() as $depart) //循环读取 depart标签下的子标签
{
var_dump($depart); //输出标签的 XML数据
}
?>运行结果如下所示。
object(SimpleXMLElement)#3 (1) {
[0]=>
string(18) “production support”
}
object(SimpleXMLElement)#5 (1) {
["employee"]=>
array(2) {
[0]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#3 (6) {
["serial_no"]=>
string(6) “100001″
["name"]=>
string(5) “Simon”
["age"]=>
string(2) “24″
["birthday"]=>
string(10) “1982-11-06″
["salary"]=>
string(7) “5000.00″
["bonus"]=>
string(7) “1000.00″
}
[1]=>
object(SimpleXMLElement)#6 (6) {
["serial_no"]=>
string(6) “100002″
["name"]=>
string(6) “Elaine”
["age"]=>
string(2) “24″
["birthday"]=>
string(10) “1982-01-01″
["salary"]=>
string(7) “6000.00″
["bonus"]=>
string(7) “2000.00″
}
}
}可以看出,使用 children方法后,所有的子标签均被当作一个新的 XML文件进行处理。
3.基于 XML数据路径的查询
SimpleXML组件提供了一种基于 XML数据路径的查询方法。 XML数据路径即从 XML的根到某一个标签所经过的全部标签。这种路径使用斜线“ /”隔开标签名。例如,对于上面的 XML数据,要查询所有的标签“name”中的值,从根开始要经过 departs、depart、employees和 employee标签,则其路径
为“/departs/depart/employees/employee/name”。 SimpleXML组件使用 xpath方法来解析路径,其语法格式如下所示。
xpath(string path)
其中的 path为路径。该方法返回了一个包含有所有要查询标签值的数组。以下代码查询了上面 XML数据中的所有 name标签。
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); //读取 XML文件 $result = $xml->xpath('/departs/depart/employees/employee/name'); //定义节点 var_dump($result); //输出节点 ?>
运行结果如下所示。
array(3) {
[0]=> object(SimpleXMLElement)#2 (1) {
[0]=> string(5) “Simon”
}
[1]=> object(SimpleXMLElement)#3 (1) {
[0]=> string(6) “Elaine”
}
[2]=> object(SimpleXMLElement)#4 (1) {
[0]=> string(5) “Helen”
}
}可以看出,所有的 name标签均被查询出来。
2.3 XML数据的修改
对于 XML数据的修改与读取 XML数据中的标签方法类似。即通过直接修改 SimpleXML对象中的标签的值来实现。以下代码实现了对上面 XML数据中第一个“ depart”标签的“ name”子标签的修改。
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); //读取 XML $xml->depart->name[0] = “Human Resource”; //修改节点 ?>
修改后,并不会对 XML文件有任何影响。但是,在程序中,对于 SimpleXML对象的读取将使用修改过的值。
2.4 标准化 XML数据
SimpleXML还提供了一种标准化 XML数据的方法 asXML。asXML方法可以有效的将 SimpleXML对象中的内容按照 XML 1.0标准进行重新编排并以字符串的数据类型返回。以下代码实现了对上面 XML数据的标准化。
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); //读取 XML数据 echo $xml->asXML(); //标准化 XML数据 ?>
2.5 XML数据的存储
将 SimpleXML对象中的 XML数据存储到一个 XML文件的方法非常简单,即将 asXML方法的返回结果输出到一个文件中即可。以下代码首先将 XML文件中的 depart name进行了修改,然后将修改过的 XML数据输出到另一个 XML文件。
<?php $xml = simplexml_load_file('example.xml'); //读取 XML数据 $newxml = $xml->asXML(); //标准化 XML数据 $fp = fopen(”newxml.xml”, “w”); //打开要写入 XML数据的文件 fwrite($fp, $newxml); //写入 XML数据 fclose($fp); //关闭文件 ?>
