
Recently, I had time to look at some PHP code.
The first is the integrated environment
First pass, phpMyAdminCreate a blogsurface.
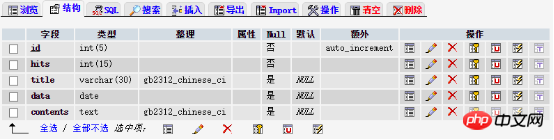
Pure interface operation, the process is relatively simple. It should be noted that id is the primary key, and Set the auto_increnent option to indicate that the field will automatically increment when it is empty. Other fields are more casual, just pay attention to the type and length.
Create a data connection conn.php
file. <?php
@mysql_connect("127.0.0.1:3306","root","") or die("mysql数据库连接失败");
@mysql_select_db("test")or die("db连接失败");mysql_query("set names 'gbk'");
?>
, the password is empty, the ## created here
is in the test library, so it needs to be connected to the test library. Addblog
at./wamp/www/blog/ Create the add.php file in the
directory.<a href="index.php"><B>index</B></a>
<a href="add.php"><B>add blog</B></a>
<hr>
<?php
include("conn.php"); //引入连接数据库
if (!empty($_POST['sub'])) {
$title = $_POST['title']; //获取title表单内容
$con = $_POST['con']; //获取contents表单内容
$sql= "insert into blog values(null,'0','$title',now(),'$con')";
mysql_query($sql);
echo "insert success!";
}?>
<form action="add.php" method="post">
title :<br>
<input type="text" name="title"><br><br>
contents:<br>
<textarea rows="5" cols="50" name="con"></textarea><br><br>
<input type="submit" name="sub" value="submit">
</form>include ## The
# (or
require) statement will retrieve all text present in the specified file /Code / tag and copy it to a file using the include statement. Then, if it is judged that the content of name='sub' in the form is not empty, the content of the form will be obtained, and then $sql will be executed. statement, null
means id is empty (incremented), now() means taking the current date, $title and $con take the content submitted by the user in the form. Finallyeche prompts for successful insertion. The lower part is a simple HTML code, used to implement a blog form submission Function.
创建blog的首页
在./wamp/www/blog/目录下创建index.php文件。
<a href="index.php"><B>index</B></a>
<a href="add.php"><B>add blog</B></a>
<br><br>
<form action="" method="get" style='align:"right"'>
<input type="text" name="keys" >
<input type="submit" name="subs" >
</form>
<hr>
<?php
include("conn.php"); //引入连接数据库
if (!empty($_GET['keys'])) {
$key = $_GET['keys'];
$w = " title like '%$key%'";
}else{
$w=1;
}
$sql ="select * from blog where $w order by id desc limit 5";
$query = mysql_query($sql);
while ($rs = mysql_fetch_array($query)) {
?>
<h2>title: <a href="view.php?id=<?php echo $rs['id']; ?>"><?php echo $rs['title']; ?></a>
| <a href="edit.php?id=<?php echo $rs['id']; ?>">edit</a>
| <a href="del.php?id=<?php echo $rs['id']; ?>">delete</a> |
</h2>
<li>date: <?php echo $rs['data']; ?></li>
<!--截取内容展示长度-->
<p>contents:<?php echo iconv_substr($rs['contents'],0,30,"gbk"); ?>...</p>
<hr>
<?php
};?>该页面包含有的功能还是比较多的。
首先是一个搜索表单,通过if判断搜索表单的内容是否为空,如果不为空,通过输入关键字匹配文章的标题并显示结果;如果为空查询所有blog内容,并循环显示每一篇文章的标题、日期、正文。点击标题会链接到该篇blog的详细页面。每一篇文章提供“编辑”和“删除”功能。
mysql_query()用于执行sql语句。mysql_fetch_arry()将返回的数据生成数组,这样就可以像操作数组一样,操作数据库中的每一条数据了。
然后是正文的显示,通过 iconv_substr() 函数提取正文前30个字符。
查看blog
在./wamp/www/blog/目录下创建view.php文件。
<a href="index.php"><B>index</B></a>
<a href="add.php"><B>add blog</B></a>
<hr>
<?php
include("conn.php"); //引入连接数据库
if (!empty($_GET['id'])) {
$id = $_GET['id'];
$sql ="select * from blog where id='$id' ";
$query = mysql_query($sql);
$rs = mysql_fetch_array($query);
$sqlup = "update blog set hits=hits+1 where id='$id'";
mysql_query($sqlup);
}?>
<h2>title: <?php echo $rs['title'];?> </h2>
<h3>date: <?php echo $rs['data'];?>
click number: <?php echo $rs['hits']; ?></h3>
<hr>
<p>contents:<?php echo $rs['contents']; ?></p>blog的正文实现比较简单,通过get请求获取blog的id,然后通过sql语句将该id对应的标题、日期和正文查询出来并显示。
并外一个小功能是显示了一个简单的计数器,每刷新页面,点击数加1。
编辑blog
在./wamp/www/blog/目录下创建edit.php文件。
<a href="index.php"><B>index</B></a>
<a href="add.php"><B>add blog</B></a>
<hr>
<?php
include("conn.php"); //引入连接数据库
//获取数据库表数据if (!empty($_GET['id'])) {
$edit = $_GET['id'];
$sql = "select * from blog where id='$edit'";
$query = mysql_query($sql);
$rs = mysql_fetch_array($query);
}//更新数据库表数据if (!empty($_POST['sub'])) {
$title = $_POST['title']; //获取title表单内容
$con = $_POST['con']; //获取contents表单内容
$hid = $_POST['hid'];
$sql= "update blog set title='$title', contents='$con' where id='$hid' ";
mysql_query($sql);
echo "<script>alert('update success.');location.href='index.php'</script>";
}?>
<form action="edit.php" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="hid" value="<?php echo $rs['id'];?>">
title :<br>
<input type="text" name="title" value="<?php echo $rs['title'];?>">
<br><br>
contents:<br>
<textarea rows="5" cols="50" name="con" ><?php echo $rs['contents'];?></textarea><br><br>
<input type="submit" name="sub" value="submit">
</form>编辑blog的功能相对复杂一些。分两部操作,第一步先将blog的标题和正文查询出来,并显示到输入框。第二步将编辑好的内容再更新到数据库中。
删除blog
在./wamp/www/blog/目录下创建del.php文件。
<a href="index.php"><B>index</B></a>
<a href="add.php"><B>add blog</B></a>
<hr>
<?php
include("conn.php"); //引入连接数据库
if (!empty($_GET['id'])) {
$del = $_GET['id']; //删除blog
$sql= "delete from blog where id='$del' ";
mysql_query($sql);
echo "delete success!";
}?>最后是实现blog的删除功能,通过id将该条blog的查询出来并显示。
因为所有页面没有使用前端样式有美化,很丑就不贴图了。功能还算完美。在此记录,算做PHP学习的整理。
=======================================================
另外,虽然每个语言都有优缺点,这里还是忍不住要吐槽一下PHP的两个不好之处。
1、符号不好写, “$” 、“ ->” 、 “=>”。这些符号虽然并没有增加代码语法的理解难度。但敲起来具恶心。每次在打“$”符号的时候,都要眼看键盘按着shift键找4在哪儿。
2、php与html的混编在我看来也不是太优雅。
The above is the detailed content of How to make a simple blog in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




