
In web development, there is a big difference between forwarding and redirection.
Intuitively speaking, forwarding will not change the URL address, while redirection will change the URL.
This is just an appearance. The request object and response object in HttpServlet are encapsulated and generated by the server based on the parameters passed by the browser when the user requests a web page. Once the request is made from the browser and the server responds back, the request and response have reached the end of their lives.
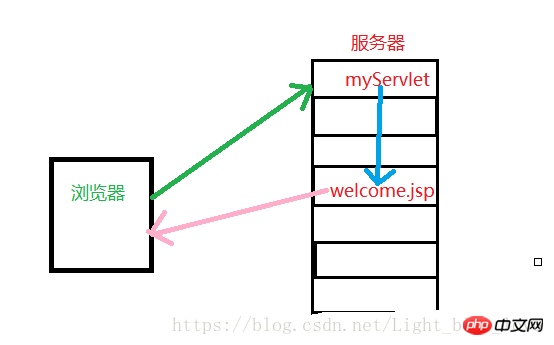
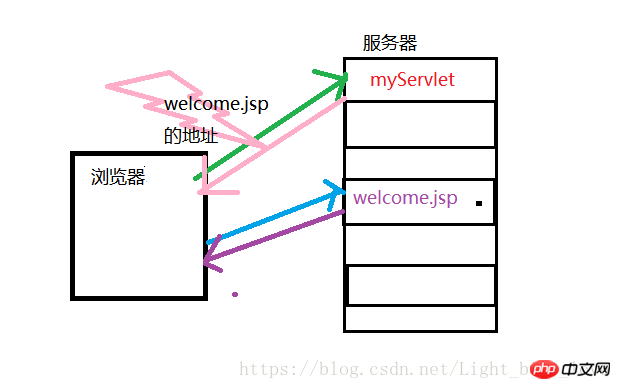
When using forwarding, the browser only requests once but the server may experience multiple jumps. If forwarding occurs during server-side execution, the server will stop the task being executed and specify the task to forward the given address.
If you use redirection, the browser will make multiple requests to the server. When the code is executed on the server side, if a redirection occurs, it will notify the browser to access another URL. The browser will request the resource from the URL sent.
Look at a piece of code:
<html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>login</title></head><body>
<form action="myServlet" method="post">
name :<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form></body></html>This is a piece of jsp code. When you click submit, the form will be submitted to myServlet.
The interface looks like this:
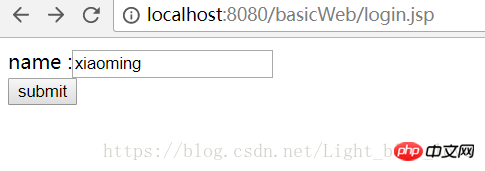 ##
##
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = (String)request.getParameter("username");
request.setAttribute("welcome", "welcome!!!");
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.jsp");
rd.forward(request,response);
}
}<html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>welcome</title></head><body>
<%=request.getParameter("username")%>
<br/>
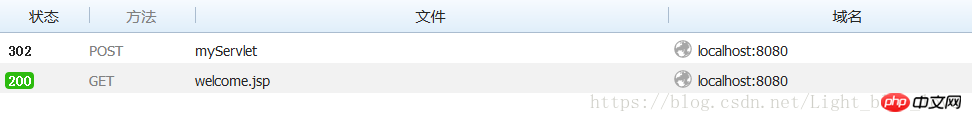
<%=request.getAttribute("welcome") %></body></html>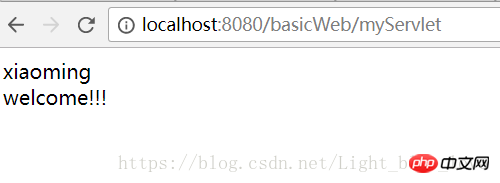 After clicking the submit button, we can take a look at the network request process.
After clicking the submit button, we can take a look at the network request process. 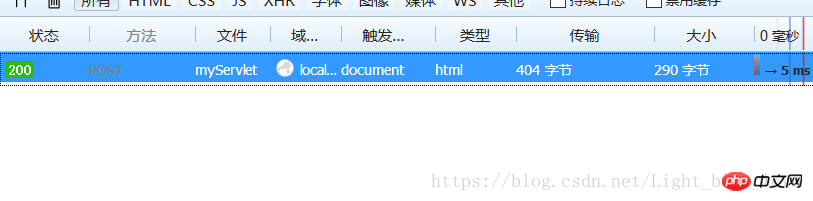
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = (String)request.getParameter("username");
request.setAttribute("welcome", "welcome!!!");// RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.jsp");// rd.forward(request,response);
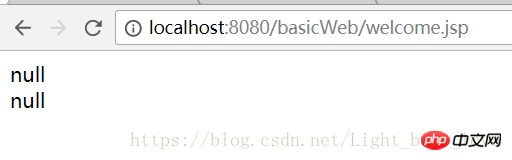
response.sendRedirect("welcome.jsp");
}
}
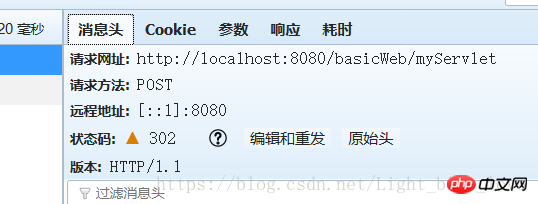
Whether it is the URL passed in the forward method or the sendRedirect method, you need to pay attention to it. If it starts with "\", it means that this URL is a request for the root of the servlet container. That is, localhost:8080. If it does not start with "\", it indicates that the request address is addressed relative to the current request URL .
<html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>login</title></head><body>
<!--这里改成了绝对地址 -->
<form action="/myServlet" method="post">
name :<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form></body></html>
Two tree array constructors without recursion
Convert HTML to Excel, and realize printing and downloading functions
The above is the detailed content of Web page forwarding and redirection. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