代码运行后,可以看到在 newxml.xml文件中的 XML数据如下所示。
可以看出,对于 XML文件的修改已经保存到输出文件中了。
3 XML文档的动态创建
在实际应用中,时而会需要动态生成 XML文档的操作。前面介绍的 SimpleXML组件并不提供创建 XML文档的方法。因此,如果需要动态创建 XML文档,往往使用 DOM组件进行创建。 DOM是文档对象模型 Document Object Model的缩写, DOM组件提供了对 XML文档的树型解析模式。以下代码使用 DOM组件创建了一个 XML文档。
<?php //创建一个新的 DOM文档 $dom = new DomDocument(); //在根节点创建 departs标签 $departs = $dom->createElement('departs'); $dom->appendChild($departs); //在 departs标签下创建 depart子标签 $depart = $dom->createElement('depart'); $departs->appendChild($depart); //在 depart标签下创建 employees子标签 $employees = $dom->createElement('employees'); $depart->appendChild($employees); //在 employees标签下创建 employee子标签 $employee = $dom->createElement('employee'); $employees->appendChild($employee); //在 employee标签下创建 serial_no子标签 $serial_no = $dom->createElement('serial_no'); $employee->appendChild($serial_no); //为 serial_no标签添加值节点 100001 $serial_no_value = $dom->createTextNode('100001′); $serial_no->appendChild($serial_no_value); //输出 XML数据 echo $dom->saveXML(); ?> 输出结果如下所示。 <?xml version=”1.0″?> <departs> <depart> <employees> <employee> <serial_no>100001</serial_no> </employee> </employees> </depart> </departs>
DOM组件除了可以用来动态创建 XML文档外,还可以用来读取 XML文件。以下代码实现了对前 面 XML文件的读取。
<?php
$dom = new DomDocument(); //创建 DOM对象
$dom->load('example.xml'); //读取 XML文件
$root = $dom->documentElement; //获取 XML数据的根
read_child($root); //调用 read_child函数读取根对象
function read_child($node)
{
$children = $node->childNodes; //获得$node的所有子节点
foreach($children as $e) //循环读取每一个子节点
{
if($e->nodeType == XML_TEXT_NODE) //如果子节点为文本型则输出
{
echo $e->nodeValue.”<BR>”;
}
else if($e->nodeType == XML_ELEMENT_NODE) //如果子节点为节点对象,则调用函数处理
{
read_child($e);
}
}
}
?>运行结果如下所示。
引用 production support 100001 Simon 24 1982-11-06 5000.00 1000.00 100002 Elaine 24 1982-01-01 6000.00 2000.00 testing center 110001 Helen 23 1983-07-21 5000.00 1000.00
上面的例子使用了递归的方式对 XML数据进行了处理,实现了输出 XML数据中的所有文本型标签的功能。
4 XML应用实例——留言本
前面介绍了 XML的基本操作,本节将以设计一个 XML留言本为例来详细说明在实际应用中如何实现 PHP与 XML数据的交互操作。
4.1 XML文件结构设计
XML文件用于存储 XML数据,也就是留言本中的留言。这里,对于每条留言,在 XML数据中主要包括三项内容:留言标题、留言者姓名、留言内容。因此,将 XML文件的格式设计如下。
<?xml version=”1.0″?> <threads> <thread> <title>这里是留言的标题</title> <author>这里是留言者</author> <content>这里是留言内容</content> </thread> </threads>
4.2 提交页面的编写
提交留言页面由两个页面组成。一个是让访问者用来书写留言的表单的 HTML文件,一个是用来处理访问者输入的 PHP脚本。表单的 HTML代码如下所示。
