Python module: logging
Many programs have the need to record logs, and the information contained in the logs includes normal program access logs, and may also include errors, warnings and other information output. Python's logging module provides a standard log interface through which you can store Various formats of logs. The recorded logs can be divided into 5 levels: debug, info, warning, error, and critical. Let’s take a look at how to use it.
First introduction to the module:
#logging初识
import logging
logging.warning("user [James] attempted wrong password more than 3 times")
logging.critical("server is down")
# WARNING:root:user [James] attempted wrong password more than 3 times
# CRITICAL:root:server is downThe above code is the simplest way, brackets The content inside is the printed information, and the method after logging. is the log level. Let’s take a look at the detailed information of the five levels of logging. If you want to write the log to a file, it is also very simple:
#日志打印到文件中
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename="example.log",level=logging.INFO,
format="%(asctime)s %(message)s", datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S [%A]")
# H 24小时格式 I 12小时格式 A 周几完整 a 周几简写 p AM/PM
logging.debug("This message should go to the log file")
logging.info("So should this")
logging.warning("And this ,too")logging .basicConfig defines the input file path, input log information level, input format, and the format can be customized; after executing the code, the example.log file will generate the following information: 
10/31/2016 17:16:17 [Monday] So should this 10/31/2016 17:16:17 [Monday] And this ,too
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#-Author-Lian
import logging
#创建logger
logger = logging.getLogger("test_log") #创建logger对象 括号内容随便写
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO) #全局日志级别
ch = logging.StreamHandler() #日志打印到屏幕上
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) #指定ch日志打印级别
fh = logging.FileHandler("access.log") #日志存进文件
fh.setLevel(logging.WARNING) #指定fh日志输入级别
formatter = logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s") #定义日志格式,可写多个
#添加日志格式到ch,fh
ch.setFormatter(formatter)
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
#添加ch,fh到logger中
logger.addHandler(ch)
logger.addHandler(fh)
logger.debug('debug message')
logger.info('info message')
logger.warn('warn message')
logger.error('error message')
logger.critical('critical message')2016-10-31 17:23:42,988 - test_log - INFO - info message 2016-10-31 17:23:42,988 - test_log - WARNING - warn message 2016-10-31 17:23:42,988 - test_log - ERROR - error message 2016-10-31 17:23:42,988 - test_log - CRITICAL - critical message
2016-10-31 17:02:06,223 - test_log - WARNING - warn message 2016-10-31 17:02:06,224 - test_log - ERROR - error message 2016-10-31 17:02:06,224 - test_log - CRITICAL - critical message
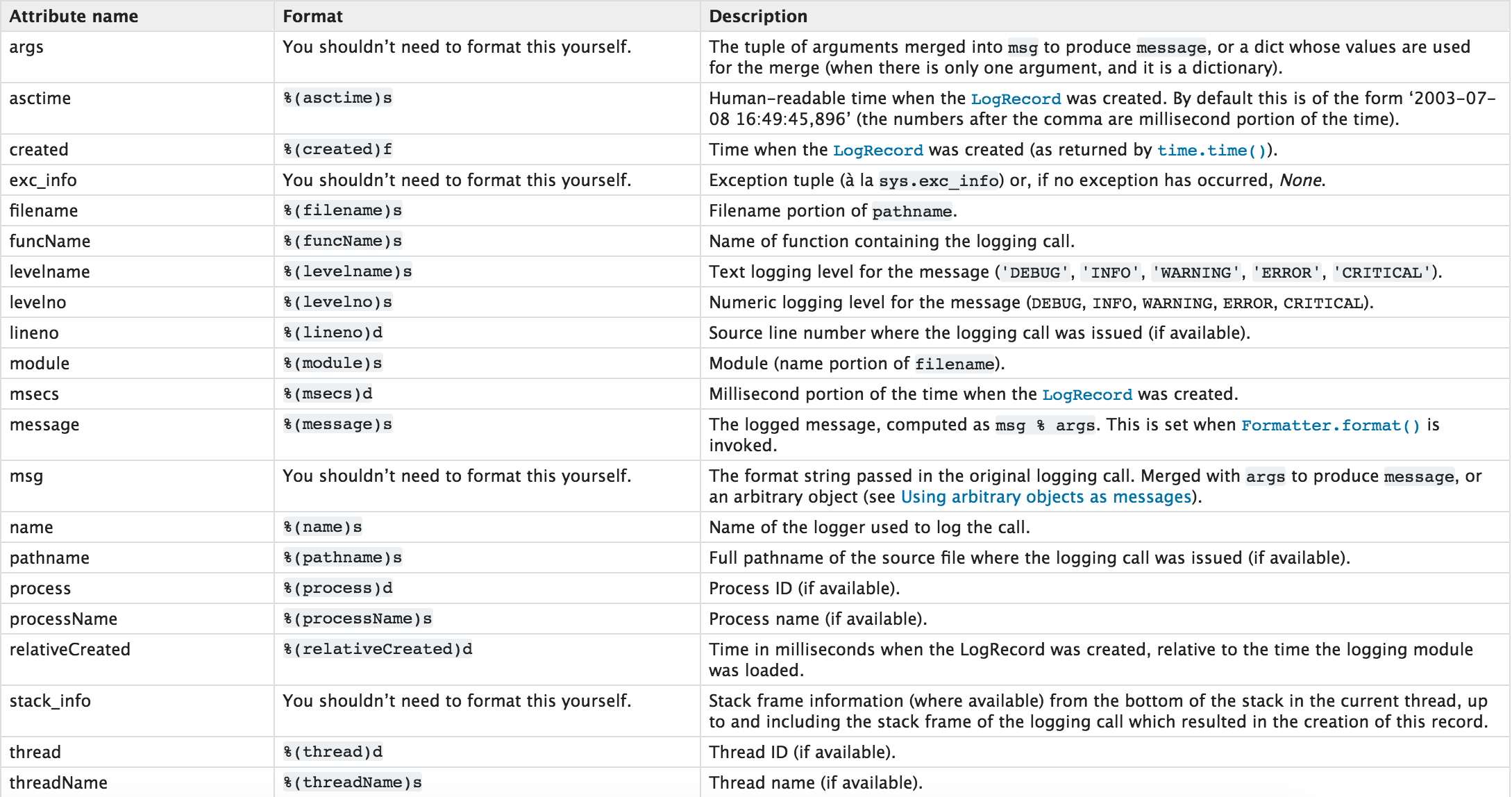
Several important formats: %(lineno)d Output print log code line, %(process) d outputs the process ID of the printing log, %(thread)d outputs the thread ID of the printing log

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1327
1327
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1252
1252
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".




