
CSS Grid (grid) layout allows us to build and control custom grids with more flexibility than ever before. Grid layout allows us to divide web pages into rows and columns with simple attributes. It also allows us to use CSS to position and resize each element within the grid without changing any HTML. It allows HTML to act purely as a container for content. HTML structure is no longer limited by style performance. For example, you don’t need to nest multiple times to achieve a certain layout. Now these can be done by CSS.
Define a grid
The Grid module provides a new value for the display attribute: grid . When you set the display attribute of any element to grid , then this element is a grid container (grid container) and all its direct child elements It becomes grid items.
Let's create a 3×3 layout and make a Tic-Tac-Toe board.
First, we will write some HTML:
<p class="game-board">
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
<p class="box"></p>
</p> As you can see, .game-board p is the grid container , and .box p is a grid item. Now we will implement the 3×3 layout through Grid layout.
.game-board
{
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: 200px 200px 200px;
grid-template-columns: 200px 200px 200px;
}Here, I also used two other properties.
grid-template-rows The property allows us to specify the number of rows in the grid and the height of the rows. Then you should guess what the other attribute is for.
grid-template-columns The property allows us to specify the number of columns in the grid and the width of the columns. You can specify the size in any unit, including pixels, percentages, and other units fr, which we'll learn about in the next step.
fr units (divided)
fr is a new unit defined for grid layout. It helps you get rid of calculating percentages and divide the available space into equal parts.
For example, if you set this rule in a grid container: grid-template-rows: 2fr 3fr , then your grid container will be divided into 2 first OK. Then add the numerical parts together, where the sum is 5, or 5 equal parts.
That is, we will have 2 rows: the first row takes up 2/5 of the vertical space. The second row takes up 3/5 of the vertical space.
Back to our Tic-Tac-Toe example, we use fr instead of px. What we want is that there should be 3 rows and 3 columns. Therefore, we only need to replace 3 200px with 3 1fr:
##
.game-board
{
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
}fr The unit is equal parts of available space, or remaining space. Look at an example
.game-board
{
grid-gap:2px;
display: grid;
width:300px;
height:200px;
grid-template-rows: 100px 1fr 1fr;
grid-template-columns: 1fr 50px 1fr;
}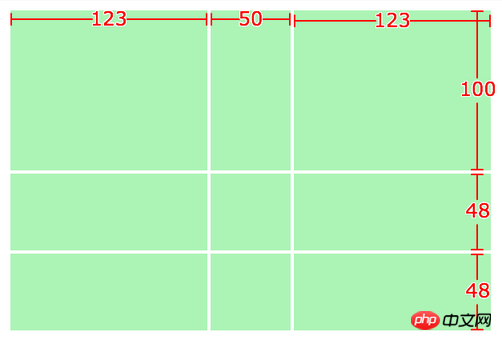 ##You will see
##You will see
The unit is the total size minus the specific size of the cell, and the remaining space is divided into equal parts. grid-gap is the gap.
In some cases, we may have many columns and rows. Specifying every value in the
grid-template property can be tedious. Fortunately, there is a repeat function , which is like any loop repeated how many times to output a given value. It has two parameters. The first is the number of iterations and the second is the value to be repeated. We rewrite the above example using the repeat function.
.game-board
{
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: repeat(3, 1fr);
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);
} .game-board
{
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
}grid-template The properties are grid-template-rows and grid-template-columns The abbreviated syntax of . This is its syntax: grid-template: rows/columns;Our example above looks very neat using this shorthand syntax.
.game-board
{
display: grid;
grid-template: repeat(3, 1fr) / repeat(3, 1fr);
}Example:
HTML
<p class="game-board"> <p class="box">X</p> <p class="box">O</p> <p class="box">O</p> <p class="box">O</p> <p class="box">X</p> <p class="box">O</p> <p class="box">O</p> <p class="box">X</p> <p class="box">X</p> </p>
.game-board
{
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: #34495e;
color: #fff;
border: 6px solid #2c3e50;
border-radius: 10px;
display: grid;
grid-template: repeat(3, 1fr) / repeat(3, 1fr);
}
.box
{
border: 6px solid #2c3e50;
border-radius: 2px;
font-family: Helvetica;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 4em;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
Grid lines are lines that exist on each side of columns and rows. One set of vertical lines divides the space vertically into columns, while another set of horizontal lines divides the space horizontally into rows. This means that in our previous example, there were four vertical lines and four horizontal lines containing the rows and columns between them.