<html> <head> <title>发表新的留言</title> <meta http-equiv=”Content-Type” content=”text/html; charset=gb2312″> </head> <body> <H1><p align=”center”>发表新的留言</p></H1> <form name=”form1″ method=”post” action=”Post.php”> <table width=”500″ border=”0″ align=”center” cellpadding=”0″ cellspacing=”0″> <tr> <td>标题</td> <td><input name=”title” type=”text” id=”title” size=”50″></td> </tr> <tr> <td>作者</td> <td><input name=”author” type=”text” id=”author” size=”20″></td> </tr> <tr> <td>内容</td> <td><textarea name=”content” cols=”50″ rows=”10″ id=”content”></textarea></td> </tr> </table> <p align=”center”> <input type=”submit” value=”Submit”> <input type=”reset” value=”Reset”> </p> </form> </body> </html>
对于用来处理用户输入的 PHP脚本,其基本逻辑是首先创建一个 DOM对象,然后读取 XML文件中的 XML数据,接下来在 XML对象上创建新的节点并将用户的输入储存起来,最后将 XML数据输出到原来的 XML文件中。具体实现代码如下所示。
<?php $guestbook = new DomDocument(); //创建一个新的 DOM对象 $guestbook->load('DB/guestbook.xml'); //读取 XML数据 $threads = $guestbook->documentElement; //获得 XML结构的根 //创建一个新 thread节点 $thread = $guestbook->createElement('thread'); $threads->appendChild($thread); //在新的 thread节点上创建 title标签 $title = $guestbook->createElement('title'); $title->appendChild($guestbook->createTextNode($_POST['title'])); $thread->appendChild($title); //在新的 thread节点上创建 author标签 $author = $guestbook->createElement('author'); $author->appendChild($guestbook->createTextNode($_POST['author'])); $thread->appendChild($author); //在新的 thread节点上创建 content标签 $content = $guestbook->createElement('content'); $content->appendChild($guestbook->createTextNode($_POST['content'])); $thread->appendChild($content); //将 XML数据写入文件 $fp = fopen(”DB/guestbook.xml”, “w”); if(fwrite($fp, $guestbook->saveXML())) echo “留言提交成功”; else echo “留言提交失败”; fclose($fp); ?>
在浏览器中运行上述 HTML文件并填写适当的留言内容,如图 2所示。
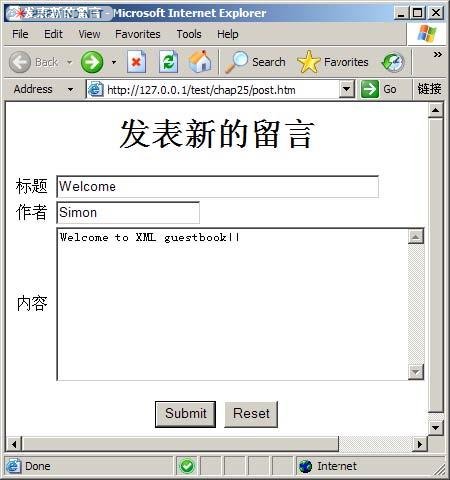
图 2 发表新留言界面
单击【Submit】按钮后,XML文件中的内容如下所示。
可以看到 XML文件中已经将留言存储起来了。
4.3 显示页面的编写
显示页面可以使用前面介绍的 SimpleXML组件很容易的实现,具体实现代码如下所示。
<?php
//打开用于存储留言的 XML文件
$guestbook = simplexml_load_file('DB/guestbook.xml');
foreach($guestbook->thread as $th) //循环读取 XML数据中的每一个 thread标签
{
echo “<B>标题:</B>”.$th->title.”<BR>”;
echo “<B>作者:</B>”.$th->author.”<BR>”;
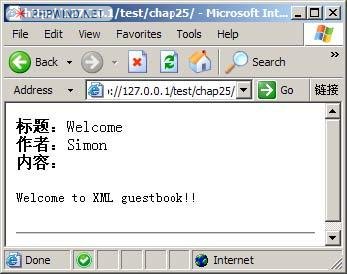
echo “<B>内容:</B><PRE>”.$th->content.””;
echo “在浏览器中查看运行结果如图 3所示。
更多PHP XML操作的各种方法解析(比较详细)相关文章请关注PHP中文网!