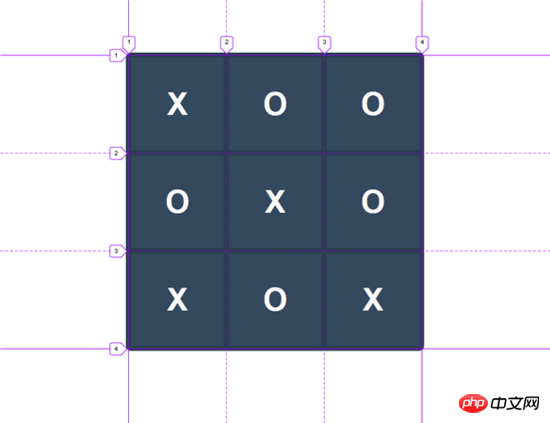 Grid lines become very useful when spanning grid items from one location to another.
Grid lines become very useful when spanning grid items from one location to another.
A grid track is the space between two lines. A grid track can be a row or a column.
网格单元格很像表格单元,是两条相邻垂直线和两条相邻水平线之间的空间。 这是网格中最小的单位。
定位网格项
我采取了前面的例子的网格,并用数字从1到9标记每个单元格,而不是X或O,下面是它的样子:
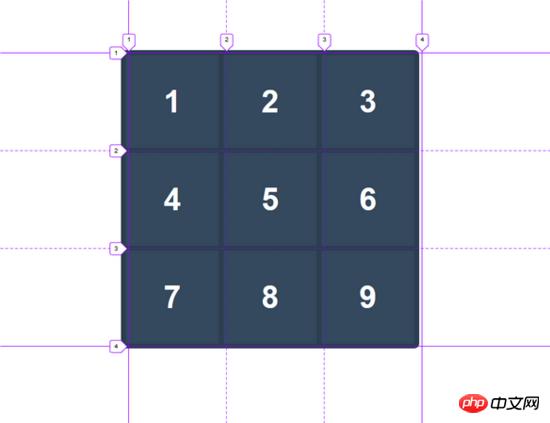
假设我想将第 6 个框移到第 2 个框的位置。没有CSS网格,不改变 HTML 的情况下,这几乎是一个不可能的任务,至少对我而言。但是如果我们使用网格模块,改变网格中网格项的位置是一件轻而易举的事情。要将第6个框移到第2个框的位置,我们必须确切知道第2个框在哪里。通过网格线编号的帮助,我们可以很容易地找到这个位置。第二个方框位于第2条列网格线之后,第3条列网格线之前,第1条行网格线之下,第2条行网格线之上。现在我们可以使用以下属性将这些网格线编号分配到第6个框中:
grid-column-start
grid-column-end
grid-row-start
grid-row-end
前两个属性对应于垂直网格线,也就是列网格线的开始和结束。 最后两个属性是指水平网格线,也就是行网格线的开始和结束。 让我们分配正确的网格线编号来移动第 6 个框。
.box:nth-child(6)
{
grid-row-start: 1;
grid-row-end: 2;
grid-column-start: 2;
grid-column-end: 3;
}
还有两个简写属性用于将行和列的开始网格线和结束网格线设置在一起。
.box:nth-child(6)
{
grid-row: 1 / 2;
grid-column: 2 / 3;
}此外,还有一个 grid-area 属性是所有四个上述属性的简写属性。 它按以下顺序取值:grid-area:
现在我们的例子可以写成这样
.box:nth-child(6)
{
grid-area: 1 / 2 / 2 / 3;
}上面的代码行也可以进一步减少。正如您所看到的,这个框只占用一行和一个列,所以我们只需要指定行和列的起始线,而无需结束线的值
.box:nth-child(6)
{
grid-area: 1 / 2;
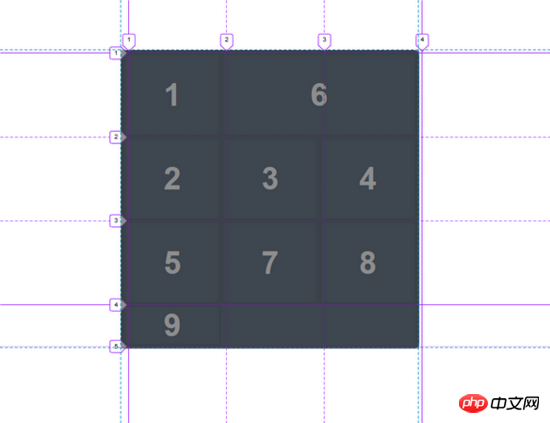
}如果我们想要第6个框跨越两个框的区域呢? 这很容易通过将 column-end 值加 1 的办法来完成。
.box:nth-child(6)
{
grid-area: 1 / 2 / 2 / 4;
}
您也可以使用 span 关键字和占据的 轨道数量,来代替指定 grid-row-end 和 grid-column-end 的结束网格线编号。 在这种情况下,第6个框是跨越 2 列和 1 行。
.box:nth-child(6)
{
grid-area: 1 / 2 / 2 / span 2;
}网格区域命名
grid-area 属性也可以用来命名网格的某一个部分,然后我们可以用 grid-template-areas 属性来定位。让我们创建一个简单的 bread-and-butter 布局,顶部有一个 top, nav,中间有 main 和 aside,下面是 footer。这是所需的HTML:
<p class="container">
<header></header>
<nav></nav>
<main></main>
<aside></aside>
<footer></footer>
</p>我们需要使用 grid-area 属性来命名每个区域:
header
{
grid-area: header;
background-color: #9b59b6;
}
nav
{
grid-area: nav;
background-color: #3498db;
}
main
{
grid-area: main;
background-color: #2ecc71;
}
aside
{
grid-area: aside;
background-color: #f1c40f;
}
footer
{
grid-area: footer;
background-color: #1abc9c;
}现在我们将使用 grid-template-areas 属性来指定每个网格区域所占据的行和列。 以下是我们如何做到的:
.container
{
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 5fr 1fr;
grid-template-columns: 2fr 5fr 3fr;
grid-template-areas:
"header header header"
"nav main aside"
"footer footer footer";
grid-gap: .75em;
}请注意,header 和 footer 单词重复三次。 这表明,header 和 footer 横跨 3 列的宽度。 你可以把它全部写在一行中,但是把每一行写在一个单独的行上很好,很干净。 你可以看到我在这里使用了一个新的属性 grid-gap 。 它所做的只是在两个网格区域之间添加一个间距。 你也可以使用 grid-row-gap 和 grid-column-gap 来为行和列指定不同的间距值。
例子:
HTML
<p class="container"> <header></header> <nav></nav> <main></main> <aside></aside> <footer></footer> </p>
CSS
.container
{
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 5fr 1fr;
grid-template-columns: 2fr 5fr 3fr;
grid-template-areas:
"header header header"
"nav main aside"
"footer footer footer";
grid-gap: .75em;
background-color: #eee;
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
}
header
{
grid-area: header;
background-color: #9b59b6;
}
nav
{
grid-area: nav;
background-color: #3498db;
}
main
{
grid-area: main;
background-color: #2ecc71;
}
aside
{
grid-area: aside;
background-color: #f1c40f;
}
footer
{
grid-area: footer;
background-color: #1abc9c;
}
结论
CSS网格布局允许我们更快地布局,并且更容易控制。在本教程中,我们学习了如何用CSS网格来定义布局, fr 单位,repeat 函数和一些网格系统中特定的术语。我们还学习了如何使用网格线和网格命名区域在网格容器内定位网格项目。
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Grid layout in CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




